A nevus is a mole that can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
Sometimes it is located in unusual places - the conjunctiva, iris, retina.
It occurs in people of any age – middle-aged, elderly, young children.
If a pigmented nevus appears, it is necessary to identify the cause and consult a specialist. Proper treatment will reduce unpleasant consequences. If a mole is left untreated or removed at home, there is a high risk of complications. The treatment for nevus is laser removal. The procedure is safe, bloodless, and does not require a hospital stay or long rehabilitation. Suitable for people of any age.
When a mole appears or for prevention, you must regularly use sunglasses.
Causes
According to its origin, nevus can be congenital or acquired. The first type appears in a newborn as a small spot on the eyeball, increasing in size over time. It does not have a negative effect on vision, since there is no effect of the mole on the capillaries and visual impairment.
The reasons why nevus appears in the conjunctiva of the eye or other parts of the organ of vision:
- hormonal imbalances (menopause, pregnancy, puberty, sexual dysfunction);
- severe stress;
- heredity;
- age-related changes;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- UV radiation;
- infectious processes;
- damage to mucous membranes and skin.
A mole can be located on the conjunctiva, iris, retina, choroid (choroid of the eye), and vary in size and color.
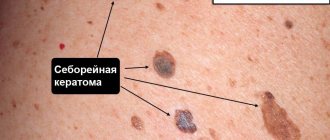
2.Types of age spots
Based on the location of the spots, they are divided into conjunctival nevi
(visible on the mucous membrane of the eye) and
choroidal nevi
(identified only during eye diagnostics, since they are located on the fundus).
According to their structure, eye pigment spots are divided into three groups:
- vascular spots (reddish or pink spots formed from the blood vessels of the eye);
- pigmented nevus (clusters of melanin pigment that are brown, yellowish or black);
- cystic nevus (a node of lymphatic vessels, often a discolored area that makes the corneal pattern look like a honeycomb or bubbles).
Visit our Therapy page
Why is a nevus on the eye dangerous?
The first thing that is dangerous about a nevus is its possible degeneration into a malignant formation - melanoma. Determining a tumor is quite difficult: any mole on the eye changes color, shape, and outline.
Other complications due to untimely removal and treatment of a mole on the eye, depending on the type:
- the spot increases in size, takes on a different shape, compresses the vessels of the organ of vision;
- tissue detachment;
- dystrophic changes in the retina and epithelium of the eye;
- nevus of the iris leads to decreased vision and the sensation of a foreign body;
- deterioration in the quality of vision and subsequent loss of it.
In some cases, moles do not lead to complications other than causing psychological discomfort to a person. They are visible to the patient and others.
Diagnostics
Detection of nevi, as a rule, occurs accidentally during ophthalmoscopy of the fundus. For a final diagnosis, their dynamic observation with regular examinations of the fundus, including examinations with color filters, is necessary. Thus, a choroidal nevus becomes clearly visible in red light, and when examined in green light, the nevus “disappears.” At the same time, only changes in the layers of the retina, which are characteristic of a progressive nevus, remain visible. Ultrasound examination, in some cases, can sometimes reveal the protrusion of the formation. With fluorescein angiography (examination of the fundus vessels using a contrast agent - fluorescein), the presence of stationary nevi is indicated by the absence of changes in the vessels surrounding the choroid. With a progressive nevus, fluorescein angiography detects the leakage of fluorescein through the walls of the vessels adjacent to the nevus.
What to do with a nevus on the eye
If a mole appears on a child’s eye, no action is required.
In adults, laser treatment is used. Medicines and physical therapy do not affect the nevus. Home methods are not suitable for removing a mole - they can harm the patient’s health and cause irreparable harm.
If a nevus appears on the eye, you need to visit a specialist and register. Regularly monitor the state of education. There is a risk of a mole degenerating into a malignant formation; it is very difficult to conduct a histological examination of eye tissue. Therefore, it is recommended to remove the nevus.
Nevus removal
The procedure is carried out in a clinic without placing the patient in a hospital. Previously, to remove a nevus, they resorted to surgery using a radio or microscalpel.
Currently, local anesthesia and laser technologies are used. The procedure is safe, does not harm the patient’s health, and does not lead to the formation of a deep postoperative scar. Another advantage of using a laser is that there is no blood.
4. Treatment methods
If for some reason, together with a doctor, a decision is made to remove pigment on the cornea of the eye, modern medicine offers gentle methods. Until recently, eye moles were operated on only with microscalpels and radioscalpels under a microscope. Currently, laser coagulation is widely used.
The procedure has become as safe as possible for nearby tissues, painless and effective: an ideal cosmetic result is achieved.
Sign up for a consultation
Prevention
A mole on the retina and other parts of the organ of vision appears due to the accumulation of melanin. The main preventive measure is to wear sunglasses or special contact lenses with UV filters to protect the eyes from exposure to sunlight.
Additional measures are to eliminate the causes that cause retinal nevus and its other varieties:
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- combating stress (taking medications if necessary);
- leveling hormonal imbalances, if possible;
- healing of damaged mucous membranes and skin in the early stages:
- regular visits to the ophthalmologist.
If you have a nevus, you need to monitor the size and color of the formation.
How to protect yourself and your loved ones
You should always remember that any birthmark contains danger within itself. It is impossible to say with certainty that this or that mole cannot develop into a malignant tumor, since there is always a risk. Therefore, such a rare phenomenon as a nevus in the eye should be kept under constant medical supervision.
If the mole is stable and does not bother the patient, then most likely surgical intervention will not be required. In such cases, ophthalmologists usually give simple recommendations to avoid further modification of the growth. The mole must be protected from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, especially during the seasons of solar activity; dark sunglasses will help you with this. Children are recommended to wear hats with a visor.
Useful video
Causes of birthmarks on the choroid of the eye. Effective treatment of this type of nevus.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 5 ratings, average: 3.20 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Removal
We should not forget that the eye is a particularly fragile organ that requires careful handling. This is why doctors do not recommend removing a mole in the eye if it does not bother you, and only aesthetic reasons motivate you to undergo surgery.
Treatment and removal of nevus in the eye is a strictly individual procedure. It depends on the patient’s age, stage and rate of change of the tumor. Doctors identify the following most common methods of nevus removal:
- Microsurgical removal;
- Laser coagulation.
Each of these methods has both advantages and disadvantages. Only a professional doctor can choose the option that is right for you.
Medical guarantees you diagnosis, treatment and removal of a mole in the eye at the highest level. Professionals with many years of experience and state-of-the-art equipment are the key to successful therapy and a guarantee of your health.
Etiological factors
Most cases of choroidal melanoma are sporadic, that is, caused by one or another mutation of the melanocytic precursor cell, which can give rise to a pathological tumor clone. In addition, there is an assumption about the hereditary cause of this disease. The influence of such a typical provoking factor for skin melanoma as increased insolation for this tumor is also not excluded.
Elderly people are at risk (the average age of tumor manifestation is 60 years). Men get sick a little more often. Those with fair skin and hair, nevi and freckles are prone to developing choroidal melanoma.
Stages of development of choroidal melanoma
According to the international classification, there are 4 stages of development of this tumor. Criteria for the prevalence of the tumor process:
- T1 - melanoma size 10 mm or less, thickness - 2.5 mm or less.
- T2 - the size of the neoplasm is 10–16 mm, the greatest thickness is 2.5–10 mm.
- T3 - measuring 16 mm and/or thickness more than 10 mm without spreading beyond the eyeball.
- T4 - the largest tumor size is 16 mm and/or thickness more than 10 mm with extension beyond the eyeball.
There are also 4 clinical stages of choroidal melanoma. Each of them is characterized by certain symptoms of the disease:
- The first, so-called “quiet eye” stage, is characterized by the absence of significant clinical manifestations and complaints. Retinal clouding may be present, and visual field defects may also be detected.
- The second stage is characterized by the appearance of pain in the eyes, inflammation, redness of the eyeball, and swelling of the eyelids.
- At the third stage, choroidal melanoma extends beyond the boundaries of the eyeball, exophthalmos is formed, and the sclera loses its integrity.
- The fourth stage is accompanied by generalization of the process. The patient's general condition is deteriorating. Patients complain of severe pain, body weight decreases, and intoxication increases. Metastases of melanoma appear in internal organs: liver, lungs, bones. Damage to one or another organ provokes the appearance of corresponding symptoms. A further decrease in visual acuity, a feeling of veil or fog before the eyes may be detected. These manifestations are caused by bleeding into the vitreous body and clouding of the lens.
Symptoms of the second and third stages of choroidal melanoma are pronounced when the tumor is located in the central or paracentral part of the fundus. Peripheral localization of the tumor is characterized by a long absence of subjective sensations. In this case, melanoma is detected either by chance or at the stage of tumor disintegration and its secondary manifestations.
Symptoms of eye melanoma
In most people, the development of ocular melanoma is usually asymptomatic. Among people who exhibit symptoms, the most common include:
- blurred (fuzzy) vision;
- changes in vision such as blind spots or shadows, flashes of light, or floaters (floaters).
The appearance of a dark spot or visible freckle on the eye can also be a sign of ocular melanoma, especially if it changes in any way over time.
Very few people experience pain.
to come back to the beginning
Types and causes of moles
Among the most common nevi that occur near the eyes or on the eyelids themselves, there are four types:
- Intradermal. They form in the deep layers of the skin and visually resemble a small ball. The color is dark (brown or black).
- Vascular. They appear as pinkish or reddish bumps (consisting of a collection of blood vessels). Often appear as a result of abnormalities in the functioning of the capillaries.
- Epidermal (hanging). The most common neoplasms are flesh-colored or dark brown.
- Mixed (flat). They are located between the epidermis and dermis and are light brown or dark brown in color.
A mole near the eye can appear for various reasons. Their growth is facilitated by a number of factors, including: genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, puberty, pregnancy, uncontrolled use of certain medications, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Types of eyelid tumors
Eyelid tumors can be benign or malignant.
Benign neoplasms
Benign eyelid tumors grow slowly, superficially, and do not affect the underlying tissue. Their course is favorable and the reason for visiting a doctor, as a rule, is a cosmetic defect. Most often, benign neoplasms develop from epithelial tissue, but the source can be hair follicles and other skin elements (trichoepithelioma, Malert epithelioma, fibromas, lipomas).
The most common benign eyelid tumors are:
- Papillomas are nodular neoplasms of a dirty yellow or dirty gray color. They can be located on a leg or a wide base. The neoplasm resembles a villous mushroom or cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes it can spread widely throughout the tissue of the eyelid, affecting the tear ducts, conjunctiva of the eyelid and even the paranasal sinuses. May become malignant.
- Senile warts (senile warts) are similar in appearance to papillomatous nevus. It looks like a brown, yellow or grayish nodule, dense to the touch, does not cause pain. Compared to papilloma, they have more pronounced keratinization. Does not malignize.
- Keratoacanthosis - manifests itself as white spots covered with scales. If left untreated, it may become malignant (risk 20%).
- Trichoepithelioma - a neoplasm arises from hair follicles, has the appearance of a dense nodule, 1-3 mm in size, rarely 1 cm. It can be multiple. In some patients, the number of tumors exceeds a dozen. Mostly young people suffer. If left untreated, they can malignize into basal cell carcinoma.
- Syringoadenoma is a tumor growing from the epithelium of the sweat glands. The tumor is a multilocular neoplasm. It grows very slowly.
- Fibroma - has the appearance of a node on a wide base or on a narrow stalk. It grows from mesodermal tissue and can reach several centimeters.
Malignant tumors of the eyelids
Malignant tumors of the eyelids have infiltrative growth and tend to destroy underlying tissues and metastasize. Basal cell carcinoma progresses most favorably. It is also called a semi-malignant tumor. The most aggressive growth is in melanoma. It not only infiltrates the underlying tissues, but also gives distant metastases.
- Basalioma is a type of skin cancer. It looks like a nodule with a ridge-like surrounding. It grows slowly, germinating into the underlying tissue. In advanced cases, it can spread to the structures of the eyeball and even the orbit. Metastases are casuistically rare. Most often, basal cell carcinoma is located on the outer side of the eye, a little less often - on the lower and upper eyelids, and very rarely in the area of the inner corner. When located in the lower eyelid area, the neoplasm proceeds more favorably. The most aggressive growth is in basal cell carcinoma of the inner corner of the eye.
- Skin cancer of the eyelids. Usually this disease is represented by squamous cell skin cancer. At the initial stage, the tumor has the appearance of redness, which eventually thickens and ulcerates. The tumor is prone to infiltrative growth and metastasis.
- Meibomian gland cancer is a very rare type of cancer and has an extremely aggressive course. The tumor is localized in the upper eyelid, looks like a basal cell carcinoma, but grows quickly and metastasizes.
- Melanoma of the eyelids is the most malignant neoplasm localized in this area. The first signs are the formation of a spot with blurry contours, surrounded by an area of increased pigmentation and redness. The stain quickly spreads over the surface of the skin. Also, melanoma of the eyelid can be presented in a nodular form. In this case, it will be a node with vague contours, which is prone to bleeding. It grows rapidly, infiltrating the underlying tissue.
Where to have the procedure done in Moscow
Due to the thin and delicate skin, the eyelids are recognized as one of the most difficult areas to eliminate tumors. Therefore, you should entrust your health only to an experienced specialist. Certified surgeon Kirill Viktorovich Listratenkov can safely remove a mole using laser technology. Thanks to extensive experience, a positive result is guaranteed. Other advantages of seeking help from Kirill Viktorovich include:
- competitive prices for services provided (the price list is presented on the website);
- confidentiality (patient data never leaves the medical institution);
- individual approach;
- convenient work schedule;
- free online consultations (you can ask a question online, the doctor will give a detailed answer to it in the near future).
To make an appointment for an initial consultation, just call the number provided or fill out a standard form on the website (leaving your contact information).