Itching in the groin can occur in men for many reasons. The condition is provoked by both physiological and pathological factors. To eliminate the risk of affecting the reproductive system, timely contact with a urologist is recommended. He will not only conduct a general examination, but also prescribe tests, which will help to timely determine the diagnosis and begin treatment.
Causes of groin itching
Identifies the following physiological or temporary causes leading to the symptom:
- poor hygiene, which causes sweat and dirt to accumulate, pores become clogged, and an active process of inflammation begins;
- the content of various substances in the urine that cause redness, irritation, diaper rash, and rash;
- use of low-quality, synthetic underwear.
If one of the listed factors occurs, it can be easily eliminated. It is enough to maintain hygiene and use natural linen. The symptom will disappear quickly. Treatment is required if pathologies become a provoking factor:
- diseases of the urinary system, due to which bacteria, fungi, and urine breakdown products accumulate;
- endocrine pathologies, for example, thyroid dysfunction;
- genitourinary system infection, sexually transmitted diseases;
- activation of painful microorganisms as part of opportunistic microflora;
- spread of scabies mite;
- decreased immune function;
- genital herpes;
- complications of diabetes.
When pathology develops, mandatory drug treatment is required.
Diagnostic stages
If symptoms appear, contact a urologist. He may prescribe an additional consultation with a venereologist, allergist, or dermatologist, depending on the developing clinical symptoms. Laboratory and instrumental tests are required to determine the exact cause.
- General inspection
. The doctor examines the man’s penis and adjacent tissues. It can detect redness, inflammation, swelling, discharge and other negative reactions. - Anamnesis collection
. The patient explains his complaints and talks about recent changes in his life. He is always asked about hereditary diseases in the family. - PCR technique
. Detects any types of viruses and bacteria contained in urine or discharge from the penis. - Bacteriological culture
. The mucus is inoculated on a nutrient medium, and the exact type of bacterial pathogen is identified. Determine the antibiotics to which it is sensitive. - General blood test, biochemical test, general urine test
. These are general clinical studies that indicate the condition of the body as a whole, separately the blood, immunity and urinary system.
Thanks to diagnostic tests, you can accurately determine the diagnosis.
Where to find the right doctor?
Regardless of what kind of doctor you need, you can find him using the “Your Doctor” service. It allows its visitors to analyze the offers of various private clinics and select those that are located in the most convenient way and have a suitable specialist on staff.
As an additional service, the site allows visitors to fill out an online form and call a dermatologist at home or make an appointment with a specialist of their choice at a time of interest.
Publication date: 2018-02-03
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Skin scraping
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
General symptoms
If the itching in the groin does not disappear even after good hygiene and the use of natural underwear, it is necessary to collect the patient’s medical history. It includes all the negative symptoms that he is currently developing or have suffered in the past. The patient may have developed a sexually transmitted disease with the following symptoms:
- rash localized to the genitals or groin;
- burning, irritation, pain, stinging;
- increased discomfort during urination or sexual intercourse;
- mucous, purulent, bloody discharge from the urethra;
- redness and swelling;
- white plaque on the head of the penis;
- discomfort, pain in the testicular area.
The following infectious pathologies affecting the reproductive system are distinguished:
- ureaplasmosis, chlamydia;
- genital herpes;
- pubic louse, mite.
These are the most common diseases affecting the urethra and other parts of the urinary tract. If pain, burning, itching and heavy infiltration occur, infection with syphilis is possible.
It is extremely rare for men to develop candidiasis. This is a fungal infection accompanied by itching and profuse discharge from the glans penis.
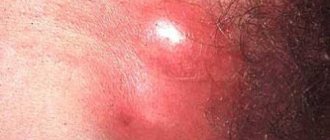
Redness in the groin in men
Redness in the groin is a cause for concern for many men. They are not always accompanied by itching. Often they indicate sexually transmitted infections, but they are also the result of sweating and tight synthetic underwear, under the influence of which the delicate skin in this area can turn red and itch.
A red rash on the scrotum sometimes signals syphilis.
Painless gray-brown, red-brown or yellow-brown spots appear as a result of a disease such as erythrasma. Men are more often susceptible to this disease due to increased sweating (hyperhidrosis).
Erythrasma and the causes of its occurrence
The causative agent of erythrasma (corynebacterium) has a very low infectiousness and is found in the microflora of a healthy person.
This bacterium has a low ability to cause disease; it multiplies in the upper layers of the skin, so only the superficial layers are affected. The course of the disease is chronic.
Transmission of corynebacteria occurs through the use of the patient’s belongings and other close contacts with the infected person.
Reasons contributing to the development of erythrasma:
- The use of aggressive washing agents and hard washcloths, which destroy the upper layer of the epidermis and weaken the protective properties of the skin in the groin;
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- Weakening of the body’s immunity due to other diseases and medications;
- Increased sweating, living in humid and hot climates;
- Wearing tight-fitting clothing that rubs the body;
- Changing the pH level of the skin towards alkaline;
- Fungal infections and allergic dermatitis, as well as increased skin sensitivity.
The appearance of round spots of different sizes may indicate the onset of the disease. The colors of these spots range from yellow to red-brown, clearly distinguishable from the flesh color. Over time, the spots increase in diameter and combine into a new formation, in the center of which a darkening forms.
During the development of erythrasma in the groin, the patient does not experience any discomfort and often does not seek help in time. In summer, when it is hot, the disease progresses. Patients suffering from obesity or diabetes mellitus sometimes experience complications in the form of additional bacterial infections, diaper rash, and eczema.
Characteristics of diseases that cause itching
The table shows the main diseases and their brief characteristics.
| Disease | Description |
| Candidiasis | When it spreads to the head of the penis, itching develops. He is strong, constant, a man rarely experiences such sensations normally. Infection occurs through transmission of the infectious agent from a sexual partner, development of immunodeficiency, and diabetes mellitus. Copious white mucus may be released from the urethra and an unpleasant odor may appear. Therapy is carried out using antifungal drugs and immunostimulants |
| Dermatomycosis | Urine can accumulate in the groin area, causing a moist environment. Pathogenic fungi begin to develop in it, leading to itching, rash, and burning. In damp conditions, a bacterial infection occurs, which aggravates the symptoms of the disease. The condition often occurs in athletes who do not use hygiene techniques after active training. Red spots appear on the dermis, blisters spread to the groin area. Treatment is carried out using antimycotic, antihistamine drugs |
| Herpes | The disease is transmitted after unprotected sexual intercourse from an infected partner. Bubbles filled with a pathogen appear on the penis. The rash gradually moves to the groin area, thighs, and buttocks. Treatment is carried out using antiviral drugs |
| Chlamydia | An infection that spreads after unprotected sex. There is severe pain and pain when urinating. Burning and itching are observed at any time of the day. Systemic and local antibiotics are used for treatment. To speed up recovery, take immunostimulants. During treatment, sexual intercourse is prohibited |
| Ureaplasmosis | These are bacteria of opportunistic microflora, activated by the action of negative factors. The patient is bothered by strong, profuse discharge and groin itching. If the disease is not treated promptly, infertility develops. Therapy is carried out in the acute period using antibiotics and physiotherapy |
| Dermatitis | An allergic reaction develops, which can be triggered by food, cosmetics, and underwear. Antihistamines with local and systemic effects are used for treatment. Increase the frequency of hygiene procedures |
| Scabies | The scabies mite is transmitted through dirty hands and bedding. Gradually it affects the deep layers of the epidermis, causing a rash and itching on the dermis. Antiparasitic agents are used that destroy the pathogen itself and its eggs |
| Diabetes | With pathology, metabolism is disrupted, the level of urea and urination increases. A humid environment is formed in which bacteria and fungi quickly multiply. A person is bothered by a persistent rash that is not affected by medications. Itching is localized in the area of the penis, testicles, anus, perineum |
If a person develops dermatomycosis, the tissues of the genital organs are not affected. Only the groin is affected.
Treatment
Patients with dermatitis, prickly heat, and eczema are advised to eliminate the provoking factor. For all diseases, it is advised to follow the rules of hygiene, use soft cosmetics, and wear loose natural underwear.
Local treatment is widely used. For prickly heat and inguinal epidermophytosis, baths with string, celandine, chamomile, and potassium permanganate are useful. For pathologies accompanied by weeping, use mash and powder, and treat with antiseptics and oak bark infusion. Antifungal, antibacterial, hormonal and keratolytic ointments are applied according to indications.
Antihistamines are recommended to reduce itching. If there is irritability or sleep disturbances caused by unpleasant sensations in the affected area, mild sedatives with herbal components are added to the treatment regimen. For large foci of erythrasma, systemic medications with antibacterial action are prescribed. For some conditions, UV therapy is effective.
To treat the skin for scabies, special emulsions and aerosols are used; to prevent re-infection, the body, underwear and bed linen are treated according to a special scheme. For lice, pyrethroids, organophosphorus compounds, polydimethylsiloxanes and essential oils are used. Carry out appropriate epidemiological measures.
Starting period of therapy
If a person is bothered by itching, he should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment as early as possible. Many infections can affect the genitals, causing many complications, including infertility. The earlier therapy is started, the lower the risk of their development.
Lack of quality hygiene
This is one of the most common problems that cause itching in the groin. You are required to shower at least once a day. To relieve disturbing symptoms, use a decoction based on plant extracts:
- chamomile, calendula, string;
- oak bark, celandine.
To prepare a decoction, take one or several plants at once and pour boiling water over it. After infusion and straining, wash the area of the penis and adjacent tissues.
After treatment, wipe the skin dry with a towel. Next, apply a regenerative and moisturizing cream. For example, Sinaflan.
Sinaflan is a glucocorticosteroid intended for external use. It eliminates inflammation, allergies, exudate, and active itching. The action is formed by suppressing the negative influence of the immune system. The drug is applied to the affected skin. Sinaflan is recommended for use for dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, and skin itching of various origins. It is used up to 3 times a day. The drug has a small list of side effects that develop extremely rarely:
- purpura, telangiectasia, skin atrophy;
- hypertrichosis, secondary infection, perioral dermatitis.
The product is not recommended for pregnant women with bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. With prolonged use, the steroid causes a decrease in blood supply to tissues, so atrophic processes may develop. Because of this factor, doctors prescribe the drug in a short course, up to 1 week.
Food allergies
Itching is provoked by foods that cause allergies. Treatment is required to relieve the acute condition:
- taking an oral antihistamine;
- application of an intimate gel with a neutral acid-base state;
- treatment with an antiseptic solution, for example, Furacilin;
- applying baby powder.
During therapy, they refuse synthetic underwear and do not visit the sauna, bathhouse, or swimming pool. Any sexual intercourse is possible after completion of therapy.
After 3-4 days, the patient’s condition completely normalizes. But in the future you will need to eliminate foods that cause hypersensitivity.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis in other words is called thrush. To eliminate it, use the following measures:
- frequent hygiene procedures, you can use herbal decoctions for treatment;
- applying antifungal ointments containing clotrimazole or fluconazole;
- in severe cases, an oral antifungal drug is used, but in a short course, so as not to cause a load on the liver.
Follow a diet low in dairy products, sugar, and baked goods.
Ureaplasmosis
It is almost impossible to completely destroy ureaplasma from the body. But it is necessary to reduce its concentration by using antibacterial agents. For example, Doxycycline, Josamycin. Additionally, immunostimulants are used so that the body can fight the infection on its own.
Ureaplasmosis is dangerous because it does not cause negative clinical symptoms for a long time. But gradually, without treatment, it penetrates deeper and deeper into the urethra, spreading to the internal genital organs. This can lead to infertility. If a man transmits a pathogenic microorganism to a woman, reproductive dysfunction occurs much faster.
Antibiotics are used for treatment, but it is impossible to completely eliminate the pathogenic microorganism, since it belongs to the bacteria of opportunistic microflora. Therefore, a man must monitor the condition of the penis and the discharge from it. If any changes occur, immediately make an appointment with a urologist.
Chlamydia
The earlier treatment for chlamydia is started, the lower the risk of damage to the reproductive system, including infertility. Treatment methods:
- oral antibiotics - Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav, Azithromycin, Macropen;
- immunostimulating drugs - Lysozyme, Dekaris;
- enzymes to improve intestinal microflora - Mezim;
- probiotics - Normobact.
If you use drugs in combination, recovery occurs faster.
Genital herpes
If a person has genital herpes, the condition is accompanied by a profuse rash, it is necessary to immediately begin antiviral therapy:
- an antiviral agent containing acyclovir;
- interferon-based immunostimulants.
Herpes is a rather dangerous disease that causes complications. Therefore, the choice of drug depends only on the doctor; it is forbidden to change its dosage on your own.
Scabies mite
The microorganism quickly causes severe, long-lasting itching. The place where it is located needs to be lubricated with special creams. For example, Crotamiton, Lindane. Therapy is long-term, at least 10 days.
Rashes due to pediculosis pubis
Pediculosis pubis is an infestation of lice in the intimate area. The disease in men is severe, sometimes the parasites spread to the eyelids and eyebrows. With this disease, a pinpoint rash and irritation appear in the pubic area.
With lice pubis, the rash in the groin area in men itches constantly. Unbearable itching leads to the formation of injuries and weeping wounds. This condition is dangerous due to the addition of a secondary infection. The pubic skin gradually thickens and becomes dense. Lice are located at the root of the hairs, so they are easy to spot. Lice practically do not move, parasitizing a certain area. Therefore, skin manifestations may be focal. Pediculosis is contagious and requires immediate treatment.
Prevention methods
To prevent the development of groin itching, it is recommended to use preventive measures in a timely manner:
- frequent hygiene of the genitals and the whole body;
- periodic preventive examination by a urologist with laboratory tests (especially for the presence of STDs);
- treatment of any pathologies with prescribed drugs, use of the full course of therapy to reduce the risk of relapse and complications;
- constantly wearing clean, natural underwear;
- frequent washing of personal hygiene items and bed linen;
- periodic use of tar soap, which eliminates fungus and reduces itching due to allergies;
- the use of barrier contraception during sexual intercourse, especially if a man prefers frequent changes of sexual partners.
It is best not to self-medicate. This can lead to negative consequences, since the patient will not be able to independently select the optimal medications and their dosage. Therapy should be selected only by a urologist, therapist, venereologist and other doctors of narrow specialties.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of formation of vulvar itching is based on the peculiarities of the innervation of the perineum, labia minora and labia majora. The branches of the iliac, pudendal, femoral and rectal nerves approach this area. When various stimuli are applied to the endings of unmyelinated C-fibers, poorly differentiated impulses, perceived as itching, tingling, burning and even pain, enter the sensitive zone of the cerebral cortex through the spinal cord.
The nature of the stimulus is usually determined by the immediate cause of the pathology. These may be drying secretions, local changes in the mucosa, metabolites, thermal, mechanical and chemical factors. Sometimes the action of irritants leads to the release of histamine, causing swelling and itching in the affected area. The pathogenesis of the disorder in mental disorders is apparently associated with a decrease in the threshold of sensitivity and increased excitability of brain structures.