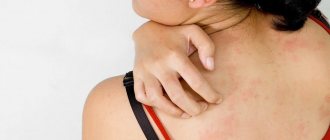
Itchy skin
- This is irritation of sensory receptors, which are free nerve endings. Strong irritation of sensory receptors is felt as pain, minor irritation as itching. However, sometimes the itching is much more difficult to endure; a person inevitably begins to itch, but this should not be done. If the itching is severe, a person may scratch himself until he bleeds. It should be remembered that scratching the skin is injured, and infection can enter the body through wounds. Scratching often causes the development of local inflammation.
What happens and what causes itchy skin?
There are localized and generalized skin itching.
Localized skin itching
Localized
called itching concentrated in one place. Most often this itching is observed in the area:
- anus (for hemorrhoids, worms, inflammation of the rectum);
- external genitalia (in case of disease of these organs, as well as in women - during menopause);
- scalp (pediculosis).
Localized itching can also be caused by dry skin, insect bites and allergic reactions.
Itching all over the body
Generalized
(that is, widespread throughout the body) itching can be caused by various reasons, including:
- liver diseases (including viral hepatitis);
- endocrine diseases (for example, diabetes);
- some blood diseases;
- skin diseases;
- mental disorders;
- some oncological diseases.
Causes of intimate itching in women
1. Itching in the groin in the genital area is only a symptom, and it can have many causes, and “bad diseases” are not always to blame. It may be behind pathological conditions not only of the urinary and genital tracts, but also, for example, of the intestines. Discomfort in the intimate organs in girls often appears as the first symptom of diseases such as diabetes, liver dysfunction (even hepatitis or cirrhosis), and allergic reactions.
2. Sometimes itching in the perineum appears due to neglect of the most basic hygiene rules. Alas, gynecologists often have to remind women that underwear needs to be changed every day and to give preference to products made from natural materials that absorb all secretions well.
3. Regarding daily washing. It is not at all necessary to boil water or add disinfectant solutions to it for this purpose. Regular tap water is fine. Intimate hygiene products (gels, soaps, etc.), like traditional soap, are also not necessary - this is a matter of habit and does not significantly affect cleanliness. You should not try to use soap or other hygiene products to “kill” the burning and itching in the intimate area due to “bad” vaginal discharge: they only dry out the skin and mucous membranes, and this can only make the problem worse. Vaginal deodorants in the form of foam or spray are now available for sale. They cannot be considered hygiene products; they disrupt the normal microflora of the vagina too much, increasing the risk of developing inflammatory diseases. Their deodorizing effect is fleeting and, again, does not eliminate the cause of the symptoms that bother you and the itching between the legs.
4. Quite often, irritation and genital itching without burning or discharge occur against the background of diarrhea (diarrhea) or frequent urination. If a girl’s inner labia are rather large and the tissues near the clitoris (hood and skin folds) are overdeveloped, then trips to the toilet “for minor needs” are always accompanied by splashing and ingress of urine into these structures and the accumulation of its remains in the depths of the skin folds. Even minimal errors in hygiene lead to a woman developing a persistent “urine” odor from the external genitalia, irritation and itching in the intimate area, and tests for infections will not show anything.
5. During menstruation, a woman is recommended to change pads every four to six hours, regardless of the amount of discharge. Menstrual flow is a very suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, and the body’s immune defenses are weakened these days. Using pads or tampons is a personal matter, but in some cases (with inflammatory diseases of the genital organs and urinary tract, after childbirth) tampons are “banned.”
What causes itching and odor in the intimate area
Irritation, discharge, redness and itching in the perineum in girls occurs more often with the following diseases:
- Candidiasis;
- Trichomoniasis (trichomoniasis);
- Genital herpes type 2;
- Spreading HPV;
- Fungal skin diseases;
- Skin diseases (neurodermatitis);
- Pediculosis pubis and scabies;
- Violation of intimate hygiene, etc.
Very often, itching between the legs is accompanied by a disruption of the normal composition of the vaginal microflora. Among other troubles, in addition to candidiasis (thrush), gynecologists find bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis). Both of these diseases occur against the background of inhibition of the “good” microflora of the genital tract.
There is another diagnosis that can cause itching in the perineum - kraurosis of the vulva. The insidiousness of this disease is that outwardly everything looks fine - no local or general lesions are detected, but even with careful hygiene, itching in an intimate place can be so severe and so exhausting that it often leads to nervous disorders. The addition of an infection to skin scratching can lead to the appearance of a specific odor. Usually occurs in women of pre- and menopausal age.
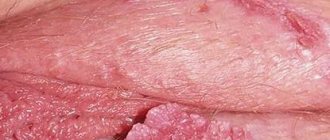
Why do the labia itch?
Why do women often experience itching of the labia minora and majora, incl.
with redness and discharge. What can provoke a strong or not so strong desire to scratch the external genitalia or the area between them and what to do about it? Find out more details using the links below! assignment_ind
Find out more at the link above
Why do I want to scratch my vagina?
What are the main causes of vaginal itching and severe irritation at the vaginal opening?
Find out about the main 11 risk factors for getting this problem. How to be treated if you have symptoms and a constant strong desire to scratch in the groin - click on the link! assignment_ind
Read more about vaginal itching
Which doctor should you contact if you have itching?
In case of localized skin itching, you should consult a dermatologist. Sometimes the allergic origin of itching is undoubted; in this case, it is recommended to visit an allergist-immunologist. Women with itching in the genital area need to consult a gynecologist.
If the skin itching is generalized, then first of all you should consult a therapist. Most likely, a comprehensive examination will be required to determine the cause of the itching.
Qualified and experienced doctors at Family Doctor will help you identify the cause of itching and prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Nature of itching in the genital area
By nature, scratching in the female genital area can be constant, periodic and occur only under certain conditions - for example, after a hot bath, beach, sexual intercourse. It is necessary to consult a specialist even in case of periodic and seemingly minor itching, because such a symptom may indicate health problems and the need for therapy. If you start to itch “there”, do not hesitate, consult a doctor.
Itching in the vagina and burning after urination
Most often, the appearance of this symptom after visiting the toilet may indicate the presence of cystitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. This disease is manifested by a frequent urge to urinate, which is an irritating factor and creates the feeling that the inflammatory process is concentrated in the genital area.
Urethritis, an inflammation of the walls of the urethra, which is affected by various types of bacteria and viruses, also leads to discomfort in the genital area.
Almost any disease of the excretory system that causes dryness of the mucous membrane, leads to microtrauma and is accompanied by the appearance of discharge, can cause a woman to complain of discomfort. Urine entering the area of microtrauma causes irritation, resulting in discomfort.
Redness of the vagina in diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus leads to changes in the functioning of the entire body. With this disease, damage to small vessels is observed, local immune forces decrease, the acid-base balance changes, the skin and mucous membranes become dry, flaky, microcracks easily appear on them, which become infected with pathogenic flora and fungi, which leads to inflammatory diseases. And of course, a woman may be bothered by discomfort in the genital area, which is manifested by itching and pain.
Unpleasant allergy symptoms
An allergic reaction can occur when the body is exposed to multiple irritants, such as medications and certain foods. Excessive use of intimate hygiene products - all kinds of scented gels, foams, panty liners - can also lead to allergies and itching in the genital area.
Wearing synthetic, excessively tight underwear, as well as regular shaving of the intimate area with subsequent hair growth can also cause itching.
Itching and burning in the vagina after intercourse
Women often experience unpleasant symptoms when they are allergic to lubricants and the latex from which condoms are made. Various spermicides can also cause irritation and itching in the genital area. If you have an allergic reaction to your partner's seminal fluid, unpleasant symptoms appear after unprotected intercourse and are accompanied by redness and swelling of the vagina and external genitalia.
Sometimes the cause of an allergy to a partner's sperm lies in his food preferences or in the medications he takes. Therefore, if there is discomfort after sexual intercourse, in many cases it is necessary to treat the couple together and contact a gynecologist and urologist.
Discomfort due to improper hygiene
Both insufficient and excessive hygiene are harmful when a woman violates the natural flora of the genital organs. Not everyone knows that regular soap is not suitable for the intimate area, because it changes the environment in favor of an alkaline one. This can additionally lead to discomfort and itching. The skin of the body and the mucous membrane of the genitals have different pH values, so in order to avoid itching anywhere, they need different care.
Problems when taking antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are often used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. As a rule, the course of treatment with these drugs prescribed by a doctor is quite long. And this does not count the cases when women self-medicate and prescribe antibiotics to themselves, for example, for ARVI and influenza. They don’t know that antibacterial drugs are powerless against viruses and can only cause harm.i
Unfortunately, as a result of taking antibiotics, the beneficial microflora of a woman’s body suffers, which causes problems with the gastrointestinal tract and other internal organs. Bacterial vaginosis may develop - vaginal dysbiosis, in which the number of beneficial bacteria sharply decreases, while the opportunistic flora grows and makes itself felt by itching in the genital area.
Dysbacteriosis also often leads to a decrease in the local defenses of the mucous membrane, which only aggravates the process and leads to secondary infection.
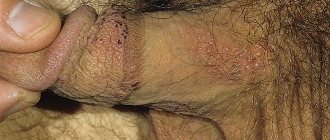
Discomfort with candidiasis (thrush)
Urogenital candidiasis is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, which, in the absence of any disturbances in the body, are normally present in the microflora of the genital organs. Candidiasis develops with intensive proliferation of fungi, which leads to a disruption of the natural balance of the environment of the genital organs. The development of candidiasis is often caused by a general decrease in immunity.
The fungal disease is manifested by swelling, hyperemia (redness), copious cheesy discharge from the genital tract (which is why this disease is popularly called thrush), pain during sexual intercourse and a feeling of irritation and itching in the vulva area.
Contrary to popular belief, men also suffer from candidiasis, which manifests itself in them as a disease such as balanitis, an inflammatory disease of the penis.
Vaginal discomfort during pregnancy
Discomfort in the genital area in a pregnant woman is caused by the same reasons as in women who are not currently expecting a child. But still, the expectant mother has one more reason for discomfort in the genital area - sudden changes in hormonal levels in the body. Hormonal imbalance leads to a weakening of the immune system, which in turn contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the genital area and the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
Treatment and relief from vaginal discomfort during pregnancy must be treated with the greatest care and only those drugs whose instructions indicate that they are approved for use by expectant mothers should be used.
Itching and burning in the vagina during menopause
With the onset of menopause, a woman’s hormonal levels also undergo enormous changes that affect all organs and systems, including the reproductive organs. Estrogen deficiency in the female body, as well as involutive changes in blood circulation, a reduction in the secretory activity of the gonads and the production of collagen fibers, which are responsible for rapid tissue regeneration, all lead to discomfort in the genital area. A woman is worried about dry mucous membranes, discomfort during sexual intercourse, and often microtrauma and the appearance of wounds.
If you detect the first signs of atrophic changes, you should contact a gynecologist to prescribe adequate treatment that will eliminate unpleasant symptoms and allow you to have a sexual life without unpleasant consequences.
Discomfort in the genital area due to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Sexual infections are one of the most common causes that lead to unpleasant symptoms in the vaginal area. Almost all infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted lead to discomfort in the genital area.ii
The following urogenital infections most often manifest as itching in the genital area:
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea.
All of these diseases are distinguished by nonspecific symptoms, one of which is scratching in the intimate area.iii To prevent partners from itching, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment when the first suspicious signs appear.