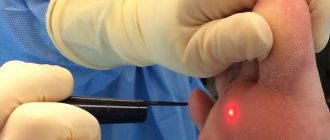
Technique
Cauterization of one papilloma takes 1-3 minutes depending on the size. Before the session, the doctor examines the tumor and determines the optimal laser power. The procedure goes as follows:
- The patient wears dark glasses with light filters to protect the eyes from accidental radiation.
- The skin is treated with an antiseptic and an anesthetic ointment is applied for 15 minutes.
- The doctor points the laser tip at the tumor and evaporates it layer by layer.
- After therapy, the treated area of skin is again disinfected and an adhesive plaster is applied.
A small papilloma is removed in one session. If the growths are large and located throughout the body, several procedures will be required. Laser removal of tumors in children is carried out according to a similar protocol.
Warts on the labia
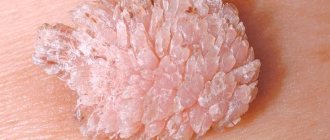
Papillomas on the labia, warts on the mucous membrane of the inner walls of the vagina, vestibule and entrance are small growths, balls, peas, “icicles” of flesh color. In most cases, these formations do not arise singly - they are a number of structures that gradually unite into tumor-like growths in the form of growths, “cauliflower”, “grapes”, “papillae”, “fringe” or “cockscombs” on a narrow stalk of various sizes . Blood vessels pass through the leg to the formation, through which the genital neoplasms are nourished and, accordingly, grow.
They can be single, more often multiple - they gather in groups, often the papillae grow very strongly and merge with each other into large conglomerates. Here you can see photos of condylomas in women.
With this localization, genital warts can be damaged by tight clothing, during intimate contacts, cosmetic and hygienic procedures, etc. Constant trauma to the external genitalia stimulates the relatively rapid growth and spread of papillomas and condylomas from the labia deep into the body - into the vagina, cervix, urethra, anus and rectum.
Photo of papilloma and condyloma on the labia
Since the woman herself usually cannot detect small formations, they are most often detected during an external examination of the genitals by a gynecologist. Although in our practice it is not uncommon for a patient with a sufficient number of small condylomas on the mucous membranes of the external genitalia to be the first to report the presence of these warts, although before that she regularly (more or less) visited other gynecologists.
Forum about papillomas of the labia
- Reasons for appearance? Infection with the human papillomavirus, and then its appearance on the labia on one or both sides, is always provoked by one of several factors: a). sexual contact with a virus carrier (a condom does not always protect against infection, since during foreplay the genitals come into contact with each other); b). sharing personal hygiene items with an infected person; V). visiting the same bath or toilet with a sick person (warmth and moisture favor the virus and condylomas grow faster); G). mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the labia minora during masturbation, petting, shaving, etc. followed by the introduction of the virus. Since HPV can remain viable for a long time in the air, it can become infected in baths, saunas, public swimming pools, solariums, if you sit on benches with your genitals bare and use other people’s personal hygiene products.
- What is the difference between a sick person and a virus carrier? There are virus carriers - women who do not have pronounced signs of papilloma on the labia. They themselves do not suffer from HPV, but are carriers. Through close household or sexual contact, primarily oral contact, transmission of the virus to a partner is possible. An infected person is likely to remain symptom-free for many weeks, months, or even years. Factors that suppress the immune system (surgeries, stress, colds, injuries, pregnancy, abortion) are the reasons for the activation of infection and the impetus for the growth of genital warts, incl. on the labia minora and majora.
- Types of genital warts? Depending on the nature of their growth, warts can have external growth (exophytic) or internal growth (endophytic). The first ones are pointed. They appear on the outside of the labia in the form of growths and papillae, fimbriae. Endophytic, so-called “flat condylomas” are growths that extend into the surface epithelium. Condylomas inside the labia are caused by a type of HPV with high oncogenic activity, and in women they often spread to the cervix.
- What symptoms might there be? After the introduction of infection or activation of the virus in the submucosa, the woman initially experiences unpleasant sensations: itching, itching, stinging, burning. After some time (from several hours to days), small papillomas form on the labia (multiple or single). Sprouts of new elements can spread through the capillary network to neighboring areas and appear on the clitoris, near the urethra and anus.
- Can girls and teenagers have papillomas of the labia or not? Warts on the genitals are not the exclusive prerogative of sexually active women. In approximately 25-35% of cases, HPV of the labia minora is transmitted through household contact and its clinical manifestations in the form of condylomas in virgins can be at any age, from childhood to older reproductive age.
- Can papillomas appear from masturbation? As is already known from what we read above, infection occurs in the presence of injuries to the skin or mucous membranes of intimate places (lips, clitoris, vestibule, and anus), through which the virus easily enters the body. Such microdamages occur under intense mechanical influence as a result of masturbation, petting, fisting, improper use of sex toys or similar improvised objects, which, if there is a virus on the affected object, can subsequently lead to the appearance of warts on the labia majora or minora.
What to do if there are papillomas on the labia, how to remove them?
- Visit a competent and attentive gynecologist;
- Undergo a complete gynecological examination;
- Do a vulvoscopy (a type of colposcopy);
- Get tested for HPV (Digen test);
- Get tested for “hidden” infections.
If warts are detected on the genitals, the patient is recommended to undergo blood tests for syphilis (genital warts on the labia must be distinguished from broad ones, which are a manifestation of syphilis) and HIV (decreased immunity may be a consequence of AIDS). The table below presents an approximate list of tests that a woman should undergo if she has papillomas or condylomas on her labia.
| Analyzes | Price | |
| HPV types 6/11 | Not really | 650 |
| HPV genotypes (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) | typing | 2 350 |
| Blood tests for syphilis (RS), AIDS (HIV) | ELISA blood | 750 |
Rehabilitation period
Recovery will be quick if you follow your doctor's recommendations. The next day after the session, remove the adhesive plaster and treat the wound with chlorhexidine or a saturated solution of potassium permanganate.
Repeat the procedure twice a day, and then apply any healing ointment to the skin.
Do not scratch or pick off the scab to avoid infection. It will go away on its own in 1-1.5 weeks. Try to wet your skin less often. Take a shower, not a bath. After bath procedures, gently pat your body dry with a towel. If the papilloma was on the face or eyelids, do not use cosmetics for 2 weeks.
During the rehabilitation period, avoid visiting the sauna, bathhouse, or swimming pool. Do not shave the treated area, do not scrub with a washcloth, or use scrubs or other products with exfoliating particles. If the treatment was carried out in the summer, you should not sunbathe on the beach or in the solarium.
Try not to expose your skin to direct sunlight and apply cream with SPF 30-50 before going outside. Postpone physical activity to avoid causing excessive sweating. Avoid drinking alcohol.
After removal of papilloma from the genitals, it is not recommended to have sex until complete healing. Wash with intimate hygiene gel or mild baby soap. After the procedure, be sure to visit a gynecologist or urologist.
What is genital papilloma?
This is a type of STI caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Appear in the form of a small tubercle or group of pimples in the area of the external genitalia. Some genital warts are so small that they are practically invisible to the naked eye.
Causes of papilloma on the genitals
Almost all cases of genital warts are caused by HPV. Most often, these formations spread through direct skin-to-skin contact during vaginal or anal sex. The virus that causes genital warts can spread and be transmitted to another person even if one of them does not even have visible signs of papilloma infection on the skin or mucous membranes.
Less commonly, they are distributed in the following ways:
- Performing oral sex on someone who has HPV or genital warts;
- Receiving oral sex from someone who has HPV or genital warts on their mouth, lips or tongue;
- During childbirth, from a woman to her child;
- Masturbation with HPV-contaminated hands or objects;
- By household means (shared towel, underwear, hygiene items, etc.).
How long does it take for them to appear?
Papillomas usually appear within a few months after a person has sexual contact with the types of HPV that cause the genital lesions. Sometimes they appear in just a few days or weeks, while for other people, genital papilloma does not appear until years later. Some people can get HPV, but never genital warts.
Find out in more detail what genital warts look like and how to remove them quickly and painlessly, how much it can cost and where is the best place to go with this problem in Moscow!
Clinical manifestations
Genital papilloma viruses usually appear in the form of various types of rashes on intimate areas. They are flesh-colored and may be flat or look lumpy like cauliflower. Some genital warts are so small that they are not visible.
In women, papillomatous lesions can be:
- Inside and on the walls of the vagina;
- On the vulva, cervix or groin;
- In or around the anus;
- In the lower parts of the rectum;
- On the lips, mouth, tongue or throat (this is very rare).
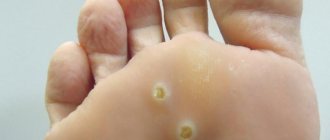
In men, genital papillomas can grow:
- On the penis (around the head);
- On the scrotum, thigh or groin;
- On or around the anus;
- Inside the anal canal;
- On the lips, mouth, tongue or larynx (very rare).
Genital papilloma viruses can cause itching, burning and discomfort. Talk to your doctor if you think you may have these growths or if there are risk factors or possible causes for them.
Treatment methods
There is no cure for HPV, but genital papillomas can and should be removed. If you decide to remove warts, do not use special medications at home on your own. Most of them are intended for professional use and can cause harm if applied incorrectly.
Methods for removing papillomas on the genitals in women:
- Electricity
- Laser ray
- Low temperatures (cryotherapy)
- Surgical excision
- Radio wave removal
Questions and answers about genital papillomas
1. Do genital warts need to be treated? Some people choose not to treat genital warts. If left untreated, genital papillomas may disappear, remain the same, or significantly increase in size and number. The prospects for the process depend on immunity, the amount and type of virus, sexual activity and the presence of concomitant STIs.
Even if you treat genital papillomas, you can still spread papillomatosis and the virus that causes it to other people. Doctors do not yet know how long you will be contagious after all the papillomas appear and are removed.
2. Will I still have HPV if I have my genital warts removed?
Yes. Even if you undergo treatment, you may still have HPV in your body. This is why these growths may return to the genitals after treatment ends. You can still pass HPV to other people after your skin tags are removed.
3. How does the disease affect pregnancy?
If you've had warts that go away on their own or after treatment, you probably won't have any problems during pregnancy. Papillomas on the genital organs in women during pregnancy often:
- Bleed and grow (in size and quantity) due to hormonal changes in the body;
- The birth canal is blocked - if this happens, a caesarean section will be required.
- Expose children to types of HPV that cause papillomas in the respiratory tract, a very rare condition called recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.
4. Can women who have sex with women get skin tags?
Yes. It is possible to get genital papillomavirus or any other STI if you are a woman who only has sex with women. Talk to your partner about her sexual history before intimacy, or better yet, visit a good gynecologist in Moscow and get tested for infections!
Prevention measures
The best way to prevent skin tags on your external genitalia or any other infections is to not have vaginal, oral, or anal sex. If you are sexually active or otherwise sexually active, reduce your risk of getting viruses by taking the following steps:
- Get the HPV vaccine. It is approved for people ages 9 to 45 and protects against the types of virus that cause most genital papillomas and most cervical cancers. Contact our clinic where you can receive this vaccine.
- Use a condom—be sure to put it on before your penis touches your vagina, mouth, or anus. The virus that causes genital papillomas can affect areas not covered by the condom. Other birth control methods, such as birth control pills, shots, implants, or the IUD, will not protect you from disease.
- Get tested - Make sure you and your partner get tested and tested for HPV.
- Be monogamous—having sex with only one partner can reduce your risk of developing the disease. Be faithful to each other - this means that you only have sex with each other and no one else.
- Your risk of getting the disease increases with the number of partners you have.
- Watch how much alcohol you drink and keep your own drink under control. Some people use alcohol or drugs to make a person drunk or high. Someone who is drunk, drugged, or under the influence of drugs may not be in control of the situation or fully understand what is happening. There is a real threat of sexual violence and possible infection with sexually transmitted diseases.
The steps listed above work best when used together. Be reasonable and careful, avoid unambiguous situations and unforeseen troubles!
home
Possible complications
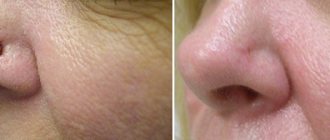
Complications rarely occur after laser therapy. If the doctor sets excessive power and incorrectly calculates the time of exposure, the damaged area may swell and hurt. The wound begins to fester when infected due to poor hygiene during rehabilitation. Also, a consequence of the removal of large growths is the formation of keloid scars.
After the laser, papillomas may appear again in even greater numbers. This complication occurs due to the intensive phase of the virus, when cauterization of the growth without additional therapy is ineffective.
Pink spots remain at the site of the removed papilloma. They will fade after 4-5 days and completely disappear in a few months.
Comparison of laser removal with other methods
In addition to laser therapy, papillomas are cauterized with medications containing salicylic acid or cantharidin. After 2-3 days, the formation heals and disappears. When removing growths on the genitals, use Podofilox or Podophyllin. But this method is less effective and does not exclude relapse.
Surgical removal with a scalpel is also performed. Unlike laser, this method causes heavy bleeding. A scar may remain on the affected area of skin. There is also a high risk of infection getting into the wound.
Papillomas are removed using cryodestruction. The doctor applies an applicator with liquid nitrogen to the tumor for a few seconds. The growth darkens and soon disappears. The procedure is painless, but it will not be possible to control the depth of the effect. Therefore, relapses often occur.
Radio wave surgery with the Surgitron device is comparable in effectiveness to laser therapy. It removes growths, leaves no marks on the body and minimally damages surrounding tissue.
Another effective method is treatment by electrocoagulation. The doctor acts on the papilloma with high-frequency electric current. During the session, you can adjust the degree of impact. Bleeding and infection of the wound are excluded. But, unlike a laser, the device injures the skin around the growth. After the procedure, pits sometimes remain.
Reviews about laser removal of papillomas
Reviews constantly appear on forums and websites of medical centers about the consequences of burning out papillomas with a laser. The effectiveness and speed of the procedure are noted. Due to anesthesia, the patients experienced virtually no pain, but there was a burning smell. In most cases, treatment helped get rid of the defect. There were no scars left, and the wounds healed quickly.
But almost everyone noted that laser therapy eliminates only an aesthetic defect. It will be useless without drug treatment for the virus.
Commentators often discuss whether it is better to remove papillomas - nitrogen or laser. Many are inclined towards the second method, because it helps the first time.
Papillomas in men: causes of occurrence
The cause of the appearance of papillomas on the body in men and women is a virus that can enter the body in various ways:
- Due to unprotected sexual contact: the most common type of infection, including because a person can be a carrier of the virus for a long time, without even knowing it, since the virus has the ability to manifest itself only under the influence of external factors. Transmission is also possible through direct contact of mucous membranes. In this case, the risk of infection increases if the skin or mucous membranes are damaged (there are cracks, scratches, cuts, etc.). Due to the prevalence of this cause of infection, it is understandable that quite often papillomas (condylomas) in men and women appear in the intimate area, at points of contact, from which the risk of infection in men is usually higher, due to their greater sexual activity, but the mucous membranes of women are less protected .
- Through household contact: it has now been proven that the HPV virus can enter the human body through ordinary contact (even a handshake), especially in public places (baths, swimming pools, gyms, etc.).
It is also necessary to remember that infection with the specified virus does not mean its manifestation.
Most often, the disease becomes more active and makes itself felt if:
- the patient's immunity is weakened;
- there were great physical or mental stress, stress, exhaustion;
- There are various types of sexually transmitted diseases.
HPV in men: consequences
The virus can cause condylomas, or genital warts, which, as the name suggests, are located in the groin, as well as on the head of the penis and foreskin. This kind of condylomas has very dangerous consequences for men and requires treatment.
Condylomas on the penis can lead to a narrowing of the foreskin, which can make it difficult to expose the head of the penis and lead to problems in your personal life.
It must also be remembered that in some cases such formations are not an indicator of HPV, but of other sexually transmitted diseases that have not yet manifested themselves (for example, syphilis).
Another danger of HPV is that a carrier of the virus can transmit it to their partner, also putting them at risk of developing cancer. Transmission of the virus is also possible to the fetus from an infected mother, so couples wishing to have children should pay special attention to HPV and other diseases of this kind.