Lichen planus is a chronic disease, prone to relapse, which is accompanied by itchy skin and inflammatory rashes in the form of purple papules.
This disease often affects the mucous membranes of the mouth or genitals. According to WHO, lichen planus accounts for about 2.5% of all dermatological diseases and 15% of diseases of the oral mucosa.
The complex of diseases that make up lichen planus includes two syndromes: Little-Lassuere syndrome, including non-scarring alopecia of the armpits and pubis and scarring alopecia of the scalp, as well as Grinshpan-Potekaev syndrome, including diabetes, hypertension and an erosive-ulcerative form of the dermatological disease.
The exact cause of the pathology is unknown. There are neurogenic, viral, bacterial, autoimmune and toxic-allergic theories of the nature of the disease.
There are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of developing lichen planus, namely:
- genetic predisposition;
- nervous system disorders;
- failure of immunity;
- allergic (lichenoid) reactions to chemical or food components;
- chronic infections in the body;
- metabolic disorders;
- stress;
- injuries to the skin and oral mucosa (presence of sharp edges of teeth, poorly made dentures);
- changes in the microelement composition of saliva due to the presence of dentures made of different metals in the oral cavity;
- aggressive effect of certain medications;
- age after 40 years, etc.
Treatment of this disease is complex and requires an individual approach. Based on the test results, the doctor selects a regimen and dosage of drugs, usually of local action, which reduce the symptoms of the pathology and prevent its reappearance.
What is lichen planus?
Lichen planus is an inflammatory dermatosis with various clinical manifestations. The pathological process involves skin tissue and its appendages (nails and hair), as well as mucous membranes. Usually the disease affects representatives of both sexes of middle and older age, but sometimes it is observed in children.
In modern medicine, it is believed that lichen planus is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in response to the action of a neoantigen of epidermal (skin) origin, since the autoimmune aspect has a significant place in the nature of the disease. Cytokines released by immune cells provoke cytotoxic mechanisms and trigger cell death (apoptosis).
Lichen planus is characterized by three stages:
- progressive, which is accompanied by the active manifestation of symptoms of the pathology: the formation of papules and itching;
- stationary with a gradual decrease in signs of the disease: pallor, flattening of papules and subsidence of itching;
- regressive, which is characterized by regression of papules, the formation of brown spots and areas of atrophy at the site of their localization, and the disappearance of itching.
Causes of pityriasis
Despite the fact that Gibert's disease is very common, the mechanism of the disease is not fully understood. The following factors are believed to play an initial role:
- Exposure to viruses (type 7 herpesvirus, etc.), bacteria and other infectious agents. This is confirmed by tests that prove the presence of pathogens in the body. Very often, skin disease appears against the background of influenza, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
- Attachment of allergic reactions.
- Bites from bedbugs, lice and other blood-sucking insects.
- Reduced immune defense.
- Frequent hypothermia and stress.
- Violation of gastrointestinal functions and metabolism.
- Introduction of vaccines.
How to identify lichen planus?
The external manifestation of lichen planus is caused by the processes of damage and regeneration of skin cells and mucous membranes.
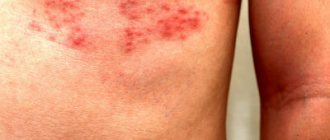
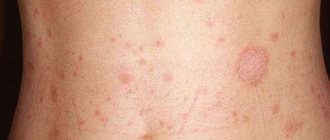
The following symptoms are characteristic of lichen planus:
- the presence of polygonal, flat-topped, colored papules 1-2 mm in diameter;
- grouping of papules with the formation of rings or lines;
- the formation of large plaques from papules (Wilham stack), along the periphery of which isolated small papules are located;
- symmetrical localization on the skin (wrist joints, forearms, legs, genitals, etc.);
- the appearance of neoplasms on the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, red border of the lips or genitals when the mucous membrane is damaged;
- thinning, brittleness, clouding of the nail plates;
- pronounced itching;
- rapid appearance of papules due to skin injuries (Koebner phenomenon);
- formation of secondary hyperpigmentation in place of the disappeared papule.
Doctors classify the main morphological forms of lichen planus as:
- typical, most common (45% of cases) form of pathology, accompanied by the formation of pearl-colored papules with a specific coating;
- hyperkeratotic or verrucous, characterized by the formation of hard red, gray-yellow or dark red infiltrated plaques on the front of the leg or upper limbs;
- exudative-hyperemic (25% of cases), causing the formation of edematous papules;
- erosive-ulcerative, often resulting from exudative-hyperemic lichen and accompanied by the formation of small ulcers or areas of erosion on the feet or in the interdigital space, etc.
Also in some cases, rare bullous, atypical and pigmented forms of the disease are observed.
The appearance of the first signs of the disease requires immediate medical response. Lack of timely treatment can lead to rapid progression of the pathology and a significant weakening of the body's defenses. What tests are done for lichen planus?
Typically, the diagnosis of lichen planus includes:
- blood test (general and biochemical);
- hormonal profile;
- scraping for histological and cytomorphological examination (affected tissues are susceptible to hyperkeratosis, degeneration of the epidermis, the presence of infiltrate, etc.);
- skin biopsy;
- consultation with a dentist and other related specialists (endocrinologist, gastroenterologist).
When visiting a doctor, it is extremely important to provide him with a list of medications taken, episodes of recent dental treatment, vaccination or viral disease. History data will greatly help in making the correct diagnosis and determining the nature of the origin of lichen planus.
Treatment of pityriasis
When a patient is diagnosed with Gibert's disease, the dermatologist develops an individual treatment regimen to avoid dangerous complications. There is an opinion that pityriasis rosea will go away on its own in a few weeks. As a result, complications arise, and the patient comes to the dermatologist with an advanced form of the disease.
Drug treatment includes the following medications:
- antihistamines that relieve the patient from itching, swelling and redness on the body
- corticosteroid, desensitizing and antipruritic ointments. Medicinal compositions containing betamethasone, hydrocortisone, etc. are applied to the affected skin and lightly rubbed in. The medications eliminate rashes, get rid of peeling, and effectively restore the skin.
- drying agents containing zinc to accelerate skin healing
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with pityriasis rosea. It is unacceptable to start taking antibacterial drugs on your own, since they are selected individually, taking into account laboratory tests.
- antifungal medications: drugs containing clotrimazole and other active substances are prescribed topically in the form of gels and ointments
- antiviral drugs containing acyclovir and other active components. Dermatological tests have confirmed that if antiviral drugs are prescribed in combination with antibiotics from the first days, the patient quickly recovers.
- neutral water-shaken preparations Dermatologists prescribe pharmacy talkers containing zinc oxide, menthol and anesthesin to patients with pityriasis rosea. These products relieve itching and pain in damaged areas and speed up recovery.
- iodine is an aggressive, but extremely effective remedy. Injured skin is treated with iodine in the morning and evening. Initially, the skin begins to peel off more actively, but then there are no extra scales left on it. Not all experts recommend that their patients cauterize damaged areas with iodine, since this drug can be harmful if used incorrectly.
Recommendations for patients
During the treatment period, the patient is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet: avoid nuts, citrus fruits, chocolates, honey, etc. Products containing artificial colors should be excluded from the menu. It is worth limiting the consumption of fried foods, carbonated drinks, fast food, strong alcohol and coffee.
- Limit water treatments within reasonable limits and give preference to the shower.
- Refuse to use aggressive hygiene and cosmetic products for the body. Gels and other detergents should not dry out the skin.
- Give preference to underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Moderate sunbathing - ultraviolet light helps the skin recover faster.
- Follow the recommendations of a dermatologist, apply to the skin only products recommended by a specialist.
- Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with your doctor.
How dangerous is lichen planus?
Lack of treatment or a severe stage of the disease can lead to damage to the entire skin, severe discomfort and a significant decrease in immunity.
Lichen planus on the scalp can cause irreversible hair loss, and on the nail plates - nail deformation (thinning, splitting, rejection of the nail plate, even nail lysis).
A pathological lesion in the eye area can lead to blurred vision or narrowing of the tear duct.
The erosive form of the disease often leads to the formation of scars, and the result of lesions of the genital mucosa can be narrowing of the vagina or phimosis.
Also, some forms of the disease are prone to malignancy and degeneration into squamous cell skin cancer.
How to cure lichen planus?
The composition and tactics of treatment for lichen planus depend on the degree of spread of the lesion, on the cause and localization of the pathology, on information about the effectiveness of previously administered therapy. Thus, treatment of the disease involves the use of systemic and external medications, as well as phototherapy.
Among the most effective medicinal groups of drugs for the treatment of lichen planus, experts identify:
- antihistamines;
- multivitamin complexes;
- antifungal agents;
- systemic corticosteroids;
- systemic retinoids, etc.
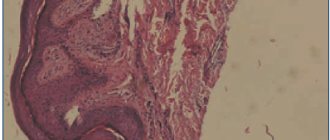
Damage to the oral mucosa in LLP
Topical and systemic corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are first-line drugs for the treatment of localized forms of LP of the oral mucosa. Strong and very strong drugs - clobetasol, triamcinolone, betamethasone, fluocytonide, fluticasone - have proven effectiveness and safety. These drugs are usually applied 2 times a day, either undiluted (eg clobetasol propionate 0.05%) or mixed with Orabase (eg triamcinolone) for 1-2 months, followed by maintenance use. It is also possible to use GCS in the form of intralesional injections, but there is insufficient data to support the advantage of this method over others (there are only isolated clinical cases). Systemic therapy using oral corticosteroids may be indicated in case of significant severity of the disease, in case of refractory to external therapy, however, the evidence base for this approach is insufficient; adequate placebo-controlled studies have not been conducted. Taking into account the wide range of side effects associated with the use of systemic corticosteroids, this group of drugs is used in the form of a short course with subsequent transition to topical therapy.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors
Interest in the possibility of using topical calcineurin inhibitors was attracted primarily by their anti-inflammatory effect, which is different from tGCs. The mechanism of action of the drugs is realized by suppressing the activity of T cells at the level of transcription factors. Published studies examining the effectiveness of this group of drugs are very contradictory - a meta-analysis performed in 2012, evaluating 3 randomized controlled trials, showed that the effectiveness of pimecrolimus was no greater than placebo. Subsequent studies were more encouraging - according to the data obtained, the effectiveness of topical calcineurin inhibitors was comparable to the effect of tGCs. A 2014 study found that pimecrolimus was slightly more effective than tacrolimus, while more recent studies found that tacrolimus and pimecrolimus were equivalent. These data were confirmed in an open randomized controlled trial (2017), a pilot randomized controlled trial, and a subsequent meta-analysis. Many physicians have found tacrolimus to be more effective in their clinical practice. Side effects of topical calcineurin inhibitors include local irritation and burning, especially on eroded lesions (which limits their use in the case of the erosive form of LP), but in general their safety profile is not inferior to long-term use of corticosteroids. The absence of side effects of TGCS determines increasing interest in the use of these drugs in clinical practice.
Topical and systemic retinoids
Retinoids have certain immunomodulatory effects due to their direct effects on T cells through nuclear retinoic acid receptors. Topical retinoids are an alternative to corticosteroids for non-erosive LP and are recommended as a second-line drug according to World Workshop in Oral Medicine IV. Despite the proven effectiveness of topical tretinoin and isotretinoin 0.1% (in placebo-controlled studies), one study showed lower effectiveness compared to tGCs. Side effects include local irritation, photosensitivity, and teratogenicity. The possibility of disease relapse within 2-5 weeks after stopping use of the drug significantly limits the widespread use of topical retinoids in everyday practice. The use of systemic retinoids (etretinate, isotretinoin) is limited due to an insufficient risk-benefit ratio, however, the use of alitretinoin may be more successful.