HPV occurs in men at approximately the same frequency as in women.
It is a mistake to believe that the fair sex, for some reason, becomes infected with the pathogen more often.
Infection occurs with the same frequency, it’s just that symptoms of the disease develop more often in women.
When patients see a dermatologist, they wonder what kind of disease it is, HPV, and what its features are.
How does the disease manifest itself, and how to get rid of it?
Pathogen
The human papillomavirus in men may not manifest itself in any way for many years after infection. This feature of the pathogen makes it dangerous, since a person does not know about his carriage, but at the same time spreads the disease. The virus is a DNA virus that parasitizes epithelial cells, disrupting their division cycle. Uncontrolled proliferation contributes to the formation of growths.
To date, science has identified more than 100 types of papillomavirus. A feature of the pathogen is the provocation of oncological processes, therefore all HPVs are divided into two groups:
- strains with a high risk of oncogenic complications;
- strains with a low risk of oncogenic complications.
The first group causes damage to the genital organs and promotes the formation of condylomas in the anogenital area. Growths are observed not only in the groin, but also on the penis. The second group provokes the formation of warts over the entire surface of the body.
Classification
- 1Anogenital warts: genital warts, lesions in the form of spots, papules and rarer forms: Bowen's disease, bowenoid papulosis, giant condyloma of Buschke-Levenstein.
- 2 Extragenital papillomas and warts:
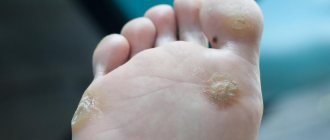
- Damage to the skin of other localizations: flat, vulgar, plantar warts, verruciform epidermodysplasia, non-warty skin formations, etc.
- Papillomas of the mucous membranes: larynx, conjunctiva of the eye, oral mucosa, etc.
- 3Dysplasia, precancerous conditions.
- 4Cancer of the anus and anal canal, cancer of the penis, etc.
According to the flow there are:
- 1Latent form (has no external signs, occurs hidden, is detected during laboratory testing).
- 2Subclinical form (erased manifestation of the disease).
- 3 Clinical form (classic symptoms of infection in the form of neoplasms, dysplasia).
It is worth clarifying that in doctor’s practice the latent form is more common. A separate group is formed by persons with severe immunodeficiency (HIV-infected, conditions after organ transplantation, etc.), weakened patients, it is in them that it is much more difficult to treat the infection.
Symptoms of the disease
Answering the question of how the human papillomavirus manifests itself in men, it should be noted that very often it is asymptomatic. The formation of growths is promoted by immunodeficiency conditions, stressful situations or hypothermia of the body. Doctors recommend seeking medical help if you experience the following symptoms.
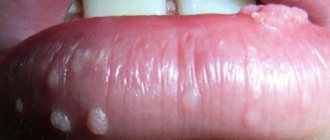
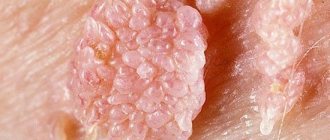
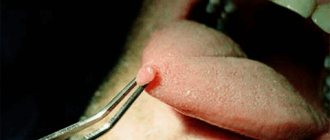
- Genital condylomas. Formations on the skin that resemble cauliflower inflorescences are flesh-colored and can be located singly or in groups.
- Flat condylomas. Concentric formations that do not rise above the mucosa. They have a high cancer risk and therefore require a biopsy.
- Tissue dysplasia or disruption of their structure. The condition is dangerous due to the appearance of atypical cells and the development of oncological pathology.
How men become infected with HPV 18
Prevention from HPV infection is very difficult, since the virus is easily transmitted from one person to another.
To develop prevention methods, it is necessary to know exactly how the virus is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person.
There are several options for the spread of the disease:
- 1. Sexual tract. It is implemented most often in modern medicine. Viral particles are found in natural lubrication in women, in semen in men, and on mucous membranes. Contact with them is inevitable during sex, they enter a healthy body and begin their active reproduction. Doctors often remind their patients that it’s not just classic unprotected sex that is dangerous. You can also become infected through anal or oral contact.
- 2. Contact path. Another common way of transmitting the virus. You can become infected by kissing, using other people's personal hygiene items, or touching injured skin in areas where growths caused by HPV are located.
- 3. Vertical path. It is often implemented, since HPV is easily transmitted from mother to child. Even if infection does not occur in utero, there is a high probability of the virus entering the child’s body during the birth itself, when the placenta no longer provides protection to the baby.
Methods of infection
- Sexual, with vaginal or anal contact.
- Vertical, a newborn can be infected through a woman's birth canal.
- Self-infection, by transferring infection from one part of the body to another.
- A household contact virus, the virus remains active on hygiene items; it can be picked up in gyms and swimming pools.
- Contact, infection occurs through damaged skin or mucous membranes.
Natural Treatment for Condyloma
- Apple Cider Vinegar – Soak a piece of cotton wool in apple cider vinegar and soak the affected area and leave it on for a while.
- Pineapple juice - apply fresh pineapple juice to cotton wool or, better yet, gauze, hold the preparation on the condyloma for about 10 minutes, then rinse. The procedure should be repeated twice a day.
- Aloe Vera – Apply a thick layer of Aloe Vera gel to the area affected by warts. Repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day for at least 2 weeks.
- Tea Tree Oil – Apply 3 drops of tea tree oil to gauze and apply to the infected area. Tea tree is known for its anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antifungal effects.
- Eat as healthy as possible.
- Wear clean underwear.
- Pay attention to the dryness of the genital area; sweating creates conditions for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi.
- Do not touch or scratch genital warts.
- Avoid intercourse because it not only causes pain and discomfort, but can also cause more problems for your sexual partner.
- Do not try to pick or squeeze genital warts, as this may lead to a more serious infection.
Establishing diagnosis
Before treating human papillomavirus in men, the pathology must be confirmed by laboratory tests. After the examination, the doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- urethroscopy;
- urethral smear;
- PCR;
- biopsy of growths.
Since condylomas have an oncological risk, you should not delay your visit to the doctor. Timely treatment allows you to stop the disease and minimize its consequences.
Risk factors
These are conditions that increase the likelihood of contracting human papillomavirus. The following risk factors can be identified:
- 1Early onset of sexual activity, a large number of partners and their frequent change.
- 2 Neglect of barrier contraception (condoms).
- 3 Associated sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, syphilis, trichomoniasis).
Vitamin deficiencies, other somatic diseases and factors leading to immunodeficiency increase the likelihood of clinical manifestations.
Therapy
When figuring out how to cure the papilloma virus in men, it is worth understanding that it will not be possible to completely get rid of the pathogen. Modern means can only stop the development of the process and remove the consequences of the pathogen’s activity.
There are general and local therapy. General assumes the following appointments:
- antiviral drugs;
- immunomodulators.
Local treatment of human papillomavirus in men involves removing growths. This can be done using the following methods:
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- cauterization with chemicals;
- thermal exposure by laser;
- electrosurgical method.
The procedure to remove growths is either painless or performed under local anesthesia. Timely therapy can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent HPV damage to large areas.
Types of immunomodulators that can be used for HPV 18
Only a doctor can decide when immunomodulators are prescribed.
The appointment is made by a venereologist, dermatologist or urologist, depending on which doctor the patient has an appointment with.
There are a large number of drugs from this group.
Among them:
- Isoprinosine, which increases the activity of the immune system in several ways at once
- Viferon is one of the most well-known products, also produced in the form of ointments.
- Genferon is a medicine similar in its effect on the body to Isoprinosine and others.
As is the case with antiviral agents, immunomodulators can be prescribed both locally and externally.
Patients often want to know how the effectiveness of the therapy chosen by the doctor is monitored.
As with antiviral drugs, the concentration of viral particles in the blood is decisive.
If it decreases during treatment, then the drugs were chosen correctly, and you don’t have to worry about your health.
If the level of viral particles persists or, even worse, has only become higher, it is worth considering that the treatment was ineffective.
Further tactics
Cystoscopy is an outpatient procedure, so the patient can return to their normal lifestyle on the same day. Within 1-3 days after the endoscopic examination, increased frequency of urination and the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the form of stinging are possible. This is due to direct trauma to the sensitive mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder during the procedure. The mucous membranes have a high regenerative ability and quickly heal on their own. During the first day after removal of polyps, a slight admixture of blood in the urine or mucous-bloody discharge from the urethra may appear.
After polypectomy, the patient is recommended to undergo a routine medical examination. Its frequency is determined by the attending physician. As a rule, after cystoscopy, the doctor prescribes a control test of blood and urine for the patient. After 6-12 months, you should undergo a repeat endoscopic examination to exclude relapses and assess the condition of the bladder mucosa.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Diagnostic measures
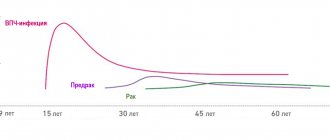
Early detection of HPV type 16 infection is only possible using molecular diagnostics.
It allows you to establish unique DNA sequences that are unique to the desired papillomaviruses.
For this, three types of techniques are used:
- non-amplification
- amplification (PCR)
- signal amplification (hybrid trap system - Digene Hybrid Capture System II)
Tests of the first type are not used in practical medicine due to the high cost and complexity of their implementation.
Amplification methods, among which PCR is the most studied, are used quite widely and are well studied.
Allows you to establish the fact of infection with HPV 16.
They detect viruses of other types (it is quite possible to become infected with several representatives of papillomaviruses at the same time).
The real-time PCR technique also determines the DNA concentration of oncogenic viruses.
This indicator has important prognostic value in dynamics.
Initially large numbers at the start of treatment should gradually fall under the influence of special therapy.
And completely disappear after any destructive treatment or surgery.
If the concentration of viral DNA in the diagnostic material is initially low, the doctor may recommend a wait-and-see approach.
Sometimes there is a 20% chance that HPV type 16 with a low DNA concentration will spontaneously clear from the lesion.
Digene (or Daijin test) differs from PCR in its unprecedented accuracy and high speed of testing (within one day).
Daijin also allows you to perform a quantitative analysis (calculate the concentration) of viral DNA.
The only thing holding us back from introducing this technique into widespread clinical practice is the significant cost of research.
To conduct such rather complex and high-tech tests, a man should contact doctors with access to modern laboratory centers.
The use of oncocytology, the most well-known method for diagnosing tumor processes, is justified only for developing treatment tactics for a man.
The method allows you to determine whether the tumor cells have degenerated into a malignant process or whether the papilloma still remains benign.
This information, provided by oncocytological examination of a tissue sample from a suspicious lesion, is decisive for the development of treatment tactics.
An immunogram in its classical concept is of little value for diagnosing HPV type 16 infection in men.
With its help, you can only establish the approximate duration of infection - based on the types of immunoglobulins identified.
IgA and IgM are detected with recent infection, and IgG - when infection is several months old.