Today you rarely meet a person with perfect skin without a single tumor. According to statistics, 70% of the population is infected to varying degrees with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Any growths on the skin cause unpleasant emotions, painful sensations or simply discomfort, both psychological and physical, which interferes with leading a full life.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a dermatologist, candidate of medical sciences | 1500 rub. |
| Consultation with a dermatologist (KMS) when removing 2 tumors | 0 rub. |
| Removal of a neoplasm (wart, mole) using the radio wave method | 500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
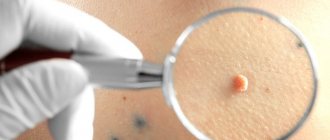
Warts and papillomas are the most common manifestations of the human papillomavirus. Due to their common nature, they have many similarities, but there are also many differences between them. Initially, warts and papillomas appear on the body as benign formations, but some of them, under certain conditions, can degenerate into a malignant form. This necessitates their removal not only for aesthetic reasons.
What are warts
The content of the article
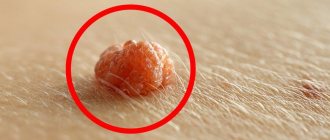
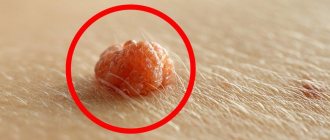
Warts are rounded elevations of the skin in the form of a papilla or nodule with clear contours and a dense structure, arising due to the active growth of the upper layers of the epithelium. They can appear in absolutely every person, at any age and on any part of the skin, from the head to the soles of the feet. The most common “targets” are exposed areas of the body that are often subject to injury: arms, elbows, knees, head. Warts can reach sizes from 1 mm to 15 mm: this directly depends on its type and location of formation. They are located on the body singly or in small groups, and their distribution depends on the functioning of the immune system. There is also a rapid increase in the number of growths when the integrity of the wart is damaged. Sometimes several warts merge, forming a large tumor with a wide base in the form of a cone or hemisphere. When they appear, the growths are flesh-colored, and over time they can acquire a brown or even black tint, sometimes gray or yellowish. Their surface can be smooth, slightly rough or pimply. Outwardly, they resemble acne or calluses, so they are quite easy to confuse. A feature of warts is the high probability of spontaneous remission, especially if they arose in childhood.
What are papillomas
Papillomas are also benign formations. They come in a variety of shapes - leaf-shaped, spherical, filamentous or lobed, often resembling cauliflower in appearance. The growths have a soft, loose structure and are located on a thin stalk. Initially, their size is about 2 mm, but gradually they are able to grow up to 1-2 cm. The color of papillomas also varies from white to dark brown. The favorite location is areas of the body with thin and delicate skin, folds and mucous membranes, i.e. these are the neck, eyelids, nasolabial fold, armpits, area under the mammary glands, genitals, groin area, perianal fold, around the anus, in the rectum, urethra, bladder, etc. Quite rarely, papillomas can form in the oral cavity and on the vocal cords. The growth can be either single or multiple. Basically, there are 5-20 papillomas in one area. Their prevalence largely depends on the immune system and its ability to resist the virus. The main feature of this type of neoplasm is the increased threat of transition to a malignant form. This is especially true for papillomas that form on the mucous membranes of the female genital organs. If left untreated, they cause cancer.
Causes of warts and papillomas
The appearance of warts and papillomas is a consequence of the human papillomavirus (HPV) entering the body. And the well-known theory that warts appear from touching a frog is just a misconception. You can become infected with papillomavirus in several ways:
- sexually;
- during childbirth;
- contact and household.
- Speaking in more detail about the household contact method, we can highlight the following ways of infection entering the body:
- direct skin contact (handshake, kiss);
- through objects of common use (in the gym, in transport);
- when using personal items (razor, toothbrush);
- wearing someone else's shoes, walking barefoot in public places (baths, swimming pools, etc.);
- when carrying out cosmetic procedures with instruments that have not been disinfected (epilation, manicure).
The virus penetrates through microcracks, cuts or abrasions on the skin. After penetration, the pathogen goes into standby mode and is activated under certain conditions. That is why there is no exact definition of the incubation period of HPV. In people with a strong immune system, neoplasms do not form; the pathogen is destroyed and eliminated from the body within a year. The following factors can “activate” the virus and thereby cause the growth of warts and papillomas:
- infectious diseases that weaken the immune system;
- stressful situations and nervous overstrain;
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- decreased immunity;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- avitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- heavy and prolonged physical activity;
- lack of hygiene;
- bad habits;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- long-term use of antibiotics that suppress the immune system.
Older people and children are most likely to become infected with the virus. This is due to the condition of the skin in this age category. Genetic predisposition also influences HPV susceptibility to some extent.
Laser coagulation
The modern non-contact method of removing tumors using a laser has become widespread not so long ago. Experts say that it is absolutely painless and low-traumatic, because... infected tissues evaporate without harming healthy ones. The procedure takes a few minutes, and the rehabilitation period lasts 2 weeks, during which you should refrain from swimming in the pool and open water, and avoid temperature changes and the sun.
The method can cause side effects such as prolonged skin redness and swelling; in case of thyroid problems, keloid scars can form. There are many contraindications for this type of treatment:
- diabetes;
- acute inflammatory processes;
- epilepsy;
- disorders of the endocrine and immune systems;
- photoderomatosis;
- thrombocytopenia and others.
According to patients, the procedure is very unpleasant and painful, and during the process “you can smell the smell of burnt meat.” In addition, healing takes a long time and relapses are possible.
Differences and similarities between warts and papillomas
It is often difficult to distinguish a wart from a papilloma, since they are very similar to each other. In some cases, it is difficult even for a dermatologist to do this during a visual examination. Warts and papillomas have the following common features:
- formation on the surface of the epithelium;
- the nature of the neoplasms is viral: they develop due to the entry of the human papillomavirus into the body;
- the initial character is benign;
- under certain conditions they can become malignant;
- may cause itching, irritation, swelling of nearby tissues;
- have blood vessels, so they bleed when injured;
- education and development are affected by the state of the immune system;
- After removal there is a risk of relapse.
Electrocoagulation
With any method of removing papillomas, there is a certain rehabilitation period.
It is used to remove small papillomas. Since the essence of the method is the thermal destruction of the affected tissue, the method is popularly called “cauterization.” A heated electrode is used to touch the neoplasm and coagulate it along with the vessels, resulting in a pinpoint burn that becomes covered with a dark crust within an hour. In the case of single papillomas, local anesthesia is used, but in the case of multiple small tumors this is inappropriate.
The rehabilitation period lasts about a week, during which the redness and swelling disappear and the dark crusts disappear. At this time, it is recommended to protect yourself from the sun and treat your skin with an antiseptic.
The use of this method is possible for any location of tumors, and patient reviews indicate its reliability. While the price for removing one papilloma is very reasonable, removing multiple tumors will cost a pretty penny.
Despite many similarities, neoplasms have an impressive list of differences
| Index | Warts | Papillomas |
| Form | Mostly round with clear contours | Mostly leaf-shaped or lobed with fuzzy, ragged contours, looks like cauliflower |
| Color | From flesh to light brown, sometimes pink, can even acquire a black tint due to the accumulation of dirt | White to dark brown |
| Localization | On open areas of the body: arms, legs, scalp, etc. | In folds and mucous membranes: armpits, genitals, neck, face, etc. |
| Structure | Dense | Soft |
| Fastening | Wide base | "Leg" |
| Size | Capable of shrinking and growing | Only increasing |
| Peculiarity | Capable of self-destruction without treatment | Do not disappear on their own, must be removed |
| Treatment | Removal, possibly drug treatment | Delete only |
| Tendency to malignancy | Almost never reborn | High probability of transition |
Types of warts
Today there are over 100 types of HPV, each of which gives rise to a certain type of warts and papillomas. The incubation period is about 2-6 months, but it largely depends on the human immune system: a strong and healthy body easily fights the occurrence and proliferation of growths. The following types of warts are distinguished:
- ordinary (simple, vulgar);
- plantar (pinuses);
- flat (juvenile);
- senile (age-related keratomas).
Ordinary (simple, vulgar) - warts in the form of small dense dry nodules with an uneven and rough surface, variable sizes and a rounded shape. They do not cause itching, pain or discomfort. Simple warts reach from 3 to 10 mm in diameter. They are usually flesh-colored, sometimes pink, yellowish, or light brown. Due to the accumulation of contaminants in the porous surface, they can turn dirty gray. The favorite localization of simple warts is the back of the hands and fingers. Sometimes they are observed on the knees and elbows, rarely on the face and feet. After some time (it’s different for everyone), the tumor increases in size, and the skin in its place begins to peel off. The progression of the pathology is manifested by the formation of a large “mother” wart with a scattering of small ones around. When removed, small ones usually self-destruct over time. Plantar warts (spikes) are warts in the form of several fused nodules with a roll of keratinized skin around them. Inside the growths, many small black dots are visible - thrombosed capillaries. Plantar warts are round in shape, rise above the skin by 1-2 mm and can reach up to 2 cm in diameter. However, 75% of the tumor is located in the deep layers of the epithelium, so their main feature is inward growth. Outwardly, these warts resemble calluses, which is why they are often confused with each other. It's important to remember that, unlike a callus, a ring of dead skin forms around a wart. Spines are localized on the feet, rarely on the palms. Usually colored yellow or dark brown. This type of wart causes significant discomfort, itching and pain, aggravated by walking, and may even bleed. In 50% of cases it self-destructs without treatment, but this may take from 8 to 18 months. As the pathology progresses, the number and size of warts will increase, which may lead to the inability to walk due to unbearable pain. Flat (juvenile) - warts in the form of small flat papules with a smooth (sometimes scaly) surface, slightly raised above the surface of the skin. Traditionally it affects people aged 10 to 25 years. They are formed in multiple clusters or singly, which is quite rare. Usually the growths are flesh-colored, sometimes white, brown, yellowish or pink. They appear on the face, neck, knees, elbows, back, legs and arms (especially on the fingers and back of the hands), sometimes on the head of the penis. As a rule, they are painless and do not cause discomfort unless they are subjected to mechanical pressure or damage. Flat warts can suddenly disappear on their own just as they appeared, especially in childhood. But sometimes they are quite difficult to treat. Senile (seborrheic keratoses) are warts in the form of dark, flat, round or oval plaques that appear in old age. They reach a diameter of 0.2-3 cm, sometimes 4-6 cm. The pathogenesis is not clear, but their appearance is definitely not associated with HPV. Senile warts can affect any part of the body except the palms, soles of the feet, and mucous membranes. As a rule, they appear in multiple clusters (about 20 foci). Initially, they appear as small light brown spots or papules with clear contours. Over time, keratoses may retain their appearance and resemble freckles, or they may harden, forming a warty surface covered with easily removable thin crusts. In most cases, senile warts take on a mushroom shape and are dark brown or black in color. They develop very slowly, over decades, never degenerating into a malignant form. Typically, seborrheic keratoses are removed for aesthetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Types of papillomas
- The following types of papillomas are distinguished:
- filamentous (acrochords);
- anogenital.
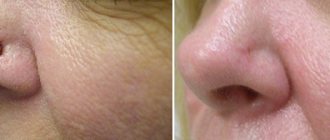
Anogenital (genital condylomas) - papillomas in the form of flesh-colored or pale pink growths of an acute shape, prone to fusion. When rubbed, they become crimson and begin to bleed. Such growths reach 1-1.5 cm and in appearance they resemble cauliflower or cockscomb due to their lobed structure. They are usually transmitted sexually and have a specific localization: on the genitals, in the perineum, on the walls of the vagina, on the foreskin, scrotum and around the anus. Although with less frequency, even in the absence of anal sexual intercourse, they can even grow in the anus and urethra, causing bleeding and discomfort during bowel movements. If the virus enters the body through oral sex, then warts appear on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, in the pharynx, on the vocal cords or trachea. Sometimes they can form in the armpits, under the mammary glands, and in children - in the nasolabial folds. Anogenital papillomas are quite dangerous for humans for many reasons, the main one of which is the high probability of degeneration into a malignant form. Being inside a woman's vagina, they cause itching and burning, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse, and after it - spotting. Therefore, regardless of position, shape and size, genital warts should always be removed. Filiform - neoplasms in the form of thin, long, racemose shoots. They are also called facial because they are usually localized on the face, especially the eyelids and nasolabial folds, and neck. Rarely they can occur on the legs, in the groin folds, under the mammary glands and in the armpits. Those. they appear in areas of delicate and thin skin, in folds characterized by high humidity. It mainly affects older people. The process of formation of a growth begins with the appearance of a small nodule; over time, the formation acquires an elongated oval shape or remains round on a thin stalk. Traditionally, thread-like growths are flesh-colored, which is why they often go unnoticed for a long time, but sometimes they become yellow, brown or pink. They grow about 0.5-1 cm, exceeding that is extremely rare. The risk of acrochords degenerating into a malignant form is minimal, but if they are injured, an inflammatory process may develop. This type of neoplasm does not self-destruct and is prone to spreading to other parts of the body and increasing in size and number. For most people, this causes psychological discomfort, emotional stress and decreased self-esteem. Therefore, a cosmetic defect is the main reason for removing filamentous growths.
How does infection occur?
Many people believe that you can become infected with HPV through sexual contact. In fact, papillomavirus is transmitted in many ways, not just sexually. Infection can occur:
- when interacting with the carrier
- when the virus penetrates through a damaged area of skin, mucous membranes
- during sexual intercourse
- when visiting a bathhouse, sauna, public shower, swimming pool, tattoo parlor
- from an infected mother to a newborn
If one of the family members is infected with HPV, the risk of transmission of the infection is very high if people interact closely with each other in everyday life, use the same bathroom and hygiene items. The same applies to visiting facilities with a humid environment: bath and health complexes, swimming pools. If they were previously visited by an infected person, the virus can enter the body through a damaged area of skin. Warm and humid environments are ideal conditions for HPV to reproduce, but it cannot exist outside the body.
However, according to statistics, the most common route of infection is sexual. During unprotected sex, the risk of transmission of infection is 75%. If a pregnant woman has HPV, the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal.
Why are neoplasms dangerous?
The main danger that warts and papillomas pose is the threat of degeneration into a malignant form. The degree of their danger depends on the type of papillomavirus:
- high (oncogenic) – 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68;
- low (non-oncogenic) – 6, 11, 26, 41, 42, 50, 61, 73, 82, etc.;
- absent – 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
There is a high probability of malignancy if warts and papillomas are constantly injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something, etc.). In this case, infection with harmful bacteria may occur. To prevent the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist and not hesitate to detect suspicious symptoms. Particularly dangerous are genital warts that affect the internal genital organs of a woman, since they can cause serious diseases: pseudo-erosion of the cervix, ectopia of the columnar epithelium, and cervical cancer. In addition, their presence is manifested by a number of unpleasant symptoms: burning and itching in the vagina, unpleasant odor, pain in the lower abdomen, pain and discharge of ichor during sexual intercourse. In men, the lack of treatment for papillomas leads to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. It can also provoke dangerous diseases: adenocarcinoma, anal cancer, diseases of the penis, oral cavity or larynx.
Many varieties are not dangerous, but ignoring the treatment of warts and papillomas will provoke an increase in their number. And the constant attack of the body by viruses will ultimately lead to a deterioration in the overall health of a person.
Diagnostics
It is extremely important to correctly determine the type of tumor, taking into account oncogenicity and external similarity. Initially, the doctor conducts a clinical examination of the growth, if located on the genital organs - gynecological in women, proctological and urological in men. This is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. To establish a reliable clinical picture, it is recommended to conduct research at the cellular level using special diagnostic methods, namely:
- cytological examination of cell morphology - to identify DNA mutations;
- colposcopy - examination of the vulva, vagina and cervix using a special microscope - colposcope;
- biopsy - sampling of cells and tissues for the purpose of diagnosing the pathogen;
- histology - a type of biopsy - to determine a precancerous condition;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques - to identify all types of virus;
- Digene test. It is the most reliable and informative diagnostic method: it accurately determines the presence and type of HPV, the level of oncogenicity, and the degree of concentration of the pathogen in the body.
Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the results of using several methods, since individually each of them is erroneous to a certain extent.
Doctors to contact regarding this issue
Denezhkina Natalya Nikolaevna
Reshanova Lyudmila Mikhailovna
Varfolomeeva Oksana Igorevna
Chaplitsky Evgeniy Aleksandrovich, urologist-andrologist, specialist
Chemical destruction
It is carried out using special liquid preparations based on acid or creams containing alkali. Such drugs are sold in pharmacies as prescribed by a doctor.
This method can be used to remove only single vulgar papillomas (warts) on the hands.
However, the slightest inaccuracy in the use of chemotherapy can lead to burns of healthy tissue or incomplete removal of the tumor. The use of such products is painful, time-consuming, does not provide a guaranteed result and can lead to the formation of unsightly scars at the site of the tumor.
When using chemicals to combat tumors, special precision is required
Methods for removing tumors
Treatment of warts and papillomas should only be performed under the guidance of a qualified specialist. There should be no self-medication, since the pathology will not only not be eliminated, but will also significantly worsen, and serious complications may arise. Under no circumstances should you resort to your grandmother’s methods of tying the growth with thread or sealing it with tape in order to deprive it of blood flow. This can only injure the neoplasm, which will inevitably lead to the appearance of new growths and increase the risk of malignancy. Treatment of warts can be carried out medicinally using the following drugs:
- Viferon;
- Salicylic and Oxolinic ointments;
- Clareol;
- Antipapillomas;
- Cryopharma;
- Panavir;
- Isoprinosine.
The main goal of therapy is to increase the patient’s immunity, so the doctor may prescribe Echinacea, Immunal, Eleutherococcus and Aloe extract, Ribomunil, Lykopid, Imudon, Anaferon, Actovegin, FiBSA, multivitamins and others.
However, the high infectivity and autoacculation of warts are arguments in favor of their removal. Papillomas can only be removed. Today, the most common methods for removing warts and papillomas are:
- cryodestruction - freezing with liquid nitrogen, after which after a while the growth disappears. It is characterized by the absence of pain and a small number of complications. Practically ineffective in the fight against genital warts;
- removal with a radio knife - cutting off not only the growth itself, but also the epithelium underneath it. The device does not come into contact with the tumor, but acts on it from a distance. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 30 minutes;
- laser removal - excision of the growth with a laser beam. During the procedure, healthy tissue is not affected, the blood vessels are sealed, which eliminates bleeding, inflammation and scarring. Removal is painless and quick;
- electrocoagulation – removal of tumors using alternating current. Rare relapses occur after this procedure;
- surgical method - indicated in the case of large and deep tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It has significant disadvantages: it causes relapses, leaves scars and scars.
Removal with a radio knife is one of the most popular procedures. It involves cutting off the growth using high-frequency radio waves. The procedure has many advantages:
- does not require special training;
- carried out quickly and painlessly;
- guarantees the absence of side effects in the future if all doctor’s recommendations are followed (relapses, scars, etc.);
- is particularly accurate and efficient;
- does not damage healthy tissue;
- bloodless and safe removal: the radio knife makes a cut, cauterizes blood vessels and disinfects;
- fast healing;
- affordable cost of the procedure.
As a rule, medical procedures are complemented by the use of measures to strengthen the immune system and destroy the human papilloma virus.
Radio wave coagulation
Removal of tumors with a radioknife occurs under the influence of directed high-frequency radiation, during which the affected tissue evaporates. The radiotherapy device has several electrodes of various shapes and purposes, which the doctor selects depending on the form of the tumor. The most widely used device in our country is the Surgitron device.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia in the form of an injection. With this method, papillomas are removed quickly, without damaging healthy tissue, leaving almost no traces. There is no rehabilitation period here, but there are many contraindications to the use of this method. Radioknife is contraindicated for:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- acute inflammatory processes;
- diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- oncological diseases of any location.
Radio wave treatment should not be used if there is a possibility of malignancy of papillomas. But in the absence of such, the method is successfully used on any part of the body. According to patients, the most unpleasant thing about this procedure is the anesthetic injection.