The causative agent of chickenpox
The main causative agent of chickenpox is the varicella zoster virus, which belongs to the general family of herpes viruses type 3.
Infection with the pathology occurs through the air through close interaction with a sick person.
The pathogen itself is very weak in the external environment, and if it does not penetrate the body, it dies instantly after 10 minutes.
If the virus infects the mucous membranes, the infection develops quickly. The pathogen spreads throughout the bloodstream, causing the appearance of characteristic clinical symptoms.
Prevention of scars after chickenpox
To reduce the likelihood of pockmarks or pits appearing, it is not enough to only monitor the condition of the crust and bubbles. Hygiene is also important.
It is recommended to change bed linen once a day: pillowcase, sheet, duvet cover - all of this is in contact with the patient’s face and body. The infection persists in the underwear, and if you use it for a long time, you can add the same virus to the unhealed wound that the body is trying to fight.
And your nails should also be clean: if you scratch the wound until it bleeds, in addition to the virus, microbes from under the nails can be introduced into the epidermis. To avoid scars after chickenpox, babies even wear mittens.
The rash must be disinfected every day with special solutions, ointment or regular brilliant green. And if chickenpox is particularly severe, doctors prescribe antiviral drugs.
In addition to the antibacterial effect, all ointments used for chickenpox cool the inflamed area and relieve itching.
Chickenpox symptoms
It is quite difficult to detect viral pathology at the initial stage. Because it has similarities with ARVI and influenza. Subsequently, after infection, characteristic signs of chickenpox appear, which help differentiate the disease from other conditions. Therefore, any doctor, taking into account the overall clinical picture, can accurately make a diagnosis.
As a rule, the main symptoms of chickenpox in adults and children are:
- Intoxication syndrome - this includes headache, high temperature, body aches, enlarged lymph nodes, chills, sore throat and sore throat.
- Weakness and malaise.
- Poor appetite.
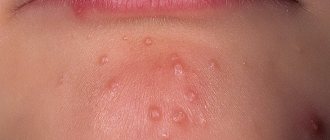
- Skin rashes. Red sores (vesicles) appear all over the body and are filled with serous contents.
- Severe itching.
The very first sign of chickenpox is considered to be an increase in temperature, which occurs 1-2 days before the dermatological rash. It is accompanied by other striking signs of intoxication, usually lasting about 5 days. Chickenpox without fever and catarrhal symptoms is quite rare.
The rash affects all parts of the body, including mucous surfaces and hair. First, spots appear, then medium-sized bubbles with a clear liquid form in their place. After some time, the formations on the skin become cloudy and dry out, becoming covered with a thin crust.
The complete disappearance of papules occurs 2-3 weeks after the onset of the pathological process. The most important thing is to not scratch the skin. Otherwise, infection may occur.
Possible complications
As a rule, the disease goes away without serious consequences, especially if you do not scratch the papules. However, in rare cases, complications after chickenpox can still occur.
Among them:
- bacterial infection caused by streptococcus;
- viral pneumonia, which is more common in children of the first year of life and manifests itself in the form of high body temperature, excessive paleness of the skin, dry cough and severe shortness of breath even at rest;
- temporary disruption of the central nervous system;
- encephalitis;
- chickenpox meningitis.
To avoid such consequences, monitoring of the development of the disease and treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician - therapist, pediatrician or infectious disease specialist.
Drug treatment of chickenpox
Local therapy plays a special role in the treatment of rashes. It helps improve the healing of skin surfaces, preventing the appearance of scars, cicatrices and secondary infection of pimples.
It is advisable to treat skin lesions with any antiseptic agents. These are brilliant green, Tsindol, Baneotsin, Fukortsin. This group of drugs eliminates re-infection of elements, promotes their rapid drying and epithelization.
The most modern medicine is Calamine. It is applied topically and has a complex antiallergic and antiseptic effect.
Also prescribed for the treatment of the infectious process:
- Antipyretic drugs. Reduces temperature and improves well-being.
- Antiviral agents. They are used to destroy the main infectious agent.
- Antihistamines. Suppresses severe itching and prevents other signs of allergies. Used for oral and external use.
- Painkillers. Fight headaches and throat discomfort. Used in tablet form.
When localizing papular elements in the oral cavity, it is recommended to use:
- Boric acid 1% as an antiseptic.
- Kamistad, Kalgel and other painkillers.
- Sea buckthorn oil or Solcoseryl to reduce irritation and accelerate epithelization.
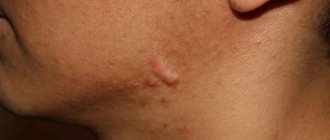
How to treat scars after chickenpox?
After recovery, scars and pockmarks will not remain, but only if you followed all the doctor’s recommendations and treated the wounds with an antiseptic. If traces of chickenpox are still present, you can get rid of them in different ways. It can be:
- salon treatments;
- creams, gels or ointments;
- ethnoscience.
The choice of a particular procedure depends on the size of the scars or pockmarks, their number, the desired speed of effect and, of course, the presence of contraindications.
Let's consider each method of getting rid of scars after chickenpox in more detail.
Salon treatments
As a rule, this method is chosen in the case of treating deep mature pockmarks in an adult. For children, many procedures are more likely to harm than correct the situation, so they usually try not to touch very noticeable scars on a child.
Salon treatments for scars include:
- Peeling . Treatment of leather with chemical acids. The rehabilitation period after the procedure lasts from a week to a month. During this time, you need to carefully monitor your skin, avoid sunlight, dust, and minor damage.
- Grinding . Laser removal of damaged top layer of skin. Does not require preliminary preparation; it acts in a targeted manner without affecting healthy tissue. Small scars can be removed in one session, but larger ones will require several procedures. Laser resurfacing is contraindicated for pregnant, breastfeeding women and those who had peeling less than 2 weeks before the procedure.
- Microdermabrasion . Removal of the top layer of skin with microcrystals. It will help with small scars; large scars and deep pockmarks will be made less noticeable. Aluminum dioxide particles under pressure penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, and the vacuum pulls them out along with dead cells. This process is traumatic and requires long-term restoration of the skin.
- Wrap . The most harmless of the listed methods: smoothing the skin, evening out the overall tone and smoothing out traces of chickenpox. A medicinal substance is applied to previously cleansed skin, wrapped in film and covered with a thermal blanket. After the session, the product does not need to be washed off.
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis, phonophoresis . Transfer of useful substances deep into the damaged area of the epidermis using ultrasound (with phonophoresis) or electricity (with electrophoresis). Can be used as a prophylaxis against scars immediately after an exacerbation of chickenpox.
- Injections . Used when there are large depressions on the face. Hyaluronic acid or various cocktails are injected under the skin. They fill the pockmark, making it convex - the surface of the skin is leveled. Over time, the drug is absorbed and pockmarks appear again: the injection should be repeated every six months to a year. However, the injections will not have any effect if you treat old scars.
Before starting any cosmetic procedure, be sure to consult your doctor about contraindications and its necessity in your individual case.
Find out which method of correcting scars and stretch marks is optimal for you!
doctor Svetlana Viktorovna Ogorodnikova.
doctor
Creams, gels, ointments
Applications of cream, gel or ointment for scars do not create such discomfort as any of the salon procedures, and they can be used by children.
It is worth remembering that anti-scar cosmetics should be applied only to an existing scar, but not to an open wound. To remove the consequences of chickenpox, he usually recommends the following remedies:
- Medgel;
- Bepanten;
- Sledotsid;
- Kelofibrase;
- Keratan;
- Zinc ointment;
- Fermenkol;
- Contractubex;
- Mederma;
- Methyluracil;
- Dermalix;
- Zeraderm Ultra.
Some of them give results faster, while others are used for six months or more before the pockmark disappears. They are chosen based on the age of the scar, price, personal contraindications and recommendations of the attending physician.
ethnoscience
For lovers of everything natural, “grandmother’s” recipes are suitable, which anyone can prepare at home:
- Lubricate your face with a slice of cucumber;
- Apply simmered onion over low heat to the pock marks (cook for about 15 minutes);
- For 1 teaspoon of cocoa butter, dilute 3 drops of sandalwood and tea tree essential oil. Rub into scars or pockmarks using massage movements.
- Pour boiling water over 1 tablespoon of dried marshmallow and leave for 8 hours. Wipe the skin with the solution up to 5 times a day.
- Finely ground oatmeal. Pour boiling water over and cool. Apply the paste for 30 minutes to adults and children.
The advantages of traditional medicine are that most recipes, with rare exceptions, are suitable for both adults and children. However, the visible effect will not appear immediately - you will have to be patient for six months, a year.
Differences from other similar diseases
Chickenpox must be distinguished from diseases that occur with a vesicular rash.
Differential diagnosis table
| Sign | Chickenpox | Herpes zoster/herpes simplex | foot and mouth disease | Streptoderma |
| Source of infection | Chickenpox patient | For herpes simplex - a patient with herpes simplex. Herpes zoster is a reactivation of the chickenpox virus. | Cattle | A patient with tonsillitis, tonsillitis or a carrier of streptococcus |
| Path of infection | Airborne | Mainly contact | Through food, contact | Airborne |
| Nature of the rash | Distributed randomly throughout the body | Grouped blistering rashes on red skin background | On the hands, between the fingers, on the feet | The blisters quickly become purulent and form more often on the face |
| Intoxication | Light to heavy | With herpes simplex, there is no or mild infection. For herpes zoster, it depends on the extent of the rash | Lightweight | Lightweight |
Contagiousness
The cause of the disease is the chickenpox virus, Varicella Zoster. It belongs to the group of herpes viruses and is also called the third type of herpes virus. It is very unstable in the environment and dies when exposed to sunlight. In drops of saliva it remains active for about 15 minutes. The chickenpox virus can spread over long distances, which is why it got its name.
The source of infection is a person with chickenpox. It becomes contagious from the last day of the incubation period - that is, even before symptoms appear. Infectivity ceases on the fifth day after the appearance of the last rash. The spread of infection occurs through airborne droplets - the virus is released with droplets of saliva when sneezing or coughing. In this case, it is not necessary to be in close contact with the patient - the virus can even pass into neighboring rooms through ventilation grilles.
Adults usually become infected with chickenpox when caring for a sick child or when being in the same room as a sick child. Only an adult who did not have chickenpox as a child can get sick. Repeated cases of chickenpox are casuistically rare. The exception is adults with weakened immune systems - cancer, HIV infection.
After chickenpox, the virus remains in the body for life. It is its presence that ensures the maintenance of specific immunity and prevents the occurrence of recurrent cases. Reactivation of the infection occurs against the background of hypothermia, stress, weakened immunity and manifests itself in the form of herpes zoster, which also occurs only once.
Prevalence
In 2022, the incidence in Russia was 570 cases per 100 thousand population. Of this amount, the incidence in adults is only 10%. Men and women get sick equally. Chickenpox is registered in all regions. Chickenpox has a clear seasonality - the peak incidence occurs in autumn and winter.
Kinds
Chickenpox occurs in several clinical forms:
- typical - with malaise and blistering rash (usually without pus);
- rudimentary - with a very scanty rash;
- hemorrhagic - the contents of the vesicles are bloody;
- generalized - with damage to internal organs.
Purulent blisters with chickenpox in adults appear in the event of a secondary infection. This is usually observed due to improper skin care and poor hygiene.
There are three degrees of severity of chickenpox:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
The severity is determined by the severity of symptoms of intoxication and the abundance of the rash.
Answers to common questions
Is there a way to prevent chickenpox?
The preventive measure – not to contact people who are sick – is not always effective. The fact is that infection can occur even before the first manifestations of the disease are detected in the patient. That is, he can communicate with friends without knowing that he is contagious.
It is possible to prevent the onset of the disease by vaccination with special live vaccines, which are based on a weakened chickenpox virus.
Which specialist should I contact for treatment?
Chickenpox in children is treated by a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist. If an adult gets sick, you should call a therapist or an adult infectious disease specialist immediately after detecting the first symptoms of chickenpox.
Is it possible to swim if you have chickenpox?
Due to the fact that the quality of tap water in most cities leaves much to be desired, in case of this disease you should take a shower (not a bath) using boiled or filtered water. Otherwise, there may be a risk of a bacterial infection joining the viral form, which, in turn, can cause serious complications. It is better to wash with warm water. It is strictly forbidden to use a washcloth, rub the skin or steam it.