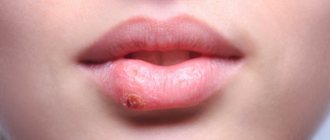
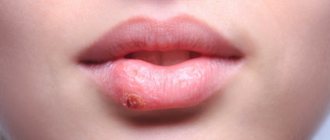
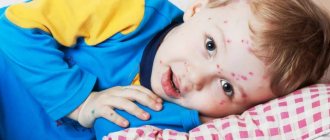
These blackheads may coalesce and form cavities containing pus (abscesses). Once resolved, they leave rough scars.
This problem usually bothers and affects adult men; it is less common in women.
Acne affects such areas of the body as the face, chest, and back. Often a type of conglobate form of acne appears - one or multiple compacted acne. The rashes are bluish-red in color, very dense and painful. There are often pustules on the surface.
What are acne conglobata?
Acne conglobata is a rare but severe form of acne. It usually manifests as comedones, nodules, abscesses, and sinus drainage (see photo). Scarring and body disfigurement are common with this type of acne. Comedones often occur in groups of three, and cysts often contain purulent, foul-smelling material that is expelled to the surface of the skin. Acne conglobata nodules are found on the chest, shoulders, buttocks, face and thighs. Acne conglobata may occur after a sudden flare-up of pustular acne, or it may occur gradually after the recurrence of acne that has not appeared for many years.
It is important not to confuse acne conglobata with acne fulminans. The main difference is that the former cause polyporous comedones and non-inflammatory cysts, while the latter do not.
Clinical manifestations of conglobate acne
Some studies show that this type of acne* is more common in men with an extra Y chromosome. Globular acne is characterized by the gradual appearance of many nodular-cystic formations communicating with each other, as well as the appearance of groups of comedones.48
Most often, the location of this type of acne is the back of the neck, chest, shoulders, back, perineum, buttocks, and armpits. Sometimes the rash appears on the face. Also, conglobate acne* on the body can manifest itself in the following:
- abundant accumulations of large comedones the size of lentils, sometimes double;
- when squeezing out acne formations, deep holes remain;
- after self-resolving acne, saucer-shaped shiny impressions may appear;
- suppuration (deep and superficial), sometimes with abscesses;
- fistulas.
Thick greenish pus accumulates inside the acne formations; when discharged, it has an unpleasant odor. Conglobate acne heals slowly; when resolved, atrophic scars often form, less often keloid or hypertrophic scars.48
Not many people know how dangerous acne* can be. During periods of exacerbation, pain and fever may occur.48 When conducting blood tests, hyperproteinemia, hyperglobulinemia, and polynucleosis may be detected. Acne conglobata is characterized by frequent relapses. Typically, by age 30, the disease subsides.48
Causes and risk factors
It is believed that Propionibacterium acnes, the same organism that is involved in acne vulgaris, may play an important role in the disease by altering its reactivity as an antigen. Hypersensitivity to this antigen causes an intense immunological reaction that manifests as a chronic inflammatory state. The presence of bacteria also leads to an infectious process with the development of pus and sinus tracts. Pus usually has an unpleasant and putrid odor.
Taking thyroid medications and exposure to halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons can cause acne conglobata. Other factors that can trigger acne conglobata include androgens (such as androgen-producing tumors) and anabolic steroids.
Acne conglobata has also been reported to occur in people who stop taking anabolic hormones, or as a reaction to other hormonal agents.
Some people with acne conglobata have an XYY karyotype. Skin disease is associated with HLA phenotypes.
What type of acne* on the face does Clindovit® help fight?
It is not enough to know what a pimple looks like to determine the severity of acne or its shape. This should be done by a doctor. At the first manifestations of acne, you should consult a dermatologist who will prescribe adequate acne treatment.
Clindovit® – clindamycin gel. This topical antibiotic helps fight acne vulgaris. When applied to the skin, the phosphate contained in the clindamycin preparation is hydrolyzed to form clindamycin, which quickly accumulates in comedones, exhibiting antibacterial activity against Propionibacterium acnes. The drug helps reduce the concentration of free fatty acids.6
*acne
Epidemiology
Acne conglobata is not very common. In general, this type of acne is more common in men than women. There have been numerous reports of athletes with this type of acne published over the past 30 years, and it is thought to be primarily related to the use of anabolic steroids. Outside the United States, little is known about conglobate eels. The condition is usually seen in young people and very rarely in children or the elderly. Onset usually occurs in the second and third decades of life. It is not known whether the disease is more common in any particular race.
Diagnosis of conglobate acne
To make a primary diagnosis, a dermatologist needs only a visual examination, since acne conglobata has a characteristic appearance. After this, the patient is prescribed a series of tests to identify the characteristics of the disease, its causes and select adequate treatment. The main diagnostic procedures include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- immunogram;
- hormone analysis.
The patient may also be referred for consultation to related specialists: gynecologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and otolaryngologist.
Pathophysiology
Acne conglobata manifests itself as deeply burrowing abscesses that are connected to each other through the sinus passages. Initially, the nodular lesion may mimic a pimple, but underneath there is a strong inflammatory reaction and the formation of pus. Over time, the pus penetrates the adjacent tissues and comes to the surface of the skin. Scarring and body disfigurement are common with this type of acne. Comedones often occur in groups of three, and cysts often contain foul-smelling, pus-filled material that oozes to the surface of the skin.
Removing the effects of acne
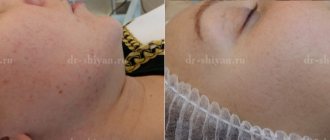
Unfortunately, the appearance of scars with conglobate acne cannot be avoided even with timely treatment. Today, there are many methods that allow you to lift sunken areas and polish protruding scar elements to the same level as the skin. Dermabrasion, acid peels, laser resurfacing are just a few methods that allow you to correct skin defects.
History and physical signs
Acne conglobata can occur after taking androgenic anabolic steroids and is quite common in bodybuilders. Many young adult men visit a dermatology clinic complaining of severe acne and facial scarring. It is important to obtain a detailed history of anabolic steroid use because discontinuation of these drugs is vital to treatment.
Acne conglobata may also occur in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa and pyoderma gangrenosum. When the disease develops after puberty, the nodules gradually coalesce and become more severe in later years. Active nodule formation usually persists for the first three decades of life and then becomes inactive.
A physical examination will usually reveal severe acne. Nodular lesions are tender and dome-shaped. When the nodules disintegrate, a discharge appears in the form of pus with an unpleasant odor. After the pus drains, a scab often appears on the affected area, followed by the formation of large, irregular scars.
A classic sign of the disease is the presence of paired or combined blackheads on the torso, neck, shoulders and buttocks.
Most patients with acne conglobata are shy and self-conscious about their skin condition. Many tell a story of withdrawal and isolation. Suicidal ideation is also common in this population. Thus, it is very important to offer psychological counseling to the patient.
What types of acne* are there?
In addition to the severe conglobate form, there are other types of acne* that are observed in patients of different ages97:
- Microcomedones. They are the precursors of comedones and are almost impossible to detect with the naked eye.
- Whiteheads. Closed comedones with a diameter of up to 3 mm. The outlet of a pimple* is difficult to detect, but the ducts of the sebaceous glands are filled with compact material. Such rashes can resolve spontaneously or degenerate into inflammatory elements.
- Open comedones. Appearing from whiteheads, the black tip is the result of the oxidation of tyrosine, which is part of the sebaceous contents, and the formation of melanin.
- Microcysts. These are whiteheads that usually appear over the joints and in the lateral cheek area. They cause aesthetic discomfort to the patient and can become inflamed.
In addition to these types of acne*, there are others that relate to the inflammatory manifestations of acne:
- Papules. Inflammatory elements that have an elastic consistency. They develop quite quickly and after resolution they leave hyperpigmented spots.
- Pustules. Bluish-red nodules with a pustule in the center, which arise independently or develop from papules. After the pustules resolve, noticeable pigmentation remains.
- Indurative acne. They usually develop from pustular acne and have a dense consistency. They develop over 3-4 weeks and may abscess or resolve, leaving behind atrophic scars.
- Abscess acne. Sharply painful formations of bright red color that arise from indurative acne or develop primarily. After resolution, scars remain in their place.
There are also phlegmonous acne, which have a diameter of more than 10 mm and a soft consistency. They develop within 3-4 weeks. After their resolution, keloid scars often remain.
Treatment
The best treatment option for acne conglobata is to use a retinoid such as isotretinoin for 20 to 28 weeks, and in some cases even longer. Some experts even recommend oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/day) for 14 to 28 days. Steroids have proven effective in the presence of systemic constitutional symptoms such as general malaise, fever, weight loss and anorexia. Topical retinoids are not as effective as oral retinoids. It is important not to prescribe retinoids to women of childbearing potential unless effective contraception is available, as these drugs are known to be teratogenic.
- Other options include using minocycline, tetracycline, or doxycycline. Tetracyclines should not be combined with oral isotretinoin as there is a real possibility of causing pseudotumor cerebri.
- In cases where the above antibiotics do not respond to treatment, dapsone can be used. There are also case reports of treatment of acne conglobata with infliximab and carbon dioxide laser with or without isotretinoin.
- In severe cases of acne conglobata that do not respond to the above methods, another option is external beam radiation.
Operation:
- Once the lesions have healed, dermal fillers can be used to improve scarring. The FDA recently approved the use of the bovine collagen filler Bellafill for the treatment of acne scars.
- When the nodules are large and fluctuating, they can be aspirated. Sometimes practitioners may use cryotherapy or triamcinolone intralesionally. Large nodules can also be removed surgically.