Streptoderma in adults, what is it and how to treat?
Streptoderma is an infectious lesion of the skin caused by streptococci. The disease occurs in both children and adults. After the infection enters the body, the disease begins to develop, going through an incubation period that ranges from 1 week to 10 days. Streptoderma infection occurs through close contact of a healthy person with a sick person.
Most often, when a disease affects one member of a family, then if the precautionary rules are not followed, other relatives also become ill, even with a fairly strong immune system. The disease can appear on the skin of any part of the body.
If you start treating the disease immediately after its first manifestations, it will be cured quickly and without any consequences for the body. If there is no treatment, then there is a high risk of complications and the disease becoming chronic.
Symptoms of streptoderma in children
The initial signs of streptoderma in children are often quite severe:
- temperature rise to 39°C;
- general intoxication;
- enlarged lymph nodes and their pain.
The condition of the skin differs depending on the form of the disease.
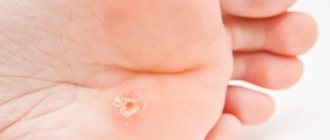
- Superficial (streptococcal impetigo). First, red spots appear on the skin. After 2-3 days they transform into blisters with a cloudy liquid inside. The blisters increase to 2 cm in diameter, then burst. In their place, yellow crusts form. Subsequently, the skin in this place heals, and the disease spreads further.
- Dry (lichen simplex). This form is more common in boys. White and pink spots up to 5 cm in diameter form on the skin. They are located on the face, neck, ears, arms and legs, and are gradually covered with a scab. After healing, scars may remain. These areas remain lightened and do not tan under the sun.
- Streptococcal infection (slit-like impetigo). The disease affects the corners of the mouth and occurs when there is a lack of vitamin B. Microcracks appear on the skin, which hurt and bleed. Then they transform into pustules that become crusty. It hurts the child to open his mouth, eating becomes difficult. Less commonly, streptococcal seizures occur in the corners of the nose or eyes.
- Felon. If streptococcus affects the periungual ridges, panaritium occurs. It is more common in children who are accustomed to biting their nails. Over time, the ulcers open up.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. This form of the disease is typical for infants. Blisters form in the folds of the skin. They gradually merge. If they are opened, pink, weeping surfaces are exposed.
- Deep (vulgar ecthyma). Develops in weakened children with poor skin care. The affected area is usually located on the legs, thighs, lower back, and buttocks. In the initial stages, blisters appear on the skin, but after they open, deep ulcers form, causing severe pain to the baby. The elements scar only after 2-4 weeks, and deep scars remain in their place.
Knowing how streptoderma begins in children, parents will be able to contact a dermatologist in time and begin treatment. If you delay going to the doctor, the disease becomes chronic, and achieving a complete cure becomes very difficult.
Basic terminology
Under the influence of an infectious infection, round purulent and flaky elements can form on the body, which are painful and can increase in size and quantity. This is how diseases of the streptoderma group usually occur. The following photos and descriptions will tell you what these diseases look like, how they begin, and how they are treated.
Causes of streptoderma in children
The causative agent of the disease is group A streptococcus. The bacterium affects the surface of the skin. But not every encounter with a microorganism leads to the development of a disease. Infection occurs if there are aggravating factors:
- cuts, abrasions, cracks and other damage to the skin into which pathogens easily penetrate;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- weak immunity;
- endocrine pathologies;
- concomitant dermatological diseases;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- washing the skin too often, as a result of which the protective film is washed off;
- intense exposure to low or high temperatures;
- intoxication;
- blood flow disturbance.
If at least one of the listed reasons is present, the likelihood of developing pathology increases significantly.
Nature and causes of skin lesions
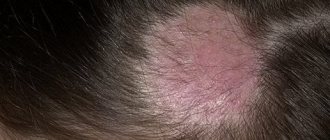
The disease primarily affects smooth areas and skin folds, with lesions prone to peripheral growth. Typically, the disease does not affect the sebaceous and sweat glands, hair follicles. The localization of lesions can be on any part of the body - on the skin of the extremities, face and scalp, torso, groin or gluteal fold, etc.
The infection affects people of all ages, and in adults it occurs most often among workers in the construction, transport, metallurgy and mining industries, for whom it is often considered an occupational disease. Streptococci in an inactive state are present in the bodies of the vast majority of people, but the most common causes of streptoderma in adults are:
- reduced immunity combined with massive transmission of infection from a sick person;
- minor skin injuries that contribute to disruption of its barrier function;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system due to stress or fatigue, leading to decreased immunity, deterioration of tissue trophism and blood circulation;
- the presence of a chronic endocrine disease, which increases the risk of developing purulent-inflammatory processes;
- taking certain medications that reduce the body's resistance to streptococcus;
- disturbances in the composition of the intestinal microflora due to poor nutrition, leading to inhibition of the function of intestinal immune cells;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, which creates favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria.
In children, streptoderma most often develops in the preschool period and accounts for up to 60% of pustular skin lesions. Bacteria are usually transmitted through household means; the development of infection is facilitated by the presence of small wounds, abrasions or scratches, and insect bites.
Treatment of streptoderma in children
Streptoderma in children requires complex and often long-term treatment, which depends on the cause of infection, the severity of the main symptoms and signs, as well as the general health of the child.
The first step is to put the baby on a therapeutic diet limiting sweets, fatty and salty foods. The course of therapy involves avoiding bathing: water procedures contribute to the spread of the disease. It is recommended to wash healthy areas with chamomile decoction, and never touch inflamed areas.
It is important to choose the right clothes for a sick child. Synthetic and wool items should be excluded from your wardrobe. These tissues cause discomfort and contribute to the spread of the disease.
If crusts form on the skin, they are treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In severe cases, a number of other oral medications are prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- anti-allergy medications;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamin complexes;
- antipyretic drugs.
The list of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. Only a specialist knows how to treat streptoderma in children correctly. Self-medication can provoke the pathology to become chronic. With an adequate course of therapy, the symptoms disappear after 7 days, but after curing the deep form of the pathology, scars remain on the skin. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible.
Conducting diagnostics before prescribing treatment
It is impossible to determine the method of therapy if the exact cause of the pathology is not established. Several types of diagnostics are used to differentiate the diagnosis. Laboratory and instrumental methods are used.
- Collecting anamnesis from the parents or child.
- General inspection. Areas of redness, inflammation, and damage to the skin appear on the body. Due to the proliferation of streptococcus, erosions and ulcers can form. Rashes containing pus are often observed.
- General clinical analysis of urine and blood, biochemical test. Determine the condition of internal organs and biological fluids. With bacterial carriage, the ESR is increased and the number of leukocytes is increased.
- Bacteriological culture. This is the main method for identifying the pathogen. A smear is taken from the affected area and inoculated onto a nutrient medium. The result is determined after 5-7 days. They identify not only the bacteria, but also the antibiotics to which it is sensitive.
Using bacteriological culture, drugs to which the microorganism is sensitive are found. This allows the doctor to prescribe the correct method of therapy. The risk of using too many antibiotics, which can lead to superinfection, is eliminated. That is, a strain of pathogenic bacteria that lacks sensitivity to any type of antimicrobial agent.
Prevention of streptoderma
To reduce the likelihood of developing streptoderma in a child, follow the rules of prevention:
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- treat skin lesions with antiseptics;
- strengthen your immune system with vitamin complexes and good nutrition;
- do not wash your child with soap too often;
- At the first symptoms of any disease, consult your doctor.
Streptoderma is a curable disease, but you need to see a doctor in time. The sooner treatment is started, the easier it is to avoid complications and transition to a chronic form. You can undergo a qualitative examination of your skin condition at the SM-Doctor clinic. Qualified pediatric dermatologists will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Streptoderma and similar diseases
Based on external manifestations and test results, not only a diagnosis of streptoderma, but other pathologies of the skin can be established.
In terms of external signs, the diseases are similar to each other, but the treatment regimen is completely different:
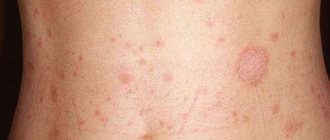
- allergic dermatitis, characterized by severe itching not only in areas of the rash;
- lichen and herpes, viral manifestations with rashes localized in the waist and abdomen, accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- eczema, appears upon direct contact with an allergen or as a complication of chronic streptoderma;
- staphylococcal pyoderma, destroys the sebaceous glands, and in severe form can cause furunculosis;
- chickenpox, a viral pathology accompanied by rashes on various parts of the body;
- pityriasis versicolor, characterized by the appearance of brown or reddish spots, the skin in the affected areas begins to peel off.
To accurately establish the disease, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination and pass the necessary tests. Based on the results, the pathogen will be identified and an accurate diagnosis will be made.
Folk remedies
We have prepared recipes for you with which you can prepare an effective ointment for streptoderma at home.
Eucalyptus ointment
Kills various microbes (staphylococci, dysentery bacillus), including streptococci, which have become the source of streptoderma.
Ingredients:
- Eucalyptus leaves - 2 tbsp. spoons
- Vegetable oil - 2 tbsp. spoons.
- Oak bark - 2 tbsp. spoons.
How to prepare: Pour boiled vegetable oil over crushed eucalyptus leaves. Leave the composition to infuse for 3 days. After this, strain it through a sieve and squeeze it out. Separately, prepare the oak bark. For this, 2 tbsp. Grind tablespoons of bark and place in the oven for 30 minutes.
Dry it as much as possible so that you can chop it later. Pour boiling water in a ratio of 1:1). Leave to infuse for 40 minutes.
Mix both compositions in equal proportions and stir until the consistency of the ointment.
How to use: Apply the ointment once a day to the affected areas for a week.
Result: The ointment effectively fights infection. After completing the course for 7 days, the skin is noticeably cleared, the infection that became the source of the disease dies.
Ointment of yarrow, nettle and sorrel
Ingredients:
- Yarrow flowers - 1 tbsp. spoons.
- Nettle - 3 tbsp. spoons.
- Sorrel - 3 tbsp. Spoons.
- Milk - 1 l.
- Honey - 4 tbsp. spoons.
How to prepare: Grind all ingredients to a powder. Pour the resulting mixture with milk and boil over low heat for 25 minutes. Add honey and boil for another 10 minutes.
How to use: Apply ointment to problem areas of the skin 2 times a day. Use 10 days.
Important! Ointments prepared at home have a short shelf life, no more than 2 days. It is advisable not to use the product after the expiration date.
Result: The ointment effectively fights the disease. After application, the effect can be observed immediately. On the second day, the rash dries up. The skin gradually clears and brightens.
Stages of the disease
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
There are three stages. At the initial, bullous stage of streptoderma, the appearance of purulent blisters is observed in the lesion. Further in the photo you can see deep skin lesions and ulcers, which dry out after some time. The third stage, and with it the chronic form of the disease, develops due to lack or improper treatment.