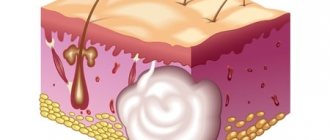
An epidermal cyst (atheroma) is a skin formation that looks like a capsule filled with sebum and particles of keratinized epithelium. Pathology of this type is often diagnosed in patients 25-45 years old. An abnormal manifestation occurs in both men and women, which excludes hormonal prerequisites for development.
Epidermal cysts occur on any part of the body where hair grows, as the formation forms around the hair follicle. The cyst can grow up to 50 mm in diameter. Outwardly, it is similar to a dense pink ball. On the surface of the formation you can see a capillary network. Enlarged pores are also visible. Inside the capsule the secret is a pasty light yellow substance.
The nature of the neoplasm is benign. But there is a risk of degeneration into a malignant form. Penetration of pathogenic microflora into the capsule provokes inflammation. If the epidermal skin cyst is located in the eye area, vision may be impaired due to its pressure. Formations behind the ear provoke headaches and nervousness. Therefore, the appearance of pathology cannot be ignored; if possible, it should be treated.
Don't forget about the cosmetic component. Cysts on the face, neck, and head can significantly spoil a person’s appearance. Large formations cause increased attention from others.
Modern dermatology offers several methods for treating atheromas. Experts from the Lasersvit clinic tell you more about the methods, as well as the causes and symptoms of the appearance of epidermal cysts. If after reading the article you still have questions, our qualified doctors are ready to answer them during a face-to-face appointment.
Epidermal cyst: causes
Unlike dermoid cysts, which are congenital, epidermal (skin) cysts appear due to blockage of the gland duct with sebaceous masses and dead epidermal cells. Provoking factors for the development of pathology:
- When metabolic processes are disrupted or hormonal imbalance occurs, sebum is secreted with a thicker consistency than that of people in good health. Due to the viscous structure of the substance, the physiologically normal outflow of the substance is disrupted. It, like a plug, closes the duct of the glands.
- When there is inflammation on the skin, for example, acne, folliculitis, tissue swelling occurs. This causes a narrowing of the lumen of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
- Scars and scars consist of dense connective tissue, which causes compression of the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
- Improper skin care and use of inappropriate cosmetics can cause blockage of the sebaceous gland.
Any of these factors can provoke the formation of this type of pathology. And if there are several of them, then with each new potential cause the risk of occurrence increases by 10-15%.
Localization
The development of a dermoid cyst is possible in almost any organ or tissue, as doctors note. Most often the presence of cysts is found in:
- the ovarian area in women of reproductive age, which can seriously affect the ability of the fair sex to conceive;
- the lower eyelid area (mostly children are affected, but the pathological neoplasm can be easily removed with the help of surgeons);
- the coccyx area, where the size of the ovarian dermoid cyst rarely reaches large sizes, and the formation can go unnoticed for a long time;
- the area of the anus, where without symptoms of inflammation, pathology is generally detected only by digital rectal examination, etc.
The discovery of dermoid cysts in any organ or tissue makes this pathology quite common. Moreover, as doctors note, the presence of dermoid cysts can either not make itself felt for a long time or cause severe discomfort.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is based on visual examination, hardware and laboratory tests. Externally, as already mentioned, atheroma looks like a painless bulge on the skin. The capsule is mobile and can move under the skin under mechanical stress. Atheroma can be detected in areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. A cyst often appears on the face, scalp, behind the ears, and on the back. Education is characterized by slow growth.
In a calm state, a cyst on the body does not cause physical discomfort to patients. However, in the presence of an inflammatory process, the tumor can look quite scary - redness and swelling of nearby tissues, thinning of the skin in the area around the tumor. Touching the subcutaneous lump can be extremely painful. The size, condition of the cyst and its location influence the choice of treatment tactics.
There are many different skin conditions that cause swelling and nodules to appear on the surface of the skin or just under the skin. This article describes the most common ones, including the following:- skin cysts
- senile hemangiomas
- dermatofibromas
- epidermoid cysts
- folliculitis
- keratoacanthomas
- follicular keratoses
- lipomas
- neurofibromas
Here you can view illustrations of the manifestations of skin diseases such as ringworm and rashes in adults and children. Learn to recognize birthmarks, skin cancer symptoms, and different types of insect bites.
- Skin cysts
Cysts are noncancerous swellings of the skin that may be filled with fluid, pus, or another substance.
Where to start
A cyst is a common condition that can appear on the skin of any part of the body. To the touch it resembles small peas located under the skin. Cysts can occur as a result of infection, clogged sebaceous glands, or around foreign bodies such as earrings.
What are the symptoms of skin cysts?
Typically skin cysts:
- grow slowly
- painless
- smooth to the touch when rolled under the skin
How to treat skin cysts?
Unless the cyst becomes damaged, infected, or inflamed, it does not cause pain. Some cysts disappear on their own without treatment, while others need to be drained, i.e. pierce with a sharp object and remove its contents. Some inflamed cysts can be treated with a cortisone injection, as this medicine causes them to gradually shrink and eventually disappear. Cysts that cannot be treated or that recur are removed surgically.
- Senile hemangioma
Senile hemangioma is a smooth, red nodule that forms on the skin.
Most often, senile hemangiomas appear on the torso, but they can also occur on the skin of other parts of the body. The cause of the appearance of senile hemangiomas is unknown; most often such nodules appear on the skin of people who have reached the age of forty.
What are the symptoms of senile hemangioma?
Senile hemangiomas are small, smooth, bright red swellings. Their size can vary from the size of a pinhead to one centimeter in diameter.
How to treat senile hemangioma?
In most cases, senile hemangiomas do not require treatment. If you don't like the way they look or if these tumors bleed, they can be removed using a laser or electrocautery, i.e. cauterization or destruction of tissue using a small sensor through which an electric current is passed. Removal of a senile hemangioma may cause a scar to appear.
- Dermatofibromas
Dermatofibromas are painless, red-brown, round swellings that most often appear on the arms and legs. Dermatofibromas are scarred and feel like hard nodules.
The cause of dermatofibromas is unknown.
What are the symptoms of dermatofibromas?
Symptoms of dermatofibromas are:
- A small red, brown, or purple swelling that may change color from time to time
- Itching, painful sensations when touching the tumor and without it, but there are also painless dermatofibromas
- A dent formed when a tumor compresses
How to treat dermatofibroma?
In most cases, no treatment is required for dermatofibromas, but they can also be removed through surgery or smoothed out using liquid nitrogen.
- Epidermoid cysts
Epidermoid cysts, also called sebaceous cysts, are benign (non-cancerous) skin growths that form as a result of blocked sebaceous glands. They are most often located on the genitals, torso and back, but can also occur on the skin of other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms of epidermoid cysts?
Epidermoid cysts are usually round in shape. A black dot is visible on the skin at the site of the cyst. If the cyst becomes infected, it becomes red and painful. When such a tumor contracts, a white, curd-like discharge appears from it.
How to treat epidermoid cysts?
Effective treatment of epidermoid cysts requires complete removal of the cyst capsule. If you squeeze the cyst and release the white, cheesy discharge from it, it will appear again. Most often, to remove a cyst, the doctor makes a small incision in the skin at the site of the cyst formation. Antibiotics may be used to treat an infected cyst.
- Folliculitis
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicles. It can be caused by infection in the hair follicle or irritation resulting from chemical or physical effects on the body's cells (for example, shaving or rubbing clothing against the body). Most often, folliculitis appears on the face, thighs and scalp.
Folliculitis is a common condition among people with diabetes. It is also common in people who are overweight and have immune system disorders.
What are the symptoms of folliculitis?
The main damage that occurs with folliculitis is considered to be papules or pimples with hairs in the middle (the hair shaft may not be visible).
Other symptoms of this disease are:
- Numerous red bumps and/or pustules on a hairy area of the body
- Rash
- Itchy skin
How to treat folliculitis?
Treatment of folliculitis may include topical and oral antibiotics, as well as antifungal medications. Treatment also includes preventing the occurrence of folliculitis in the future. The steps by which this goal is achieved include:
- Reducing friction between clothing and skin
- Stop shaving in damaged areas if possible, and if not, use a new razor blade or electric razor each time.
- Keeping the affected area of skin clean
- Keratoacanthoma
Keratoacanthoma occurs when the hair follicle cells grow abnormally. Most likely, the tumor is causing slight damage to the skin in an area that was previously exposed to the sun. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is considered the greatest risk factor for keratoacanthoma.
Keratoacanthoma typically appears on sun-damaged skin and appears as a firm tumor with a crusty plug in the middle.
Most often, keratoacanthoma occurs in people over 60 years of age.
What are the symptoms of keratoacanthoma?
Keratoacanthoma rapidly increases in size, is red in color, dome-shaped, and has a crater in the center. Some keratoacanthomas can reach particularly large sizes - from 7 to 15 cm in diameter.
How to treat keratoacanthomas?
Keratoacanthomas can be removed using:
- Apparatus for cryotherapy (freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen)
- Curettage (cutting and cleaning the core of the tumor)
- Keratosis follicularis
Keratosis pilaris appears as a bumpy surface of skin consisting of nodules that most often appear on the upper arms and thighs, as well as on the cheeks, back and buttocks. Although keratosis pilaris is not very attractive, it is harmless.
What are the symptoms of keratosis pilaris?
This disease appears as small, rough red or white nodules that do not hurt or itch. Keratosis pilaris usually worsens during winter or dry weather when the skin begins to dry out. Deterioration also occurs during pregnancy and childbirth.
How to treat keratosis pilaris?
Although this disease can last for years, in most cases, it gradually disappears by the age of thirty. From a medical point of view, treatment of keratosis pilaris is not mandatory, but it can be treated if the patient wishes.
Treatment of keratosis begins with intensive moisturizing of the skin. Creams such as Acid Mantle, Complex-15 or Vaseline should be used after taking a bath and several times a day. Treatment options such as:
- Creams containing urea (Carmol-20) or alpha hydroxy acids (Aqua Glycolic, Lacticare), which should be used twice daily
- Opening the pores by soaking in a hot bath for a long time and then rubbing the affected area with a rough terry towel or stiff brush.
- Lipomas
Lipomas are soft subcutaneous tumors or nodules that grow slowly in size and are considered benign (harmless). Inside they are dense elastic fabrics. Lipomas often form on the torso, shoulders, and neck, but can also occur on other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms of lipomas?
Lipomas can appear as single nodules or groups of nodules. Most are less than 5 cm in diameter and do not cause pain, but if they press on a nerve, pain may occur.
How are lipomas treated?
Lipomas should be removed only for cosmetic reasons, when they press on nearby structures, or when the diagnosis is unclear. Typically, lipomas do not invade other tissues, so they can be easily removed through excision.
An alternative to excision to remove a lipoma is to squeeze it out through a small incision. This technique is used for parts of the body with thin dermis, such as the face and limbs. Liposuction followed by lipectomy can be used to remove large lipomas with minimal scarring.
- Neurofibromas
Neurofibromas are soft, fleshy tumors that appear on or under the skin, and sometimes even inside the body. These tumors are benign, but in some cases they can become malignant or cancerous.
What are the symptoms of neurofibromas?
Symptoms of neurofibromas vary depending on their location and size. The most commonly observed symptoms are:
- Painless, slowly increasing swelling
- Occasional pain
- Electrical-like shocks when the affected area is touched
- Neurological problems when the tumor affects the motor and sensory nerves or when the nerve is pinched between the tumor and dense structures
How to treat neurofibromas?
If the tumor does not cause any symptoms, treatment is not necessary. But if it negatively affects the functioning of the nervous system, the doctor may decide to remove it. Neurofiuromas are successfully treated and do not reappear.
Materials prepared by doctors from the Department of Dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic
Website illustrations: © 2011 Thinkstock.
Treatment methods
Since the formation takes a long time to develop and is benign, it is not necessary to remove it. The decision to undergo surgical intervention is made for cosmetic reasons or in the event of an unsuccessful pathology location or frequent mechanical damage to a neoplasm protruding above the surface of the skin. This increases the risk of bacterial infection with subsequent transition to purulent processes. In this case, radical treatment in the form of removal is the only way to prevent more serious diseases and complications.
Epidermal cysts are treated in several ways:
- If the formation is large, it is removed with a scalpel. A scar remains at the site of the incision.
- Laser removal of atheroma is considered the preferred method of choice due to the minimal list of contraindications and excellent results.
- Burning with liquid nitrogen is affordable, but has its drawbacks - inaccuracy of the effect, prolonged healing of the burn.
Important: Do not try to treat epidermal cysts or other skin formations with folk remedies. This is fraught with serious damage and the appearance of a scar at the site of exposure. In addition, without histology it is impossible to accurately determine the nature of the neoplasm, therefore it is impossible to talk about its benign quality. Any unprofessional interventions can cause serious health problems.
Carrying out the operation
It is often performed under general anesthesia, but if it is small and located subcutaneously, local anesthesia may also be used.
As a rule, a skin incision is made and, if necessary, the cavity is opened, access is provided and complete excision is performed. If possible, laparoscopy is performed; if this is not possible, then open intervention is performed.
Surgical removal of the formation can be performed on part of an organ or the entire organ. We are, of course, talking about paired organs. Removal of the ovary is recommended for significant size pathological formations and for postmenopausal women. Removing one kidney with a cyst is only advisable if it is not possible to save the organ. The liver and pancreas can only be resected to the extent that the remaining part of the organ can cope with its function.
That is why, when pathology is localized in the liver, pancreas or other unpaired organs, it is recommended to eliminate them at the earliest stages, including in children, since an increase in the size of the formations can lead to damage to most of the organ and the impossibility of performing radical surgery.
Epidermal cyst: laser removal
Removal of a subcutaneous cyst with a laser is a simple procedure that is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization or long-term rehabilitation. After conducting an examination and determining the exact location and size of the capsule, the doctor sets the intensity and depth of the laser beam, taking into account the data obtained. The laser acts in a targeted manner without affecting healthy tissue.
During manipulation, the wound is disinfected and cauterized, which eliminates the risk of infection. Laser pulses are short, pain receptors do not have time to react to the impact. Therefore, during the operation, light local anesthesia is used to prevent discomfort.
The whole procedure takes 15-20 minutes. Almost immediately after it, the patient can return to his usual lifestyle. The recovery period involves wearing a sterile bandage for several days until the wound is completely healed.
After laser surgery, there are no scars or scars, which is important if the pathology has formed on the face. And if the epidermal cyst is on the head (pilar), then the laser method is the only way to preserve the hair without the risk of developing a bald spot at the site of the operation.
How much does it cost to treat atheroma?
The cost of treating epidermal cysts depends on the size and location (availability). You will also have to pay for the necessary package of studies, without which the operation is impossible. The advantages of the Lasersvit clinic are that we offer a comprehensive service - from seeing a dermatologist to monitoring the patient during the recovery period after surgery. A comprehensive service is always cheaper, and all manipulations and procedures are carried out in one building. This increases the safety and comfort of treatment.