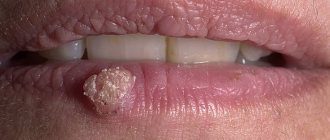
How does seborrheic dermatitis manifest in adolescents?
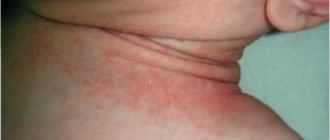
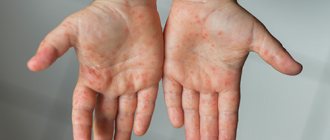
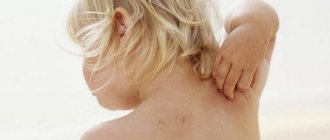
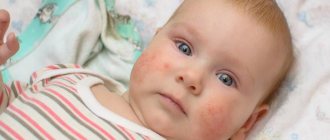
Foci of inflammation appear primarily on the face: on the nose, forehead, around the eyes, as well as on the chest and between the shoulder blades, on the scalp. In all these areas there are a large number of sebaceous glands, and it is because of disturbances in their work that seborrhea develops. The causative agent of seborrheic dermatitis is considered to be a fungus from the Malassezia family, which feeds on fatty acids that are part of the secretions from the sebaceous glands. It is part of the natural human microflora. When the body works normally, the amount of fungus does not threaten health. But when the balance is disrupted, the functioning of the sebaceous glands changes, and the fungus begins to actively develop and cause harm.
Types of seborrhea in adolescents:
- oily: with increased sebum secretion, acne appears, skin and hair become greasy;
- dry: sebum production decreases, pores narrow, which also causes acne, comedones, and dandruff to appear on the head.
In some cases, seborrheic dermatitis is mixed.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis:
- skin irritation accompanied by itching, swelling, redness;
- peeling, which can be very intense;
- acne in large quantities;
- painful sensations on the skin, especially when touched.
In the absence of proper care and treatment, skin scales constantly flake off, and the skin underneath becomes red and wet. If you scratch the inflamed areas, it causes pain, leads to scratches and microtraumas, through which secondary infection occurs.
On the scalp, flaking leads to dandruff.
Factors of occurrence
Doctors are still debating the reasons why hemangiomas appear in children. But the prevailing theory is that the main reason for the appearance of such formations is viral and infectious diseases that were suffered by the child during its development in the womb. Most often, tumors occur in newborns born prematurely or with low weight. Girls are more often affected than boys.
Infantile hemangioma
In addition, risk factors are:
- a woman taking antibiotics and other medications while pregnant;
- viral diseases of pregnant women in the first two trimesters;
- living in an area with poor environmental conditions;
- a history of endocrine diseases in the mother of the child, especially if there are exacerbations during pregnancy;
- premature birth;
- development of gestosis or preeclampsia in a woman during pregnancy;
- female age over 35 years;
- carrying multiple pregnancies;
- Rh conflict in the mother and child.
Consequences of Rh conflict
Hemangiomas do not always appear immediately after childbirth. There are cases when formations appeared in adolescents. In this case, the main factor in their development is the changed hormonal background. Hemangiomas often appear due to pathologies in the functioning of the liver.
In most cases, hemangiomas disappear with age in children. This occurs due to their regression in the first five years of a child’s life. More often this is typical for simple small hemangiomas. Less commonly, they degenerate into malignant tumors.
Hemangioma on the head
What happens if seborrhea in teenagers is not treated?
Often, when skin problems appear during puberty, parents think that they will go away on their own with time. Yes, sometimes that happens. But often teenage seborrhea becomes chronic, from which a person suffers throughout his life.
The consequences of seborrheic dermatitis can be eczematous conditions and severe forms of acne. If seborrheic manifestations are localized on the head, this leads over time to hair loss and even baldness. If the dermatitis affects the area around the ears, it can spread inward and lead to ear infections.
Description of the disease
Balanoposthitis is a common problem in pediatric practice.
Almost every boy has encountered this disease. It manifests itself as simultaneous inflammation of the foreskin and head of the penis. Most often, pathology develops when the rules of hygiene of the intimate area are violated. Therefore, statistically, the disease occurs mainly under the age of 12-14 years. The local inflammatory process does not pose a direct threat to the child’s health. However, the danger lies in the complications that arise against the background of the transition of an acute process to a chronic one. In the absence of targeted and timely treatment, adhesions form between the foreskin and the glans penis - phimosis develops. Sometimes the disease causes deformation of the head of the penis, which creates psychological discomfort for a man in adulthood and can worsen the quality of sexual life.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, balanoposthitis in children is divided into 3 forms:
- Catarrhal. This variant of the disease occurs in 70-80% of cases. It is characterized by moderate severity of symptoms and responds well to treatment.
- Erosive. A more severe form of the disease. Tissue defects form on the head of the penis. Infection penetrates into these areas more easily, causing the development of complications.
- Gangrenous. A particularly severe form of the disease, which is characterized by a sharp deterioration in the child’s condition. Due to the massive penetration of bacteria, partial necrosis of the penile tissue occurs.
Balanoposthitis can occur acutely or chronically. The first option is more favorable, since it can be cured fairly quickly. The main thing is not to delay visiting a doctor if characteristic symptoms of the disease are detected.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis in adolescents
As mentioned above, the causative agent of dermatitis is a fungus. However, it does not begin to multiply and function too actively without any reason. It becomes overly active only when the balance in the body is disturbed, the reasons for which are the following factors:
- puberty;
- heredity, genetic predisposition;
- disturbances in the functioning of the gonads, adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid gland;
- disruption of the endocrine system, which disrupts the production of sebum;
- severe nervous tension, stressful situations;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, as well as disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- incorrect mode: lack of sleep, lack of walks and physical activity, sedentary lifestyle.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of dermatitis, especially if it lies in disturbances in the functioning of internal organs or systems. The doctor will order tests and examinations, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. But before visiting a doctor, you can analyze your health status, evaluate your lifestyle and guess the main reason. Often, normalizing your lifestyle allows you, if not to get rid of seborrheic dermatitis, then at least to slightly improve the condition of the skin.
Stork spot. What is it and why is it formed?
In the medical literature, the stork spot has a completely non-fairy-tale scientific name: nevus of Unna or simple nevus. It can be located not only on the back of the head or on the back of the neck, but also on the baby’s forehead and eyelids. In this case, it is called “the kiss of an angel.”
One may come across the opinion that these spots are a consequence of a traumatic birth, in which the child’s head was compressed for a long time, but scientists refute this. They say that a simple nevus is formed in utero. It is formed due to a failure in the formation of blood vessels: in this area they are slightly dilated and the blood flow in them is increased, so the skin here is more pink. Another version is that the stork spot is formed in the place where the baby’s head is pressed to the mother’s sacrum in the later stages. Due to pressure, the capillaries expand and a spot is formed: have you ever woken up with red marks from a pillow on your face? It's about the same here.
Be that as it may, almost half of babies are born with a simple nevus on the face. There is no need to be afraid of him. This is not a disease. It is not the mother’s fault that the child is born with a mark on the back of the head, and she cannot prevent its appearance in any way.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adolescents
If the cause of seborrhea in a teenager is diseases of internal organs, disruptions in the functioning of body systems, then it is necessary to treat or at least stabilize them. Otherwise, the fight against seborrhea will be ineffective.
If there are no serious health problems, to treat seborrhea you need to carefully care for your skin and use specialized products for this.
Since the main cause of seborrheic dermatitis is an increase in yeast, it is necessary to combat it. For this you need antifungal drugs. These are medicated shampoos and gels, creams. They may have different active substances, for example, ketoconazole or sodium sulfide. The main thing is that they reduce the activity of the fungus and reduce its quantity. Such drugs are applied topically, that is, directly to the skin affected by the fungus. The frequency of application is in accordance with the instructions, but usually it is 1-3 times a week during the entire period of therapy, and after improvement of the condition - once a week to maintain the effect and prevention. Creams and gels are applied for absorption and do not wash off. And shampoos are applied and left for at least 5 minutes so that they have time to be absorbed into the skin and hair, and only then washed off.
There are entire lines of skin care products for seborrheic dermatitis on sale. For example, preparations from the Sulsen series contain selenium disulfide, which suppresses the activity of the fungus Pityrosporum Ovale and restores the balance of the scalp. The series includes shampoo, peeling, paste, cream, oil. You can choose hair care products for both boys and girls. They can be used from the age of 14 and are suitable for teenagers. They have a natural composition and do not cause allergies. The products are used twice a week. Typically, seborrheic symptoms disappear within a month, but you can use these drugs longer - until the effect is achieved, and then once every 1 - 2 weeks for prevention.
Symptoms of balanoposthitis in children
The clinical picture of the disease is caused by the formation of a local focus of inflammation in the penile area. The severity of symptoms depends on the form of balanoposthitis, the severity of the episode of the disease and the individual characteristics of the boy’s body. The main clinical signs of the acute form of balanoposthitis in childhood are:
- redness of the foreskin area;
- swelling of the tissue around the head of the penis;
- itching and pain that intensifies when touching the penis or urinating;
- moodiness, sleep disturbance, which are the result of constant discomfort;
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39°C.
It is worth noting that in 80% of cases the child’s general condition changes little.
He continues to play actively and eats normally. The severity of fever can vary depending on the intensity of the body's defenses and the activity of the inflammatory process. The chronic form of balanoposthitis is characterized by alternating episodes of exacerbation and remission. Discomfort in the area of the head of the penis, swelling and redness are not so pronounced. White discharge forms in the area of the preputial sac, which is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria with the subsequent formation of adhesions.
Drug therapy
If cosmetics do not bring the desired effect, which happens quite rarely, then you need to contact a dermatologist who, after an examination, may prescribe drug therapy, for example, ointments containing glucocorticosteroids. There are also preparations for oral administration. They are released strictly as prescribed and prescribed by a doctor. These are serious drugs that have many side effects when used for a long time. For a teenager whose body is undergoing restructuring, this can have unpleasant consequences, so such methods should be resorted to only in extreme cases. You cannot use such products for more than a month.
Folk remedies
To alleviate the patient’s condition, you can use improvised means, for example, shampoos or ointments containing natural tar. They do not treat seborrheic dermatitis, but suppress excessive proliferation of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Tea tree oil has an antifungal and soothing effect. It is applied pointwise to inflamed seborrheic areas of the skin.
Any folk remedies do not treat seborrhea. Herbal infusions, decoctions, and lotions may cause short-term minor improvement in some adolescents, but for most they have no effect. They need to be used constantly, for a long time. And many natural remedies cause allergies, so the skin condition only worsens. They can be used as auxiliary, but not as the basis of treatment. If you rely on traditional medicine and natural remedies, you can waste time, so the recovery will be longer than when you immediately start using special remedies.
What else is needed for treatment
Most often, seborrheic dermatitis in children is associated with puberty. This condition is temporary. While seborrheic peeling and irritation persist on the skin, it is important to choose skincare products and lead a correct lifestyle:
- do not be nervous;
- Healthy food;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- get enough sleep.
If you have seborrheic rashes on your face, you should never cover them up with foundation. The skin must breathe, it is important to clean it promptly and regularly. Otherwise, the recovery process will take longer. Do not overuse visits to the bathhouse, sauna, or solarium.
If you follow these simple recommendations, seborrheic dermatitis will be less painful, and the skin disease will go away without a trace.
When should you see a doctor?
If the spot on the back of a child’s head is a simple nevus, he will not need to see a doctor. Most likely, they will show it to you in the maternity hospital and explain that there is no need to worry. It’s another matter if another pathology of vascular development is mistakenly mistaken for a stork spot: a flaming nevus or hemangioma. These conditions require a different approach to monitoring and sometimes need to be treated. If the condition of the spot worries you for some reason: for example, it does not turn pale for a long time or, on the contrary, it begins to darken, increase in size, peel, or become inflamed - be sure to show your child to the doctor to clarify the diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Let's summarize:
- The stork spot, or scientifically known as Unna's nevus (simple nevus), is a bright pink or red patch of skin on the back of a newborn's head. The capillaries on it are dilated, and the blood flow is increased, hence the intense coloring. This spot is formed in utero and does not depend on the course of labor.
- The stork spot may disappear by the age of two, or it may fade and remain on the skin forever.
- There is no need to treat a simple nevus; observation is enough.
- You should consult a doctor if the condition of the spot worsens: it has become brighter, larger, inflamed, peeling or rashes have appeared. The doctor will clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
(3 ratings; article rating 2.7)
Share Share Share