Eczema is a lesion of the auricle and external auditory canal, which can be acute or chronic. It occurs as a result of skin irritation from ear discharge, allergies to medications, exposure to iodide preparations or industrial dust, mainly coal and cement.
Causes and course of the disease
Eczema occurs and develops when the skin of the ear canal and pinna is irritated:
- discharge from the ear, which is observed in acute or chronic otitis media of a purulent nature;
- iodine preparations;
- with prolonged exposure to cement and coal dust.
The allergic form of eczema occurs when there is intolerance to certain medications, as well as against the background of the development of diabetes and certain metabolic disorders. In children, the appearance of eczema is promoted by rickets, diathesis, and in some cases tuberculosis. Sometimes eczema occurs after an injury, when the body's local immune system is weakened.
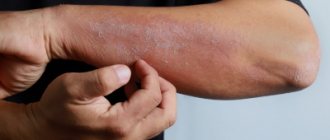
Eczema can have acute or chronic forms. In acute eczema, only the superficial layers of the skin are involved in the process. If the process has become chronic, then the skin of the ear canal and pinna becomes thicker, the lumen narrows, and cracks appear at the entrance to the external auditory canal.
In children, the weeping form of eczema is more common, and in adults there is both weeping and dry, in which peeling of the skin epidermis is observed.
Possible causes of flaking and itching in the ear
Itching in the ear is easy to feel, because normally such manifestations should not occur. If it appears, this is a clear sign of trouble. With peeling in the ear, the situation is somewhat more complicated. Visual inspection of the ear canal is somewhat difficult, therefore, as a rule, peeling in the ear is detected only when the auricle is affected or in a developed form.
It is worth noting that such symptoms can occur either on their own or in conjunction with other manifestations, for example, pain, noise, discharge of pus, ichor or excessive formation of sulfur. The combination of these signs, as well as the time and conditions of their appearance, help the ENT specialist to discover the cause of the disease. And most often it turns out to be the following factors:
- Fungal infections.
The ear canal is protected from sunlight and maintains constant temperature and humidity. This creates optimal conditions for the development of fungal infections, but, as a rule, the growth of pathogenic fungi is inhibited by a natural protective mechanism - sulfur. If it is disturbed, a fungal infection may appear, one of the manifestations of which is itching and flaking in the ear. - Various forms of dermatitis
. Minor mechanical damage to the skin of the ear canal due to cleaning the ears with inappropriate objects can create conditions for the penetration of bacteria and the onset of an inflammatory process. It can have various manifestations - discharge of pus, wax, pain, as well as itching and flaking in the ear. - Allergic reaction.
The skin in the ear canal is also prone to allergic reactions. They can be triggered by exposure to shampoo, detergents, and local medications. And one of the symptoms of such conditions is irritation, itching and flaking in the ear. - Diabetes
. One of the symptoms of diabetes is dry and flaky skin. Because the ear canal is not subject to regular mechanical cleaning, peeling may be more noticeable than in other areas. - Psoriasis
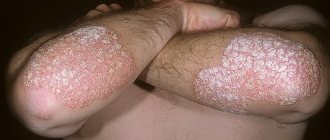
. This is a fairly rare reason, but it also needs to be considered. Psoriasis is primarily manifested by peeling skin of various localizations, primarily on the knees and elbows, where it is rougher and denser than in other areas. And the ears are also prone to similar manifestations, since regular cleansing is difficult.
The listed reasons can lead to flaking and itching in the ear. It is necessary to understand that this is not just an unpleasant condition, but a sign of diseases that can be quite dangerous, especially if they spread to the middle or inner ear.
Clinical picture
At the beginning of the development of the disease, hyperemia (redness) and thickening of the skin of the ear concha and external auditory canal is observed, which occurs due to infiltration. Then the ear canal narrows. Then constant itching occurs in the ears and as a result of scratching, abrasions appear, and then small bubbles with serous fluid form, when opened, weeping is observed and grayish-yellow crusts appear.
If a secondary infection occurs, limited or diffuse external otitis develops. When a patient has serious general diseases, eczema often becomes chronic, and the process penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin. This disease is characterized by frequent relapses.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
What to do about itching and flaking of the ear?
This symptom cannot be ignored, since it indicates the onset of some disease that must be detected and eliminated as quickly as possible. The “Your Doctor” website will help with this, which will allow you to quickly and easily find an ENT specialist or call an ENT specialist to your home in order to carry out a diagnosis and begin treatment as soon as possible.
Useful information on the topic:
- Diagnosis of itching in the ear
- Itching in a child's ear
- Itchy ears and discharge
- Itching in the ear
- Treatment for itchy ear
- Causes of itching in the ear
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Mumladze Koba Vazhaevich Anesthesiology and resuscitation
Back to section
Diagnostics
Taking into account the medical history and such characteristic manifestations of the disease as weeping, redness, thickening of the skin, crusting or peeling, diagnosing the disease does not cause difficulties. The acute form of eczema must be differentiated from erysipelas of the external ear and fungal external otitis. With erysipelas, there is no itching, the boundaries of inflammation are clearly defined, and palpation of the affected area is sharply painful. In the case of a fungal process, the diagnosis is made after conducting mycological studies.
1.General information
The appearance of any discharge where normally there should not be one is always a symptom, i.e. a sign of pathology, and in all cases this symptom is quite serious. With regard to the hearing organs, vigilance should be maximum, taking into account their location, anatomical complexity, intensity of innervation and blood supply. Any, even mildly symptomatic or latent pathology in this zone is dangerous. There are many cases where the primary problem could be eliminated relatively quickly and simply, provided timely contact with a doctor, but in the absence of medical care, complications turned out to be extremely severe, disabling, and sometimes fatal.
The discharge of liquid or mucopurulent discharge from the ear canal in medicine is called otorrhea. The reasons for this condition are very diverse, but it is certainly necessary to have at least a general idea of them.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment
The affected areas are wiped with alcohol or ether, powdered with talc or zinc oxide, the skin is irrigated with an oxycort aerosol, and for peeling, hecortone, celistoderm with garamycin are used.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Removal of crusts is carried out only after wetting them with vegetable oil or Vaseline. After this procedure, oxytetracycline or prednisolone ointment is applied. In addition to drug treatment, ultraviolet training (UVR), laser therapy sessions, ultrasonic medicinal irrigation, and UHF are prescribed.
2. Reasons
The least dangerous cause can be considered abnormally liquid sulfur, as the secretion of the ceruminous glands of the external auditory canal is colloquially called. Due to individual characteristics and/or under the influence of certain irritating factors, the sulfur glands can produce protective “lubricant” in excess quantities and with atypical rheological properties. This situation, however, also requires mandatory consultation with an otolaryngologist.
Relatively rare is cholesteatoma, a complex encapsulated formation of dead cells, connective tissue and cholesterol; this is a pseudotumor, which, in the case of an associated infection, can lead to otorrhea (discharge from cholesteatoma, as a rule, has a specific putrefactive odor).
However, in the vast majority of cases, when examined for otorrhea, the causes are identified as inflammatory processes in various parts of the hearing organs, which are infectious (bacterial, fungal, viral, combined), allergic or mixed infectious-allergic in nature:
- otitis externa;
- acute otitis media;
- chronic purulent otitis media;
- exudative otitis media (accumulation of volumes of non-purulent fluid requiring release);
- mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone);
- furunculosis of the external auditory canal (a bacterial, usually staphylococcal infection of the hair follicles and/or sebaceous glands in the ear canal, which is often one of the first symptoms of diabetes).
The immediate cause of otorrhea in purulent and exudative “internal” otitis is perforation of the eardrum, which provides an outlet for the accumulated masses.
Relatively less common:
- traumatic otoliquorrhea (leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the ear canal, usually due to a fracture of the base of the skull);
- otorrhea caused by a progressive tumor process.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The amount, color, clarity, smell, consistency of ear discharge, as well as accompanying symptoms, vary widely. So,
- the discharge of pus is inherent mainly in infectious and inflammatory processes of bacterial or fungal etiology;
- an admixture of blood in one concentration or another is characteristic of otorrhea due to trauma or cancer;
- clear flowing discharge is typical for allergic external otitis, exudative otitis media, traumatic liquorrhea (see above).
In most cases, otorrhea is accompanied by the following symptoms (single or in various combinations):
- decreased hearing acuity, feeling of congestion or a foreign body, perception of external sound as if through cotton wool or from under water;
- otalgia (pain syndrome localized in the external or internal structures of the ear);
- headache;
- vestibular disorders (dizziness, incoordination, loss of balance, etc.);
- various types of noise in the ear;
- rhinitis (runny nose), often with symptoms of sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses);
- low-grade fever, less often high body temperature.
Diagnosis requires, first of all, the collection of complaints and anamnesis. Then an otoscopy is required, and in some cases a microotoscopy. Various laboratory tests are prescribed (to identify the pathogen in infectious and inflammatory processes, assess the intensity of the immune response, identify tumor markers, etc.). When examining for a head injury or ear injury, as well as for diagnosing bone abnormalities and tumor processes, CT, MRI, and radiography are used.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Natural causes
Brownish discharge is practically the only type of ear discharge that can appear for physiological reasons. This phenomenon is due to increased activity of the sulfur glands: during the hot season, with a sharp change in climatic conditions or with serious physical activity. As a result, body temperature and sweating increase, the cerumen glands begin to produce excess secretion (wax), and a brown substance appears, which is earwax with a softened consistency. This is a normal physiological process that gives no cause for alarm.
Pathological causes
Pathological brown discharge from the ear can be a consequence of:
- Head or ear injuries. Reddish-brown fluid indicates possible local bleeding.
- Bullous otitis. It is characterized by the appearance of bloody blisters that burst and turn the sulfur brown.
- Cholesteatomas. This is a benign neoplasm that affects the middle ear. Damaged vessels in it begin to produce a reddish-brownish liquid.
How to understand that brown discharge from the ear is caused by pathological reasons?
Pathology always has accompanying symptoms that help the doctor clarify the cause of the disease. This:
- pain, itching in the ear;
- extraneous noise;
- hearing loss;
- temperature increase;
- edema;
- dizziness;
- redness of the auricle and external auditory canal;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult an ENT doctor.