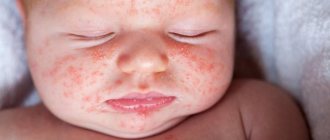
When you are finally shown your newborn baby, you will be unable to take your eyes off him. But, after counting all his fingers several times, you can notice spots on his face, head and body. Newborn babies often have spots on their skin that go away quickly. However, some stay long term or for life. They are called birthmarks, moles, and one type of vascular birthmark is hemangioma in newborns. Some birthmarks on newborns fade over time and become invisible, others remain for life, and others require medical intervention. After reading this article, you will learn which moles children are born with and which ones appear as they grow older, what hemangioma is in newborns, and in what cases medical attention is needed.
What are birthmarks in newborns?
Each baby is unique, and not a single birthmark on a newborn is similar to another. As the name suggests, these are spots that a baby is born with. Sometimes moles in children form in the womb and are visible on the baby’s body from birth. Others are still indistinguishable and appear only over time. In appearance, birthmarks differ greatly from each other. Some are flat, others are convex, some can be regular in shape, while others have jagged edges. Moles also differ in color: they can be of a wide variety of shades - from light or dark brown to red or blue. As a rule, moles in children and birthmarks in newborns do not pose a danger. As the baby grows, some decrease in size and turn pale. However, in rare cases, such spots may indicate health problems. If you are concerned about a birthmark on your newborn, consult your pediatrician.
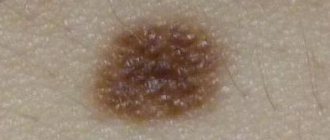
Types of nevi
The spots have clear boundaries and color from pale brown to black.
Small and medium-sized formations, due to their light tone, can be practically indistinguishable in the first 2-3 months after the birth of the child. However, as they grow, they darken and grow proportionally in size. Nevi can also be non-pigmented, then they can be identified by touch by the different structure of the skin.
Spots are divided by size into:
- small - up to 1.6 mm;
- medium - from 1.6 to 10 mm;
- large - from 10 to 20 cm;
- giant - from 20 cm.
Another criterion for classification is clinical type. According to it, nevi are:
- Adenomatous. They are located on the face and head, have a convex shape, clear boundaries, and the color varies from yellowish to dark brown.
- Warty. Located on the torso or limbs. They are characterized by uneven outlines and surface, dark color.
- Giant pigment ones. They often develop in utero and can be located on one or both sides of the body. The surface is covered with hairs, often accompanied by a scattering of small neoplasms around them.
- Blue. They are located in the upper body, on the face and hands. The color is bluish or gray-blue, the surface is dense and glossy. The nevus protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin and does not exceed 2 cm in diameter.
- Papillomatous. They are located on the head and do not have clear boundaries or outlines. The surface is heterogeneous, the color ranges from light to almost black. When injured, it becomes inflamed.
- Epidermal. They are usually located on the limbs one at a time. They have an uneven surface and color from light to dark.
A characteristic sign of a non-malignant neoplasm is the presence of hairs on the surface.
Types of birthmarks in newborns
There are two types of birthmarks in newborns:
Age spots Vascular spots
Dark spots
Pigmented birthmarks are dark or light brown or grayish. They are formed in areas where there is a higher concentration of cells responsible for skin pigmentation. Read more about the most common types of age spots:
Cafe au lait spots Cutaneous melanocytosis Nevi (mole/ birthmark)
Café au lait birthmarks
These spots are similar in color to coffee with milk (they are light brown). They usually appear on the skin of children immediately or in the first few years of life. A few spots like this are not a cause for concern. However, if there are spots on the baby's body the size of a large coin, this may be a symptom of neurofibromatosis, a genetic disease associated with impaired growth of nerve cells. A large, coffee-colored spot with jagged edges may be a sign of a rare genetic disorder, McCune-Albright syndrome. If a birthmark on a newborn causes you concern, it is better to take your baby to the doctor.
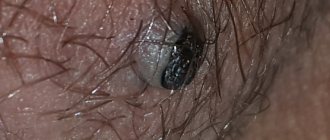
Cutaneous melanocytosis (Mongolian spots)
Mongolian spots are birthmarks that can vary in size. They are usually flat and brown, gray or even bluish in color, similar to a bruise. Melanocytotic birthmarks are noticeable, as a rule, in the area of the baby’s lower back or buttocks. They are especially common in black children and most often disappear completely by age six or seven.
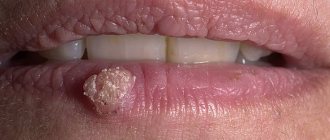
Nevi (moles)
Nevi, or ordinary moles, can be present in a child from birth or appear later. They grow with the child. The color of birthmarks varies from light brown to black. They occur quite often - about 1% of all children are born with them. Nevi are usually not dangerous, but in rare cases, they can develop into melanoma, a malignant growth of the skin, in adulthood. It is recommended to periodically show the child's moles to the pediatrician. It is best to report any changes in the appearance of the wart to your doctor immediately. It is extremely rare that nevi can reach a size of more than 20 cm in diameter. The likelihood of such an abnormal increase is one in 20,000 people. Such warts can be either flat or raised and covered with hairs. It is best to show such nevi to a doctor. If necessary, he will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Vascular spots
Vascular spots occur due to the rapid growth of blood capillaries. Due to the large number of capillaries under the skin, such a mole may be red or even purple in color. Such moles can be either flat or convex. Here are some of the most common varieties:
Hemangioma in an infant Simple nevus Port-wine stains
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Newborn care
Rash in a child: the most common types
Hemangioma in an infant
Hemangioma in newborns occurs as a result of the accumulation of a large number of capillaries under the skin. Hemangiomas in newborns do not always appear immediately. In the first couple of weeks they may be pale or even white and only then turn red. Hemangioma in infants aged two months occurs in 10% of cases, but most often it appears in the second or third week. These spots can appear anywhere, but usually appear on the head or neck. Hemangioma in newborns is more common among Caucasians, girls, twins, premature and low birth weight newborns. A baby's hemangioma often grows with it. It reaches its largest size by about three or four months of age. However, by the age of six or seven, such spots usually disappear. If your baby has a hemangioma and it worries you, take your child to the pediatrician. As a rule, such spots do not require treatment, but sometimes, when they are very bothersome - for example, they are close to the eye, in the mouth or in the throat - they may need to be removed. Spots and moles that begin to bleed or fester also require removal. Most often, children have solitary hemangiomas. In rare cases, a child may have several hundred small hemangiomas throughout the body. Also, sometimes hemangioma in newborns can lie in deep layers under the skin. In such cases, topical and oral medications, injections, laser therapy or surgery are prescribed. All of these options can be discussed with your doctor.
Simple nevus in newborns
Nevi in the form of pink spots are also called salmon spots, “stork bites” and “angel kisses”. Most often they appear on the baby's neck, forehead, upper eyelids, nose and upper lip. Spots of this type occur in more than 80% of newborns, more often in fair-skinned children. As a rule, they pass during the first years of a child’s life. Wine stains
These large, flat, dark red or purple spots with jagged edges sometimes appear on your baby's face or neck. The reason for their appearance is a violation of the growth of capillaries under this area of the skin. Such spots practically do not go away over time, but only become darker, so they require treatment or removal. Sometimes children are recommended to treat port-wine stains with a pulsed dye laser. This is supposed to reduce the likelihood that they will darken during adolescence and adulthood. It is recommended to discuss all possible treatment options in detail with your doctor. A port-wine stain near the eye, on the forehead, or on the scalp may be a sign of a brain and eye disorder called Sturge-Weber syndrome. This is a very rare neurological disease that causes seizures, glaucoma, and delayed physical and mental development. Your pediatrician can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment, such as laser lightening.
Causes of age spots
The color of human skin depends on the concentration of pigments. A lack or excess of melanin, carotene and other pigment substances leads to the formation of pigment spots of different colors and sizes. Discolored patches of skin may be congenital or appear with age. Ultraviolet light often triggers the process - when tanning in the sun or in a solarium. This is because melanin, which gives the brown color, protects the skin from the effects of ultraviolet radiation. The more it gets on the skin, the more melanin is produced.
There are many other reasons why pigment spots form on the face and body. Often this is a consequence of serious disorders in the body. Therefore, if you notice new age spots, you should consult a doctor. The production of pigments is enhanced by:
- Natural and premature aging.
- Hormonal problems associated with thyroid diseases, pituitary tumors.
- Liver diseases.
- Neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorder.
- Gynecological diseases.
Medicines and cosmetics can provoke the problem. Also, age spots are not uncommon during pregnancy.
Do not confuse pigment spots and malignant skin tumors - these are completely different processes. If pigment spots can be left untouched or removed, and in both cases this will not affect general health, then oncological formations require long-term, serious treatment.
Methods for treating nevi
Treatment is allowed only in patients over 2 years of age. Therapy has 4 main directions:
- surgical removal;
- laser excision;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation.
As a rule, nevi that have grown deeply into the tissue are surgically removed. Giant neoplasms are removed in several stages, but the disadvantage of this method is the formation of scars at the site of the nevi.
Laser coagulation is used to remove dysplastic pigmented nevi and other clinical types of spots. The method allows removal of the formation without pain and without subsequent scarring.
Cryodestruction involves exposing the affected area of skin to very low temperatures. As a result, the altered cells die and are replaced by healthy ones. After cryodestruction, a small crust appears, which quickly disappears.
Electrocoagulation affects the nevus with high temperatures. Typically this method is used to remove small and medium-sized stains.
Treatment
There are various methods to get rid of unwanted coloring. Their choice should primarily depend on the pathology itself, the person’s age, and whether he or she has any other problems. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to carry out a competent diagnosis, which is impossible without special equipment and experienced specialists.
Cosmetical tools
If the unwanted coloring is not a consequence of any disease, then you can use some cosmetic preparations. Effective creams and masks usually contain:
- parsley or jojoba extract;
- arbutin;
- kojic acid;
- vitamin C;
- hydroquinone.
It would be worth repeating that you should use any means only after consulting a doctor.
Cosmeceuticals
In addition to cosmetics, you can purchase effective, safe and high-quality placental preparations to eliminate various skin defects.
- Bb Laboratories - the line is highly effective due to the combination of biologically active substances, peptides, herbal extracts, hyaluronic acid and other components.
- GHC Placental Cosmetic is a series of products that saturates cells with beneficial biologically active compounds, activates the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers, improves the regeneration process, and reduces wrinkles.
- PlaReceta & PiloPla - the line fights the signs of facial aging, restoring the dermis. The products are especially aimed at those with sensitive, dehydrated, flaky skin, providing effective care and maintaining youth.
- LAENNEC SkinCare - LNC is a placental and vitamin line aimed at eliminating age-related changes. It also helps in restoring the condition of the skin after photodamage. The products restore an even complexion, improve the condition of the skin during inflammation and prevent the formation of wrinkles.
Anti-age drugs
Bb Laboratories – Hyaluron-elastin-collagen extract
Laennec – solution for injection
Curacen Essence (20 fl x 2 ml)
Two-phase placental serum concentrate
Laser skin resurfacing
Often, girls and women choose similar salon procedures that help to quickly and without a trace cope with certain types of skin defects. The laser penetrates deeply into the epidermis and destroys melanin, eliminating everything quickly and safely. Problems usually do not arise after such “cleaning”, but you should only contact reliable and trusted specialists.