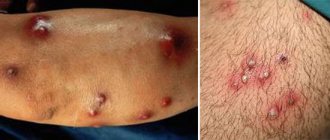
A boil can appear anywhere on the body, including on the labia. An abscess in the intimate area causes pain and discomfort.
The disease involves damage to the hair follicle and the surrounding area.
Any formation in such a place suggests a sexually transmitted disease. But the boil does not belong to this group of diseases.
Its appearance is caused by bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus or white Staphylococcus. Boils in the genital area in women are localized mainly on the labia majora.
Reasons for appearance
Opportunistic bacteria are present on human skin in a so-called latent state. A strong immune system prevents microorganisms from displaying their harmful qualities.
But under certain conditions, staphylococci, like other pathogens, become active, multiplying rapidly and causing organ damage.
A boil on the labia majora appears as a result of purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous glands and surrounding tissues.
Boils do not form on the labia minora and clitoris due to the absence of hair follicles in these areas.
There are main provoking factors in the development of this disease:
- weakened immunity, when the body's defenses are unable to resist the action of pathogenic microflora;
- infectious diseases – chronic and recent;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body, changes in hormonal levels;
- hypothermia;
- hyperhidrosis – as a result of increased sweating, a moist environment is formed in which bacteria actively multiply;
- insufficient hygiene of the intimate area;
- scratches, cuts, skin damage during depilation, irritation of the skin as a result of friction with uncomfortable tight underwear or due to sweating caused by synthetic fabrics;
- vitamin deficiency, which develops due to a lack of essential minerals, trace elements and vitamins.
Suppuration may occur on the intimate lips, which is not a boil. These types of formations appear on the labia minora as a result of bartholinitis or inflammation of the Bartholin glands.
The pathology is characterized by the development of seals on the mucous membrane, which become inflamed and fester. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
What is a boil
A boil is popularly called a boil. This inflammatory process can affect the armpits, groin areas, arms and legs, and face. In a word, suppuration appears in areas of thick hair. A boil in an intimate area affects the follicle from which the hair grows and the area around or near it, forming a purulent sac. The causative agent of subcutaneous suppuration is the bacterium white or aureus Staphylococcus, which in no way relates to sexually transmitted diseases and other pathologies in this area.
Symptoms of an abscess (ulcer) on the vulva
The appearance of a boil on the labia gives a woman a lot of unpleasant sensations.
This pathology has characteristic, pronounced symptoms. It is extremely difficult not to notice the development of an abscess, since the process is accompanied by pain in the intimate area.
Symptoms depend on the stage of development of the disease:
- At first, when the boil just begins to mature, slight redness and swelling can be detected at the site of its formation. It can be painful as a result of friction from clothing and pressure.
- As the boil grows, the discomfort intensifies - this area itches, pulsates, and the woman experiences a tugging pain. There is swelling of the labia and soreness of the tissues adjacent to the boil.
- General symptoms of the pathology include weakness, temperature, sometimes exceeding 38°C.
- The boil becomes purplish-red in color, and a necrotic core forms inside.
- In some cases, enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes may occur.
- When the boil opens and the purulent contents come out, the unpleasant symptoms gradually subside.
Operation to remove a boil
In some cases, a ripening boil cannot come out on its own. In such a situation, the patient will feel severe pain in the inflamed area and an increase in body temperature. If such symptoms are present, then it is necessary to contact a specialist surgeon for urgent surgical removal of the boil. The boil is opened under local anesthesia, which completely blocks the pain during the operation. The surgeon removes the pus and cleans the bottom of the wound. After this, a tampon soaked in an antiseptic solution is applied to the operated area. The patient's further stay in the hospital is not advisable. That is, the operation takes place under one-day surgery conditions and lasts no more than 10 minutes.
What does a boil on the labia look like (photo)
How it is formed
The appearance and further development of chiryak takes place in several stages or stages:
- Primary stage (infiltration) - in the place where the infection has entered the body, there is a slight swelling, then thickening and redness of the skin and swelling of the tissues appear. This stage usually lasts from 3 to 5 days, accompanied by mild itching, pain when pressing, and pulsation in the affected area. A small boil is usually about a centimeter in size, while a large one can reach 3 cm.
- Secondary stage (progressive necrosis) - the boil suppurates, inside which a necrotic core is formed. The light-colored purulent head stands out against the background of the burgundy boil. After 3–4 days, a mature boil breaks out on its own, sometimes requiring its opening with the help of a surgeon. During this period, the patient’s temperature often rises, nearby lymph nodes become enlarged, and muscles ache. After the pus drains out, a hole (crater) remains at the site of the wound.
- Tertiary stage (healing stage) - within a few days, the crater becomes scarred. The small scar will lighten over time and then disappear. How quickly the recovery period will pass will depend on the quality of hygienic and therapeutic procedures. It is important to follow all recommendations prescribed by your doctor.
What are the symptoms of Epstein-Barr virus in children? How to treat a sick child? The answers to these and other questions are discussed in this article.
The symptoms of herpes in the intimate area in women are described in detail in our publication.
Find photos of herpes on the tongue and gums here: https://udermatologa.com/zabol/gerp/gerpes-na-desnah-i-yazyke-lechenie-foto-simptomy/
Treatment of boils on the labia and vagina
Treating a boil on your own is dangerous; it is fraught with complications and deterioration in your overall health. The necessary medications and procedures must be prescribed by a doctor.
In some cases, local therapy will be sufficient, and sometimes surgery is required.
Local therapy
To treat boils, external medications are used in the form of ointments, which help draw pus out of boils, relieve inflammation, and reduce pain.
The choice of ointments that have a beneficial therapeutic effect is quite wide:
- Ichthyol - promotes the maturation of the abscess. It is applied in the form of compresses several times a day;
- Heparin - helps draw out pus from the boil, has an antiseptic and antimicrobial effect;
- Synthomycin - has a gentle effect without irritating the mucous membrane, so it is recommended for use in the treatment of boils on the labia;
- Zinc – a drug with a healing effect, used after opening the abscess;
- Vishnevsky's liniment is a reliable, proven remedy that helps accelerate the maturation of boils, remove purulent masses, cleanse and heal wounds. But many are put off by the specific smell of the ointment;
- Levomekol - ointment has an antibacterial effect, successfully fights microorganisms that cause suppuration. This product also promotes tissue restoration;
- Baneocin is an effective drug with antibacterial action;
- Clotrimazole - an ointment that successfully fights bacteria that cause boils, but it has a number of contraindications.
Local therapy involves careful treatment of the affected skin area. At the very beginning of the formation of a boil, the sore spot is wiped with salicylic alcohol to disinfect and relieve discomfort.
Chlorhexidine is used as an antiseptic at all stages of treatment - a cotton swab is moistened in the solution and applied to the boil.
Depending on the severity of the disease, antibiotics may be necessary. The need to prescribe such drugs is determined by the doctor.
To treat ulcers on the labia, use:
- Tetracycline;
- Minocycline;
- Dicloxacillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Sumamed.
It is strictly forbidden to open an abscess on the labia on your own in order to avoid infection and further bacterial damage to the genitals.
Surgical intervention
There are situations when a boil that has arisen on the labia cannot open for a long time. If compresses with ointments do not help to break through the abscess, the help of a surgeon is required.
The surgical intervention takes place in several stages:
- local anesthesia is used - the doctor administers an anesthetic drug that relieves pain;
- then an incision is made using a sterile instrument and the purulent contents are removed;
- After cleaning the cavity of the boil, the doctor will treat the wound with disinfectants and apply ointment. The therapeutic bandage is changed at least once a day.
After removing the internal contents of the boil, a small scar may remain. For resorption, the drug Contractubex is used.
Read more about this process in the material at the following address.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures help speed up the healing process of the boil after its opening:
- IR – infrared irradiation;
- darsonvalization - exposure to high-frequency pulsed currents of low strength;
- UHF – ultra-high frequency therapy;
- electrophoresis with copper and zinc salts.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine can complement or, in some cases, partially replace drug therapy.
Here are a few recipes for treating ulcers on the labia:
- In order to speed up the ripening of the boil, apply an aloe leaf cut lengthwise to it, fix it with a bandage and hold it for 3 - 4 hours. You can apply agave several times during the day.
- Applying a baked onion will help speed up the breakthrough of the abscess - the cut onion is placed on the affected area overnight.
- A compress of dried calendula flowers mixed with ghee is applied to the affected area for 2 to 3 hours.
- To draw out pus from a boil, you can make compresses with laundry soap - rub it on a grater and mix with water, then soak a napkin in the mixture and apply it to the abscess. The duration of the procedure is from 6 to 8 hours.
- Lotions made from medicinal herbs have an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. To do this, prepare an infusion of calendula, string, chamomile, sage, thyme and apply it to the boil for 30 - 60 minutes.
Treatment
Technique for opening an abscess. Preparation of the surgical field is usual. The hair on the external genitalia is shaved off, the vagina is washed with some kind of disinfectant solution (potassium permanganate solution, etc.) and, to avoid contamination with pus, it is tamponed with a strip of sterilized gauze. For pain relief, we usually use ether or chlorethyl stunning. The incision area is lubricated with iodine tincture. The incision should be made large and brought to the lower pole of the abscess, otherwise there will be pockets in which pus will accumulate, resulting in a purulent fistula that does not heal for a long time. An incision is made at the site of clearest fluctuation, where the tissue covering the abscess is thinnest. After the pus has drained, the abscess cavity is sprinkled with white streptocide or wiped with a small tupper moistened with iodine tincture; then a strip of gauze or a thin rubber tube is inserted into the cavity to prevent the hole from closing prematurely. At the end of the operation, the end of the gauze strip is removed, and after a day it is completely removed. A pad of gauze and cotton wool is placed in front of the vulva to absorb the pus flowing from the wound. It is unnecessary to apply a bandage. The drainage tube is replaced after 2 days with a fresh gauze strip or a drainage tube of a smaller diameter. It is necessary to ensure that the hole does not stick together before the granulations fill the abscess cavity. Vishnevsky ointment gives satisfactory results. Gauze turunda soaked in Vishnevsky ointment can be used immediately after incision of the abscess of the Bartholin gland. If the inflammation recurs or a purulent fistulous tract remains for a long time, then a radical operation is necessary, i.e., removal of the gland along with its excretory duct.
How to treat women during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The body of pregnant women becomes vulnerable due to a decrease in protective forces. The immune system weakens and the expectant mother is susceptible to infections and inflammations, including the formation of boils in the intimate area.
Women during pregnancy and nursing mothers should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor. The choice of medications for therapy is limited, since many drugs can harm both the expectant mother and the fetus.
Antibacterial and immunostimulating agents are rarely used, in exceptional cases. To strengthen the immune system, use a balanced diet enhanced with vitamins and microelements.
Of the medicinal ointments that effectively help in the treatment of boils, it is worth noting Ichthyol and Zinc. They are quite safe and are approved for pregnant and lactating women.
For local therapy, traditional medicine is used:
- To speed up the ripening of boils, you can use onions boiled in milk as a compress. Duration of the procedure: 6 – 8 hours.
- Mix a fresh chicken egg with 1 teaspoon of natural honey, add flour to obtain a thick consistency. Form cakes from this mass and apply one at a time to the boil for several hours.
- Pour the crushed flax seed into cotton bags. Place one of them in hot water one by one and apply it to the boil.
- At night, make a compress from a plantain leaf washed in hot water. This procedure has an antibacterial effect on the affected area.
What is the danger?
The danger of a boil is that it can cause complications if it is untimely or incorrectly treated, as well as if you squeeze out the abscess yourself or do not follow the rules of antiseptic treatment.
An abscess on the labia, where many blood vessels are located, is fraught with the spread of infection through the bloodstream into neighboring tissues and internal organs.
What complications can a boil in the intimate area lead to:
- furunculosis - the formation of multiple ulcers at different stages of maturation. Foci of inflammation of the hair follicles occur constantly, due to which the body is subjected to severe intoxication;
- phlegmon - a purulent process in the subcutaneous fatty tissues. The disease progresses rapidly due to the absence of a restrictive capsule and spreads through different layers of the skin, muscles and internal organs; we wrote about how it can be cured in this material;
- lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymph nodes mainly in the groin area;
- phlebitis - an inflammatory process in the walls of venous vessels;
- sepsis - the spread of infection through the bloodstream with further purulent inflammation throughout the body. The disease is serious, difficult to treat and often fatal.
Do you think it is possible to get chickenpox a second time? Find the correct answer to the question in this publication.
Carbuncle - what is it? What are the reasons for its occurrence? How is it different from a boil? How and with what is it treated? Our article will talk about this.
Therapy in our clinic
If you notice lumps on your genitals, we recommend that you do not hesitate to contact our qualified specialists. You will be examined by our gynecologists, after which, if necessary, they will be referred to a surgeon. We will carry out the appropriate treatment, choosing the best option for you. We always strive to choose gentle techniques, but if this is not possible, our surgeon will eliminate your tumor quickly, painlessly, with a guarantee of no complications.
Many years of practice and extensive experience of our specialists allow us to vouch for the health of each patient. We recommend that you consult a doctor in a timely manner to avoid serious complications and relapses of the disease.
Prevention measures
Prevention of the formation of boils on the labia is to eliminate any causes that contribute to the development of the disease.
Preventive measures relate to strengthening the immune system, maintaining personal hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and eradicating bad habits:
- care should be taken to strengthen the body's defenses, strengthen the immune system - for this you need to take multivitamin complexes, minerals, and sometimes the prescription of immunostimulating drugs is required;
- you need to reconsider your diet - limit the consumption of fatty, fried, smoked foods, increase the amount of vegetables and fruits in the menu;
- It is worthwhile to reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages as much as possible and quit smoking;
- it is important to monitor the hygiene of the intimate area - use suitable cosmetics for daily care, wash the genitals twice a day;
- You should wear underwear made from natural, breathable fabrics, of a suitable size so as not to rub the intimate area, and change it daily;
- hypothermia or overheating of the genital organs should not be allowed (excessive sweating provokes the occurrence of boils);
- depilation in the intimate area must be carried out very carefully to prevent microtrauma and damage to the mucous membrane and labia;
- it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist in order to promptly identify female diseases and eliminate inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- if necessary, you should undergo a comprehensive examination, consult an immunologist, surgeon, dermatologist and other specialized specialists.
A boil is not such a harmless sore, especially if it pops up on the labia.
In addition to discomfort and pain, an abscess is fraught with complications, which can be prevented by timely treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Diagnosis of gynecological abscesses
The diagnostic process begins with identifying the patient's disturbing symptoms and complaints. After the interview, the doctor conducts a gynecological examination by palpation and using gynecological speculum. Some genital abscesses (for example, bartholinitis) can be diagnosed during a gynecological examination. Others require more in-depth diagnostics - laboratory and instrumental studies.
The doctor gives a referral to donate blood and urine for general and specific laboratory tests (CBC, OAM, tests for sexually transmitted infections), which can identify various viruses and inflammatory processes. Hardware research methods include computed tomography and transvaginal ultrasound.