Senile itch
Age-related changes affect all human organs, including the skin.
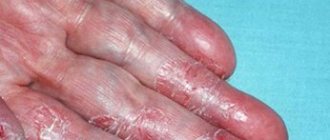
In older people, the skin becomes thinner, dries out, and becomes sensitive to allergens and mechanical irritants. These factors, as well as various diseases of internal organs and systems, cause the so-called senile itch - an unpleasant sensation that can be constant or occur periodically. Senile, or senile, itching can cover the entire body or only certain areas. The pathological condition is accompanied by peeling of the skin. Most often, unpleasant sensations occur in the evening and at night.
Preventive actions
Effective preventive measures will help minimize the occurrence of itching:
- Moisturizing the skin with special cosmetics.
- Proper nutrition.
- Avoiding underwear made from synthetic fibers.
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to the sun without sunscreen.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Preventative examination once every six months.
Senile itching in old age is a fairly common pathology, the treatment of which should be approached comprehensively. This is the only way to eliminate discomfort and alleviate the condition of an elderly person.
Causes of senile itching
The main reason for the condition is natural aging of the body. As a person ages, the synthesis of hormones “responsible” for the elasticity of the skin decreases. Metabolism slows down, resulting in slower tissue regeneration. The skin becomes dry and wrinkled.
Several contributing factors increase the likelihood of aging itch. These include:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- liver diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- atrophy of the skin glands;
- cognitive disorders;
- violations of water-salt metabolism;
- dehydration.
Often, an unpleasant sensation can appear due to changes in air temperature, wearing synthetic clothing, swimming in too hard water or using products with an inappropriate pH level.
Symptoms of pathology
Characteristic signs help identify senile body itching:
- thinning and drying of the skin (skin becomes papery);
- the appearance of red spots, rashes, pustules on the body;
- absence of scratches and wounds in areas of the body that are prone to itching;
- itching worsens in the evening and at night;
- The duration of discomfort can range from several days to several months.
Sometimes patients may itch different parts of their body every day.
Diagnostics
With a similar problem, patients come to see a dermatologist. As a rule, the diagnosis is made based on a survey and examination.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the dermatoscopy method is used - studying the biomaterial using magnifying lenses.
In some cases, it is appropriate to conduct additional examination:
- take blood, urine and stool tests;
- test for allergens.
If the cause of the pathology is a disease of the internal organs, the patient is referred to a therapist or other specialized specialist who will supervise the underlying disease.
How to treat?
The goal of therapy for senile skin itching is to relieve symptoms. Several techniques are used to alleviate the condition. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the cause that provoked the pathology and the nature of the manifestations.
Preparations for senile itching
The following types of drugs are used to treat senile itching:
- antihistamines (Diazolin, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin);
- neuroleptics (Promazine, Clozapine);
- immunostimulants (Cycloferon, Echinacea tincture);
- corticosteroids (Betazon, Betaderm, Kremgen);
- vitamin complexes;
- alcohol tinctures;
- pharmaceutical ointments and creams with a soothing and cooling effect (Fenistil, Clotrimazole, Menovazan, etc.).
Corticosteroid drugs are taken only as prescribed and under the supervision of the attending physician. In general, hormone therapy is used for patients with autoimmune diseases, with the doctor carefully weighing the benefits and risks of treatment for each patient.
If the cause of itching is stress and other cognitive conditions, the patient is prescribed mild sedatives: valerian infusion, Novopassit, etc.
You can quickly stop an attack with warm water. The itchy area is showered with water for a few minutes. Before water procedures, you can apply 2-3 drops of peach tree essential oil to the skin.
Body hygiene
When symptoms of senile itching appear, it is important to pay attention to hygiene. For bathing, you need to use soft products with a neutral pH, and if possible, wash with water that is not too hard.
When bathing, do not use hard washcloths or scrubs.
The patient's underwear and bedding should be made from natural fabrics.
Senile body itch and diet
If you have senile itching, you should exclude the following foods from your diet:
- grilled meat;
- marinades;
- baked goods;
- citrus;
- coffee;
- spices;
- alcoholic drinks.
The diet includes seafood, herbs, fresh vegetables, pumpkin seeds, nuts, and unrefined oils.
Folk remedies
Some types of senile itching can be successfully treated with folk remedies.
Traditional methods of treatment:
- herbal baths;
- applying vegetable oil to flaky areas;
- using homemade ointment made from aloe and Vaseline.
Before using unconventional recipes, you should consult your doctor.
Other techniques
For patients who experience itchy skin as a response to stress, it is very important to control their emotions. In such cases, it is useful to do yoga, auto-training, and use various relaxation techniques.
Treatment
Various medications and methods are used to relieve itchy skin. Therapy is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms that cause discomfort.
Drug therapy
The following medications can help relieve pain:
- Antihistamines.
- Neuroleptics.
- Pharmacy ointments.
- Immunomodulators.
- Corticosteroids.
- Salicylic acid.
- Folk remedies.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
In addition, you can improve the condition of the epidermis using effective folk methods.
Folk recipes
The following remedies will help relieve itchy skin:
- Healing lotions. Dissolve 2 g of mumiyo in 150 ml of water. Apply lotions to itchy areas 2-3 times a day.
- Healing baths. 2 tbsp. l. dry medicinal herbs (oregano, birch buds, elecampane, chamomile, string, peppermint) pour boiling water, leave for several hours, add to the bath.
- Propolis tincture. 1 tsp. Mix propolis with 100 ml of oil (olive, vegetable) and keep for 30 minutes. in a water bath. Treat itchy areas.
- Apple cider vinegar, diluted in a 1:1 ratio, is used to wipe the skin.
- Ointment. 3 tbsp. l. birch tar, 2 tbsp. l. Vaseline oil mixed with 50 ml of Sophora tincture, leave in a dark place for 3-5 days. Apply to itchy areas several times a day.
- Sea salt. One of the remedies that relieve itching and inflammation of the skin is a weak solution of sea salt, which significantly relieves the symptoms of itching and eases the course of the inflammatory process.
An infusion of valerian, violet, and licorice is taken internally. Take medicinal herbs in equal proportions, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, take 1 tbsp three times a day. spoon.
Diet
If you are bothered by senile itching of the skin of the body, you can get rid of or alleviate the symptoms with the help of a special diet. Nutritionists recommend that older people limit the consumption of spicy and salty foods, processed foods, citrus fruits, strong coffee, tea, and alcoholic beverages. Such products contribute to the exacerbation of unpleasant symptoms.
For many skin diseases, including senile itching, it is recommended to eat a lot of vegetables, fruits, and foods rich in iodine and Omega-3 acids.
Physiotherapy
An effective treatment for itching and other diseases of the epidermis is the use of various physiotherapeutic procedures. This method is quite effective because it stimulates the immune system and enhances the protective properties of the epidermis.
Popular questions about senile itch
Can it develop in young people?
Young people may also suffer from itchy skin, but the term “senile itch” is not applied to them.
Where is itching most often located?
The localization of pathology is individual. The patient may itch the whole body or individual areas, and it may be different every day.
Which doctor treats senile itch?
If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a dermatologist. If the patient has a history of chronic diseases, you should also visit a specialized specialist.
Can atopic dermatitis occur in adulthood?
22.01.2022
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic dermatological disease that is diagnosed quite often. Its symptoms usually first appear in childhood, even in young children. If inflammatory skin lesions appear on the skin in adulthood, could they indicate atopic dermatitis ? What other diseases manifest themselves in this way? Find out some information about this.
How does atopic dermatitis manifest?
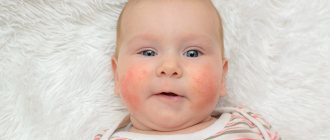
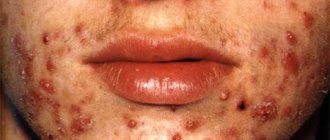
topical dermatitis is a chronic, recurrent, inflammatory skin disease. Initial symptoms include redness, papules, vesicles and sometimes oozing sores. Over time, thickening and lichenification of the skin occurs. A characteristic symptom is increased dryness, as well as itching, intense, constant and sometimes difficult to remove.
The location of the lesions varies depending on the age of the patient. In young children, symptoms of AD usually appear on the cheeks, forehead and head; in children of preschool and school age, predisposed areas are the elbows and hollows of the knees , the area around the wrists, the skin of the neck and hands. Adults usually have lesions on the face , upper chest , palms ; at the age of 30-40 years, quite characteristic foci of inflammation appear in the area of the joint bends, but symptoms can also appear on other parts of the body.
At what age does atopic dermatitis appear?
In half of the cases, the disease first appears in infants under one year of age. In contrast, 95% of patients develop symptoms by the time the child is 5 years old. Therefore, this disease is unlikely to manifest itself in adolescence or adulthood, although such a scenario is possible. It should also be noted that about one in four people who develop AD in childhood eczema into adulthood, or the symptoms return after a few years of calm.
Skin lesions in an adult - is it really atopic dermatitis?
Sometimes symptoms resembling atopic dermatitis may indicate another dermatological disease with similar changes. Conditions with which AD is differentiated include: seborrheic dermatitis , dermatitis , contact dermatitis and nonspecific dermatitis , psoriasis or scabies. Therefore, as soon as inflammation appears on the skin, it is important to immediately consult a dermatologist to identify the cause.
It is important to note that atopic eczema is a complex disease, but genes play an important role in its development - a positive family history is found in approximately 60% of patients. Therefore, if someone in your family has been diagnosed with blood pressure, allergies or asthma , then you are more likely to develop the disease.
How to care for your skin?
Do you suffer from atopic eczema ? Although this is an unpleasant disease, with systematic preventative measures you can prolong the symptom-free period and enjoy good skin condition. The basis of therapy is emollients, that is, drugs that restore the water-lipid membrane of the skin. The use of emollients is important during periods of exacerbation and remission.
What to choose for daily use so that the product is easily distributed, quickly absorbed and does not leave a greasy film? A moisturizing and lubricating lotion can be a suitable remedy to help relieve dryness, redness and irritation and prevent their reoccurrence in the future. By supporting the barrier function of the skin, the balm makes it more resistant to harmful weather conditions (dry air, frost), clothing or irritants.
Although some patients require the application of medications to the skin, and sometimes systemic pharmacotherapy is necessary, emollients and avoidance of aggravating factors (infections, allergens , stress) are the basis of skin care, which needs support every day.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic