Factors complicating the course of the disease
Among the accompanying factors that can provoke the appearance of rosacea and aggravate its course, a significant place is occupied by:
- adverse effects of climatic conditions, for example, intense UV radiation, excessive heat, frost, traumatic effects of wind or dust;
- use of irritating cosmetics/procedures (peelings, waterproof cosmetics removers, “hot” masks, etc.);
- menopausal syndrome;
- systemic medications that increase erythema;
- consumption of spicy foods, strong drinks, overeating, and other factors that cause a rush of blood to the face.
It is worth noting that identifying and eliminating these factors greatly facilitates the process of treating rosacea and accompanying symptoms of blepharitis.
Atypical forms of rosacea
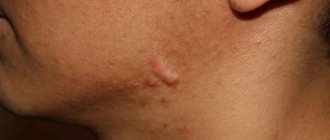
- Lupoid or granulomatous. Accompanied by the development of granulomas - yellow papules that leave scars on the skin after opening.
- Conglobat. Accompanied by large nodes, fistulas and the development of a purulent process.
- Halogen. Develops while taking bromine- or iodine-containing drugs.
- Steroid. Develops while taking steroid drugs.
- Gram negative. Develops against the background of uncontrolled or improper use of antibacterial drugs.
- Fulminant, or lightning fast. It most often occurs in young women and is characterized by the rapid development of all three stages of the disease. Accompanied by swelling and the formation of papules with purulent contents.
Classification
There are many classifications of rosacea. Depending on the course of the disease and the intensity of the formation of skin elements, the pathology may have the following stages:
- erythematous;
- papular;
- pustular;
- infiltrative-productive.
Taking into account the clinical picture and symptoms, rosacea is divided into the following forms:
- Persistent swelling of the face.
— Ophthalmic rosacea (with this form, eye damage is observed in the form of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis).
- Granulomatous rosacea (multiple elements located around the mouth and eyes, leading to characteristic symptoms in the form of many granules).
- Steroid rosacea (formed as a result of the use of local corticosteroids for a long time, while the skin is atrophic, and the elements of rosacea are brightly colored).
- Gram-negative rosacea (the name comes from secondary gram-negative microflora, which leads to pustular lesions of the skin and hair follicles).
— Conglobate rosacea (severe form of the disease, characterized by the formation of drain cavities and abscesses).
— Lightning-fast course of rosacea (observed in young women, has a fast and violent course).
— Halogen-induced rosacea (activation of the process occurs as a result of the influence of halogen-containing substances, such as iodine).
— Rhinophyma and other fibrotic changes in the skin of the face.
How to treat rosacea?
Rosacea should be treated by a dermatologist. In cases where we are talking about the ocular subtype - ophthalmic rosacea - which has severe symptoms of blepharitis or conjunctivitis (with the risk of vision damage), an ophthalmologist is involved in the process.
Sometimes it can be productive to consult with the following doctors:
- A microbiologist, whose help may be required to identify pathogenic microflora and select antibiotics.
- A gastroenterologist who will help in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases that can cause reflex dilation of facial vessels.
- Endocrinologist - his intervention is necessary if the patient has hormonal disorders.
- A neurologist who can help in cases where the disease is a consequence of vegetative-vascular dystonia or neurosis.
- A nutritionist, whose consultation will help you determine the list of foods that provoke exacerbations of the disease.
- A surgeon - he may be needed in cases where drug treatment is ineffective.
Diet for rosacea
Can
- Fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, milk, low-fat sour cream, fermented baked milk);
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, veal), preferably steamed or roasted
- Vegetables, especially all types of cabbage, zucchini, squash - preferably eaten raw or semi-raw
- Fruits (hypoallergenic)
- Berries (hypoallergenic, not too sour)
- Long-term carbohydrates (cereals: buckwheat, oats, barley).
- Vegetable oil (any in small quantities)
- Dried fruits (as dessert)
- Greenery
- Fish (low-fat types)
- Rye or whole grain bread
Must be excluded
- Fatty meats
- Spices
- Snacks (chips, crackers)
- Smoked products
- Pickles
- Light carbohydrates (cakes, pastries, buns, any other types of baked goods, sweets)
- Coffee and strong tea
- Canned foods
- Alcohol
- Fast food
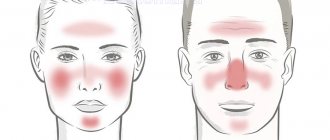
Stages of the disease and symptoms
Rosacea is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. During periods of exacerbation, 3 main stages can be distinguished:
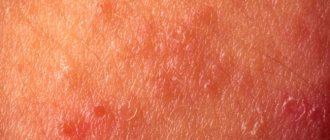
- Erythematotelangiectatic
. In the area of the cheeks, cheekbones and nose, small vessels, spider veins and red spots - erythema - appear. Their appearance is accompanied by burning and itching. - Papulopustular
. Swelling of the face appears, and large pink-red acne (papules) appear in the area of the cheekbones, forehead, nose and chin. A person may initially mistake them for an allergic reaction or regular acne. - Pustular nodular
. Erythema and papules spread throughout the face, papules merge with each other, and the skin becomes denser. The inflammation is not relieved and the swelling intensifies. Scars and depressions appear on the skin.
At all stages of the disease, there is a risk of ophthalmic rosacea - damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes due to the development of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, chalazion, keratitis, etc.
The disease should not be taken lightly. It is better to consult a doctor at the first stage in order to begin treatment before the consequences become irreversible.
Phymatous subtype
Subtype III is also called hypertrophic. The skin becomes lumpy, tissue thickening occurs. Pathology can be localized on different parts of the face16:
- on the nose - rhinophyma;
- on the forehead - metaphima;
- on the chin - gnathophyma;
- in the auricles - otophima;
- on the eyelids - blepharophyma (very rare).
With this type of disease, large pores are also observed. In addition to the symptoms associated with this subtype, symptoms of other forms of rosacea may occur227.
Maintenance therapy
Since rosacea is a chronic inflammatory dermatosis, after completing the main course of treatment, maintenance therapy is necessary: azelaic acid (gel 15%) or Metronidazole (gel 0.75%), applied 2 times a day externally for 6 months.
Although rosacea is an incurable disease, with the right approach it can be treated with medication, which can significantly improve the patient’s well-being. It should be remembered that treatment of rosacea should be carried out exclusively under medical supervision.
Treatment
Treatment of rosacea is complex and includes the prescription of products for external and systemic use.
Patients should be attentive to hygienic facial skin care. Women should opt for cosmetics that do not contain alcohol, acetone and oils, as well as other irritants. It is better to avoid creams and ointments containing hormonal additives, and also avoid using masks and balms with vasodilating ingredients. To wash, use water at room temperature. Apply the cleansing liquid with a light touch of your fingertips and use a soft face towel. Men with rosacea should use an electric razor instead of razor blades when shaving.
It is necessary to protect the skin from the sun, avoid sunburn, because... ultraviolet radiation leads to exacerbation of the disease. In winter, women need to use rich cream and powder, and in hot weather - special products with sun filters (SPF - sun protection factor must be at least 20).
It is also necessary to follow a gentle diet, especially if rosacea is caused by functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to limit the consumption of hot, salty, sour and spicy foods, avoid alcoholic beverages, coffee, strong tea, etc. Diet correction must be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Local treatment includes various creams, gels with azelaic acid, metronidazole, anti-inflammatory and astringent lotions, the use of thermal water, and also, if a Demodex mite is detected, antiparasitic drugs.
In the presence of severe inflammation, antihistamines are prescribed.
It is important to use vitamins that help strengthen the vascular wall (vitamin C, P (rutin)).
In severe forms and the addition of gram-negative microflora, the use of antibiotics is indicated.
To eliminate dilated vessels in the later stages, methods such as electrocoagulation (exposure to a weak electric current), cryodestruction (exposure to liquid nitrogen), dermabrasion and special types of lasers are used.
Differential diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, the presence of persistent erythema of the central part of the face is required, which has bothered the patient for at least 3 months. A more accurate determination of the subtype is possible if at least one of the additional symptoms is present.
In order for the treatment to be prescribed correctly, the doctor needs to differentiate rosacea from such serious diseases as:
- Polycythemia vera;
- Systemic connective tissue lesions;
- Carcinoid tumors;
- Mastocytosis;
- Rosacea-like or steroid dermatitis;
- Contact dermatitis.