December 3, 2020
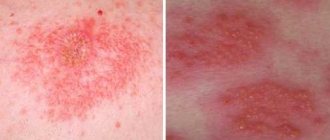
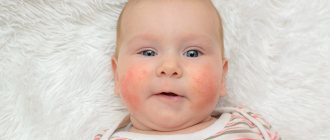
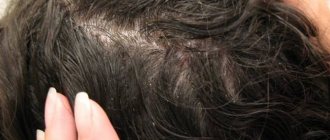
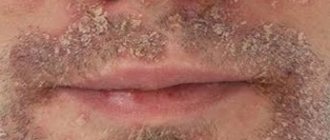
Contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin in an area that has come into contact with an irritating substance or environmental factor. Children under 12 years of age are most susceptible to the disease. The point is the structural features of children's skin and the weakness of its protective mechanisms. The disease manifests itself in any area that has been in contact with the irritant, but more often on the face, arms, neck, and groin area.
If the provoking agent is recognized in time and the child is protected from it, the inflammation is well treated and the symptoms quickly pass. When the cause is difficult to identify or parents do not consult a doctor on time, the course of the disease becomes more severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- simple - local irritation by some factor;
- allergic.
The second option will appear when the child has an increased sensitivity to this substance. The first interaction with it is outwardly unnoticeable, but chemicals are formed in the skin that bind to immune cells - T-lymphocytes. Immune cells remember the stimulus. Upon repeated contact, which can occur after a long time, T-lymphocytes trigger an allergic reaction and cause skin symptoms.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
Types of rashes
Various childhood diseases manifest themselves as primary symptoms in combination with secondary symptoms. The initial rash varies. Equally important is the quick reaction of the parents and the determination of what formation has formed on the child’s body:
- Tuberous. Any detail of such a rash is located deep in the dermis, in other words, the rash is not superficial. There is no cavity, there is a small protrusion in the form of a tubercle, the color of the skin may change to red or purple.
- Blisters. This is what people call almost any formation on the skin. However, in reality, the blister is a round, pink formation that lacks a cavity and contents. A real blister is short-lived, it can last from a couple of minutes to a couple of hours, then disappears without a trace. As an example, we can recall a nettle burn.
- Papular eruptions. This rash is also called nodular, since the papules are similar in appearance to nodules, which differ in shade from the normal color of the skin. Papular rash can be superficial or deep, and papules can disappear without a trace.
- Vesicular rash. This rash appears as blisters on the skin. There may be a serous, colorless or serous-bloody liquid secretion inside. Vesicles can be single or fused, forming a formation with numerous chambers. Opened vesicles leave erosion on the skin, the size of which is equal to the area of the bottom of the vesicle.
- Bullous. This type of rash also appears in the form of vesicles, but compared to vesicles, the bulla has a more impressive size - at least 5 mm in diameter. Such blisters may, like vesicles, contain serous or serous-bloody liquid contents.
- Pustular. Pustules are a pustular rash. It can be superficial or located deep in the skin. The opening of superficial pustules passes without a trace. If medium and deep pustules (boils, carbuncles) are opened, unsightly scars may occur.
- Spot-like rashes. This type of rash does not appear on the surface of the skin, but is characterized by a change in shade in some areas of the body. Such rashes can be vascular or petechial.
- Roseola. This is the name for rashes that appear in many pathologies of an infectious nature. All elements of the rash are pink or moderately reddish in color. The structure of roseola resembles specks. When the skin is stretched and pressure is applied, the rash turns pale and disappears for a while.
- Hemorrhagic rashes. This type of rash appears as red blood spots that form in the area where the blood vessel burst. When the skin is stretched, hemorrhage does not disappear.
Secondary rashes also vary. It manifests itself in the form of scabs, which are accompanied by the transformation of elements of the primary rash (usually vesicular or pustular) into crusts after opening. The development of cracks, erosions, detachments of epithelial cells, abrasions, scars and ulcers is also often observed as secondary manifestations.
External causes of the development of allergic dermatitis in children
The disease can be caused by one of the factors or a combination of several.
- Physical - friction or pressure on the skin of fabrics, leather products, high or low temperatures, humidity, electric current, ultraviolet or x-rays.
- Chemical - various acids and alkalis, substances included in creams and hygiene products, medicines, tobacco smoke.
- Biological - sap and pollen of plants, bites and secretions of insects and animals.
Of the plant agents, the most dangerous are the juice of celandine, hogweed, nettle, pollen of meadow and weeds.
In industrial cities in winter, there are widespread cases of contact dermatitis under the eyes and on the hands of children. Three factors are combined here: cold, chemical impurities in the air and touching the skin with wet mittens.
In infants, allergic inflammation can be caused by a combination of high humidity in diapers, fabric friction and the action of inappropriate cream.
A special type of contact dermatitis is phototoxic, when sunscreens degrade in sunlight and cause allergic damage to the epidermis.
Symptoms
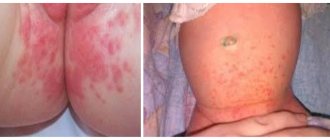
The main and most obvious symptom of the pathology is a rash. Most often, rashes appear on the head, chest, back, groin, armpits, and buttocks. The rash appears as scattered blisters with clear, white or yellow contents, or as small grains with an inflammatory outline.
During the day, the rash may intensify or decrease, and the severity of its manifestation depends on changes in temperature and care for the baby’s skin. In some cases, the child does not show concern, but sometimes may experience itching, pain and demonstrate discomfort with whims, unstable sleep, and lack of appetite.
In mild forms of the disease, other symptoms may not occur. But in more advanced cases, which are accompanied by complications and infection, clinical manifestations may be supplemented by:
- elevated temperature up to 38 degrees;
- the appearance of light plaque, ulcers, ulcers;
- the formation of weeping cracks with an unpleasant odor;
- general deterioration of condition.
When assessing symptoms, it is important to prevent the development of advanced forms of prickly heat and consult a doctor promptly, without waiting for complications to develop. Source: Skin care for a newborn. Solntseva O.A. Medical Council, 2014. p. 35-39.
Dermatitis in a child and psychosomatics
Skin health directly depends on a person’s mental well-being. Stress changes hormonal levels and metabolism, causing disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. Therefore, a calm emotional state will prevent exacerbation of the disease and delay the first appearance of symptoms.
When faced with contact dermatitis, analyze the causes and identify the allergen that caused it.
It's not always easy. To be sure of the correct diagnosis, conduct the necessary tests and receive treatment, come for a consultation at our center. In addition to treatment, you will learn how to properly prevent this disease. December 3, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Why is urticaria dangerous?
In most cases it causes discomfort, but nothing more. By itself, it is not capable of causing damage to the child’s organs and systems. However, there are a number of situations in which it can be deadly:
- Acute urticaria may be accompanied by an anaphylactic reaction. The child quickly develops swelling of the larynx and begins to choke. At the first suspicion of swelling, call an ambulance immediately!
- If the cause of hives is cold, this can lead to suffocation and a drop in blood pressure, which is also deadly. Dial 112 without hesitation if you see that after hypothermia the child breaks out in hives and feels unwell!
Such cases occur infrequently, but it is better to be aware of dangerous symptoms so that they do not take you by surprise.
| Our expert |
Marbled leather
During the first month of life, a baby's skin sometimes looks marbled. A uniform mesh pattern of white, purple, and reddish spots is the reaction of skin vessels to cold. Therefore, this phenomenon is most often noticed during swaddling. If the marbling is symmetrical and disappears when warmed, then there is no cause for concern. In other cases, it is worth discussing this symptom with your pediatrician so as not to miss the early diagnosis of diseases of the heart, lungs or skin itself.
Infantile hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign tumor of endothelial cells (endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels). It may be congenital or appear at 1-2 weeks of life. Superficial hemangiomas are bright red and protrude above the surface of the skin. Deep - blue-purple, sometimes warm to the touch. The element size ranges from a few millimeters to an entire anatomical area (hand, buttock, etc.). In the first 5-6 months, the hemangioma may increase in size and become brighter, then the growth ends and spontaneous regression begins.
Up to 90% of hemangiomas can resolve without treatment.
In this regard, surgical treatment is no longer used routinely. The child is observed by a pediatrician and a surgeon; if hemangiomas are located on the face and neck, in the genital area and near large vessels, conservative treatment is prescribed. The operation is indicated only if it is ineffective.
Prevention
Effective prevention consists of proper and thorough hygienic care of the child: regular bathing, frequent changing of diapers or diapers. During the hot season, you can bathe your baby up to 2-4 times a day, but it is important not to use soap, oils, lotions and other products with each water procedure that can disrupt the acid balance and clog the glands.
It is also important to select clothes from natural, breathable fabrics and avoid synthetic and semi-synthetic fabrics that do not ensure normal evaporation of sweat. You need to dress your baby appropriately for the weather and not wrap him up in a warm blanket on a summer night. Source: Skin care for infants. Prevention of diaper dermatitis. Starostina L.S. Medical Council, 2022. p. 41-49.
Sources:
- Skin care for infants. Prevention of diaper dermatitis. Starostina L.S. Medical Council, 2022. p. 41-49
- Newborn skin care. Solntseva O.A. Medical Council, 2014. p. 35-39
- Modern dermatological and cosmetic products for the care of children's skin. Kotlukov V.K., Kuzmenko L.G., Antipova N.V. Medical Council, 2013. p. 8-12
Date of publication: 10/20/2017
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Infant acne
The same rash in children after three months of age is called infant acne. It persists as persistent acne of newborns or reappears at 2-3 months. It differs from newborn acne only in the age of the children and the duration of the rash. Self-resolution occurs within 6-12 months. Infantile acne may be a risk factor for acne during adolescence.
Treatment
The main method that allows you to remove rashes and cure skin pathologies is hygienic care. It is important to change the diaper immediately after a bowel movement and every three hours, washing the baby with running water. Between shifts you need to give air baths and leave the baby without clothes for a few minutes. At the same time, it is necessary to abandon synthetic clothing and low-quality children's cosmetics.
Bathing is carried out in water with a decoction of medicinal herbs. You can add chamomile, yarrow, and string. After bathing the child, dry thoroughly and powder the skin with powder.
In some cases, the doctor also prescribes treatment of rashes with drying antiseptics (“Furacilin”, “Chlorphilipt”), and creams containing panthenol (“Bepanten”, “Dexpanthenol”). White, red and deep miliaria are treated with antifungal and antibacterial ointments. However, it is not recommended to use any medications without prior consultation with a doctor. Source: Modern dermatological and cosmetic products for caring for the skin of children. Kotlukov V.K., Kuzmenko L.G., Antipova N.V. Medical Council, 2013. p. 8-12.
Doctors recommend setting the air temperature in the nursery at 20-22 degrees and monitoring the humidity, which should not exceed 50-70%. A good solution would be to purchase an air humidifier that will help create the right microclimate. These simple steps can help you get rid of the conditions that increase your risk of developing heat rash.