Eczema belongs to a group of skin diseases. It manifests itself in the form of skin rashes that look like papules with serous fluid and swelling. There is an itching sensation in the affected areas. The disease can manifest itself in wet and dry forms. The causes of the disease can be various factors. After diagnosing and identifying the cause of eczema, a complex therapy is drawn up, which includes various remedies. Non-hormonal ointments for eczema are often used. With their help, you can eliminate symptoms and ease the course of the disease.
Boric ointment, an inexpensive and effective remedy for eczema
Characteristics of the disease
The disease is chronic, which causes periodic relapses. Eczema can be of different types, but its causes are caused by the same factors. Their list includes:
- disorders of the digestive system, kidney problems,
- diseases of the nervous system, disorders of the endocrine system,
- influence on the skin of allergens in the form of chemicals, acids, alcohol and other substances,
- exposure to ultraviolet rays, frequent hypothermia and overheating of the body,
- skin susceptibility to injury, drug allergies,
- deficiency of fatty acids,
- vitamin deficiency, parasitic infestations,
- problems with the pancreas, disorders of the gallbladder,
- immune system disorders.
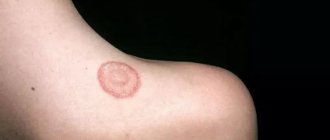
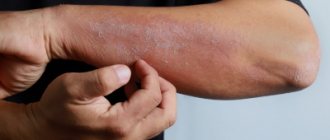
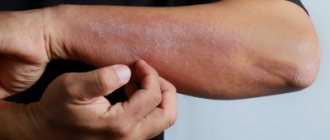
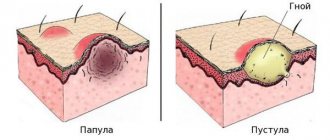
Like all diseases, eczema has its own characteristic symptoms. The symptoms are sequential. If you do not treat at the first signs of eczema, it will progress. The disease manifests itself in the form of the following problems:
- skin redness,
- formation of red-pink nodules,
- filling the nodules with fluid,
- cloudiness of the fluid and accumulation of pus,
- the appearance of erosions,
- hair loss in affected areas,
- the formation of dry crusts and their exfoliation.
In order for treatment to be effective, a thorough diagnosis is carried out, which helps to identify the causes. Based on the results of the examination, it is possible to create a complex of therapy, which consists of various drugs and agents.
The nervous system can malfunction, causing eczema
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Eczema requires a careful approach to treatment, as it can be caused by various factors. As a rule, the beginning of treatment begins with the elimination of symptoms. This allows you to improve the psychological and physical health of the patient and continue to identify the cause of the disease.
To eliminate itching, the doctor prescribes antiallergic drugs. To slow down the development of the disease and eliminate lesions, boric acid is used. Taking B vitamins improves the skin regeneration process, which speeds up recovery.
If the disease has reached an advanced stage and the patient experiences severe pain, corticosteroids are used.
In the initial stages, eczema can be treated with various creams, gels and ointments, which can be either non-hormonal or hormonal.
Correctly selected ointment allows you to get rid of negative manifestations on the skin. Many people believe that the final stages of eczema should be treated only with hormonal agents. Non-hormonal ointments can also provide effective assistance.
Eczema on the hands is not easy to get rid of using conventional means. Treatment should be comprehensive and include certain drugs, both external and internal use.
Hormonal ointment for eczema has certain contraindications and side effects, so if possible it is not used. Hormonal agents are used in cases where severe symptoms and advanced degrees of eczema are present.
Using ointment is just one part of treating eczema
Bibliography
- Akhtyamov, S.N. Practical dermatocosmetology / S.N. Akhtyamov, Yu.S. Butov. M.: Medicine, 2003. - 391 p.
- Arkhangelskaya, E.I. Materials on the clinic, etiology and pathogenesis of diffuse streptoderma and microbial eczema: abstract. dis. Dr. med. Sciences / E.I. Arkhangelskaya. L., 1973. - 38 p.
- Aizikovich, JI.A. Abstracts of scientific works of the VIII All-Russian Congress of Dermatovenerologists / JI.A. Aizikovich, T.V. Sokolova. 4.1. // Dermatology. - 2001.- P. 205.
- Buxton, P.K. Dermatology / P.K. Buxton. M.: Publishing house BINOM, 2005, - 175 p.
- Belousova, T.A. Neurogenic factors in the pathogenesis of eczema: abstract. dis. . Ph.D. honey. Sciences/T.A. Belousova. M., 1984. - 18 p.
- Demidova, M.A. Epidemiological and pharmacoeconomic aspects of the use of antihistamines in the treatment of patients with eczema / M.A. Demidova, E.V. Bogdanova // Ross. magazine skin and venereal diseases. 2009. - No. 2. — P. 46-49.
- Kudryavtseva, E.V. Lokoid and modern approaches to external therapy of atopic dermatitis / E.V. Kudryavtseva, AB Karaulov // Immunopathology, allergology, infectology. 2003. - No. 4. — P. 57-62.
- Mikhailenko, A.A. Allergy and allergic diseases /AA Mikhailepko, G.A. Bazanov. M.: Med. information agency, 2009. - 304 p. thirty.
- Prokhorenkov, V.I. Eczema / V.I. Prokhorenkov, T.A. Yakovlev 3rd ed. - Krasnoyarsk: PIK "Offset", 1994. - 255 p.
External products
Drugs that do not contain hormones help no worse than corticosteroids. Non-hormonal ointments, unlike hormonal ones, are used for a long time. They have fewer contraindications and side effects. Their only drawback is that the treatment period will be longer. If eczema is advanced, it is better to use corticosteroids.
The non-hormonal drugs recommended by experts include only the list that has already been tested and given the necessary results.
- Zinc ointment. The product contains zinc oxide, which has an antiseptic and antimicrobial effect. The ointment is low cost and works well, so it is in high demand.
- Dermasan. Used in the initial stages of eczema. It eliminates the inflammatory process well.
- Skin cap. A very common ointment that has an antifungal effect. When used, antimicrobial and antiallergic effects are observed. Quite effective for dry eczema, which is caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
- Aurobin. Effective in the first stages of disease development. Restores damaged skin cells, accelerates the healing process of wounds.
- Eplan. It has an anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect, relieves pain and softens the skin.
- Boric ointment. Effective in eliminating bacteria, fungi and germs. Relevant in cases where infections are associated with the disease.
In advanced cases of the disease, hormonal cream is used, as it is more effective and produces results faster.
Eplan quickly softens and anesthetizes the skin
Eczema: a differentiated approach to the choice of external therapy
Eczema is a widespread skin disease, which affects from 2% to 10% of the working population, reaching up to 20% in industrialized countries, and is the most common pathology in the practice of a dermatovenerologist, accounting for 30–40% of all skin diseases [1] . Eczema is a chronic relapsing disease with acute inflammatory symptoms caused by serous inflammation of the epidermis and dermis, characterized by multifactorial genesis, variability of clinical course with evolutionary polymorphism of rash elements, often with a tendency to a severe course with frequent relapses and refractoriness to many methods of therapeutic intervention [2, 3] . According to the classification based on the clinical and pathogenetic features of the course of the disease, in the Russian Federation there are true (idiopathic, dyshidrotic, pruriginous, horny), microbial (numular, paratraumatic, mycotic, intertriginous, varicose, sycosiform, eczema of the nipples and the isola of the mammary gland of women) , seborrheic, childhood and occupational varieties of eczema [4]. Each of which can occur acutely, subacutely or chronically, with periodic exacerbations under the influence of trigger factors.
Taking into account the polyetiology of the disease, treatment of patients with eczema implies a complex effect on the body with the development of a personalized algorithm of therapy and rehabilitation, taking into account the severity, nature, localization of the pathological process, duration of the disease, previous treatment and its effectiveness, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant pathology. Systemic therapy usually begins with an exacerbation of the disease and, taking into account all of the above, includes the complex use of desensitizing, antihistamine, psychotropic and immune drugs. If necessary, correction of concomitant pathological conditions is carried out by appropriate medical specialists. At the same time, an obligatory and important part of the complex treatment of this disease is adequate external therapy aimed at eliminating skin itching, stopping allergic inflammatory reactions, eliminating dry skin, preventing/eliminating secondary infection, stimulating reparative processes and restoring the barrier function of the skin. A differentiated approach to the choice of external therapy, taking into account the patient’s age, the nature of the disease, the localization and extent of the skin process, the possibility of combination with other drugs used, and the expected duration of therapy will directly affect the degree of its effectiveness.
Eczema is a steroid-sensitive dermatoses, the treatment of which requires a suppressive effect on the cells of the immune system of the skin, with a high therapeutic effect from therapy with topical glucocorticosteroids (TGCS), as a result of which they occupy a leading position among all drugs for external therapy of patients with this pathology. Acting as a powerful pathogenetic effect, TGCS can quickly reduce or reduce inflammatory changes in the skin and eliminate the subjective symptoms of dermatoses (itching, burning), which actively contributes to the restoration of ability to work, daily activity, has a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state and significantly improves the quality of life of patients [5] . The therapeutic effect of TGCS is due to their strong anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictive, antiallergic and antiproliferative effects [8], which are realized as a result of: inhibition of the migration of neutrophils, monocytes and eosinophils to the site of inflammation; increased expression of genes encoding the synthesis of lipocortin proteins that inhibit the activity of lysosomal phospholipase A2, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators; activation of histaminase and reduction of the associated histamine level in the inflammation site, reducing the sensitivity of nerve endings to histamine; reducing the activity of hyaluronidase and lysosomal enzymes, which reduces the permeability of the vascular wall; reducing the formation of free radicals; reducing the number of antigen-presenting and mast cells; inhibition of mucopolysaccharide synthesis; inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis [9]. Unlike systemic drugs, TGCS have a number of advantages: high affinity for receptors; pronounced local anti-inflammatory activity; minimal systemic effect, which is associated with their use in low concentrations and low bioavailability [6, 7].
At the same time, TGCS are not without undesirable side effects (Table 1), which is due to the peculiarities of the mechanism of their pharmacological activity. The severity of the systemic effect depends on the degree of binding of THCS to transcortin and the rate of metabolism of THCS. The development of local side effects is mainly associated with TGCS inhibition of fibroblast proliferation, collagen and mucopolysaccharide synthesis, which causes a delay in mitosis of epidermal and dermal cells [10].
The incidence of side effects of TGCS is determined primarily by the structure of the active substance, the content of halogen atoms, the strength of anti-inflammatory activity and the duration of use of the drug.
In order to minimize the undesirable effects of TGCS, it is advisable to:
- apply strictly according to instructions;
- use TGCS in the absence of effect from indifferent therapy;
- do not mix with other external therapy drugs;
- prescribe in short courses (continuous use in adults should not exceed 1 month, in children - 7-10 days), taking into account the location and severity of the disease;
- use drugs with high efficiency and an optimal safety profile (determined by the benefit/risk ratio);
- apply the drug in a thin layer, without rubbing or massaging;
- apply various methods of using TGCS (Table 2);
- in pediatric practice, preference is given to non-halogenated topical steroids, which, unlike halogenated ones, can be used on the face, skin folds, and genitals;
- if secondary infection is suspected, combined TGCS containing antimicrobial components should be used;
- use the dosage form of TGCS in accordance with the nature and localization of the inflammatory process.
The greatest preference when using topical steroid therapy is given to drugs of the latest (IV) generation - non-fluorinated TGCS (hydrocortisone 17-butyrate (Lokoid), methylprednisolone aceponate (Advantan), mometasone furoate (Elocom)), which have an optimal safety profile and high therapeutic efficacy, which can be Apply to the face, skin folds, genitals, including children. The drug is applied to the affected area of the skin once a day; if necessary, the frequency of application can be increased to 2-3 times a day, in short courses in accordance with the severity of the disease and the location of the lesions.
It should be noted that along with an extremely serious attitude towards the active components of the drug, it is necessary to pay great attention to the features of its dosage form. The basis of modern means of external therapy is far from inert, exhibiting a physical (cleansing, moisturizing or drying, keratolytic, fattening, protective) and chemical (antipruritic, bacteriostatic, proteolytic, analgesic, astringent) effect on the skin, it is capable of providing a therapeutic effect, often significantly complementing effect of active substances. Significantly modifying the rate and magnitude of absorption of the active component, influencing changes in the permeability of the stratum corneum and the rate of release of the active substance, it leads to significant differences in the activity of different forms of the same THCS, which can differ significantly (for example, an ointment containing 0.05 % of betamethasone dipropionate, according to the American classification of TGCS activity, belongs to I (extra-strong), and the lotion belongs to V (moderate) class) [11], which, undoubtedly, should be taken into account when choosing the form of the drug.
Modern glucocorticosteroids for external use are presented in a fairly wide range of dosage forms, allowing a differentiated and more narrowly targeted approach to the choice of topical therapy. Along with the “classical” dosage forms in the form of ointments and creams, THCS are available in the form of lotions, emulsions and such unique forms as lipocrem and crelo, which significantly expands the possibilities of therapeutic tactics. When choosing a dosage form of TGCS, it is necessary to be guided, first of all, by the nature and localization of the pathological process. In acute and exudative forms of the inflammatory reaction, the effect on the skin should be as gentle as possible; bases with a high alcohol content or highly occlusive should be avoided. The cooling and drying effects necessary in these cases are achieved thanks to the non-aggressive effects of external agents with a high water content (according to the postulates “wet is wet”, “irritated do not irritate”): lotions, lotions, crelo. The transition to more active forms with a moderate content of the lipid fraction (allows you to moisturize and improve the penetration of the active substance): pastes, emulsions, creams, is carried out as the skin process improves. In the chronic course of the eczematous process with pronounced dryness, lichenification, and symptoms of hyperkeratosis, it is recommended to use ointment, fatty ointment, lipocream, which, due to the high lipid content due to hydration of the stratum corneum, increase the percutaneous absorption of TGCS, reducing transepidermal water loss, fixing corticosteroids in the thickness of the skin. The release of the active substance from the ointment is, as a rule, slower than from the cream, which is extremely important for these clinical characteristics. In this regard, it should be noted that patients, due to the low cosmetic acceptability of the ointment (feeling of grease, visibility on the skin after application, smell, staining of clothes, etc.), often avoid its application or replace it with a cream, which undoubtedly affects the effectiveness of treatment . A recently introduced new form of the topical steroid hydrocortisone 17-butyrate, Lokoid Lipokrem (emulsion structure with a high (70%) lipid phase content) combines the properties of a cream and an ointment. Possessing high clinically proven effectiveness comparable to ointment, it is at the same time easy to apply, quickly absorbed, practically invisible on the skin, does not stain clothes and is easily washed off, which makes it cosmetically more convenient and acceptable for patients than ointment, increasing treatment compliance and as a consequence, the effectiveness of therapy [12, 13].
The choice of dosage form of a topical agent will be largely determined by the localization of the eczematous process. When the face is affected, given the high sensitivity of the skin of this area to steroids, as well as skin folds, preference is given to emulsion, crelo, and cream. In case of damage to the scalp or other areas of the skin with abundant hair, it is recommended to use a solution/lotion, crelo, or cream. When the skin process is localized in the area of the torso or limbs, preference should be given to crelo, cream, lipocrem, ointment, depending not only on the nature of the course of the dermatosis, but also on climatic conditions. At high temperatures and relative air humidity, the percutaneous penetration of the substance increases, and an enhanced macerating effect of the base may be observed due to increased sweating, which must be taken into account when choosing bases with a high occlusive effect. At the same time, at low air temperatures, the use of products with a high percentage of the aqueous fraction (solutions, mash, hydrogels, crelo) should be avoided, since the formation of ice crystals may cause irreversible damage to the properties of the base and damage to the epidermis [11].
The next important point in external therapy of patients with chronic eczema is the need to pay great attention to rational skin care with regular adequate use of skin moisturizers, which is determined by the characteristics of the stratum corneum of the skin in such patients (impaired lipid structure, increased transepidermal water loss, significant changes in the secretion of the sebaceous glands , disturbance of keratinization). Clinically, this is expressed in dryness and flaking of the skin, the appearance of micro- and macrocracks, while its protective and barrier properties in relation to exogenous allergens, microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses) are significantly reduced and sensitivity to irritants increases. High efficiency in the implementation of the protective, therapeutic and cosmetic effects of moisturizers in combination with topical steroid drugs during an active inflammatory process (alternating with the use of TGCS) and further long-term use in the inter-relapse period has been repeatedly proven by clinical studies [14, 15].
Among the wide range of modern drugs that help moisturize the skin of patients with chronic eczema, special importance is given to products that, in addition to a moisturizing effect, can have a pronounced softening effect due to the lipids they contain, identical to skin lipids, penetrating into the stratum corneum of the epidermis and replacing the lack of lipids that form skin barrier. At the same time, the product should not contain dyes, fragrances and other allergens that provoke an exacerbation of dermatosis. The use of such moisturizing and lipid-replenishing products (Xerodian, Locobase Ripea, Trixera, Physiogel, etc.) as needed from 1 to 4 times a day for a long time will allow achieving better biorevitalization and restoration of the protective barrier properties of the skin.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that a differentiated approach to the selection of topical therapy for patients with eczema, based on the rational, adequate use of groups and forms of external medications as part of complex treatment, will increase the effectiveness of therapy during an exacerbation, avoid undesirable effects, significantly reduce the systemic pharmacological load, and achieve stable , long-term remission of the disease and ultimately significantly improve the quality of life of such patients.
Literature
- Charles J., Pan Y., Miller G. Aust Fam Physician // Eczema. 2011, Jul: 40 (7): 467.
- Potekaev N. S. Eczema: remarks on modern ideas // Clinical dermatovenerology. 2009. T. 1. P. 67–73.
- Sohn A., Frankel A., Patel R.V. et al. Eczema // Mt Sinai J Med. 2011, Sep-Oct, 78 (5): 730–739.
- Clinical recommendations. Dermatovenerology. Ed. A. A. Kubanova. M.: DEX-Press. 2010. 428 p.
- Belousova T. A., Lukashova N. N. Differentiated approach to the selection of external glucocorticosteroids in the treatment of dermatoses // Clinical dermatology and venereology. 2006. No. 3. P. 74–78.
- Hoare C., Li Wan Po A., Williams H. Systematic review of treatments for atopic eczema // Health Technol Assess. 2000. V. 4. P. 1–191.
- Bakulev A.L. On the role of topical glucocorticosteroids in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children // Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology. 2010. No. 5. P. 4–9.
- Barnes PJ New directions in allergic diseases: mechanism-based anti-inflammatory therapies // J. Allergy Clin. Immunology. 2000. V. 106. P. 5–16.
- Allergology and immunology. National leadership. Ed. R. M. Khaitova, N. I. Ilina. M.: Geotar-Media. 2009. 656 p.
- Elisyutina O. G. Experience of using fluticasone propionate in the treatment of skin diseases // Russian Journal of Allergology. 2010. No. 5. pp. 106–112.
- Kochergin N. G., Petrunin D. D. Modern view on the problem of choosing the dosage form of external therapy // Clinical dermatology and venereology. 2011. No. 6. pp. 84–92.
- Guillet G., Nougue J. Etude comparative en double aveugle de deux dermocorticoides dans I'eczema aigu ou chronigue 17-butyrate d'hydrocortisone creme epaisse versus dipropionate d'betamethasone pomade // Ther Pharmacol Clin. 1989. V. 7. P. 10–17.
- Gip L., Verjans HL Hydrocortisone 17-butyrate 0.1% Lipocream vs betamethasone 17-valerate 0.15 crem in the treatment of patients with dry severe chronic eczema // Curr Ther Res. 1987. V. 41. P. 258–264.
- Goldstein Adrian M., Abramovits William. Ceramides and stratum corneum: structure, function, and new methods to promote repair // International J. of Dermatol. 2003. V. 42. P. 256–259.
- Kucharekova M., Vfn De Kerkhof PC, Van Der Valk PG A randomized comparison of an emollient containing skin-related lipids with a petrolatum-based emollient as adjunct in the treatment of chronic hand dermatitis // Contact Dermatitis. 2003. V. 48. No. 6. R. 293–299.
E. I. Yunusova, Candidate of Medical Sciences
GBOU DPO KSMA Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Kazan
Contact information about the author for correspondence
Zinc ointment
The composition of zinc ointment includes two components, including petroleum jelly and zinc oxide. It very rarely causes allergic reactions, so it is used by many patients. Zinc has a drying effect, but Vaseline does not dry out the skin. In the production of the drug, purified petroleum jelly is used, which has a positive effect on the skin.
The main advantages of the ointment include the following positive effects:
- antibacterial and antiseptic effect,
- elimination of inflammation and irritation,
- acceleration of the regeneration process,
- improvement of the general condition of the skin,
- drying effect
- adsorbent and astringent effect.
The ointment is as safe as possible, so it is used even during pregnancy. The only contraindication for use is individual intolerance to zinc.
The product is available in the form of liniment, ointment and paste. Before applying the product, it is necessary to treat the affected areas. It can be used up to six times per slot. The course of treatment is determined by a dermatologist, depending on the severity of the eczema. The amount of ointment that needs to be applied depends on how extensive the skin lesion is. When using the ointment, the manifestation of exudation is reduced, the inflammatory process is eliminated and a protective skin barrier is provided that prevents exposure to external irritants.
This is a fairly good ointment for eczema on the hands, but only in cases where the disease is not very advanced. Adverse reactions can manifest themselves in the form of skin itching, rash and hyperemia. The product combines well with various drugs, therefore it is included in complex therapy.
Zinc ointment is also safe for pregnant women
Prevention
For prevention, two types of care products are used.
- Moisturizing products with powerful emollients, such as urea and glycerin, soften and prevent the body from drying out due to the fact that, distributed in the outer layers of the epidermis, they attract moisture. They are applied throughout the day as needed.
- Natural oils, waxes and silicones create a protective barrier on the surface of the skin, preventing moisture evaporation. They are best used after a shower and applied to a damp area of the body.
Skin cap is like a life preserver for a drowning man
Skin-cap cream is one of the best remedies for eczema on the hands, face and other parts of the body. It is included in the treatment and prevention of eczema. The drug belongs to the group of non-hormonal drugs, has a large list of properties and shows good treatment results. The product is also available in the form of ointment, shampoo, lotion and aerosol. For eczema on the hands, use cream or ointment. If the disease is localized on the scalp, shampoo or aerosol is used.
Skin cap provides the following results:
- quick and gentle relief of itching,
- antibacterial and antifungal action,
- antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory effect,
- decrease in intracellular ATB level,
- promotes the death of bacteria and fungi.
The cream is used 2 times a day. It is evenly distributed on the surface of the affected areas. The duration of the course depends on the stage of the disease, but reaches 2-3 weeks.
The product can relieve symptoms, eliminate pain and burning. It is also used in cases where the disease is accompanied by an infection.
There are no side effects when using the drug, since it consists of natural ingredients. The active substance that has the main effect is zinc pyrethionate. It is able to reduce the level of adenosine triphosphate in the structure of cells that form epithelial tissue, which contributes to the death of bacteria.
Before applying the product, you need to cleanse the skin using skin care products for eczema. The drug can also be used during pregnancy.
Skin-cap, a line of highly effective eczema products
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Doctors cannot give a definite answer to the question of what are the basic conditions for the development of pathology. Among the causes of eczema in patients, the following factors are considered:
- genetic conditioning;
- chronic allergies;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- psycho-emotional triggers.
Dermatologists distinguish several types of eczema: true, microbial, occupational and seborrheic. The clinical picture in each case turns out to be unique, as are the factors that provoke the inflammatory process on the surface of the skin.
| Types of eczema | Symptoms | Diagnosis of eczema |
| True | Symmetrical foci of inflammation in open areas of the skin, hyperpigmentation, weeping surface. Later, numerous vesicles form, in place of which microscopic erosions gradually develop. Exudate accumulates on them. Patients experience attacks of itching, and as the vesicles heal, peeling of the skin occurs | Diagnosis is carried out by a dermatologist during an examination of the patient. Symmetrical rashes on the arms, legs or face indicate that a child or adult is experiencing true eczema. |
| Microbial | Develops against the background of traumatic skin injuries, fungal, bacterial or viral infections. The lesions are asymmetrical and concentrated on the patient’s lower extremities. Varicose veins become a risk factor. Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene leads to the accelerated development of pathology. Under the skin adjacent to the pathological focus, accumulations of infiltrate are formed | The diagnosis is established by taking a history and visual examination of the patient. The doctor pays attention to traumatic injuries to the skin of the lower extremities, mycoses, and varicose veins. Bacteriological studies of scrapings are performed to identify the resistance of the eczema pathogen to antibiotics |
| Professional | It develops against the background of the patient’s professional activity due to regular contact of the skin with allergens: chemicals, dust, cleaning products, air with atypical humidity. The size of the rash varies. Foci of inflammation can be located on any part of the patient’s body. A characteristic symptom of eczema is an abundance of small vesicles | The main diagnostic technique is to exclude the factor that provokes inflammatory processes. If the professional nature of the rash is confirmed, the dermatologist can prescribe the appropriate course of treatment to the patient. |
| Seborrheic | Affects the skin of the scalp. The affected areas are dry and profusely peeling. Itching intensifies after performing hygiene procedures. Zones of inflammation have distinct boundaries. In some cases, the course of the disease is complicated by the formation of swelling and weeping cracks in the surface layers of the skin | Some dermatologists do not agree that seborrheic eczema can be considered an independent type of pathology (changes in the skin are considered a special case of the true type of disease). The main diagnostic technique is histological examination of cells to exclude microbial eczema from the diagnostic report |
Are you experiencing symptoms of eczema?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Dermasan is a good alternative
Ointments for eczema on the hands are used very often. There are a lot of them, so when choosing a remedy it is necessary to base it on the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as the degree of the disease and its course.
Dermasan is often used in the treatment of eczema. The drug is a solution that has the following properties:
- softening effect
- antiseptic effect,
- elimination of inflammation,
- increasing skin elasticity.
Before using Dermasan, you need to clean the surface of the affected areas, then apply a small amount of the product to them. Must be used up to three times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the dermatologist. Individual intolerance may be a contraindication. It is not recommended to apply the drug to those places where there are erosions and purulent wounds.
Dermasan will help in the initial stages of the disease
Protective products for skin protection
In addition to medicinal ointments, effective therapy for eczematous rashes localized on the arms and legs depends on proper care of damaged skin. At home, several additional means are used:
- moisturizing and nourishing creams for dry eczema (Ozone C, Balyan MB, D-Panthenol);
- regenerating (Perfectil, Radevit, Retinoic ointment, Aloe liniment);
- antipruritics (Afloderm, Advantan, Beloderm, Elopsor).
Connoisseurs of oriental medicine use Chinese ointments for dermatitis (Eczema, Zudafu). These and mild products similar in composition and action provide proper care for thin skin, help restore the skin and minimize the effects of eczematous processes.
Aurobin is a good choice
Non-hormonal ointment aurobin is a combination drug with a wide spectrum of actions. It contains: dexpanthenol, prednisolone and lidocoine. Together, these components can provide the following results:
- eliminating the feeling of itching,
- anti-inflammatory effect,
- providing local anesthesia,
- reparative effect,
- acceleration of wound healing,
- reduction of exudative manifestations,
- stimulating the regeneration process.
The ointment must be applied to problem areas, after cleaning them first. The period of use and dosage are determined by the doctor. As a rule, the drug is applied up to 4 times a day. The product is quite safe, so it is used during pregnancy and in the treatment of children. Contraindications may include individual intolerance to the components and the first trimester of pregnancy.
The drug "Eplan" contains active substances that can have many positive effects in the treatment of eczema. The list of main effects includes:
- eliminating itching and relieving pain,
- improvement of regenerative function,
- preventing the death of affected tissues,
- preventing the formation of a dry crust on rashes,
- protecting the skin from exposure to chemical elements,
- providing an anti-inflammatory effect,
- acceleration of wound healing,
- preventing the appearance of pus in the affected areas.
Before use, you need to thoroughly clean the surface of the affected areas, then apply a generous amount of cream to them. Apply as needed. The duration of the course depends on the patient’s condition and symptoms.
Aurobin quickly heals wounds
Causes of eczema
The exact cause of this condition is unknown, but the process is based on an overactive reaction of the body's immune system to an irritant or allergen. Substances are formed in the cells of the dermis that cause inflammation, which is associated with the main symptoms. It is also known that the tendency to this disease is inherited.
The therapy is aimed at suppressing inflammation and allergies, as well as healing, eliminating itching and dryness.
Topical medications are available in various forms. Each type of skin lesion has its own dosage form.
- Ointment - has a fatty base with which the medicine is mixed directly, it is more suitable for dry eczema and dermatitis on the hands, it cannot be used on wet areas, it may not be hormonal, or contain hormones. The active components penetrate the skin well, and the fat base itself is not absorbed.
- The cream contains water with a medicine dissolved in it, which is mixed with a fat base. Contains significantly less fat than ointment, so it is suitable for weeping eczema. It is better absorbed and does not leave greasy marks on clothes. The healing components of the cream penetrate the skin less well and usually act in its upper layers.
- In the paste, the concentration of dry substances is more than 25%.
- Lotion is a liquid dosage form (usually an aqueous solution of a drug plus oil). Lotions are suitable for wet conditions, as well as on the head under the hair.
Expert opinion
— The selection of hormonal/non-hormonal agents for external use is carried out by a specialist after collecting an anamnesis, identifying the causes that provoked the disease, and examination.
Firsakova Svetlana Sergeevna, dermatovenerologist, Melanoma Unit Moscow clinic
Boric ointment
In the treatment of eczema, boric ointment is used very often. This is an inexpensive remedy that provides a good healing effect. The main properties of the product include:
- antiseptic and disinfectant effect,
- antibacterial and antifungal effect,
- antiparasitic effect.
The active substance of the drug promotes coagulation of microbial cell proteins and disruption of the permeability of their membranes. The product copes well with bacteria, fungi and parasites. Contraindications for use may be pregnancy, individual intolerance, age under one year, renal failure, skin inflammation in remission.
Treatment of eczema should be comprehensive. Using ointments alone is not enough. The therapy should include medications and products that will provide the fastest and most effective treatment.
It is necessary to eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the cause of the disease. Undoubtedly, non-hormonal ointments help eliminate skin lesions, but this is not enough, since the disease will return until the main problem is resolved. It may consist of a disease of the internal organs and systems responsible for the proper functioning of the entire body.
If eczema has reached the last stages of development, non-hormonal ointment will have a minor effect, which will not be enough for effective treatment. Sometimes taking hormonal drugs is simply necessary.
Detoxification and desensitization therapy for eczema
Calcium preparations are often used for desensitization purposes, among which calcium chloride and calcium gluconate are considered the most common. Infusion of calcium chloride is not recommended. 5-10 ml of the drug is diluted in 100-200 ml of saline and administered intravenously using a system (drip). It is also not recommended to use this product for intramuscular administration, as this will lead to necrosis (necrosis) of muscle tissue. In the future, an abscess may form in the injection area, which in most cases requires surgery to eliminate. In turn, calcium gluconate can be used for intravenous administration or prescribed in tablet form. Also, for the purpose of desensitization, methenamine and sodium thiosulfate (intravenously) can be prescribed.
Detoxification therapy consists of prescribing gomedoz intravenously and taking sorbents internally (enterosgel, polysorb, activated carbon). As a rule, medications are taken after or before meals 1.5-2 hours.