The surface of the oral mucosa in a healthy child does not have any spots or pimples, so the appearance of red or white pimples on the tongue clearly indicates pathology
. This symptom is characteristic of many diseases, and not only dental ones.
What is this disease?
Herpetic stomatitis is a pathological process that develops in the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity. The causative agent of this disease is herpes simplex virus type 1. In children under the age of five, this virus is detected in 60% of all cases. By adolescence, it is detected in the vast majority of people. Herpes stomatitis in children develops during the baby’s first contact with the virus. This occurs most often before the age of three.
The high incidence is explained by:
- low level of production of own antibodies;
- immaturity of cellular immunity;
- the fact that the baby does not receive antibodies from mother's milk;
- high reactivity of the child's body.
If the baby is bottle-fed, he may get sick in the first months of life. Viral infection often goes into a latent state. It persists in the nerve ganglia.
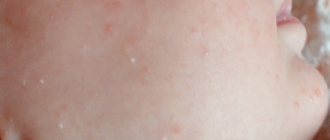
Quite often, children develop pimples on their tongues caused by an allergic reaction of the body.
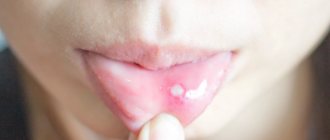
If there is an allergy, the child's tongue becomes covered exclusively with white blisters. This is their main feature. First, you need to exclude foods that could cause allergies from your diet. You will also temporarily have to give up scented soaps, powders and other detergents of synthetic origin. Believe me, regular baby soap or laundry soap will be much more beneficial in this case. Try to wet clean your home and remove dust more often. It is recommended to treat blisters on the tongue of infants with a regular soda solution.
Dear mothers, do not forget that only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of bubbles on the child’s tongue and prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Do not self-medicate at home, because the most valuable thing is at stake, namely the health of your baby! The main reasons for the formation of bubbles on a child’s tongue
Causes
The cause of the development of the pathology is the herpes simplex virus type 1. It belongs to DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae viral family. The pathogen multiplies rapidly in the epithelial cells of the oral mucosa. Then it enters nearby lymph nodes (submandibular) and continues to reproduce in them. Then it enters the blood and migrates to the parenchymal organs (spleen, liver, kidneys). There it multiplies and enters the bloodstream again. As a result, it again appears in large quantities in the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. They are massively defeated. It is localized in the oropharynx, oral cavity, nose, lips, and nearby skin. Stomatitis and herpes of the skin and mucous membranes develop when the infection generalizes simultaneously.
Children become infected with it as follows:
- through contact and everyday life (using shared utensils, toys, through kissing);
- airborne (coughing, sneezing);
- from a sick mother to the fetus through the placenta or during childbirth.
A baby can become infected from sick adults, children, and carriers.
The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- previously suffered inflammatory processes;
- previous antibiotic therapy;
- deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the body;
- mechanical damage to the skin and mucous membranes;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- poor oral hygiene.
In children, the virus is especially easily transmitted through contact. The infectious process quickly spreads to healthy areas.
The appearance of a pimple on the tongue: diseases and treatment
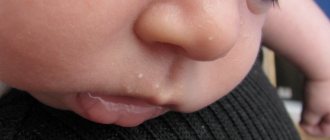
The most harmless reason for the appearance of a pimple on the tip of the tongue is mechanical damage. Regular antiseptic treatment is enough to get rid of the problem. To relieve inflammation, you can use decoctions of sage and chamomile. A prerequisite is not to touch the wound with your hands, as you risk causing a more serious infection.
Allergy
It usually manifests itself as a scattering of small pimples throughout the tongue plate; if treatment is not addressed immediately, the pathology penetrates the root of the tongue, the frenulum and affects the larynx.
Classification
According to the flow, acute, chronic, and wave-like variants of the pathology are distinguished. The following degrees of severity of the pathological process are distinguished:
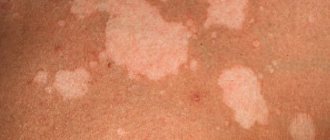
- Mild - it is typically characterized by a slight increase in body temperature, moderate inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. Rashes form on the mucous membrane and skin.
- Medium – high temperature rises. Severe weakness and sudden deterioration in health. The baby begins to vomit and the pain in the mouth increases. Significant rashes appear in the mouth and the skin around it.
- Severe - a severe headache is added to the pathological process. High temperature rises, severe muscle pain. Not only regional but also distant lymph nodes enlarge. The rashes are located not only in the oral cavity, but on the skin next to it. They appear on the mucous membrane of the eye, on the eyelids, and on other parts of the face.
The severity of the pathology depends on the viral load (the amount of virus in the body) and the general reactivity of the body.
What diseases does a red tongue hide?
A red tongue can be a symptom of diseases of various etiologies, including:
- angina;
- flu;
- chickenpox,
- scarlet fever;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- pneumonia;
- Kawasaki disease;
- gastritis;
- severe poisoning;
- renal failure;
- vitamin deficiency (vitamin B deficiency).
As you can see, the list of diseases is quite wide and requires visiting not only an otolaryngologist, but also, if necessary, other specialized specialists: dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.
Clinical manifestations
Stomatitis in children is characterized by a gradual onset of the disease. Clinical signs of the disease do not appear immediately after infection. The incubation period is typical for this pathology; it lasts from two days to three weeks.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis in children appear starting from the prodromal period.
Each period has its own clinic:
- Latent – lasts up to two weeks. The child's sleep is disturbed and he refuses to eat. The baby becomes restless and whiny. He has increased salivation, possible nausea and vomiting. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
- The height of the disease - at this time rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes. They are located on the soft, hard palate, gums, cheeks, lips and tongue. They are group or single, up to three millimeters in size. They are thin-walled bubbles filled with a clear liquid. Their formation lasts up to four days. The vesicles quickly open, then erosions and painful aphthae form. They are shallow ulcers covered with a white coating. The mucous membrane in the mouth is swollen and bleeding. The child develops a high temperature of up to 40 degrees. A runny nose, cough, and conjunctivitis occur.
- Fading - aphthae, erosions gradually heal and epithelialize. These formations heal without scarring. Often there is a wavy course of the disease. The periods of appearance of rashes alternate with rises in temperature.
The illness usually lasts up to two weeks. In children under one year of age, generalization of the process is possible. The development of sepsis, damage to all internal organs and meninges is likely.
Changes that should alert parents
In addition to changes in the color of the taste organ, parents should be wary of other accompanying symptoms, including:
- swelling, against which the imprints of teeth can be seen;
- insufficient moisture or obvious dryness of the surface of the tongue;
- enlarged papillae, especially pronounced in the root part;
- formation of persistent plaque on the surface of the tongue;
- burning sensation and impaired taste perception;
- the appearance of a specific odor from the mouth.
Parents can notice these changes during a visual inspection, which is best done in the morning in natural light. If the situation continues for a long time, the plaque thickens and the color of the tongue does not return to normal, there is every reason to consult a doctor to find out the reasons and identify hidden pathology.
Diagnostics
A patient suspected of having this disease is examined by a dentist. He asks the child’s parents about how the disease progressed. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the characteristic clinical picture of stomatitis, revealed during examination, anamnesis and characteristic complaints. Upon examination, typical mucosal lesions are revealed.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory testing of scrapings of the oral mucosa, the contents of ulcers, the patient’s saliva and blood is used.
The following are used for research:
- cytopolymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- serological blood tests (RSC, ELISA, immunoglobulin M test);
- HSV test for the detection of immunodot G-specific glycoprotein.
These methods are used only for severe infections, as they are quite expensive.
A red or pale tongue is not the norm!
Both options indicate pathological changes occurring in the child’s body:
- A crimson-red tongue always indicates the presence of an infection (viral, bacterial or fungal). Most often it is tonsillitis, scarlet fever, stomatitis or glossitis.
- A red and shiny tongue is a sign of anemia, exhaustion and severe stomach disease;
- A cherry tint is a sign of influenza and measles, as well as general intoxication or kidney dysfunction;
- A bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen; there is reason to suspect disorders in the cardiovascular system or lungs;
- Purple color may indicate blood and lung diseases, heart failure.
- A too pale tongue, being penetrated by blood vessels, a priori cannot be lighter than blood. In most cases, this sign indicates exhaustion, deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B 12.
Let us remind parents that very often there may be a coating on the surface of the tongue, the color of which also has its own characteristics.
Treatment
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children with mild and moderate forms is carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe cases and the development of complications, the baby is hospitalized. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a pediatric dentist or periodontist.
Children are prescribed bed rest and a diet with pureed, non-irritating food. He is given separate hygiene items and dishes. Plenty of warm fluids are recommended.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Paracetamol, Nurofen) are used to relieve temperature and inflammatory reactions.
- Antihistamines (Clemastine, Loratadine) are used to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Zovirax) are used at the beginning of treatment or in severe cases.
- Immunomodulators (Lysozyme, Gamma globulin, Thymogen) are used to enhance immunity.
During treatment, vitamin-mineral complexes and fish oil are used in monthly courses.
Local drugs that act directly on the mucous membrane are widely used.
For local treatment of herpetic stomatitis the following are used:
- antiseptics (Hexoral, Miramistin) - they are used to rinse the mouth every four hours for two weeks;
- ointments and gels with anesthetics (Kamistad, Lidochlor gel) are used for pain relief, they are lubricated with mucous membranes three times a day for up to two weeks;
- antiviral agents (Ganciclovir, Acicovir) - destroy the viral cell, gums are treated with these ointments five times a day, two weeks;
- proteolytic enzymes (Trepsin, Chymotrypsin) are used to cleanse the necrotic surfaces of ulcers; they are washed with these solutions twice a day.
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile, sage) is carried out after each meal for up to two weeks;
- epithelializing ointments (Solcoseryl, Methyluracil) are used to enhance the healing of erosions and ulcers, used in the recovery stage, used up to four times a day for ten days.
Physiotherapy is applied locally. Irradiation of affected mucous membranes with ultraviolet and infrared rays is used.
Location: on the base
Pimples at the base of the tongue interfere with swallowing and even speaking, they hurt and cause a lot of trouble. The reasons for their appearance can be very diverse. It could be stomatitis, a fungal infection, a sore throat or pharyngitis. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis. We can only suggest what you should pay attention to.
If a pimple appears on the base of the tongue, you should carefully analyze other symptoms - fever, enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of allergic reactions. For example, with a sore throat, pimples form in the throat quite often. They are painful, make swallowing difficult and cause pain when talking. In this case, the patient also has enlarged tonsils and submandibular lymph nodes, and an elevated temperature. As a matter of fact, acne and fever almost always occur either with a sore throat, or with tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
It is undesirable to ignore pimples on the tongue near the throat, since in particularly advanced cases they can interfere with breathing, which can lead to suffocation. Therefore, having discovered them in yourself, you need to contact an ENT specialist for a diagnosis.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing infection. This presents certain difficulties, since the vast majority of the population is infected with it. It is better if the child gets sick from it at an older age.
For this it is recommended:
- avoid contact with infected people;
- will provide personal utensils and personal hygiene products for the child;
- Kissing people with herpetic rashes is prohibited;
- strengthening the baby's immune system.
It is recommended that the child be provided with adequate nutrition and regularly given vitamin and mineral complexes.