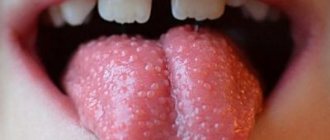
- What is a bloody pimple in the mouth?
- The reasons for the appearance of blood blisters in the mouth, on the lip, cheek, and tongue?
- Bloody pimples on the walls of the mouth
- Blood blisters on the tongue, sides, and tip of the tongue
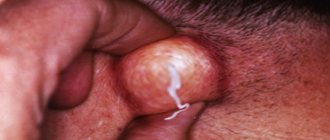
- Bloody pimples under the tongue
- Blood blisters on or inside the cheek
- Blood blister on the lower, upper, or inner lips
- How to deal with bloody pimples inside the mouth?
A blood pimple, whether in the mouth, tongue or lip, forms due to damage to the tissue and blood vessels under the skin. These pimples, also known as blood blisters, often look like pimples and can be very painful. Inside the blister is a mixture of blood and lymph fluid that appears dark red in color. These pimples can be severe and caused by a serious problem. Therefore, it is important to know what causes these pimples and what you can do to get rid of them as quickly as possible.
What is a bloody pimple in the mouth?
Blood blisters or large pimples can appear anywhere in the mouth Because these pimples are often caused by injury, they may appear on or under the tongue. Thin, blood-filled blisters and pimples also appear on the inside of the cheeks, the walls of the mouth, or the inside of the lip. .
According to the United Kingdom's National Health Service, blood pimples form when fluid collects under broken skin. Depending on the cause, blisters may be filled with blood, clear fluid, or pus.
Some of the causes of injury that lead to a bloody mouth pimple are friction, irritation from chemicals, or a burning sensation in your mouth.
The reasons for the appearance of blood blisters in the mouth, on the lip, cheek, and tongue?
Poll: When did your acne appear? (Number of votes: 4295)
I've been suffering all my life
It's been a couple of years now
About a few months
Recently
To vote, click on the desired answer. results
- Trauma: Trauma appears to be a common cause of bloody pimples in the mouth, tongue, or lip. Injuries are usually caused by pinching, impact, or friction. However, they can also be the result of burns and frostbite. The bottom line is that trauma damages the tissue underneath. skin without disturbing its structure. There are many factors that can cause injury to the mouth, tongue, lips or cheeks, which leads to the formation of blood blisters in the mouth. The most common of them are:
- Frictional injury: Sometimes when you chew food, your teeth can rub against the inside of your cheek or lips, causing friction that can cause irritation. If this friction happens constantly, then it can cause injuries that lead to blisters and blood pimples during inner cheeks or inner lips Friction can affect the inner right cheek, inner left cheek or both Similarly, such actions can affect the appearance of blood pimples on the inner upper or lower lip It all depends on the structure and arrangement of the organs of the mouth and the coordination of them movements when you chew food or talk. The situation may likely be worse in people with bleeding gums or sharp teeth, which can also produce this friction. Friction can also result from chewing hard, rough-textured foods.
- Hot foods: If you consume too much hot food or drinks, including coffee or tea, you can burn your delicate linings on your cheeks and tongue. Damage caused by burns may show up as blood blisters forming in the affected area in the mouth. Blood pimples usually appear around two days after receiving burns.
- Frostbite: If you live in a very cold region, you may be susceptible to frostbite on your cheeks or lips. Frostbite can lead to injuries in the mouth, which can cause blood blisters to appear on the gums, cheeks and lips, or on the inside of the cheeks or lips. These blood blisters usually appear two days after frostbite Frostbite can be caused by both flat blood blisters and blisters with increased blood content.
- Impact Forceful contact is also a common cause of injury to the mouth, inner cheeks and tongue. You may accidentally hit your lips, cheek or jaw against an object while moving, or bite your tongue hard.
Most common reasons
Sometimes, the causes of glossitis are congenital, for example with a folded tongue. But most often the disease develops against the background of:
- Chemical and thermal burns.
Putting garlic paste on a sore tooth may not be such a good idea. And hot food is harmful to the mucous membrane of the tongue and stomach. - Infections.
Do you have a red spot on your tongue and it hurts? This may be a symptom of a fungal (candidiasis), viral (herpes), bacterial (Helicobacter, spirochete, staphylococcus, streptococcus) infection. - Mechanical damage.
Gnawing on nuts is dangerous not only for teeth, but also for the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue. Sometimes constant mechanical impact is caused by incorrect prosthetics. - Lack of vitamins
, especially group B. This affects tissue metabolism, resulting in inflammation of the mucous surface. - Psychoneurological factors.
With stress or neurological disorders, the tongue becomes inflamed quite often.
Blood blisters on the tongue, sides, and tip of the tongue
Bloody pimples and blisters are also very common on the tongue. Typically, a huge blister of blood appears on the tongue or close to the middle or tip of the tongue. Bloody blisters can also form on different sides of the tongue. It is also possible to have more than one blood blister on the tongue if there are many of them. , they are usually smaller in size.
Bloody bubble on tongue
The most common causes of small to medium-sized blood blisters on the tongue are injuries, most often due to tongue biting. However, the infections and diseases and conditions discussed can cause blood blisters on the tongue. They are usually very painful and cause a lot of discomfort .
Depending on the size and severity of the blood bubble, you may have difficulty and pain in speaking, or may not be able to speak at all. Chewing and swallowing food can also become very painful processes.
Treatment of glossitis of the tongue
First of all, the treatment plan depends on the type of inflammation. It is compiled individually, based on clinical and diagnostic data. For acute catarrhal glossitis, it is important to remove the irritating factor: replace the crowns or, conversely, put crowns on the damaged tooth. Change your eating habits, stop chewing nuts, hard candies, and crackers.
For a folded tongue, oral hygiene comes to the fore.
If lumps and papillomas grow during rhomboid glossitis, they are excised. Laser surgery allows you to do this quickly, with virtually no blood.
The main recommendation for black tongue is treatment of somatic diseases and smoking cessation. Liquid nitrogen is used to remove papillae, as well as applications to keratinized areas.
But there is a general approach to treatment:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- vitamin complexes;
- iron supplements for anemia;
- for pain - light anesthetics in the form of applications;
- for burning - oral baths and irrigation;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- checking for fungal infections.
There are many recommendations on the Internet for treating glossitis with folk remedies. No one disputes the anti-inflammatory properties of chamomile, sage and plantain. When a spot appears on the tongue, applications of sea buckthorn oil and aloe juice can bring relief. But these measures are temporary, they affect the symptoms, but the cause of the disease remains unattended. As a result, it is easy to miss the point when it was not difficult to fix the problem.
Glossitis is closely related to common diseases and psychological causes. Effective treatment is only possible using an integrated approach. How to treat glossitis and what examinations you need to undergo can only be advised by a qualified doctor. Glossitis can be cured quite quickly, but if left untreated, abscesses, tumors, and necrotic tissue changes can form. This is much more serious and the prognosis is not so favorable.
Blood blisters on or inside the cheek
The main cause of blood blisters on the inside of the cheeks is friction against sharp or ingrown teeth when you eat. Gentle rubbing usually results in the formation of a painless blood blister on the inside of the cheeks.
In case your teeth are very sharp, you can fix them through dental surgery by cutting off the sharp ends. Otherwise, you will often bite or rub them on your inner cheeks and cause injuries, which may lead to blood blisters from time to time. In some cases, you You may bite your cheek when speaking or chewing food.
Super plant Kalanchoe for acne!
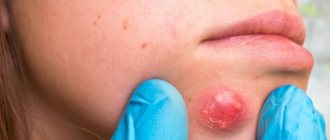
Blood blister on the lower, upper, or inner lips
Blood spots that form in the inner upper or lower lips are usually caused by trauma. Often these injuries are caused by friction or accidental biting of the teeth. However, this does not exclude the possibility of other causes such as viral or infectious symptoms.
On the other hand, blood blisters that form on the outer upper or lower lips are usually caused by infections and viral diseases. However, in rare cases, they can be caused by injuries.
Bloody pimple inside the lip
How to deal with bloody pimples inside the mouth?
While blood in a blister in your mouth will usually disappear spontaneously, there are things you can do to speed up the process. Here are some tips:
Typically, getting rid of blood blisters entails using home remedies or treating the underlying cause. Home remedies are more common, especially if the cause is known and is an allergy or injury.
Home Remedies for Bloody Pimples
There are some home remedies that you can try to get rid of blood blisters in your mouth.
- One is to use ice. Placing ice on a bloody pimple or sucking pieces of ice close to the pimple area will compress the blood bubbles, which will stop the bleeding.
- Tea tree oil is an astringent that will reduce pain and dry out blisters, reducing inflammation in the process. Can heal blood blisters because it has anti-inflammatory properties that will also cool the area where it appears and help relieve pain. To use it, you should dilute the oil with water in the proportions of 1 : 1 and rinse your mouth with it.
- Sandalwood powder can be mixed with rose water to make a paste that can be applied to the blood blister. It absorbs heat from the blister so that healing occurs faster. It also helps with inflammation and pain.
- You can also use turmeric paste mixed with rose water or honey. It is an antiseptic and can prevent you from getting an infection.
Oral hygiene
You should not use a toothbrush when you have blisters in your mouth as this can only cause more damage to the tissue. Even a soft toothbrush can irritate the lining of your cheek. Instead of using a toothbrush, gently use your fingers to clean your teeth by resuming use toothbrush when everything has healed.
As tempting as it may be, do not squeeze or attempt to pop a blood pimple or blister on any area inside the mouth, as this will prolong the pimple's healing time, possibly leading to scarring or further infection. Instead, you should aim to suppress swelling and minimize discomfort you feel You can try the following remedies to treat blood pimples:
An effective natural remedy for Peppermint that quickly kills any acne!
- When this is not the first time you notice a blood lump in any area of the oral cavity, you definitely need the help of a doctor, which you should seek immediately.
- Rinse your mouth regularly with an antibacterial mouthwash or water mixed with a teaspoon or two of sea salt or table salt.
- Be careful when you brush your teeth.
- Avoid any salty or strong foods that irritate the affected areas of the mouth, such as salty chips, nuts or pickles, as well as chocolate and other sweets, as these can irritate the sores, worsening the pain and prolonging your blood pimple healing symptoms.
- You should also avoid acidic fruits and vegetables, including oranges, lemons, grapefruits and tomatoes.
- Avoid eating raw vegetables, as they are too strong and may further injure sore areas in your mouth; instead, consume soft foods that are easier to chew and swallow.
- Consumption of hot foods should also be strictly limited during this period, so wait until your food and drinks have cooled to room temperature before eating them.
Most blood pimples and blisters clear up on their own in about a week, although larger pimples may take longer. If you have persistent pain, or if your symptoms recur, you may need to see a doctor to get checked.
Types of glossitis
All inflammatory processes are divided into chronic and acute, independent and secondary, accompanying other diseases. In any case, problems with the tongue indicate the presence of a disease, so it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Sometimes glossitis occurs without pronounced manifestations, but the doctor will definitely notice changes in the tongue during a routine examination.
Independent diseases (when only the tongue is affected) include several types of inflammation.
Acute catarrhal glossitis
Most often it develops as a result of mechanical damage from sharp edges of decayed teeth, unsuccessful dentures, candies and nut shells. It is a sign of allergies, acute respiratory viral infections or gastrointestinal diseases.
Patients develop red spots on the base of the tongue. Patients experience pain while eating and talking. The tongue swells and becomes covered with a thick coating. Saliva production increases.
Desquamative glossitis
It has many names: geographic tongue, migrating, exfoliative glossitis. It is he who begins with red spots on the tongue. This occurs due to epithelial detachment (desquamation).
The reasons are not completely clear, but diseases play a certain role in the development of inflammation:
- stomach and intestines;
- edocrine glands;
- hematopoietic organs.
Infectious diseases can provoke inflammation
and
vitamin deficiency
.
All of them disrupt tissue nutrition and, as a result, the epithelium begins to slough off. The red spots are growing. As the spots increase in size, the process of keratinization begins in the center, and the keratinized areas, on the contrary, begin to flake off. This is how glossitis “migrates” from one part of the tongue to another. At the same time, its outline resembles a map, hence the name “geographical”.
In the vast majority, desquamative glossitis is discovered during routine examinations. For a long time it does not cause any inconvenience. But in advanced cases, the tongue begins to react to spices and sours. There are complaints of tingling and burning. The tongue becomes covered with cracks, which can become infected. In this case, the disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, general malaise, and weakness.
Diamond-shaped glossitis
This is an inflammation of the tongue in which red spots have clear boundaries
and
geometric shape
.
Among the reasons are:
- congenital nature of the disease;
- housing and communal services diseases;
- candidiasis of different nature and location.
There are 3 types
rhomboid inflammation. The flat look is the easiest, patients are unaware of it, and only a doctor can see the characteristic red spots on the root of the tongue.
The lumpy and papillomatous types are irritating with the sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. Sometimes patients complain of a burning sensation.
Black “hairy” tongue
With desquamative glossitis, the epithelium peels off too much. When the keratinized epithelial cells stop exfoliating at all, they speak of a “hairy tongue.” The size of the papillae increases. They change color as a result of the interaction of iron in food and oral microflora. Most often, the papillae become black or brown.
The reasons may be:
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- infections;
- tuberculosis;
- venereal diseases;
- smoking;
- alcoholic drinks in excessive quantities.
The disease develops gradually and for a long time patients do not pay attention to the changes. Therefore, the sight of a “hairy” tongue can cause a lot of stress. Patients complain of burning, itching, dryness, and foreign body sensation. Sometimes, when talking, gagging occurs. Taste sensations often change.
Folded tongue
This congenital anomaly is detected in children and adults. It is diagnosed less often in children due to the fact that the folds are small. During the period of intensive growth, in puberty, with the growth of muscle tissue, the tongue also increases, the folds appear more clearly. Characterized by changes in the shape and size of the tongue. The transverse folds are smaller, the longitudinal folds are well defined. The main problem of pathology is the accumulation of food debris and bacterial waste products in the folds. This is a favorable environment for microorganisms. They penetrate small cracks and provoke the development of other forms of glossitis. In particular, in 50% of cases, a folded tongue is combined with migrating glossitis. Often inflammation is caused by fungal infections, such as candidiasis.
There is no specific treatment. In the presence of a fungal infection, drugs with a fungicidal effect and ointments against the fungus are prescribed. It is recommended to carefully observe oral hygiene and, along with brushing your teeth, clean your tongue with special scrapers.
Glossodynia
Glossodynia
is a burning mouth syndrome. It usually starts with the appearance of red spots on the tip of the tongue. The tongue is sore and tingling. Pain appears, which subsides while eating, but intensifies in the evening. In 80% of patients, saliva production decreases. The tongue swells, desquamation (detachment of the epithelium) begins. The tongue becomes covered with cracks.