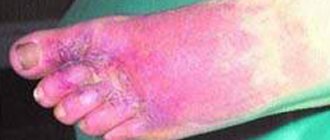
Gynecomastia in men is a disease based on unilateral or bilateral enlargement of the mammary glands. The disease can progress both against the background of hormonal disorders and in relatively healthy men who do not have problems with hormones, but are obese.
There are two forms of gynecomastia in men: physiological and pathological. The physiological variant of breast tissue enlargement occurs in newborns and adolescents, as well as in older people, in whose body the level of testosterone sharply decreases and female sex hormones - estrogens - begin to predominate. Gynecomastia during the newborn period occurs due to the influence of maternal hormones that reach the child in utero.
During puberty, many adolescents suffer from bilateral breast enlargement, which usually goes away on its own without any treatment. The problem is associated with changes in hormonal levels, namely with an increase in the amount of estrogens and their predominance over male sex hormones.
In most cases of gynecomastia in men, there is a bilateral increase in the volume of the mammary glands. At the CONSTANTA Clinic you can seek qualified medical care, make an appointment with experienced specialists who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and determine the true causes of the disease. Doctors will develop individual treatment tactics for gynecomastia, in accordance with the diagnostic data obtained and the general well-being of the patient. Read more about the treatment of gynecomastia in men in our Clinic.
The main reasons for the development of gynecomastia in men
Normally, the mammary glands in men and adolescents are underdeveloped, formed by a small amount of glandular tissue. With obesity, adipose tissue begins to predominate. Breast volume is determined by the influence of female sex hormones - estrogens, as well as prolactin - a pituitary hormone. When, for various reasons, the androgenic index decreases and the amount of estrogen increases, excessive growth of the mammary glands in men is observed according to the female type with a predominance of glandular cells.
Unlike physiological gynecomastia in men, which is considered a passing phenomenon and in most cases resolves on its own, the pathological form of the disease is often associated with organic pathology and serious internal disorders. It is often necessary to involve highly specialized specialists in treatment: therapists, endocrinologists, oncologists, surgeons.
The main causes of true pathological gynecomastia:
- a similar condition is typical for neoplasms of the pituitary gland and testicles, primary hypogonadism, prostate adenoma and other hormonally active tumors;
- an increase in the amount of prolactin - increased secretion is associated with neoplasms of the pituitary gland and a lack of thyroid hormones;
- treatment with drugs that stimulate the synthesis of estrogen and prolactin;
- taking steroids;
- infectious and inflammatory processes, immunodeficiency states;
- chronic intoxication;
- excess body weight;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- diseases that are accompanied by metabolic disorders and dysfunction of the endocrine glands.
Drug addiction has an extremely adverse effect on the condition of the liver and mammary glands. Potent drugs, especially the opiate group, help increase the synthesis of prolactin, disrupt the functional abilities of the liver, disrupt the course of metabolic reactions, change the condition of the gonads and reduce the amount of testosterone produced. All this increases the synthesis of female sex hormones and leads to the development of gynecomastia.
External causes of acne on the back
External causes of subcutaneous acne on the back are associated with the influence of environmental factors. In particular, external causes of acne on the back include:
- use of inappropriate cosmetics;
- insufficient hygiene (rare washing) of the back;
- wearing synthetic and too tight clothing, which absorbs sweat and dirt.
External causes of back acne also include loose hair, the ends of which irritate the skin, causing excess sebum production. Sunbathing without protective equipment can also cause acne. After all, under the influence of sunlight, the stratum corneum of the epidermis thickens, which leads to the accumulation of sebum and clogging of pores.
Main symptoms of gynecomastia
The main sign of the development of gynecomastia is excessive growth of the mammary glands. As a rule, in men there is an increase in predominantly glandular tissue. When the amount of fatty tissue in the breast area increases, experts diagnose pseudogynecomastia. In addition to the appearance of mammary glands that are not typical for the male constitution, other signs of the disease may be present:
- pathological discharge from the nipples;
- pain in the chest area;
- increased nipple sensitivity;
- thickening of breast tissue;
- discomfort when the chest rubs against clothing.
If pathological growth of the mammary glands is detected, it is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as possible. Only doctors, having wide diagnostic and treatment capabilities, can make an accurate diagnosis and select an effective treatment regimen for gynecomastia in a man. Specialists are especially wary of unilateral enlargement of the mammary gland, which can be observed with the development of malignant pathology, as well as the appearance of bloody discharge from the nipple and suspicious lumps. Sometimes, against the background of male gynecomastia, the axillary lymph nodes become enlarged, which can also be considered an alarming symptom that requires consultation with a doctor and a detailed examination of the mammary gland and surrounding tissues.
Types of acne on the back
Acne on the back can be non-inflammatory and inflammatory. Non-inflammatory acne includes closed comedones (whiteheads) and open comedones (blackheads).
Inflammatory types of acne on the back include:
- papules (dense pink pimples with a diameter of one to three mm);
- pustules (small collections of pus in the upper layer of the epidermis with a white head in the middle);
- nodes and cysts (deep subcutaneous seals with a diameter of up to five mm.).
There are four degrees of development of acne on the back. In the first and second stages there are few acne. At the third stage of acne development, the number of rashes increases, redness and itching appear on the skin. At the fourth degree of pathology, nodes and cysts predominate, and the skin becomes pitted.
Examination for gynecomastia
To make a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor only needs to conduct a standard examination and palpation of the breast tissue and nearby lymph nodes. But an accurate diagnosis of gynecomastia is carried out only on the basis of the results of modern research. Ultrasound is considered the main diagnostic method. Specialists conduct ultrasound examinations of the mammary glands, scrotal organs, and axillary lymph nodes.
Laboratory tests are actively used, which include determining the level of testosterone, hCG, estradiol and prolactin, as well as other hormones (as indicated). If the development of a malignant tumor is suspected, a breast biopsy is prescribed. Additionally, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of internal organs are used.
At the CONSTANTA Clinic, patients have access to many types of modern diagnostic and laboratory tests, which allow them to obtain the most reliable information about the patient’s condition and the functioning of all his internal organs, including the endocrine glands. We provide professional assistance to men with gynecomastia and provide both symptomatic and surgical treatment.
Gynecomastia is a serious disease that requires an integrated approach and the participation of experienced specialists. Delayed visit to the Clinic or the use of questionable home methods for treating gynecomastia in men can lead to the development of serious complications. Our specialists have modern therapeutic and surgical methods to combat this disease, which are highly effective and safe. You can discuss treatment options with your doctor. Do not hesitate to ask a specialist any questions that interest you. The doctors of the CONSTANTA Clinic are focused on respecting the interests of their patients and maximum concentration of professional forces on solving the problems of each patient.
Rash caused by digestive problems
The condition of the skin largely depends on the functioning of the internal organs. Using a map of rashes on the face, you can determine which organs have problems.
- pimples on the forehead indicate problems with the intestines;
- a rash along the hairline indicates problems with the gallbladder;
- pimples on the bridge of the nose - liver problems;
- ulcers on the temples - problems with the spleen;
- rashes above the lip - disruption of intestinal function;
- pimples on the nose - heart disease or endocrine disorders;
- rash on the chin - gynecological problems.
Gynecomastia and steroids
Taking anabolic steroids often leads to the development of male gynecomastia. Steroid hormones contribute to the excessive formation of female sex hormones, in particular estradiol. As a result of long-term use of anabolic steroids by athletes, female-type adipose tissue deposition and bilateral enlargement of the mammary glands are observed. Athletes taking steroids should take care in advance to prevent gynecomastia. It involves taking special medications that block estrogen receptors. Ideally, an athlete’s career should be built without the use of steroid drugs, which have a detrimental effect not only on hormonal status, but also on the entire male body.
Rashes due to liver diseases
In the early stages of liver disease, they practically do not manifest themselves at all. The earliest symptom is specific skin rashes. They are caused by an increase in the amount of bile acid in the blood, which causes general intoxication of the body. The skin takes on a yellowish tint.
With cholestasis (blockage of the bile ducts), the rash is localized on the feet and palms, looking like marks from a burn. With cirrhosis, liver cells die and the whole body becomes covered with spots. Parasitic liver diseases cause rashes resembling hives. They are localized in the lumbar region and abdomen.
Also characteristic is a combination of rash and spider veins, which cause severe itching, which intensifies at night. Taking antihistamines (allergy medications) does not provide relief. Increased bilirubin gives the skin a yellowish tint.
Gynecomastia in endocrine pathologies
Endocrine diseases often cause the development of gynecomastia in men. Various pituitary tumors lead to hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism. In this condition, the synthesis of gonadotropins and testicular function are impaired, and spermatoginesis may decrease. As a result, men note a decrease in potency and disappearance of libido. Adolescents in this state do not have clearly expressed secondary sexual characteristics.
Hyperprolactinemia is observed with the growth of prolactinoma, as well as with other pituitary adenomas and the presence of hormonally inactive adenomas. In childhood, gynecomastia can occur with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid hormones help increase estradiol levels. To get rid of gynecomastia caused by hyperthyroidism, it is first necessary to treat the underlying disease.
Pneumonia and bronchitis: what is the difference?
Both diseases affect the human respiratory system, which means they have similar symptoms. It is often difficult to distinguish the two pathologies from each other.
| Pneumonia | Bronchitis |
| In most cases, it is accompanied by a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39° and a feverish state. There is a slight increase in temperature. | Accompanied by a strong dry cough. In some cases, sputum may appear greenish or streaked with blood. Wet cough, sputum is light in color. |
| When listening to the chest, “wet” rales are heard. | When listening to the chest, “dry” wheezing is heard. |
Gynecomastia and genetic pathologies
Genetic abnormalities often underlie the development of gynecomastia. Most often, excess growth of breast tissue is diagnosed in men with Klinefelter syndrome, in which an extra X chromosome is detected in the cells. These men have increased sensitivity to estrogen. With this disease, hyperprolactinemia occurs, which also increases the manifestations of gynecomastia.
In Klinefelter syndrome, puberty may occur on time, but puberty is often delayed. Patients exhibit predominantly tall stature and abnormal physique, in which the lower part of the body is significantly larger than the upper part. The size of the testicles is reduced. For chromosomal abnormalities, treatment of gynecomastia is predominantly surgical. The nodular form of the disease requires constant medical supervision and a biopsy after surgery or at the diagnostic stage.
Reifenstein syndrome occurs with increased estrogen synthesis and the development of gynecomastia. Symptoms of the disease usually appear during adolescence, when hormonal changes in the body occur. At the same time, experts identify signs of underdevelopment of the genital organs. Such patients require hormone replacement therapy with individual dosage selection.
True hermaphroditism also occurs with symptoms of gynecomastia. The patient usually learns about his problem at the beginning of puberty, when active growth of the mammary glands begins and other signs of the formation of a female-type figure appear.
Gynecomastia and liver diseases
Some liver pathologies can lead to the development of gynecomastia. Important metabolic processes occur in the liver tissues. This organ is responsible for the metabolism of steroids. Therefore, if its work is disrupted, with the development of hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, the risk of mammary gland growth in men increases. Specific kidney enzymes lead to the destruction of prolactin and gonadotropins, as well as slowing down the release of body tissues from metabolic products. All this often leads to an increase in the level of prolactin and estrogen, causing the progression of gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia and breast neoplasms
Tumors in the mammary glands are often mistaken for true gynecomastia. The process is most often one-sided, but sometimes the neoplasms involve two mammary glands at once. To the touch, the tumor has a dense consistency, is usually fused with adjacent tissues and has unclear contours. With breast tumors in men, bloody discharge from the nipples may appear, and sometimes the lymph nodes in the armpit become noticeably enlarged.
When a tumor is detected, specialists refer the patient for mammography, ultrasound, MRI and prescribe a biopsy, based on the results of which they can determine the nature of the tumor and make appropriate predictions for the future.
Symptoms of acne (acne)
- Increased oiliness of the skin of the face and head (increased sebum production);
- Small or large red rash;
- The appearance of white ulcers;
- Soreness of the skin in the areas of the rash;
- Scars and pigmentation after acne heals.
In the first stage, acne affects only certain areas of the face - most often the forehead, cheeks and chin. In the future, acne spreads to the neck and chest areas. At the third stage, ulcers and acne increase in size, covering increasingly large areas of the skin, and after healing they leave large scars.
Iatrogenic gynecomastia
Iatrogenic gynecomastia occurs when taking certain medications. The risk group includes patients who undergo hormonal treatment with estrogens, as well as other hormones (gonadotropins, glucorticoids). Against the background of hypogonadism, specialists often prescribe testosterone, which is toxic to the liver and can cause signs of temporary gynecomastia. Cardiac glycosides have a similar effect, stimulating the active production of steroids and disrupting the functional abilities of the testicles.
Drug-induced gynecomastia is most often a reversible process that can be stopped after stopping the medication that caused excessive breast growth. But it is necessary to stop taking medications as soon as possible. If you do not pay attention to the appearance of gynecomastia during drug therapy for 6-12 months or more, irreversible fibrotic processes will begin to occur in the breast tissue. The advanced form of the disease is subject to predominantly surgical treatment.
Principles of treatment of gynecomastia
Treatment of gynecomastia in men can be therapeutic and surgical. The physiological form of the disease in adolescents and newborns usually disappears spontaneously and does not require specific therapy. According to indications, specialists can carry out hormonal correction with drugs that reduce the level of female hormones. But any medications used to treat gynecomastia in men should only be prescribed by qualified specialists who are familiar with your clinical case. Self-administration of medications, without studying hormonal status and diagnostic results, can lead to adverse health consequences and increased symptoms of the underlying disease.
Conservative therapy for gynecomastia consists of prescribing hormonal drugs containing testosterone. Such drugs are effective in the initial period of development of the disease, in the first months, when scarring and other complications requiring surgery have not yet occurred.
The severe form of gynecomastia does not respond well to conservative treatment. It is extremely important to seek medical help promptly when drug therapy can be highly effective. If the doctor recommends surgical treatment, you should not refuse it. Today, men with gynecomastia have the opportunity to undergo minimally invasive surgical interventions, which do not leave rough keloid scars in the mammary glands. These are the types of operations that are performed at the CONSTANTA Clinic. Excess tissue is removed through a subareolar approach or using an endoscopic method with access from the armpit. In the second case, absolutely no scars remain on the skin of the breast.
For false gynecomastia, liposuction is indicated. The surgeon sucks out excess fat through small punctures in the skin or removes it using the classic surgical method. The operation is performed under general or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and his wishes.
Wen on the body: reasons, how to get rid of it
A small growth on the skin, a pea-sized “nodule”, can cause anxiety and concern. Concerns increase if the formation begins to gradually increase in size. The specialist’s diagnosis of lipoma only adds fuel to the fire of worry, since it is very similar to the name of many dangerous malignant tumors.
In fact, there is no real reason for concern, since wen extremely rarely (almost never) degenerates into a malignant neoplasm. This is a benign tumor that is characterized by slow growth or stable size over a long period of time. Why wen appears on the body and how to deal with them, you will learn from the publication presented to your attention.
What is a wen?
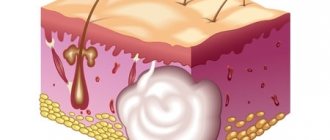
Wen is an unofficial, “folk” name for a subcutaneous formation formed by adipose tissue. In official medicine, the scientific term “lipoma” is used, which reflects the histological composition of the tumor.
Lipoma is a benign tumor that remains as such throughout its existence. A wen on the body is not characterized by malignant degeneration. From this point of view, it does not pose a health threat. The problem is mainly of an aesthetic nature, especially if the tumor is located on an open area of the body - on the face, on the neck, on the skin of the distal parts of the arms.
A distinctive feature of any benign tumor is that it is formed from cells surrounded by a fibrous capsule. In this way, wen on the body differs from atheroma - another neoplasm, the appearance of which is caused by fat. Atheroma is an accumulation of sebum secreted by the sebaceous glands. Atheroma is formed due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. The secretion of the gland cannot come out, accumulates under the skin and manifests itself in the form of a small or medium-sized formation that rises above the skin.
Lipoma, unlike atheroma, does not consist of the secretion of the sebaceous glands, but of fat cells surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue. A skin formation appears as a result of abnormally active division and growth of adipocytes. All cells, regardless of the size of the wen, remain differentiated, that is, they retain their typical characteristics, which makes it easy to distinguish a lipoma from a malignant tumor. A cancer tumor is characterized by impaired differentiation and atypical cell structure. In the case of lipoma, these signs of malignancy are not present.
Lipoma is a benign tumor of adipose tissue, which consists of differentiated adipocytes surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Malignant degeneration is not typical for wen on the body; they do not pose a danger to health or life.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
Numerous studies devoted to the problem discussed in the publication have not made it possible to establish a single cause of lipomas. Currently, it is generally accepted that a wen on the body appears as a result of the combined action of a number of predisposing factors, among which endogenous causes predominate.
Among the risk factors, the most important role is played by metabolic disorders associated with enzymatic deficiency. Particularly dangerous in this regard are disorders affecting the biochemical mechanisms of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. The cause of lipoma can be hormonal disorders not related to the pathology of the endocrine system. In particular, in women, a neoplasm can appear during pregnancy, lactation or after the end of the lactation period.
Endocrine diseases are also among the risk factors. If a person has wen on the body, the reasons should be sought in the functioning of the hormonal system. Dysfunction of the pituitary, adrenal, thyroid (hypothyroidism) or pancreas (diabetes) may be the root of the problem. A risk factor is an imbalance in the secretion of sex hormones, which is important for women taking oral contraceptives and athletes using pharmacological agents to accelerate results.
A fatty deposit on the body can occur even against the background of complete well-being, that is, in the absence of any endocrine disorders, hormonal changes or metabolic problems. Doctors explain this by genetic predisposition: people whose relatives have encountered a similar problem have a higher risk of developing lipoma. Hereditary, or familial, lipomatosis is characterized by the appearance of multiple wen at a young age.
Among exogenous factors, nutrition is of greatest importance. The risk of lipoma is higher if a person's diet is dominated by simple carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery, flour), as well as saturated and hydrogenated fats. A risk factor is systematic alcohol consumption. All these substances interfere with the natural course of metabolic processes, which is fraught with the formation of a benign tumor of adipose tissue.
Another possible cause of the appearance of a wen on the body is mechanical trauma, which leads to neurotrophic disorders in the integumentary tissues. They, in turn, can provoke the proliferation of subcutaneous fat cells. It is possible that exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin plays a certain role, but the connection between this factor and the appearance of lipomas has not been proven.
Localization, appearance, symptoms
The concept of “typical localization” does not apply to wen on the body. The tumor can appear on any part of the body: on the back of the foot or hand, on the shoulder or forearm, on the back, on the chest, on the face or on the abdomen. In short, lipoma does not have a “favorite” location; the tumor can appear anywhere.
As for the symptoms, that is, the appearance of the tumor, there is more certainty. Externally, the lipoma looks like a pea; it is characterized by a rounded shape with regular and even edges. On palpation, the adipose tissue tumor is soft or moderately dense. The surface is smooth. The color can be flesh-colored, reddish or brownish, depending on how abundantly blood vessels grow into the tumor.
An important diagnostic criterion is the mobility of the tumor. The subcutaneous wen on the body is always mobile; it is not fused to deeper tissues and moves freely with the skin. This symptom makes it easy to distinguish a lipoma from a malignant tumor. The latter grows into deep tissues, which is why it becomes immobile.
Size is difficult to use as a diagnostic criterion because it can vary over a wide range. Typically, a fatty tissue tumor has a diameter of 0.5 to 1 cm, but there may be exceptions to this rule. Wen on the body can reach 2-3 cm in diameter. There are cases when, as a result of growth, a lipoma reached gigantic sizes - more than 10 cm in diameter.
The last symptom - pain - is not typical for wen. As a rule, education does not remind us of itself. The exception is situations when a person mechanically injures him. When struck, scratched or pinched, a sharp pain may occur, which is not too intense and passes quickly. However, if a tumor of adipose tissue puts pressure on superficial vessels and nerves, the clinical picture may include moderate or even severe pain.
Are wen dangerous?
As already mentioned, the prognosis for this benign tumor is extremely favorable. The neoplasm is not characterized by malignant degeneration, so nothing threatens life. However, this does not mean that you can forget about lipoma, since certain health risks are still present.
In case of mechanical damage (cut, pinching, blow) inflammatory processes may begin in the depths of the formation. If the integrity of the skin is damaged, there is a risk of infection in the wound. The result of this may be the development of a necrotic or purulent-inflammatory process, after treatment of which visible scars will remain on the skin.
Scars can also form after removal of a large tumor. A small lipoma can be removed without leaving a trace, so that there are no noticeable scars left on the skin. When removing large and giant wen, it is difficult to avoid scar changes. Meanwhile, large wen must be removed, since sooner or later they will begin to put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels. It follows from this that it is better to get rid of the wen at an early stage, before it grows to a large size, the only question is how to do this?
How to get rid of wen?
Many people, in an attempt to get rid of the tumor, resort to traditional medicine recipes. Numerous publications devoted to this problem offer various remedies: compresses made from onions, garlic or sprouted wheat, applications of celandine and other medicinal herbs. Unfortunately, such an approach is doomed to failure; it is not possible to get rid of education using folk remedies. Traditional recipes are unlikely to provoke the growth of a lipoma, but they certainly will not lead to a reduction in its size.
Official medicine offers two options for solving the problem. You can get rid of small lipomas using a minimally invasive procedure, which involves injecting a special solution deep into the formation that destroys adipocytes. The disadvantage of this method is that there is a high risk of relapse, the capsule is not removed, and the method can only be used for small (up to 2-3 cm) tumor sizes.
Surgical removal of a wen on the body is an effective and universal treatment method. The lipoma is removed along with the surrounding capsule. Minor surgery is performed using a traditional, radio wave or laser scalpel. Accordingly, traditional surgical, radio wave and laser removal are distinguished.
All methods of surgical treatment are effective, but from an aesthetic point of view they are not equivalent. After traditional surgical removal of a tumor, small scars often remain, even if the doctor removes a small tumor. Radio wave surgery allows you to minimize the severity of scars, and the laser method makes it possible to perform the operation absolutely without leaving a trace.
Laser lipoma removal has many benefits. The laser knife seals the vessels immediately after they are damaged, reduces bleeding, and injures the skin to a lesser extent. Since laser pulses have a detrimental effect on pathogenic and opportunistic microflora, there is no risk of infectious complications. In addition, the laser stimulates regeneration, which shortens the recovery period, accelerates skin healing and avoids scar formation.
The problem is that the laser method is used only for medium-sized and small-sized wen; large and gigantic ones (more than 10 cm in diameter) are forced to be removed by the doctor using the traditional surgical method. Given their size, it is almost impossible to avoid scar formation.
Since the aesthetic component of the operation is a concern for all patients, doctors recommend removing lipomas in the early stages. The deciding factor is the size of the education. A tumor on the face can be removed without a trace if its diameter does not exceed 1 centimeter. Wen on the body are removed without scarring if their size is no more than 2.5-3 cm.
Laser removal of wen is the most effective and safe method. It is better to remove lipomas in the early stages, when their size does not exceed 1 cm if localized on the face or 3 cm if localized on the body.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia; only giant lipomas require the use of general anesthesia (anesthesia). The patient returns home on the day of surgery. During the recovery period, it is necessary to protect the skin from ultraviolet rays and avoid exposure to high or low temperatures. It is advisable not to wet the wound with water and regularly treat it with antiseptic solutions.
Removal of fatty tissues on the body: price
Surgeries to remove fatty tissue are carried out in aesthetic medicine and plastic surgery clinics. It is advisable to contact a medical institution equipped with modern equipment for laser manipulation.
The price of removing wen with a laser is low.
The exact cost depends on the size of the education. The cost of removing a small lipoma (up to 3 cm) in Moscow clinics is about 5 thousand rubles. The cost of treating a tumor up to 10 cm in size increases to 8-9 thousand rubles. Treatment of large and giant lipomas costs more - up to 15 thousand rubles, depending on the size of the formation and the category of complexity of the operation. You will receive more detailed information about lipoma removal methods during a consultation with a doctor at the Galaktika aesthetic medicine clinic (Moscow)
Preparation for surgical treatment of gynecomastia in men
No complex preparatory activities are carried out. The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination, which allows him to assess his health condition and choose the appropriate tactics for surgical intervention. Based on the diagnostic data, the doctor makes predictions for the future and selects the correct treatment regimen that prevents the development of complications, both during surgery and in the postoperative period.
The operation is performed on an empty stomach. The doctor will tell you in detail about the features of the surgical stage and recovery period. You must strictly follow your doctor’s prescriptions; if you have any questions or feel unwell, it is recommended that you contact your doctor without delay.
Preventive measures against the appearance of bacne
To prevent the appearance of bacne, you need to follow simple recommendations. Prevention measures for acne include:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- maintaining good back hygiene (regular washing);
- proper back skin care (use of suitable cosmetics).
In addition, to prevent the appearance of black spots on the back, you should follow a sleep and rest schedule. You should also avoid overheating and sunburn on your back.
Recovery period after surgical treatment of gynecomastia
In most cases, surgical treatment of gynecomastia in men proceeds without complications. As a rule, long-term hospitalization is not required. The patient is discharged home, given detailed recommendations about the rules of behavior and the prevention of complications.
Gynecomastia in men can develop due to many endocrine and non-endocrine pathologies, so treatment should primarily be aimed at the cause of increased estrogen levels and excessive growth of mammary gland tissue. Medical tactics must be strictly individual. It is necessary to determine the factors that provoke the development of the disease in order to eliminate their adverse effects on the male body. Then both drug and surgical treatment will be highly effective, and the risk of recurrence of the disease can be minimized.
If you have any questions or make an appointment with a specialist, please call: (4852) 37-00-85 Daily from 8:00 to 20:00
Sign up for a consultation
Popular questions
1. Is it possible to do a massage if there are acne on the back?
If during a massage course acne appears on the neck, shoulders and back, first of all, you should change the massage product, which can provoke the appearance of rashes. If the rash does not go away after replacing the cosmetic product, you must first treat the acne on your back, and then continue the massage course.
2. What foods cause back acne?
Rashes on the back can appear due to poor nutrition, including excessive consumption of fatty, fried and smoked foods. Therefore, nutrition for acne should be correct and balanced. Fast food, confectionery and carbonated drinks should be excluded from the diet.
3. What does the appearance of acne on the back indicate?
The appearance of acne on the back indicates problems in the functioning of the body. To cure back acne, you need to determine the cause of its appearance. And only a doctor can do this. Therefore, if a rash occurs, it is important not to delay visiting a dermatologist.
0
0
0
Article rating:
4.67 out of 5 based on 3 ratings
Author: Kaspruk Elena Aleksandrovna
Dermatovenerologist. Highest category. Work experience 28 years.