One of the most striking signs of inflammation of the genital tissues in men is redness on the head of the penis.
Various factors can provoke the appearance of redness on the mucous membrane of the penis and foreskin - both infectious and non-infectious in nature.
Non-infectious reasons in this case may be the following:
- 1. Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the head due to sharp frictions during sex. Her irritation due to too long and frequent sexual intercourse.
- 2. Allergic reaction of tissues to chemical components of lubricants, local contraceptives, condom lubricants.
- 3. Inflammation of tissue due to accumulation of smegma and urine under the foreskin.
This is observed with insufficient hygiene of the genital organs, phimosis, and diabetes mellitus.
Blisters on the penis due to candidiasis
Blisters on the penis after sex may be due to another sexually transmitted infection.
Candida fungus can provoke an inflammatory reaction.
The first symptoms appear a few days after infection.
The risk of their occurrence is higher if:
- weak immunity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- violation of personal hygiene;
- sweating
Taking antibacterial agents initiates or aggravates the course of urogenital candidiasis.
Spots, papules, and sometimes ulcers appear on the skin of the penis.
Most often the head and foreskin become inflamed.
The infection can also spread to the groin folds.
It is characterized by redness, white deposits, a sour odor, and severe swelling of the inflamed organs.
Treatment of herpes type 3
Herpes simplex virus type 3 (HSV-3) is the cause of infectious diseases such as varicella (chickenpox) and shingles.
Most people experience a viral infection during preschool age, but cases of infection in adulthood are also not rare. Herpes zoster most often occurs in adulthood and old age.
This type of herpesvirus is also characterized by a lifelong existence in the human body: it is impossible to completely recover from the virus; throughout life, the virus “dormants” in the tissues of the nervous system.
Symptoms of chickenpox include fever, rash on the skin and mucous membranes, itching; in mild forms of the disease, a small amount of elements may form on the skin; body temperature does not rise.
Shingles is also characterized by skin rashes, general weakness, itching, and fever.
Treatment of viral herpetic infection type 3 is multi-stage, complex. Since it is not possible to get rid of the virus, the goals of therapy are as follows:
- Reduce pain during acute illness
- Shorten the regeneration period of skin manifestations
- Reduce the likelihood of complications such as postherpetic neuralgia
- Etiotropic (directed at the cause of the disease) therapy: antiviral drugs are used in the first three days from the onset of symptoms. These drugs can suppress the spread of the virus; they reduce the activity of viral particles. The duration of treatment is on average 7–10 days.
- Symptomatic therapy: due to severe pain, itching and discomfort accompanying skin manifestations of HSV-3, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen-based drugs) are prescribed; At elevated temperatures, antipyretics are recommended. Anticonvulsants prescribed for acute HSV-3 (carbamazepine) also reduce the severity of pain. Treating skin rashes with antiseptic solutions prevents the risk of developing infectious complications.
- Increasing the body's defenses with the help of interferon inducers and immunomodulators.
- Specific immunotherapy: it is necessary for infection with HSV-3 during pregnancy; such therapy consists of the administration of specific immunoglobulin in the early postpartum period.
- Antidepressants: this component of therapy is aimed at reducing discomfort and correcting the psychological state.
- Physiotherapy: successfully used due to positive treatment results. Methods of influence such as electrical neurostimulation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, hyperbaric oxygenation, and reflexology are used.
The duration of treatment for herpes zoster is from 7 to 14 days for an uncomplicated process and up to 3-4 weeks for a process complicated by pustular infection or neuritis.
Condylomas on the penis
Sometimes blisters under the head of the penis are called condylomas.
These are growths of the papillary layer of the dermis (vegetation), which are formed as a result of infection with the papilloma virus.
This virus is transmitted sexually.
True, not everyone develops clinical signs of the disease.
The risk is higher in people with weak immune systems.
Symptoms appear six months, and sometimes even a year after infection.
In the classic version, condylomas are protrusions on a thin stalk.
They are red or pink in color and rich in blood vessels.
Less common are flat or inverted condylomas.
Usually these formations do not reach large sizes.
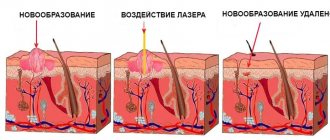
If a person has a large blister on his penis due to a human papillomavirus infection, it can be easily removed.
For this, a laser, radio wave method or liquid nitrogen is used.
With a large number of condylomas, immunomodulatory therapy is required to eliminate the virus from the body.
Blisters on the penis due to allergies
Another cause of blisters on the penis may be allergic dermatitis.
It is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction.
This disease is characterized by the alternating appearance of areas of skin redness, papules, transparent blisters on the penis, erosions and crusts.
This is how a classic acute reaction occurs.
It occurs upon contact with an allergen: most often it is a condom (latex allergy), less often - other substances included in the composition:
- drugs;
- lubricants;
- hygiene products;
- underwear, etc.
An allergy occurs in the area that has been in contact with the substance.
But small blisters on the penis can spread somewhat beyond this area of skin.
The longer contact with the allergen continues, and the more often this happens, the further the rash spreads.
Blisters on the penis due to scabies
The disease called scabies is caused by mites.
The pathology is transmitted sexually.
It is also contracted through shared beds.
Rashes on the penis do not always form.
The main manifestation of the disease is itching.
At first, only the genitals itch, but after a few weeks the whole body begins to itch.
The rash is usually minor.
Small papules appear.
They don't look much like blisters.
Sometimes papules transform into vesicles.
This happens especially often in the case of a secondary bacterial infection.
Its attachment is facilitated by scratching due to severe itching of the skin.
Pubic lice and blisters on the penis
If a person has blisters on his penis, the cause may be phthiriasis.
This disease is caused by pubic lice.
They live mainly on the pubis, penis, thighs, and lower abdomen.
Sometimes they spread to the eyelashes and armpits.
But these insects cannot be found on the head: there is a different shape of hair, lice are not able to attach to them.
Blue and red spots are usually found on the skin.
Blisters occasionally appear.
They may be the result of scratching the skin.
Diagnosis of blisters on the penis
As you can see, there can be many reasons for the appearance of blisters on the penis.
It is not always possible to determine the disease with a single examination.
In this case, laboratory tests come to the rescue.
When making an appointment, the doctor examines the patient and examines the condition of his genitals.
He looks at what blisters have appeared on the penis, what size and color they are, palpates the lymph nodes, and conducts clinical tests.
Some diagnoses can be made clinically, others require laboratory confirmation.
The standard examination is microscopy of scrapings from the area of the rash.
The doctor receives the material, which is then examined under a microscope.
This way you can detect many pathologies:
- scabies;
- candidiasis;
- other fungal pathologies;
- bacterial infections.
Microscopic examination is not enough to identify some pathogens.
For example, herpes or papillomavirus can only be identified using PCR.
Sometimes bacteriological culture is required.
Using a microscope, a doctor can see a large number of bacteria.
But many of them are similar, so establishing the type of microorganism is impossible.
For this purpose, cultural diagnostics are used.
Knowing what type of bacteria provoked the appearance of blisters on the penis, the doctor can choose adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of allergies requires:
- confirmation of the fact of an allergic reaction (a blood test can be performed for this);
- identifying the allergen to prevent contact with it in the future (allergy tests are used, which are done during the period of remission of the disease).
Pubic lice are identified during a patient examination.
A doctor can use a magnifying glass to detect nits.
The insects themselves are rarely detected, as they are located at the root of the hair.
Diagnosis of diseases
After the patient contacts the doctor, the specialist performs a visual examination of the problem area and prescribes additional tests. It is mandatory to undergo an examination by a venereologist and take a general clinical blood test to check for infection. Using gloves, the urologist examines the man's anus and assesses the general condition of the prostate gland.
As medical practice shows, prostatitis and prostate adenoma are the most common cause of such problems. This is due to decreased immunity. Sometimes men are embarrassed to go to the doctor, as a result this leads to the development of serious inflammatory processes and diseases of the genitourinary system.
An alternative research method can be ultrasound. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the specific clinical picture. Based on the test results, the doctor prescribes treatment. Indicators are assessed:
- general clinical blood test;
- bacterial culture of prostate juice;
- visual inspection;
- Ultrasound examinations;
- Analysis of urine.
These studies make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and select comprehensive and effective treatment.
During therapy, sexual activity is prohibited. This will only cause additional irritation and inflammation of the skin. If the recommendations of the attending physician are not followed, treatment will take longer. Perhaps even in a hospital setting.
Treatment of blisters on the penis
Different methods are used to treat different blisters.
After all, it is not the blisters themselves that are usually treated, but the disease that caused the rash.
When hives appear as a result of an allergic reaction, it is often enough to take antihistamines.
Most allergy sufferers have them in their home medicine cabinet.
Delayed allergic reactions, which occur as contact dermatitis, are more difficult to treat.
Antihistamines are not always effective.
Local ointments with corticosteroids are more often used.
With each contact with the allergen, the blisters will appear again.
Therefore, allergy tests are required to determine the substance to which the patient develops pathological immune reactions.
After this, contact with these substances is completely excluded.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections of the penis.
Streptococcal pyoderma can be cured with any penicillin or cephalosporin.
These bacteria are rarely resistant to drugs.
Staphylococcal infections are more difficult to treat.
When boils or deep folliculitis develop, doctors sometimes perform a culture to obtain data on the sensitivity of the bacteria to various antibiotics.
Prior to this, empirical antibiotic therapy is usually prescribed.
But after receiving the results of the antibiogram, the regimen is adjusted.
Fungal infections of the penis are treated with antimycotics.
Usually, when blisters appear due to candidiasis, local remedies are sufficient: miconazole or clotrimazole.
In severe or recurrent cases, as well as in the absence of effect from ointments, the doctor prescribes fluconazole or itraconazole orally.
Acyclovir is used to treat herpes.
It is taken during every flare-up to help the blisters go away faster.
For severe and frequent exacerbations, suppressive therapy, vaccination or immunomodulatory treatment are prescribed.
Immunomodulators are used to treat human papillomavirus infection.
The condylomas themselves can be removed using radio waves, laser or other methods.
Treatment of herpes type 1
Herpes virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a type of herpes virus that affects the trigeminal nerve. Most people know this common virus as a cold sore. Manifestations of the virus appear on the skin around the lips and directly on the red border and wings of the nose. They look like bumps against a background of redness, which then transform into blisters, erosions, and crusts. The course of the infection consists of periods of exacerbations and remissions; the virus is constantly located in the nervous tissue and is activated under favorable conditions (hypothermia, weakened immunity, various diseases, stress). Complications of a viral infection are possible, such as damage to other areas of the skin and internal organs.
Treatment of herpes type 1 during exacerbation
- The use of drugs whose action suppresses the further development of viral infection. Both external (creams, ointments) and internal (tablets, injections) and combined treatment are possible. Therapy with antiviral drugs is necessary during exacerbation of the disease.
- The use of immunomodulators, prostaglandin inhibitors, interferon inducers: this is necessary to activate the immune defenses to fight the virus.
Treatment during an exacerbation period lasts on average no longer than 10–14 days.
Treatment of herpes after remission
After the disappearance of external manifestations of infection, immunomodulatory drugs, physiotherapy, ozone therapy, and plasmapheresis are used. The patient is advised to reconsider his lifestyle, give up bad habits, and eat right. When 2–3 months have passed after recovery, vaccine therapy is carried out in order to form an immune response. Special vaccines used:
- live weakened
- inactivated (“dead”)
- split vaccines (“divided” into proteins and nucleic acids)
Due to the proven oncogenicity of the herpes simplex virus, the use of vaccines is a rather controversial method of treatment. Thus, live and inactivated vaccines are considered dangerous in terms of the risk of developing cancer pathologies, and split vaccines, despite their apparent superiority and novelty, may have low effectiveness.
Based on the above, it is obvious that the herpes simplex virus type 1 must be suppressed during exacerbations, and it is better to prevent the development of exacerbations as such.
Prevention of blisters on the penis
To prevent blisters from appearing on the penis, you need to:
- be selective in sexual relations and always use a condom;
- maintain cleanliness of the reproductive organs;
- avoid prolonged exposure to moisture on the skin of the penis;
- if you are prone to allergies, pay attention to which substances cause blisters to appear and stop using them;
- lead a healthy lifestyle to have good immunity;
- timely cure or compensate for chronic somatic diseases.
Traditional treatment
Doctors are skeptical about traditional methods of treatment, since all herbs are not harmless plants. If used incorrectly, they can greatly harm your overall health.
According to some men, a decoction of yarrow and oak bark will help fight a fungal infection. It is applied to the affected area in the form of a lotion several times a day. Cooked porridge of garlic and white radish helps eliminate bubbles on the penis. Such porridge has a detrimental effect on harmful microorganisms. It is also useful to treat problem areas with a decoction made from birch leaves.