The appearance of condylomas in the vagina and labia of women occurs due to infectious infection. The causative agent is the human papillomavirus, transmitted through sexual intercourse. It is important to treat this disease in a timely manner, since most often these growths indicate a precancerous condition.
General information
In appearance, condylomas are similar to small warts. The increase in growths begins to occur from small pimples, which are very difficult to identify. To detect the presence of condylomas, you need to conduct a special test for HPV. It can be taken at any hospital. Condyloma is a benign tumor. Based on their appearance, growths are divided into papillary and warty. With timely measures taken and proper treatment, condylomas are not life-threatening for a woman. But most often, HPV is accompanied by additional diseases that are associated with microflora disturbances:
- ureaplasma;
- mycoplasma;
- gardnerella;
- candidiasis.
All these pathologies can cause the appearance of HPV, which is characterized by the growth of warts in the vagina and labia.
What is papilloma?
Often, papillomas look like small nodules that form in the vaginal area. They can acquire pigmentation from flesh to pink. There are both single specimens and several formations in one area. By merging with each other, they can form quite large clusters. If such a process develops, then we can talk about papillomatosis.
The emergence of such formations occurs under the influence of the human papillomavirus on the body. This pathogen is sexually transmitted and is quite common among the sexually active population.
In this article, we have already covered in detail the issue of human papillomavirus in women.
Why do vaginal papillomas occur?
Of particular importance is the presence of disease-provoking factors:
- endometritis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- vulvovaginitis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea.
They lead to the rapid development of the virus inside the female body.
The development of papillomas in the vagina is also promoted by:
- early intimate life;
- avitaminosis;
- dysbiosis in the vagina;
- nervous shocks.
- decreased immune strength in the body;
- taking corticosteroids;
- performing surgical interventions on infected skin;
- pregnancy.
Papillomavirus has about a hundred different strains, of which only a few are capable of leading to the emergence and development of papillomas.
When the virus enters healthy tissue, a number of processes occur:
- The pathogen penetrates the basal layer of the dermis.
- Damages the cell membrane.
- Viral DNA is introduced into the center of the cell.
- The virus is waiting for favorable conditions.
Vaginal sizes: truth and myths
(excerpt from the “Intimate Book”) Questions about the vagina are of interest to many people, primarily regarding the correspondence of the penis to the size of the vagina. I have repeatedly heard complaints from women who experience discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse that their vagina is obviously too small and not adapted to accept the male sexual organ. This complaint simultaneously became a justification for refusing sexual relations to one’s partners.
Often, having fallen into the hands of a female doctor, such women become hostages of endless diagnostic studies and treatments, which not only harm the female body, but ultimately kill her sexual attraction to men, and also in many cases leads to the collapse of a marriage, official or civil.
What is the mystery of the vagina if it can attract a man no less than cars, cigarettes and other male hobbies?
For information, the vagina (vagina) is a kind of muscular canal, stretchable and elastic, connecting the external genitalia and the uterus. The size of the vagina is individual for each woman, but on average the depth of the vagina is 7-12 cm (not in a state of arousal). Smaller sizes can only occur with malformations of the genital organs or after operations when the vagina was sutured. Thus, a normal vagina can accommodate normal penises. What if the penis size is more than 12 cm? Then you need to take into account the fact that the vagina is elastic, which means it expands and stretches during sexual intercourse, adapting to the erect penis.
We will talk a little more about the size of the vagina using data from the Vagina Institute. Let me remind you that measurements of the external genitalia and vagina of women have been carried out (and are still being carried out) since 1995 and almost 900,000 women took part in the research.
In a non-excited (relaxed) state, the vaginal size is 7-9 cm in 78.34% of women. In an excited state, the size of the vagina increases to 13-19 cm, and in 86.96% of women it is 15-16 cm. Remember these numbers so that you can later compare them with the size of the penis, especially in a state of excitement.
With childbirth, especially rapid, large children, the size of the vagina, its elasticity, may change, and sensitivity during sexual intercourse may decrease. As studies show, the size of the vagina changes slightly only in a relaxed state - by the age of 60 its length increases by 1-2 cm, but in a state of arousal it remains almost unchanged.
The smallest vaginal sizes are in Australian and New Zealand women (15.9 cm when aroused), and the largest are in African women (17.03 cm when aroused). By country, Zambia, Tonga and Bermuda lead the way. Japanese women have the smallest size of an unexcited vagina.
There is a lot of talk among men about the fact that before pregnancy and childbirth, the vagina is smaller and “tighter.” To what extent is this true and not some speculation of men? The study showed that in single women, the vaginal size is 8.21 cm in a relaxed state and 16.3 cm in a state of arousal. In married women, many of whom have had pregnancies and childbirths, the vaginal dimensions are as follows: 8.52 cm in a state of relaxation and 16.55 cm in a state of arousal. Thus, the difference is only 2-3 mm, which is very insignificant.
The problem is most likely not in the size of the vagina, but in the fact that after childbirth the relief of the vaginal walls is slightly smoothed out. In addition, married women, having experience of sexual intercourse and childbirth, are able to relax better during intercourse and do not tighten the muscles of the vagina, as young women who have no experience of sexual activity often do. Most often, if you use certain sex positions and techniques, the sensations and pleasure you receive, including orgasm, do not change after childbirth. In addition, there are certain exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pelvis and perineum to improve the quality of sexual life. In extreme cases, you can resort to vaginal plastic surgery - surgical treatment of prolapse and prolapse of the vaginal walls.
The vaginal size of straight men and bisexuals is the same, but that of lesbians is slightly smaller, which is due to the fact that this category of women has fewer cases of pregnancy and childbirth.
It turns out that the size of an aroused vagina is directly proportional to a woman’s height. Therefore, we can safely say that the taller a woman is, the longer her vagina is when aroused. The dependence of vaginal sizes (average sizes) on height is shown in the table:
| Height (cm) | Relaxed vaginal size (cm) | Vaginal size in aroused state (cm) |
| Up to 139 | 8.0 | 13.97 |
| 140—149 | 8.08 | 14.88 |
| 150—159 | 8.28 | 15.55 |
| 160—169 | 8.4 | 16.57 |
| 170—179 | 8.33 | 16.77 |
| 180—189 | 8.31 | 19.46 |
| Above 190 | 8.0 | 20.73 |
From the above data it is clear that every additional 10 cm of growth “adds” approximately 1 cm to the size of the vagina in a state of arousal.
The structure of the vagina is such that its mucous membrane does not have special sensory nerve receptors, due to which a woman can feel pain and itching. Such symptoms appear only when the skin of the vaginal vestibule (vulva) is irritated by secretions, mechanical irritants (penis, instruments, fingers, vibrator, etc.) or chemical irritants (soap, washing powder, medicinal solutions, etc.). However, a woman may complain of pain and itching “inside”.
Pain may occur with strong contraction (spasm) of the muscles of the vagina and perineum. More than 60% of women have experienced or are experiencing pain during sexual intercourse, but in the vast majority of cases, pain occurs due to women’s inexperience in sexual relations, poor arousal and relaxation during sexual intercourse, and very rarely due to vaginal infections and inflammatory processes of the reproductive system . Painful sensations are often associated with a negative mental attitude (fear, reluctance) towards sexual intercourse, and muscle contractions are controlled by the woman’s consciousness. Therefore, most often such women need the help of a psychotherapist, sexologist, or psychiatrist.
If you are interested in women's health issues, read my articles and books on this topic (1000 questions and answers on gynecology (2017), Preparing for pregnancy (2012), Desk aid for pregnant women (2011), etc.).
To be continued…
Share link:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Skype (Opens in new window)
- Send this to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
By
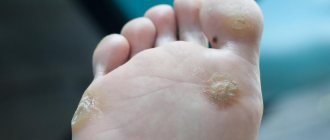
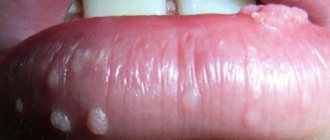
What do condylomas look like?
Quite often, the reason for visiting a gynecologist is the formation of condylomas on the intimate organs of women. Genital warts or condylomas are growths of the papillary epithelium, resulting in the formation of growths.
While condylomas are growing, the virus is not contagious. But as soon as the pathogen reaches the epidermis, there is a high risk of infecting its sexual partner.
There are two types of condylomas:
- Exophytic. The formations resemble genital warts in appearance. They are formed in the superficial layer and have a papillary surface. Such condylomas are provoked by HPV with low oncogenic activity. A photo of genital warts in women is presented here.
- Endophytic. They form flat condylomas. Very often they grow deep into the epithelium. Can provoke changes within healthy tissues. In the absence of timely treatment, they can cause oncological formations.
Condylomas can grow greatly, causing inconvenience:
- may bleed or be injured;
- interfere with intimate life;
- are in the nature of a cosmetic defect, while causing psychological discomfort;
- create problems during childbirth.
Photo
To understand the location and external signs of condylomas, use the photographic material provided below.
Reasons for education
Once HPV enters a woman’s body, it quickly activates and spreads. This is where the main danger lies. It is necessary to take appropriate measures to treat the pathology as quickly as possible and prevent the subsequent proliferation of growths. The virus divides in the cells of the vagina. This process is responsible for the rapid development of tumors, which cause a lot of inconvenience to women. One of the main reasons for the appearance of condylomas in the vagina is the presence of these growths in one of the partners. During unprotected sexual contact, the virus is naturally transmitted to another partner. HPV is activated only under certain factors:
- lack of sleep, irregular routine, stress;
- weakened immunity;
- excessive physical activity;
- excessive doses of antibiotics;
- the presence of wounds on the vaginal mucosa;
- poor nutrition, hormonal imbalance;
- hypothermia.
Symptoms of vaginal papilloma
Often, with HPV in women, the formation of papillomas is asymptomatic at first.
In case of prolonged development and progression of the disease, symptoms may appear:
- There is a feeling of itching and burning in the vagina.
- Bleeding may occur.
- Detection of growths in the vagina upon palpation.
Depending on the speed of development of the disease, a diagnostic examination of the patient will be necessary, followed by removal or treatment of the growths.
Vaginal cancer treatment
The proximity of the vagina to the rectum, bladder, and urethra limits the dose of radiation that can be administered and also limits the margins of resection during surgical treatment. Moreover, for most patients, maintaining vaginal function is the most important factor when planning treatment tactics.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is based on achieving “clean” resection margins, that is, without tumor cells.
1. In stage I and damage to the posterior wall of the upper third of the vagina. A radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and surrounding parametric tissues), partial colpectomy (removal of part of the vagina with a tumor) and removal of the pelvic lymph nodes are performed.
2. If it is necessary to carry out radiation therapy in young patients, before it is carried out, it is recommended to perform an operation to transpose the ovaries in order to remove them from the radiation zone.
3. In patients in stage IVA, when there is a complication such as rectovaginal or vesicovaginal fistula, pelvic exenteration is the method of choice in treatment.
4. In patients with localized (solitary) recurrence of the disease, surgical resection is also the only treatment option.
Radiation therapy
- the method of choice in the vast majority of cases when treating patients with vaginal cancer. It is a combination of teleradiotherapy and intracavitary therapy.
Small tumors can be treated with brachytherapy, but in cases of more extensive disease, treatment usually begins with 5,000 cGy of external radiation to shrink the tumor and target the pelvic lymph nodes and continues with intracavitary radiation.
A combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is also used.
Complications after a course of therapy are associated, as a rule, with dysfunction of adjacent organs: rectum, bladder, urethra, in 13-19% of cases - up to the complete loss of their functions, which certainly has serious consequences for the quality of life of patients. Less serious complications are cystitis and proctitis after radiation therapy, rectovaginal and vesicovaginal fistulas, and rectal strictures.
Forecast
The five-year survival rate for vaginal cancer is about 77%, 52%, 42%, 20%, 12% for stages I, II, III, IVA, IVB, respectively.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, a gynecologist needs a complete diagnosis:
- History of the disease. It includes knowledge of information:
- how long ago the growths appeared;
- whether there were unprotected intimate relationships;
- how long ago the last act of this kind took place.
- Examination by a gynecologist . In this case, the affected epithelial cells are collected for subsequent PCR analysis.
- PCR diagnostics. In this analysis, the number of pathogens and the type of papilloma viral infection are determined.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. It is necessary to confirm the presence of antibodies to the virus in a person. Based on which, one can judge the degree of development of HPV in the human body.
- Colposcopy. Inspection of the vaginal walls to determine damaged areas. It is carried out using a special colposcope device and staining the cervix with iodine solution.
- Anoscopy. Involves examining the anal area for the presence of papillomas.
- Cytological examination. Study of cells under a microscope, detection of damaged areas and their characteristics.
- Histological analysis. Studying the structure of damaged areas.
- Oncocytology. Study of cells in scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal under microscope magnification.
You might be interested! Why are papillomas on the head of the penis dangerous and how to treat them?
When papillomatosis is confirmed, timely treatment and correct selection of therapy are necessary.
Vaginal cancer diagnosis and staging
A biopsy is required to make a diagnosis. This can be done already at the examination stage, without anesthesia.
In case of changes in cytology and in the absence of clinical data in favor of the presence of a tumor or precancerosis, colposcopy is necessary. If the patient has previously undergone a hysterectomy and, according to colcoscopy, there are changes in the mucous membrane in the vaginal dome, complete resection of the vaginal dome is performed for a thorough histological examination.
The TNM system is used to stage vaginal cancer. In order to adequately determine the stage of the disease, it is recommended to carry out not only a basic range of examinations, including a gynecological examination, cystoscopy and colonoscopy, but also the use of radiation diagnostic methods (CT or MRI) to obtain a complete picture not only at the site of the primary tumor and in the pelvis, but also in the abdominal cavity, liver, retroperitoneal lymphatic nodes, as well as the urinary tract.
There are different stages of development of vaginal cancer
- Tx - Primary tumor cannot be assessed
- Then - There are no signs of a primary tumor
- Tis - Carcinoma in situ (pre-invasive carcinoma)
- T1 - Tumor limited to vagina
- T2 - Tumor grows into peri-vaginal tissue
- T3 - Tumor extends to the pelvic wall
- T4 - The tumor has invaded the lining of the bladder/rectum or has spread beyond the pelvis. The presence of bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4.
- M1 - There are distant metastases
Treatment of vaginal papilloma
Therapy for curing papillomas can be carried out in several approaches:
- Conservative treatment methods. Necessary to prevent the tumor from degenerating into a malignant formation. Includes purpose:
- Immunomodulators. They are used after testing the sensitivity of the papilloma virus to a specific medication. These include Viferon, Reaferon, Kipferon.
- Inducers of interferon production. Prescribed after determining the effect of such drugs on the affected areas. Representatives of drugs: Tamerit, Neovir, Larifan.
- Specific drugs that have an antiviral effect. Most often prescribed: alpirazine.
- Surgical techniques for the treatment of papillomas. Several types of formation removal are used:
- Chemical coagulation. Carry out under the influence of drugs: solkovagin, podophyllin.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is effective for small affected areas.
- Electrocoagulation. It is carried out using a laser.
- Radio knife or excision with a scalpel. Prescribed only for extensive lesions.
Drug treatment
Very often, treatment of papilloma virus occurs under the influence of a whole range of medications.
They have the following properties:
- cauterizing;
- bactericidal;
- oppressive.
The main means of fighting infection include:
- lapis pencil;
- drops;
- pills;
- ointments.
If removal of papillomas is not practical, then you can get rid of the growths in 2-3 weeks with the help of medications.
The following have a detrimental effect:
- Feresol.
- Phenol in glycerin solution.
- Super clean.
- Salicylic acid.
- Cryopharma.
In addition to the direct effect of solutions on papilloma, general-effect drugs are also used that increase the immunological status of the body.
Removal
Sometimes it is impossible to cure papilloma without removing the affected area.
Then they resort to the following procedures:
- Excision of formations. It is carried out in cases of large lesions of the skin.
- Treatment with chemical drugs that have a detrimental effect.
- Freezing the damaged area. It is possible to carry out this procedure in the vagina. The advantage of this manipulation is to control the effects of cold without touching healthy tissue.
- Use of chemical removal techniques.
Paths of spread of the tumor process (metastasis)
1 – direct path (implantation or “per continuitatem”). The tumor grows into nearby organs and tissues - the rectum, bladder, pelvic wall, pelvic bones.
2 – lymphatic pathway to the pelvic and then para-aortic lymph nodes. The region of lymph node involvement depends on the location of the primary tumor. If there is a tumor in the lower third of the vagina, the first to spread are the inguinal lymph nodes.
3 - hematogenous (through blood vessels) - to distant organs (lungs, liver and bones).