Moles (nevi) are benign pigmented formations on the skin. They do not pose a health hazard, but under certain conditions they can transform into malignant neoplasms (melanoma). For this reason, many people worry about moles and want to have them removed.
- When should you visit a specialist?
- Causes of moles
- Symptoms of degeneration
- Injury to nevi
- Which doctor should I contact about a mole?
- Diagnostics
Causes of moles
Some moles are congenital. They are formed in connection with local disturbances in the division of skin cells during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, and appear as the child grows. The location and size of some nevi can be inherited.
The main factor that provokes the appearance of new moles is prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet rays. The formation of nevi is also often observed during hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy).
Be careful if you have a lot of moles and age spots!
The skin is the largest organ of our body. It consists of three layers: epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer. The epidermis contains melanocyte cells that produce the protective pigment melanin. Melanin makes the skin yellowish-brownish or brown, which helps protect the deeper layers of the skin from the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma is a malignant tumor characterized by early metastasis. It is melanoma metastases that cause the death of most patients. All malignant skin tumors are divided into melanomas and non-melanoma neoplasms.
Non-melanoma skin tumors (basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma) are the most common. They are called non-melanoma because they do not develop from melanocytes. They rarely metastasize and are therefore less dangerous than melanomas. Their treatment is different from that of melanomas. Benign skin tumors include seborrheic keratomas, hemangiomas, lipomas and warts. Most skin tumors are benign and rarely turn into cancer.
Melanoma most often develops on the torso of white men and on the lower extremities of white women. Typically, melanoma is brown or black in color due to the production of melanin by melanocytes. Melanoma is much less common than basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma, but is a much more serious disease.
The main risk factors for developing melanoma are:
Nevi (moles). They belong to benign melanotic tumors. Nevi are usually absent at birth but begin to appear in children and adolescents. Some types of nevi predispose to the development of melanoma. White skin, freckles and blond hair. The risk of melanoma is 20 times higher among white people compared to African Americans. This is due to the fact that skin pigment has a protective effect.
Family history. The risk of melanoma is increased if one or more close relatives (mother, father, brother, sister, child) have had melanoma.
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation and tanning. The main source of ultraviolet radiation is sunlight. Ultraviolet lamps and booths are other sources. People who receive excess exposure to light from these sources have an increased risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
Age. Almost half of all melanomas are detected in people over 50 years of age. However, melanoma can also occur at a younger age (20-30 years). The development of melanoma does not have a clear age and gender, but women still get sick more often.
Can melanoma be prevented?
For this we can recommend the following:
Staying in the shade. The simplest and most effective way to limit your exposure to ultraviolet rays is to minimize your exposure to sunlight. This is especially important from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when the effects of ultraviolet rays are most pronounced. Remember that the sun's rays can be reflected from water, clouds, sand, cement and snow. Protect your skin with clothing. You can protect most of your skin with clothing, such as long-sleeve shirts and a wide-brimmed hat. Thick fabric usually works well to provide the best protection for the skin.
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers, and most often it develops on the face, neck, head, that is, on those parts of the body that are usually exposed and exposed to adverse factors:
- solar radiation (ultraviolet rays), especially for persons with congenital or acquired nevi
- chronic skin irritations
- chemical, mechanical or temperature injuries to nevi, chapping, frostbite, etc.
- non-radical cosmetic interventions.
- state of endocrine function of the body (puberty, menopausal changes)
- family history (persons who have previously had melonoma, as well as their relatives)
- endogenous features, such as skin color, hair, eyes, the presence of freckles on the face, neck, hands, moles on different parts of the body.
Self-examination.
Melanoma can be diagnosed in its early stages when it is treatable. You must know all your moles, spots, freckles and other features of your skin in order to notice their changes. Self-examination is best done in a well-lit room in front of a large mirror. A husband or wife, or anyone else, can help with self-examination of the skin, examining the back and back of the thighs. All areas of the body should be examined, including the palms, soles, scalp, ears, subungual areas, and back. Any suspicious areas of skin should be reported to your doctor. In men, one in three melanomas occurs on the back.
The appearance of new spots on the skin, changes in their size, shape, feel or color should alert you and force you to conduct an examination. An unusual sore, lump, spot or change on the skin may be a sign of skin cancer or a precursor to a tumor. The skin may become scaly or crusty and may become weeping or bleeding. The skin may itch, become very tender or painful. Redness and swelling may develop. Since moles can turn into melanoma or increase the risk of melanoma, it is better to see a doctor to be more sure. If you have any of the above signs, do not delay visiting a doctor, reasonable alertness to existing changes in the skin will allow you to maintain health for many years.
Instructor-valeologist N.A.Dudarchik
Symptoms of degeneration
Doctors have identified the main signs that may indicate malignant degeneration of moles. These include:
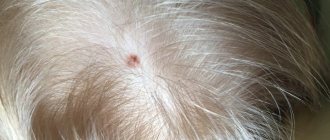
- Rapid increase in size. One of the alarming symptoms is asymmetrical growth, which leads to a change in the shape of the nevus.
- Change in color, namely rapid and uneven darkening of the mole.
- The appearance of pain, burning at the site of localization of the formation.
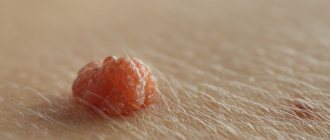
- The appearance of ulcerations and cracks on the surface of the mole.
- Changes in surrounding tissues in the form of a swollen reddish corolla.
If you detect at least one of these signs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Within a short time, an ordinary mole can degenerate into a malignant skin tumor - melanoma. This tumor metastasizes quickly and has high mortality rates.
The location of a mole on areas of the skin that are constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation (face, hands) is also a reason to consult a doctor. Intense exposure to sunlight is one of the main triggers for malignant degeneration.
Injury to nevi
Another factor that can trigger the onset of malignancy is trauma to the mole. Moreover, the formation can be injured either over a long period of time, for example, due to constant friction or squeezing by clothing, or as a result of a more serious external influence, for example, when a mole is cut.
If a mole is accidentally damaged, it must be thoroughly treated with a disinfectant solution. If bleeding occurs, it should be stopped using a sterile bandage or gauze. The injured formation should be examined by a doctor as soon as possible in order to determine a further course of action. The specialist may recommend removing the remaining part of the mole or undergoing routine examinations for malignancy over a period of time.
Indications for removal of moles (nevi):
1. Cosmetic.
2. The presence of constant irritation of a mole (location on the neck, chest, waist area, scalp, perineum). Removal of moles on the palms, soles, and genitals is mandatory. Undesirable effects on moles are also tanning, solarium, trauma during massage, washing, or haircut. It is unacceptable to pull hair out of a mole - if you are not tired of the sight of a “hairy” mole, it should be removed.
3. Atypical appearance of the mole (intense and/or uneven pigmentation, irregular and poorly defined borders, large sizes (more than 10 mm), asymmetrical shape, as well as similar changes and rapid growth of the mole, the appearance of a pigment corolla around, inflammation and itching, erosion and bleeding).
4. Congenital nevi.
The above points are the reason for a mandatory examination and diagnosis of the mole by a dermato-oncologist, who will determine further tactics.
Removing moles on the back immediately after surgery:
Doctor: Grishko R.V.
I would also like to refute the common myth about the inviolability of moles, because... Only removal of the formation followed by histological examination is a guarantee of your health.
FAQ
Today, the “gold standard” is the removal of moles using an ablative laser.
The CO2 laser used in the clinic has the following advantages:
- Thanks to the small thickness of the beam (200 µm), it is possible to precisely influence the tissue;
- The procedure for removing a mole is radical and one-time;
- Lack of direct contact of the device with the wound, asepsis, hemostasis (the wound does not bleed);
- Favorable effect on regeneration, rapid wound healing, virtually no scar.
Which doctor should I contact about a mole?
There are several medical specialties that treat nevi: dermatologist, oncologist, surgeon. There is also a separate doctor for skin tumors - an oncodermatologist.
Visit to the dermatologist
A dermatologist is the first doctor you should contact about a mole. It is this specialist who, in most cases, is able to exclude a malignant process based on the results of examination and dermatoscopy.
Why go to a surgeon?
If the mole turns out to be benign, but is constantly subjected to friction or pressure, then it can be removed by a surgeon. You can contact a plastic surgeon if you have an aesthetic problem such as a mole on the face or other visible areas of the skin. For such nevi, if they do not raise questions regarding their benignity, laser removal is recommended.
When should you contact an oncologist?
If you have a mole with signs of malignant degeneration, you can immediately contact an oncologist. A doctor in this specialty has the necessary knowledge and skills for the surgical treatment of melanoma and other malignant skin tumors. The earlier cancer is detected, the more favorable the future prognosis will be.
Can the problem be solved by a cosmetologist?
Removal of moles in beauty salons and offices is possible only by a cosmetologist who has a higher medical education. There are several ways to remove a benign formation on the skin: laser method, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation. The patient needs to consult an oncologist before having the nevus removed by a cosmetologist, since, for example, after laser removal the possibility of histological examination of the tissue is lost.
Oncologist-mammologist
Women who have moles on the skin of the breast with signs of a possible malignant process should be examined by a breast oncologist. A doctor in this specialty selects a treatment plan taking into account the characteristics of the structure and functioning of the mammary glands.
Types of moles
Regular stain
They occur during childhood, mainly in areas exposed to the sun. Round, symmetrical in appearance, with a smooth and clearly defined edge, up to 5 millimeters in diameter. They rarely become cancerous, but people who have 50 or more moles in common are at increased risk of developing melanoma.
Congenital spot
They are present from birth and can vary greatly in size and be quite large in area. They are usually benign, but have a predisposition to the development of melanoma, especially very large congenital moles.
Atypical spot
Or dysplastic moles, these can develop anywhere on the body and are usually larger than normal moles. They differ in color and texture, irregular edges with many colors. Some atypical moles can become cancerous, so regular checkups with a dermatologist are necessary.
A rare type of mole that looks like melanoma, but is not cancerous. It usually occurs in fair-skinned children and young adults under 20 years of age. They grow quickly and vary in size from a few millimeters to centimeters.
Diagnostics
In the process of diagnosing nevi, the doctor uses both standard methods (history collection, visual examination) and instrumental diagnostic methods. In this case, studies such as dermatoscopy, biopsy and histological analysis of the mole are highly informative.
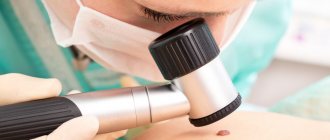
Dermatoscopy
The essence of the dermatoscopy method is to examine the skin under magnification. During the examination, the doctor evaluates the color and structure of the epidermis, identifies the main characteristics of skin rashes, examines the epidermal-dermal junction and the papillary layer of the dermis.
To perform the study, a special device is used - a dermatoscope. This device may resemble a small magnifying glass (manual dermatoscopy) or be a special device that can be equipped with a digital photography function with the possibility of subsequent detailed, even computerized, analysis of various skin structures.
The dermatoscopy method is simple and accessible, but at the same time very informative. Examination of moles by a doctor using a dermatoscope significantly increases the chance of detecting malignant skin tumors, primarily melanoma.