Keratoma is a benign formation on the skin that appears due to a local accumulation of horny cells of the epidermis. Outwardly, such manifestations resemble convex pigment spots with hard scales on the surface. And they are often located on the face, forearms, upper back, and arms.
Single or multiple keratomas are typical for mature people over 40 years of age. This skin pathology is rarely encountered in children and young people. They appear equally in men and women. Cases of self-healing have been recorded when formations of this type disappeared by themselves. But often raised dark spots reappear in the same areas of the skin.
Are keratomas dangerous? Do they need to be treated or not? How to get rid of keratomas at home? The specialists of the Medical Center for the Diagnostics of Moles “Lazersvit” have the answers to all these questions.
Keratomas: causes of appearance?
Keratoma, according to dermatologists, develops for one of two reasons - excessive ultraviolet radiation and the physiological processes of aging of the skin. The predisposition to the development of pathology, according to medical experts and geneticists, is inherited. But there are no clear reasons for the appearance of a formation, such as, for example, in condyloma, which is caused by the human papillomavirus. At one point, an accumulation of cells is observed, which leads to an anomaly.
Skin keratoma, as a rule, does not pose a threat to health. But dermatologists strongly recommend observing the spots. After all, individual formations have a tendency to reproduce and grow. And in rare cases, they degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
What does senile keratoma look like?
- Skin-colored spots and papules that are pinkish or yellowish-brown;
- The size is often up to 1 cm in diameter, sometimes merging lesions of several papules are formed;
- Often determined not visually, but by palpation;
- Present in areas exposed to the sun (fairy, back of hands, forearms);
- Signs of photodamage on surrounding skin;
- There is no sensation, sometimes itching is possible.
Initially, an oval, scaly spot appears on the skin. Localization – open areas of skin. then quickly turns into keratoacanthoma.
There are no general complaints about health.
There are 2 options for resolution: it goes away on its own, or it degenerates into a malignant form. Biopsy required!
Why should a keratoma be observed?
The skin disease keratoma is considered by oncologists to be a borderline formation, especially in patients with an increased risk of cancer. The probability of malignancy into melanoma or basal cell carcinoma varies in different age groups in the range of 8-35%. For this reason, people who have one or more formations of this type are recommended to see a dermatologist. Regular visits to the doctor allow you to notice signs of degeneration in the early stages and begin treatment in a timely manner. Well, it’s better to remove the protruding spot in order to prevent even the minimal likelihood of pathological processes.
The risk of cancer is not the only reason to see a doctor. Keratoma on the face is perceived as a cosmetic defect, attracts the attention of others, and becomes the cause of complexes. A convex formation on the body can be injured by tight clothing or accessories. In this case, there is a threat of secondary infection.
Age-related keratoma “loves” to grow on the scalp. The formation is often damaged by a comb and hairdresser's accessories during cutting and styling.
Each case of keratoma requires an individual approach. And only a qualified doctor can give recommendations to the patient - treat or remove, ignore or observe.
Prices for keratoma removal:
- Initial appointment with an oncologist-dermatologist
- 2,400 rubles. (candidate of medical sciences, surgeon, doctor of the highest category). The appointment includes digital dermatoscopy. - Removal of keratomas on the body
- from 900 rubles. (per unit, laser or radio wave method). - Removal of keratomas on the face and delicate areas
— from 1,300 rub. (per unit, laser or radio wave method).* when removing 4 or more tumors - a 10% discount on the initial price (for education of lesser cost).
- Histological examination of skin neoplasms
- RUB 3,500.
Removing keratomas at home
Removing keratomas at home is categorically unacceptable, since the patient is not able to independently assess the degree of aggressiveness of the process, as well as adequately eliminate the formation. The risk of getting a serious and sometimes life-threatening complication is extremely high. Do not self-medicate, trust your health to professionals.
Classification
Keratomas are classified as follows:
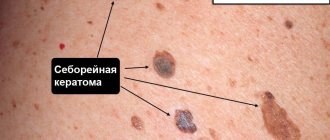
- Seborrheic keratoma appears most often on the chest, back and scalp. Initially, this is a yellow-brown spot, the diameter of which can reach 3 cm. Over time, the surface of the formation becomes dense, and scales appear on it. The color changes to dark brown or black. Externally, this skin pathology looks like dried raisins stuck in the skin.
- Senile keratoma affects the skin of people over 35 years of age. A spot with a diameter of up to 2.5 centimeters appears on the skin. Over time, it thickens, becomes crusty, cracks, and changes color from yellow to black. The growth grows slowly, but over time it can protrude above the skin by a centimeter or even more. Senile keratoma, as this type of neoplasm is also called, is often localized on the shoulders, head, and back. Less common on the face and neck. Senile keratomas can grow in colonies. They also often become inflamed due to physical damage.
- Horny keratoma, which dermatologists often call “cutaneous horn,” has an increased risk of degeneration. First, a gray or brown spot appears on the skin, which eventually becomes covered with scales. A convex tubercle with a rough surface is suitable for placement of the arms, chest, and back. But other parts of the body are no exception. Sometimes patients are diagnosed with multiple horny keratomas.
- Follicular keratoma appears on the cheeks, lips, nose, eyelids. The skin first turns pink, then small tubercles grow at the site where the spot appears.
- Angiokeratoma is a nodular formation of red, black or blue color. Its size can reach 10 centimeters, but most often the growth grows to 2-3 centimeters. Often such skin pathologies form on the back, abdomen, legs and genitals.
- At the first stage, solar keratoma looks like a flat mole. Gradually it begins to peel off. Scales form on its surface. Dense lesions are often found in men over 40 years of age. Location: back, face, feet. Education is rarely singular. As a rule, this is a whole colony of growths. In some cases, degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma is diagnosed.
The type of keratoma and its risks for the patient are diagnosed by a dermatologist after examining the formation.
Effective ointments for the treatment of keratosis
The main causes of keratoma are associated with age-related changes in the epidermis. They do not pose a health hazard, but cause serious aesthetic discomfort.
You can fight skin tumors at home using pharmaceutical ointments. Medicines help reduce senile tumors and reduce their number, exfoliate and soften the skin in the area of keratomas.
| Medicine | Active substance | Manufacturer | average cost |
| Papilleque | Celandine extract, acetic acid | KP KOS "Pharmaceutical Factory", Kyiv, Ukraine | 300-380 rubles |
| Solcoderm | Nitric acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid | MEDA Pharmaceuticals Switzerland GmbH | 815-1050 rubles |
| Aldara | Imiquimod | 3M Health Care Ltd (UK) | 4400-4680 rubles |
| Methotrexate | Methotrexate | EBEWE Pharma (Austria) | 190-350 rubles |
| Bleomycin | Bleomycin | Nippon Kayaku Co. (Japan) | 1500-1550 rubles |
| Fluorouracil | Fluorouracil | EBEWE Pharma (Austria) | 200-230 rubles |
| Flucinar | Fluocinolone acetonide | LLC VALEANT, Russia | 250-260 rubles |
| Fluorocort | Triamcinolone acetonide | JSC "Gedeon Richter", Hungary | 215-240 rubles |
When selecting the most effective drug, you must make sure that these are keratomas and not warts or papillomas. You can get rid of small, isolated tumors yourself. In case of multiple lesions of the skin or affecting the deep layers of the dermis, surgical removal methods are used, most often with a laser.
Treatment with Papilleq
Papillek is one of the most effective pharmacological drugs for the removal of senile keratomas. Thick oil contains extract from celandine, extracts of medicinal plants, citric and acetic acids, potassium and polysaccharides.
Papillectomy affects not only keratomas, but also warts, calluses and papillomas.
To remove tumors, the medication should be applied to clean skin, being careful not to get on healthy skin. The medication should be left until completely dry for 15-20 minutes; the medication should be washed off only after 10 hours. If necessary, the application site can be sealed with a band-aid - this does not affect the effectiveness of the product. Papilleque is applied to the tumors every other day.
Affected skin must be treated for at least 14 days. Papillectum affects the epidermis according to the principle of chemical peeling - it effectively exfoliates the stratum corneum of the skin and accelerates the process of regeneration of its cells.
The drug is used for extensive keratosis, when other medications have proven ineffective. When applying Papilleka to the skin of the eyelids, you must be careful to ensure that the medicine does not get into your eyes.
Treatment with Solcoderm
Solcoderm is a drug recommended for use if the keratoma is seborrheic. This pharmacological agent has pronounced bactericidal properties. The medication is used to remove benign tumors. When regularly applied to affected areas of the skin, Solcoderm causes gradual mummification and death of the altered tissues.
When using Solcoderm, the tumor begins to dry out, acquire a brownish-black tint and fall off. After using the medicine, no scars remain. The medication accelerates the process of renewal and regeneration of damaged tissue, resulting in clean, healthy skin at the site of the tumor.
It is recommended to apply Solcoderm directly to the affected area, after cleaning it with alcohol. It is necessary to ensure that the medicine does not come into contact with healthy skin.
The drug may cause side effects - redness or the appearance of a white “ring” of the skin around the site of application of Solcoderm. This is a temporary reaction of the epidermis that disappears on its own and does not require medical intervention.
Aldara against keratomas
Aldara is a drug for external application based on the active ingredient imiquimod. The medication has an antitumor effect. It does not directly affect viruses that cause skin tumors, but stimulates local immunity. Thanks to this, cells of the immune system are activated, the process of renewal and regeneration of affected tissues is accelerated.
Aldara is used to remove senile keratomas on the face and body, papillomas, warts, genital warts, and basal cell carcinomas.
The medicine must be applied exclusively to the site of the skin tumor, rubbing with light movements until completely absorbed. Aldara should be applied in the evening, before bedtime, and the ointment should be left for 9-10 hours. The medication is used three times a week.
The product applied to the skin should not be covered with a patch or bandage. After the specified time has expired, Aldara is washed off with plenty of warm water and soap. Depending on the number and severity of skin lesions, treatment will take 12-16 weeks.
Application of Prospidin ointment
Prospidin ointment is a non-hormonal, antitumor, cytostatic drug. Available in the form of a thick white emulsion for external application, intended for the treatment of keratomas, papillomas, basiliomas, and melanoma.
With regular use, Prospidin has a pronounced alkylating, anti-inflammatory, and hypotensive effect on the epidermis, preventing the further development of benign neoplasms.
The active substance contained in the drug acts directly on the tumor at the cellular level, destroying it. As a result, the keratoma shrinks and completely disappears.
For treatment, Prospidin ointment must be mixed with lanolin or vegetable oil, then applied to the area of the tumor and secured with a sterile bandage on top. The medicine should be applied to the skin once a day for 3-4 weeks.
Prospidin has several contraindications for use - the ointment cannot be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, for kidney and liver diseases, cardiovascular pathologies, as well as in case of individual intolerance to the medication.
Treatment with Metatrexate
Metatrexate Ebeve is an anticancer drug with immunosuppressive effects. The pharmacological agent acts on the DNA of skin neoplasm cells, stopping their further reproduction - as a result, the keratome stops growing and begins to decrease in size. The drug is also prescribed for the treatment of malignant neoplasms of the skin.
Methotrexate Ebeve has a number of contraindications for use:
- presence of alcoholism;
- renal and liver failure;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- all trimesters of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- hypersensitivity to the active components included in Metatrexate.
The most effective solution in the treatment of age-related formations is the Metatrexate Ebeve solution, which is injected locally, directly into the neoplasm tissue. The dosage of the drug is selected individually, depending on the extent and severity of skin lesions.
Application of Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil ointment is a drug intended for the treatment of benign and malignant skin tumors. The pharmacological agent belongs to the group of antimetabolites and contains the active substance fluorouracil at a concentration of 5%.
The drug has a rapid anti-inflammatory effect, inhibiting chemical processes that contribute to the growth of skin tumors. Fluorouracil blocks the formation of DNA structures in the neoplasm, as a result of which it begins to decrease in size and its further development stops.
Fluorouracil ointment is applied to the affected skin at a dosage of 0.5 g for 5 days, after which it is necessary to take a break for 30 days and continue treatment according to the same regimen.
In the most severe and advanced cases, the dosage of the drug can be increased to 0.6 g. Fluorouracil ointment is applied to the affected skin once every 7 days, the duration of treatment in such cases is 8-12 weeks.
The drug should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, during exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease, in the presence of anemia, herpes and chicken pox, as well as in case of hypersensitivity to fluorouracil.
Colchamine ointment
Colchamine ointment is a non-hormonal drug for external application with cytostatic and anti-inflammatory effects. The pharmacological drug is used to treat age-related keratomas, papillomas of viral origin, as well as oncological skin lesions.
With regular use, Colhamin ointment has an effective anti-inflammatory and anti-miotic effect, stopping the development of neoplasms on the face at the cellular level. The medication also contains the antibacterial component syntomycin, which destroys pathogenic bacteria.
It is recommended to apply colhamine ointment to the affected area of skin in a thin layer, then secure the medicine with a gauze bandage and adhesive tape. Before applying the medication, the epidermis must be cleaned and dried. The product is applied every day; 10-14 days are enough to get rid of keratoma.
The main contraindications to the use of Colhamin ointment are a wound or ulcer at the site of application, the patient’s age under 18 years, all trimesters of pregnancy and lactation, as well as hypersensitivity to the active ingredients in its composition.
Diagnostics
An appointment with a dermatologist begins with taking an anamnesis. The doctor clarifies how long ago the formation was, asks the patient about sensations - painful manifestations, itching, and studies the symptoms. Next, the skin is examined to determine the size and location of the keratoma. The instrumental method - dermatoscopy - allows you to clarify the diagnosis and exclude other skin diseases.
A special device allows you to identify the formation, examine the structure of its tissues, and the depth of its occurrence. The dermatoscope magnifies the image many times, so errors are excluded. And if there is a risk of the keratoma degenerating into a tumor, the doctor will determine this. In some cases, histology is recommended - the formation is sent to the laboratory to determine the cellular composition.
Keratoma: how to treat?
To help the patient get rid of keratoma or actinic keratosis, the doctor prescribes a conservative or surgical treatment method. If drug therapy does not produce results, if the location of the formation is unsuccessful, if it is perceived as a cosmetic defect, surgery to remove the keratoma is prescribed.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment involves the use of various ointments, solutions or emulsions with active substances. It is immediately important to note that such methods are effective in the initial stages, when the stain has just appeared. Therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is strictly not recommended, as it can cause complications in the form of damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Keratoma: how to remove surgically?
The keratoma is surgically removed using one of the following methods:
- laser method;
- cryodestruction;
- radiosurgery method.
The leader of choice is laser removal, since it minimizes the risks of negative consequences, bleeding, wound infection, and relapses. In a few minutes the formation is completely removed. And the wound heals within a few days.
Possible risks
Attempts to remove the keratoma yourself by tying it with thread or cauterizing it with aggressive media are strictly prohibited. This can lead to serious consequences, including the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer.