Recently, the journal Expert Opinion On Drug Safety published an article by gynecologists from Taiwan who reviewed the use of BTA in pregnant women, and the doses of botulinum toxin were therapeutic and used in patients to treat neurological diseases1.
All of these conditions were successfully treated both before and during pregnancy with BTA injections, which allowed doctors to monitor the effect of botulinum toxin on the course of pregnancy and the effect on the fetus. Scientists say BTA injections have shown relative safety during pregnancy.
Below we provide excerpts from the material.
Botulinum toxin in the systemic circulation
To begin with, we should remember: in order to act on the myometrium or reach the placenta and negatively affect the fetus, the active substance must enter the systemic circulation.
Some reports indicated that, at high doses, BTA could diffuse from facial muscle tissue into the arm, as measured by single-fiber electromyography (EMG)2, 3. However, this effect appeared to be subclinical because no muscle weakness was detected in the affected individuals. If the dose of the drug did not exceed the recommended one, then during intramuscular injection BTA did not enter the systemic circulation4.
BTA is classified by the FDA as a Category C drug, which means that animal studies have shown adverse effects of the drug on the fetus and there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women, but the potential benefits associated with the use of this drug in pregnant women may justify its use despite existing risk.
In addition, studies have shown that molecules larger than 500 Daltons cannot cross the placenta5. The molecular weight of BTA exceeds 500 D, so BTA is unlikely to cross the placental barrier and is unlikely to be present in fetal blood.
To date, animal studies have found no evidence for transmission of toxins to the fetus. In rabbits, BTA was not detected in the placenta or in embryos when high (lethal) doses of the toxin were administered intravenously. Malformations and abortion were recorded only if rabbits received high-dose injections of BTA daily; conversely, pregnant mice treated with BTA did not show similar adverse outcomes6.
What procedures are contraindicated during pregnancy?
Biorevitalization
The essence of the procedure is to saturate the skin with hyaluronic acid through injections. This procedure allows you to correct existing wrinkles and give elasticity to the skin. The procedure can also be performed to prevent skin aging.
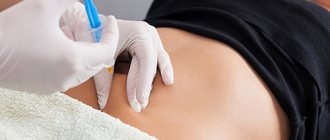
Botox injections
Botox or botulinum toxin is a weak and highly processed botulism neurotoxin. Injections of this toxin allow you to correct the shape of your face and smooth out facial wrinkles without surgery. The main purpose of Botox injections is to prevent the formation of wrinkles. When Botox is administered intramuscularly, the muscle is temporarily paralyzed. This allows the skin above expression lines to smooth out.
Electroprocedures
This type of procedure has many positive effects on the human body. However, how the body of a pregnant woman will behave under the influence of such procedures is still unknown to science. Electrical procedures are contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women.
Insolation procedures
The attitude of doctors towards these procedures is two-sided. “D” is the main hormone that is produced by cells under the influence of sunlight. If there is a lack of this hormone in the body of a pregnant woman, diabetes or rickets may develop in the child.
Most often, a lack of the hormone is observed in residents of northern countries where there is little sun. Therefore, if the supervising doctor deems it necessary, he can prescribe a course of insolation procedures for the pregnant woman.
Laser cosmetic procedures
The effect of laser procedures on the body has not yet been studied. However, during test studies, some cell disturbances were noted. Based on this, during lactation and pregnancy, procedures using radio waves and lasers are completely excluded.
For any pregnant woman, the health of the child should come first. Doctors categorically do not recommend resorting to injection and hardware procedures during pregnancy. If the doctor nevertheless prescribes something (most often it is lymphatic drainage, massage or insolation), then there is really a need for it.
LPG facial massage is your path to beauty
Dystonia
Dystonia is a syndrome in which there is a constant spasmodic contraction of muscles, spasms are often unpredictable, change the normal position of the body, can be chronic and cause significant discomfort, pain and disability.
Article 1 examined the use of BTA in the treatment of idiopathic torsion dystonia, oromandibular dystonia, and spastic dystonia (Table 1).
As a rule, the disease begins before the onset of reproductive age and persists throughout life. Common in pregnant women. Currently, BTA injections are the preferred treatment option. Moreover, in 10% of patients the disease began suddenly in connection with pregnancy and childbirth. Ankola showed (a study of 350 patients) that pregnancy or pregnancy-related hormonal changes may be a risk factor for the disease7. Morgan found that in a survey of 396 doctors, nine pregnant women received a BTA injection during pregnancy. One patient had a spontaneous abortion, but the other eight patients gave birth to healthy children8. Blitzer11 summarized the data of 1300 patients with dystonias such as adductor and abductor dysphonia, and over 24 years, according to his data, the effectiveness of BTA was 91.2% and 70.3%.
Table 1.
Use of BTA for the treatment of dystonia during pregnancy (according to Wu Li, Min Tang1)
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Newman, 20049 | 3 | 15 weeks / 200 units. 21 weeks / 100 units. 32 weeks / 300 units | BTA improved the symptoms, which recurred approximately every 3–4 months. Over the next 9 years, the patient became pregnant three times and received BTA several times during each pregnancy. The injections gave good results in all three pregnancies, the patient gave birth to healthy children |
| Aranda et al.10 | 1 time in the second and third trimesters | The injection site and dose were identical to those used before pregnancy: 40 IU into the left sternomastoid muscle, 150 IU, and an additional 60 IU divided between the trapezius and right elevator scapula muscles. The total dose during pregnancy is 500 IU. | At the 40th week, the patient gave birth to a healthy baby (weight 3400 g). |
| Morgan8 | _ | _ | The patient experienced relief of symptoms and gave birth to a healthy baby20. |
Strabismus
Deviation of the visual axes from the direction towards the object in question, in which the coordinated work of the eyes is disrupted and it becomes difficult for both eyes to fixate on the object of vision. BTA is considered an alternative to surgery.
Table 2.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Morgan, 20048 | Two patients with strabismus received BTA during pregnancy | 1.25 to 300 IU | The therapeutic effect did not cause complications or fetal abnormalities |
| Lee Yim12 | 17 year old woman. The drug was administered before the patient knew she was pregnant | 2.5 IU | A healthy baby was born |
What are the consequences of botulinum toxin injection?
For mother
Scientists have found that the administration of Botox during pregnancy can provoke the following consequences for the mother:
- Dizziness and general weakness of the body.
- Allergic reaction due to individual intolerance to the component. As a result of an allergy, symptoms such as cough, itching, swelling and a general deterioration of the immune system may appear.
- Since during pregnancy a woman’s body produces a large number of special hormones, one cannot be 100% sure how exactly the body will react to the injection of Botox.
Important! The result of such injections can be completely unpredictable and lead to dire consequences. - After the botulinum toxin injection procedure, digestion may worsen.
For the fetus
As mentioned above: there is no genuine evidence that the administration of Botox harms the health of the unborn child . However, it should also be taken into account that as a result of numerous studies conducted on animals, scientists have identified a high risk of miscarriage, as well as the birth of a child with various abnormalities.
Esophageal achalasia
Functional obstruction of the esophagus. Characterized by loss of lower esophageal sphincter (LES) activity and esophageal motility; the main symptoms are dysphagia, chest pain and reflux.
Treatment options include diet, calcium channel blockers, and Heller myotomy. BTA can be injected locally into the stomach area. The procedure does not require deep anesthesia, and can relax the LES and relieve esophageal obstruction.
Table 3.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Wataganara et al., 200913 | From 18th week | 80 U BTA | A healthy infant was born at 36 weeks' gestation and no swallowing problems were noted until 6 weeks postpartum. |
| Hooft 201514. | BTA at 14 weeks of pregnancy | 100U | Healthy baby |
| Holliday 201615 | BTA at 31 + 3 weeks of pregnancy | – | Eclampsia and childbirth at 37 + 4 weeks of pregnancy |
Is it possible to enlarge lips during pregnancy?
Many girls got used to constant filler injections before pregnancy, and decide to inject them again during pregnancy. Fillers act locally and should not pass into breast milk or cross the placental barrier, but due to the lack of confirmed scientific data on the safety of such a procedure, it is not recommended.
- Due to hormonal fluctuations and swelling, lips can change shape during pregnancy. As a result, after childbirth, when appearance returns to normal, they will look unaesthetic. Asymmetry may even appear.
- An altered metabolism can lead to the fact that the fillers will dissolve in a month or two, and the procedure will simply be useless.
Therefore, lip augmentation during this period is not worth it due to medical contraindications and the unpredictability of the result.
Chronic pelvic pain (CPP)
A common syndrome with various causes: the main and only symptom is pain, sometimes accompanied by defecation disorders. In addition to daily pain, patients often complain of dyspareunia and dysmenorrhea. In women, pain was significantly reduced after BTA injections.
Table 4.
| Study | Number of BTA injections | Dosage/Duration of treatment | Result |
| Abbott 200616 | 30 | 80 IU | Two women became pregnant 4 and 5 months after the injection; One woman (41 years old; complex medical history) had an elective caesarean section at 40 weeks and the baby had a ventricular septal defect that required surgical correction. However, it is unclear whether it was caused by BTA administration. |
| Abbott 200917 | Two cases during pregnancy | – | Both mothers had good results. |
Migraine
Some migraine medications are considered unsafe for pregnant women18.
In 2000, Binder et al were the first to report that BTA was successfully used in patients with headache19. In a meta-analysis of 17 studies involving 3646 patients with chronic migraine, Brula et al found that BTA significantly reduced chronic migraine symptoms after 3 months of treatment compared with placebo; therefore, BTA was considered safe and well tolerated20.
Complication statistics
Wu Li, Min Tang1's findings on complications showed that rates of spontaneous abortion and fetal malformations in pregnant women treated with BTA were similar to those reported for the general population.
Tan reported 28 cases occurring before 2013 in patients who received BTA during pregnancy; including 25 normal births, 1 therapeutic abortion and 2 spontaneous abortions21.
In 2016, Brin et al. reported results in pregnant women who had received local injections of BTA within the previous 24 years. Of the 137 births (139 fetuses), 110 (79.1%) were live births, 29 (20.9%) were fetal loss (21 spontaneous abortions) and 8 abortions22. Among the live births, 106 (96.4%) were normal, only 4 patients had a poor outcome, two had minor fetal malformations and one congenital complication; the overall incidence of fetal malformations was 2.7%. They may not have been related to BTA treatment.
Botulinum poisoning
There have been cases in the literature where high doses of BTA could cause symptoms of systemic botulinum poisoning.
However, a report by Brin et al. (2016) states that clinical botulism has no adverse effects associated with pregnancy or the fetus22. Badell studied maternal and fetal outcomes associated with botulinum poisoning in 16 women during pregnancy (11 cases in late pregnancy) and 1 woman after injection23. Although the pregnant women showed signs of poisoning, all babies were born healthy and only six patients experienced premature birth. Newborn blood tests did not show the presence of BTA in the systemic circulation; these findings also supported the hypothesis that BTA does not enter the fetal circulation24,25.
What procedures are acceptable for women “waiting for a miracle”?
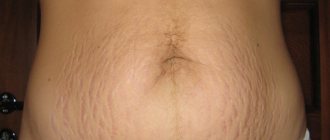
The most important problem during pregnancy is swelling and, as a result, cellulite.
Cellulite is a change in the structure of the subcutaneous fat layer that disrupts the original shape of the adipose tissue. The reason for its appearance is increased production of estrogen. This hormone is produced in order for the body to maintain pregnancy.
The most effective method of treating cellulite is lymphatic drainage.
Lymphatic drainage is one of the methods of physiotherapy, based on the removal of excess fluid and metabolic products from the space between cells. This procedure restores venous circulation and lymph flow, which is evenly distributed throughout the body.
It should be remembered that any cosmetic procedure must be agreed upon with the observing specialist. In the event that a doctor for some reason does not recommend performing procedures, this is due solely to safety considerations.