Eye tumors are benign or malignant tissue tumors that can form in any part of the visual organ.
They affect the eyelid, retina or choroid.
Malignant tumors on the eye are rare compared to other types of cancer.
The most common tumor in adulthood is venous melanoma. Develops in one in 100–200,000 adults. Retinoblastoma usually occurs in children. On average, 1 case per 20,000 births.
Eye cancer is a dangerous disease because it affects vision and can lead to the death of the patient.
Causes
The causes of the pathological process have not been established, but there are a number of factors influencing the development of cancer. A person's genetic predisposition plays an important role:
- Monosomy. Studies of melanoma tumor samples have shown that this form of eye cancer is closely associated with the absence of chromosome 3. Thus, patients have only one intact chromosome 3, which is medically called Monosomy 3. Unfortunately, there is not enough research at present to be able to cure the disease. Therefore, the mortality rate is still very high.
- Retinal cell mutations. When it comes to retinoblastoma, almost 45% of all victims have a genetic predisposition inherited from an autosomal dominant parent. In particular, these are mutations of both alleles of the retinoblastoma RB1 gene, which cause degradation of retinal cell growth. Therefore, retinoblastoma often appears during embryonic development in the womb. As a rule, both eyes of the child suffer from hereditary retinoblastoma.
- Common mutations in body cells. Intangible forms of retinoblastoma occur in somatic mutations. Here, during embryonic development, spontaneous rearrangement of body cells occurs, which contributes to the appearance of eye cancer.
Another contributing factor that has been discussed as a possible cause is ultraviolet radiation. The influence of this factor is beyond doubt among doctors specializing in the treatment of cancer.
The development of neoplasms in tissues is influenced by HIV infection and unfavorable environmental conditions.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
The disease is most often detected in people over 50 years of age and is the main cause of irreversible vision loss. The risk of the disease increases with a genetic predisposition, as well as in patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Symptoms of the disease are associated with damage to the macula area of the retina.
The initial manifestations of AMD do not have any clinical manifestations and can only be detected during an examination by an ophthalmologist. As the disease progresses, symptoms such as distorted outlines of objects, blurred vision, and blurred vision appear.
The dry form of AMD does not require special treatment. To treat the wet form of age-related macular degeneration, intravitreal injections (injections into the vitreous cavity) of drugs that block the growth of defective vessels under the retina (anti-VEGF drugs) are used. In addition, photodynamic therapy and laser photocoagulation of the retina are indicated.
Read more about AMD treatment >>>
Classification
According to statistical data, secondary tumors occur more often than primary ones. The following types of cancer of the optical system are distinguished:
- Benign tumors of the eyelids. Hyperkeratosis - the keratin layer of the eyelid skin grows excessively. Xanthelasmas are fatty deposits on the eyelids.
- Malignant tumors also form in the eyelids. Most often basal cell carcinoma. This is a basal cell skin cancer that develops in the corners of the eye and on the eyelids. Spinal cell carcinoma or malignant melanoma are found much less frequently. Experts believe fair-skinned people who are exposed to sunlight for many years are more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Melanoma. It is an extremely dangerous pathological process. Develops on the conjunctiva, eyelids, and affects the choroid. Melanoma tends to metastasize early and the prognosis is poor.
- Retinoblastoma is the most common malignant neoplasm in childhood. Affects the retina and develops for genetic reasons. Parents already carry the gene mutation and pass it on to their child. However, this hereditary form of retinoblastoma occurs in only 10% of cases. In 90% of cases, the gene defect occurs spontaneously.
Other types of tumors: squamous cell carcinoma and sarcoma. The latter type of cancer progresses rapidly. Sarcoma makes it difficult for the eyeball to move, causing the patient's optic nerve to atrophy.
Based on the location of formations, there are two types:
- Extraocular. Localized on the eyelids, third eyelid, conjunctiva, orbit and optic nerve. Extraocular types include lymphoma, melanoma, adenoma, SCC, basal cell carcinoma, mastocytoma, viral papillomatosis, meningioma, osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma.
- Ocular. Cancer is localized on the cornea and sclera, iris and ciliary body, retina and choroid. The ocular type includes corneal SCC, lymphoma, ciliary body adenoma, retinoblastoma, melanoma and medulloepithelioma.
Benign neoplasms on the eyelids
Such eyelid tumors have different etiologies: they develop in the epithelium (papilloma, senile wart), in soft tissues (lipoma, fibroma). It can also be pigmented neoplasms (nevus). Papillomas and warts are characterized by a course of many years without developing into a malignant tumor - only a visual defect causes inconvenience.
Trichoepithelioma is a tumor of the eyelids that occurs on the hair follicles. Typically develops in children and adolescents. Externally, it is a dense nodule measuring 1-3 mm, which can reach 1 cm in diameter. The tumor can be single or multiple, and sometimes develops into malignant. It is removed by excision or cauterized.
Fibroma, lipoma are mesodermal tumors of the eyelids, the size of which can reach several centimeters. They grow quite slowly and respond well to surgical treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease vary. They are directly related to the form of the disease. All types of cancer lead to impaired visual perception, its deterioration, and in severe cases, complete loss of vision. Some tumors cause noticeable changes in the eyelids and conjunctiva, which can be seen in the mirror on your own. The symptoms that occur depend, in part, on the type, location, and size of the tumor.
Malignant tumors often grow unnoticed for a long time and cause discomfort only in the last stages of development.
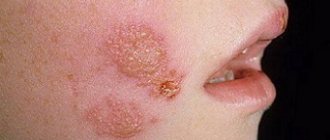
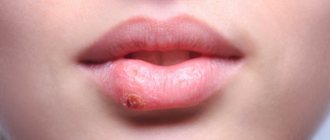
If tumors in the eye are localized on the conjunctiva or iris, color changes, spots, nodules, or other skin tumors appear. However, vision usually does not deteriorate. Basalioma on the eyelids in most cases affects the lower eyelid and is expressed as a spotted nodule that sometimes bleeds slightly.
If tumors form at the back of the eye, they can be difficult to detect. Such formations are often asymptomatic and appear in later stages. Possible displacement of the eyeball, squint, frequent flashes before the eyes, sudden pain.
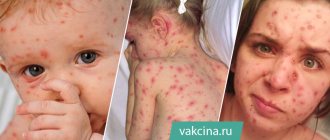
Retinoblastoma occurs primarily in infants and young children and has a noticeable symptom that when light shines on the pupil, it appears whitish. In photographs taken with flash, it does not look reddish or black, but milky. The second sign is squint.
The first symptoms of eyelid melanoma look somewhat different. Along with a noticeable deterioration in vision, double vision occurs, dark spots appear on the iris or in the patient’s field of vision.
All symptoms of eye cancer:
- hyperemia;
- inflammation;
- glaucoma;
- pupil dilation;
- accumulation of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye;
- developmental disorders in a child;
- retinal disinsertion;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased appetite.
Conjunctival cancer of the eye
Tumors of the conjunctiva come in different types. They usually appear between 40 and 60 years of age. Here are the benign tumors known in modern ophthalmology:
- Papilloma is a common tumor of the conjunctiva. It looks like a cluster of nodules with many small vessels, which is why the neoplasm acquires a reddish color. Sometimes papillomas can degenerate into malignant ones. They are treated surgically, by cryodestruction (freezing), and in case of large areas of growth, laser therapy is used;
- Nevus is another common formation on the conjunctiva. Simply put, it is a mole that appears as a flat spot that is yellowish or brown in color. If the nevus does not grow and does not cause concern, then no treatment is required;
- Hemangioma is a vascular tumor that is congenital in nature. Outwardly it looks like a bluish spot. To remove such a tumor on the eye, laser treatment is prescribed, and at the second stage - electrocoagulation.
Dermoid, lymphoma, lymphangioma are other types of benign neoplasms of the conjunctiva. All of them can be successfully treated if appropriate measures are taken in time. But malignant tumors pose a much greater danger to the eyes. Squamous cell carcinoma develops against the background of damaged conjunctiva: for example, due to a burn, precancerous conditions, etc. In this case, the conjunctiva turns red, there is a sensation of a foreign body in the eye, profuse lacrimation, pain, and the tumor begins to grow rapidly.
Conjunctival melanoma usually occurs against the background of nevus or melanosis.
If a pink or brown spot appears on the eye, this is a reason to immediately visit a doctor for a diagnosis.
Cancerous tumors of the eyes develop quite quickly, so it is important to start therapy on time. The main method of eliminating such tumors is microsurgical (radio wave knife) with the additional use of radiation and chemotherapy. For benign tumors, cryotherapy is the most justified method.
Diagnostics
Eye cancer is detected during routine examinations. Retinoblastoma is detected very early in photographs. However, special tests are needed to make a conclusion.
If melanoma is suspected, an ultrasound examination is performed to determine the exact location and extent of the tumor. Retinoscopy is used to detect retinal detachments. Fluorescein angiography provides additional information about the health of blood vessels.
The diagnosis of retinoblastoma is somewhat different and primarily involves ophthalmoscopy. In this case, the patient is most often prescribed drugs to dilate the pupil, allowing him to better see the fundus. Then the eyes are illuminated with special light sources, and the retina is examined for tumors.
Additionally carried out:
- biopsy to find out whether the patient has a malignant or benign formation;
- magnetic resonance imaging (allows you to determine the extent of tumor spread to other structures).
After all the studies have been carried out, the type of cancer tumor and the degree of its development are determined. The correct treatment strategy depends on this.
Retinal dystrophies
The cause of dystrophic changes in the retina is usually disorders in the vascular system of the eye. Most often, dystrophies are found in elderly patients, as well as with moderate and high myopia. The myopic eye is usually extended in the anteroposterior direction, and the resulting overextension of the posterior parts of the eyeball is accompanied by the appearance of dystrophic changes in the fundus. Retinal dystrophies can also occur with various vascular and inflammatory diseases of the eye.
The main method of treating retinal dystrophies is photocoagulation of altered tissues using an argon laser to strengthen thinned areas of the retina and delineate the area of detachment, if one has been identified.
Read more about the treatment of retinal dystrophies>>>
Treatment
Treatment for eye cancer is as follows:
- Percutaneous radiotherapy. Externally applied radiation treatment is possible both for melanomas and retinoblastomas and local irradiation of the eye. The eye lens remains intact during treatment. Percutaneous radiation therapy is used for early stage cancer.
- Brachytherapy is performed if the cancer is already at an advanced stage, when there are metastases. Radioactive circuit boards are placed inside the eye using local anesthesia. Leave inside for 2 weeks. Irradiation allows for targeted treatment of large tumors and is suitable for melanomas.
- Chemotherapy. Like most cancers, eye cancer is treated with chemotherapy drugs. This is usually a concomitant therapy for radiation treatment. A relatively new treatment method is thermochemotherapy, in which doctors use the sensitivity of tumor tissue to heat. This treatment method causes dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, pale complexion and lack of appetite.
If necessary, surgery is performed, in which the affected areas are removed, the tumor is excised and sent to the laboratory. Surgical excision of tumors in the eye is the most common treatment.
Sometimes the optic nerve is completely removed or enucleation is performed. Enucleation is an operation to remove the eyeball. An implant is inserted as a replacement. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia.
Even after successful treatment, follow-up examinations should be performed regularly over the next few years.
Retinal hemorrhages
Hemorrhages in the retinal area can occur as a result of injury to the eyeball, vascular pathologies or dystrophic diseases of the retina. Retinal hemorrhages are found in diabetes mellitus, thrombosis of the central retinal vein, defects of the cardiovascular system, blood diseases, and burns.
The blood in the cavity of the eyeball has a toxic effect on the internal structures of the eye, changes the structure of the vitreous body and reduces the transparency of the optical media of the eye, which is accompanied by a deterioration in the quality of vision. Severe complications of retinal hemorrhage are increased intraocular pressure and secondary glaucoma, retinal detachment, degenerative changes in the retina, etc.
To treat hemorrhages in the retina, conservative methods are used (injections of drugs that accelerate the resorption of hemorrhages), laser treatment (laser vitreolysis, laser coagulation), and surgical techniques (vitrectomy with replacement of the clouded vitreous).
Read more about the treatment of retinal hemorrhages >>>
Complications
A serious complication of cancer is complete blindness. But the worst thing is the formation of metastases. In approximately 50% of cases, melanoma leads to metastases, they occur in the liver. Distribution occurs through the blood circulation. Metastases are found in the brain, larynx, and lymph glands.
In addition, unpleasant side effects occur during therapy due to aggressive treatment methods. These include permanent damage to the retina, optic nerve, lens, or tear glands.
Forecast
The likelihood of healing depends on whether the tumor was completely removed or not. Melanoma develops by metastases. If not, then the prognosis is favorable.
If retinoblastoma is detected at an early stage, the chances of recovery are high. With a non-hereditary form, complete recovery is observed in 90% of cases. The hereditary form tends to metastasize, so the prognosis is less favorable.
With timely treatment of eye cancer, the chances of complete recovery are 85% if the tumor is detected at an early stage. At a late stage, only 47% of patients can be cured.
Malignant tumors of the eyelids
Eye cancer (squamous or metatypical) usually appears against the background of precancerous skin diseases of the eyelid. The tumor grows quite quickly, and in this case early diagnosis and timely therapy are very important. Typically, surgical removal of the tumor, concomitant chemotherapy, and radiotherapy are used.
Meibomian gland cancer is a rare type with a high degree of malignancy. Typically, the tumor occurs on the upper eyelid and is characterized by rapid growth with metastases. Meibomian gland cancer is treated using radio wave therapy, but in 90% of cases, even after proper treatment, relapses occur within two years.
Melanoma of the eyelid is the most dangerous neoplasm of the eyelids. Usually localized in the lower eyelid, outer or inner corner of the eye. It appears as a flat, yellow to almost black spot. For tumors up to 10 mm in size, microsurgical excision is used; for larger locations, radiation therapy is prescribed.
Treatment of eye tumors depends on their etiology. Benign ones can be easily removed using excision, cauterization, cryodestruction, and laser therapy. To eliminate malignant tumors, surgical treatment, contact radiation, radio wave or chemotherapy are prescribed.