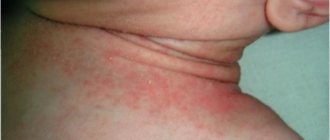
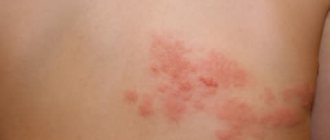
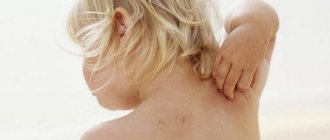
Quite often, men and women suffer from unbearable itching and burning in the genital area. In some cases, the reasons may be trivial - poor hygiene or an allergic reaction. But often various diseases can provoke discomfort, which in most cases can be easily treated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner.
If you experience any discomfort in the genital area, you should consult a doctor, as a possible cause may be diseases that, if not treated promptly, can cause complications.
Causes of itching and burning of the genitals in women
In women, burning and itching in the vagina can be caused by:
- Inflammatory diseases:
- cervicitis – inflammation of the cervix;
- endometritis – inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometrium);
- vaginitis – inflammation of the vagina;
- vulvovaginitis – inflammation of the vagina and vulva.
In addition to itching, pain in the lower abdomen and discharge from the genitals are noticeable, which is explained by the infectious origin of the disease. Possible pain during urination and sexual intercourse.
- Hormonal changes. During menopause, due to a decrease in the synthesis of sex hormones, the mucous membranes and skin around the vulva dry out and become thinner, which causes discomfort. The genitals may itch during pregnancy and during the menstrual period, which is explained by hormonal imbalances.
- Contraceptives. Birth control pills change hormonal levels, which affects the functioning of the entire body. There may be a decrease in lubricant production, resulting in dryness and increased sensitivity of the vagina, which causes itching. Some contraceptives (condoms, vaginal caps) can cause allergies, which also causes itching.
- Atrophic vaginitis, kraurosis of the vulva. During menopause, estrogen synthesis decreases, which is accompanied by atrophy and dryness of the vagina and vulva. Due to insufficient hydration, a woman may feel a burning sensation after sexual intercourse or even while walking.
- Lichen sclerosus. A rare disease that mainly affects postmenopausal women. Usually the pathology is localized on the labia and anus. The skin acquires a characteristic shine, and white spots are clearly visible on it. Over time, the mucous membranes and skin crack, which causes itching and burning, especially when urinating.
Why does your intimate area itch?
The most common causes of vaginal itching include general or local inflammatory and infectious processes, various allergic reactions, as well as structural changes in the tissues of the genital organs during the decline of hormonal function in patients who have entered menopause.
The skin and mucous membranes of the vulva and vagina are supplied with a large number of nerve endings. They are located shallowly in the groin area and easily respond to any mechanical or chemical impact of external or internal factors. The feeling of moderate to severe itching between the legs is a reaction to such irritants. Its intensity varies widely: a girl may occasionally be bothered by only a slight itching in the vagina and/or the skin of the external genitals, and sometimes it becomes constant, unbearable and forces her to urgently seek help from a gynecologist.
Indeed, in girls and young women, the most common causes of itching in the labia and vagina are genital infections and sexually transmitted diseases, which cause inflammation of the mucous membrane - colpitis and vulvitis. Such diseases are accompanied by pathological discharge (leucorrhoea); they contain a large number of pathogenic bacteria, the waste products of which irritate the mucous membrane and cause itching in the vagina and groin.
Moreover, it should be borne in mind that the intensity of itching in intimate places is not a valuable criterion for determining the nature and severity of the disease. This refers to the subjective feelings of the girl herself and depends on the individual parameters of the reaction of her skin and mucous membranes to irritants.
In postmenopausal women, slight itching in the vulva is accompanied by a feeling of dryness or burning. The decrease in vaginal discharge in this age group is associated with physiological reasons - a gradual decrease in hormonal levels, and primarily estrogen hormones. The vaginal mucosa looks atrophic (thin and pale), there is very little discharge - it is easily injured by any external influence and does not cope well with local inflammation.
Other causative factors for such annoying sensations may be:
- HPV and condylomas,
- vaginal dysbiosis,
- kraurosis and leukoplakia,
- diabetes,
- violation of intimate hygiene,
- hormonal disorders,
- liver diseases,
- urethritis and urethral papilomatosis,
- allergic reactions,
- worms and parasites.
Moreover, all these manifestations occur not only in adult women who are sexually active. Virgin girls, children and teenagers can also itch in the intimate area.
Intimate itching in a girl
Vulvovaginitis in children 10-11-12-14 years old is an inflammatory process in the area of the external genitalia and vagina, which is most common in childhood and adolescence. The main signs of inflammation of the vulva in girls and adolescents are vaginal itching, discharge from the genital tract, redness, burning and pain when urinating. Sometimes these symptoms are sluggish, the child periodically scratches in an intimate place. What should mom do in this case? Without delay, visit a pediatric gynecologist and get tested.
If you do not pay attention to all this in time, complications are inevitable - with a long course of vulvitis, it can contribute to the formation of synechia (fusion of the right and left labia with each other), the formation of polyps, papillomas of condylomas in intimate places, cicatricial changes in the vagina. One of the serious consequences of itching and burning in teenage girls is synechia (sticking together) of the walls at the vaginal opening, atresia (fusion of the hymen) and subsequent, with the onset of menstrual function, the formation of hematocolpos.
Intimate itching during pregnancy
The most common cause of itching in the intimate area in pregnant women is vaginal candidiasis. It is an inflammatory process of the mucous membranes caused by an overgrowth of a fungal infection (Candida fungi) in the vagina. The provoking factor is a physiological decrease in the number of lactobacilli due to changes in hormonal levels. Thrush occurs three times more often during pregnancy, is important in obstetric practice and requires mandatory elimination.
If we talk about specifics, then expectant mothers will be told by their obstetrician-gynecologist who monitors the course of pregnancy about how and how to treat intimate itching.
Diagnostics
If a man or woman has itching in the intimate area, testing for hidden infections is the first thing to do before starting treatment.
Minimum requirements: Gynecological examination, smear for flora, PCR tests for infections, bacteriological culture for flora, general urine test.
Tests according to indications: Since the vagina and labia can itch for reasons unrelated to infectious or sexually transmitted diseases, the range of tests for intimate itching can be expanded. Thus, a gynecologist can prescribe tests such as colposcopy, cervical smear cytology, blood tests (hormones, allergens, biochemical, general analysis), ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Causes of itching and burning of the genitals in men.
In addition to general causes, intimate itching in men can be provoked by:
- Urolithiasis disease. The main signs are frequent, usually painful, intermittent urination, purulent and bloody impurities in the blood, digestive disorders, and lower back pain. But in some cases, burning, tingling and pain in the penis area are possible.
- Balanoposthitis. When the glans penis and foreskin are inflamed, redness, swelling, itching, burning and pain in the genital area are observed. Rashes, cracks, erosions and ulcers appear on the foreskin. Lymph nodes swell. Symptoms worsen with sex.
- Prostatitis. Inflammation of the prostate gland disrupts the process of urination. There may be difficulty urinating, as well as frequent urge to go to the toilet, spontaneous release of urine. Itching and burning in the urethra, at the tip of the penis and in the perineum, early ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, pain in the lower back, pain during defecation, and a general deterioration in health are also observed.
Itching, odor and discharge in women in the intimate area
Normally, every woman periodically experiences vaginal discharge. In young girls they can be more abundant than in women of reproductive age and menopause. They should be inconspicuous, transparent, or cream or white in color. There is no smell from such secretions. Their consistency is liquid; during the ovulation process, the discharge can become stretchy and mucous.
If the discharge gives off an unpleasant odor and provokes a feeling of itching, then this is considered a deviation from the norm.
Such discharge requires attention and consultation with a doctor:
- A sour odor and change in consistency (curdiness) may indicate the onset of vaginal candidiasis. There are many reasons for this disease (hormonal disorders, dysbacteriosis, taking medications, using inappropriate hygiene products, etc.);
- Clear foamy discharge may be a symptom of chlamydia infection;
- If the leucorrhoea has a grayish tint and an unpleasant fishy odor, then this may indicate gardnerellosis, bacterial vaginosis. In this case, the vaginal microflora, represented by lactobacilli, is disrupted, the beneficial flora is replaced by anaerobic bacteria and gardnerella. As a rule, such discharges do not leave marks on the laundry. However, during sexual intercourse, the smell of rotten fish appears, and the discharge intensifies after intimacy. There can be many reasons for grayish leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor - a decrease in immune defense, menopause, hormonal dysfunction, pregnancy, menopause, intestinal dysbiosis, etc.;
- If the discharge acquires a greenish tint, has an unpleasant odor, and becomes abundant, then this speaks in favor of an inflammatory reaction and suppuration. It is the abundance of leukocytes that die in the fight against inflammation that gives the discharge a greenish tint. The stronger the inflammatory reaction, the richer the color, stronger the smell and itching in the intimate area;
- If the discharge has a yellowish tint, is accompanied by itching and odor, then this may be a sign indicating infection with Trichomonas. This color is caused by damage to the vagina by Trichomonas, and there are not too many leukocytes in it.
Increased leucorrhoea can be caused by inflammation of the appendages, vagina, cervix (cervicitis) or body organ.
The following types of discharge, accompanied by itching and odor, should be the reason to consult a doctor:
- Abundant, white, with curdled inclusions;
- Clear foamy discharge;
- Brown spots on underwear between periods. Any pathological change in the color of the discharge;
- The appearance of a putrid, sour, “fishy” smell;
- Leucorrhoea, accompanied by a burning sensation when urinating against the background of an increase in body temperature, when a feeling of dryness and discomfort occurs both after sexual intercourse and regardless of intimacy.
Copious discharge without odor or itching
Females should have discharge, as this is the result of the normal functioning of the vaginal mucosa. It is thanks to the secretions that it produces self-purification, gets rid of various bacterial microorganisms, dead epithelial cells, menstrual blood, and accumulated mucus.
In the vast majority of cases, vaginal discharge is neither color nor odor. But sometimes their volume can increase, which makes the woman wary. In some cases, there is indeed cause for concern, since heavy discharge may indicate serious illness. However, the discharge changes its consistency and smell, causing discomfort and itching. In this case, you need to seek help from a specialist.
An increased volume of colorless and odorless discharge may indicate the following reactions and processes occurring in the body:
- The period of ovulation has arrived;
- The next menstruation is approaching;
- The woman is sexually aroused;
- There was a change in climate zone;
- There is a pregnancy;
- Severe stress was experienced;
- The girl has entered puberty.
It is worth remembering that the volume of vaginal discharge throughout the day should not exceed one teaspoon or 2 ml. They should have a uniform consistency and not have an unpleasant odor.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor asks about complaints, studies the medical history and conducts an external examination, after which he sends for a diagnostic examination.
For women, diagnosis includes:
- gynecological examination;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- blood test for hormones;
- analysis of vaginal smear and discharge;
- DNA-based tests;
- Pap test;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- colposcopy or biopsy.
If necessary, the gynecologist will refer you for consultation to other specialists: urologist, dermatologist, venereologist, allergist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist.
Men are referred for tests:
- blood and urine;
- smear and scraping;
- sperm and prostate secretions;
- DNA.
Itching in the intimate area during pregnancy
Itching of the skin, which occurs in the perineal area while a woman is carrying a child, is an unfavorable manifestation of pregnancy. Most often, its cause lies in the hormonal changes that occur in the body of a pregnant woman.
Serious hormonal fluctuations often cause a malfunction of the immune system. As a result, the vaginal microflora changes and the number of pathogens increases. This can provoke colpitis, candidiasis, dysbacteriosis and other diseases. Therefore, if itching appears in the intimate area at the time of pregnancy, it is necessary to urgently seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist. He will perform the necessary tests and, if necessary, select the appropriate therapy. Self-medication during pregnancy is strictly prohibited, as this jeopardizes the health of the unborn child.
When detecting vaginal candidiasis, a pregnant woman should not panic. According to available statistics, it affects 80 to 90% of all women bearing a child. With timely and correct therapy, its success without consequences for the fetus is almost 100%.
In addition to the fact that itching can be triggered by hormonal changes, the cause can be both general diseases and gynecological pathologies, as well as the exogenous and endogenous factors listed above.
It is important to remember that from the 14th week of pregnancy, vaginal discharge intensifies, which is provoked by the work of the placenta, which begins to produce progesterone. Therefore, during this period you need to pay increased attention to intimate hygiene. It is worth making sure that the discharge does not emit an unpleasant odor, since its presence is a sign of a woman’s ill health.
Special requirements for the hygiene of pregnant women are also imposed due to possible urinary incontinence and increased work of the sebaceous and sweat glands. All this can also cause itching in the intimate area, especially due to insufficient care.
The underwear worn by the expectant mother should be comfortable and made from high-quality natural materials.
Summing up
Irritation and inflammation in the groin area often occurs due to improper and irrational nutrition. In most cases, changing your diet is enough to eliminate the problem. Fungi and similar microbes thrive in an acidic environment, which is created by sugar, dairy products and yeast bread
.
If you exclude them from your daily diet, you can completely forget about any problems with inflammatory processes and irritation in the groin area. Very often, to completely get rid of pathology, it is enough to simply cleanse your body. Literally after a couple of days there is a significant improvement in the general condition, all irritating symptoms go away.
Which doctor should I go to if I have itching after intercourse?
If you are concerned about itching after sexual intercourse, you should consult a dermatologist. Men will also be helped by a urologist who will examine the external genitalia, as well as palpate the prostate gland through the rectum. A gynecologist examines women in a gynecological chair, drawing conclusions about the condition of the genital organs: the presence or absence of hyperemia, swelling, pathological discharge. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on examination alone, so laboratory and instrumental tests are prescribed:
- clinical blood test,
- general urine analysis,
- a smear from the urethra, cervix, vagina, followed by examination using PCR, microscopy, bacteriological culture on media with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. This study allows us to detect inflammation of the urethra in men, colpitis and cervicitis in women.
In order for the examination data to be as accurate as possible, it is not recommended to urinate two hours before taking a smear; you should abstain from sexual intercourse for two to three days.
Also prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women, ultrasound of the scrotum and prostate gland in men: this allows us to identify inflammatory diseases of the uterus and its appendages, orchitis and prostatitis in men.
- MRI and CT are more accurate methods and, as a rule, are prescribed in controversial cases.
Herbal treatment
In treatment, medicinal herbs provide invaluable assistance. At the same time, herbs are an ideal preventive remedy; they are no less popular in cosmetology.
Chamomile
This is an effective quality plant that can save a woman from a huge number of problems and various inflammatory diseases.
You can use a decoction or infusion of chamomile to care for your intimate area. This is an ideal replacement for modern hygiene products in the cosmetology industry.
Calendula
This is a magical remedy that ideally helps with problems such as candidiasis and various forms of inflammation. This plant is used for douching. For this purpose, take a tablespoon of herb to about 200 ml of boiling water, all this is infused at a temperature of about 60 degrees.
You can take it after cooling the infusion to a comfortable room temperature. Procedures based on calendula can effectively replace all medications for thrush. There are no side effects observed. Herbal treatment can take a long time, but gives a fairly long-term effect. With the help of herbs, you can slowly and at the same time truly get rid of serious pathologies and inflammations.
If the process of treatment with chemicals has already begun, herbs should not be excluded
.
Herbal infusions will significantly speed up the overall healing process, and also neutralize the most negative consequences of the adverse effects of microbes on the body. [media=
https://youtu.be/MNVTAJcqGW4
]
How to treat vaginal itching
The question of how to get rid of vaginal itching arises acutely immediately after the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
An attempt to use traditional methods of influencing the problem only worsens the clinical picture.
Therefore, the only correct way to quickly relieve vaginal itching is to consult a specialist for medical help.
The general principles of therapeutic action on a painful condition include the following steps:
- establishing the cause of the disease;
- external treatment - apply ointment or gel for vaginal itching;
- antihistamine antiallergic drugs locally or systemically;
- restorative therapy;
- systemic antimicrobial therapy - tablets or injections for vaginal itching;
- anti-relapse treatment.
Only a medical specialist can decide how to relieve vaginal itching based on diagnostic results or at least a preliminary examination.
However, before you begin medicinal correction of the problem, you need to start with hygiene issues.
Plays an important role as a wash when itching in the vagina.
Highly alkaline soap solutions only irritate the mucous membrane, so neutral agents are always preferable.
If there is a rash on the skin of the pubis and itching in the vagina, then it is necessary to exclude the presence of lice.
When lice are detected, all that is required is shaving, douching with antiseptic solutions and anti-pediculosis treatment.
Pubic lice are removed quite easily and quickly, and the problem of unpleasant sensations disappears.
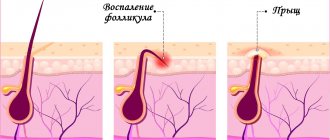
If there are pimples and itching in the vagina, then the likely cause is herpes.
In this case, antiviral therapy is used.
The drugs of choice are acyclovir and its derivatives.
An ointment for vaginal itching containing this drug is prescribed for up to 1 month.
In parallel, acyclovir or valacyclovir is taken orally.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce burning sensation, a woman needs to carefully monitor the hygiene of her genitals and use special products for intimate areas. It is best to choose natural underwear that does not cause excessive sweating and does not press on the skin. For vaginitis, it is worth regularly changing sanitary pads, which will absorb discharge and reduce maceration of the skin around the vulva.
A burning sensation in the intimate area is often caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microbes. To destroy them, you can irrigate the external genitalia of women with a weak solution of chlorhexidine or chamomile decoction. It is not recommended to do vaginal douching without a gynecologist's prescription. It is impossible to effectively eliminate burning in the perineal area without etiotropic treatment, so the woman should consult a doctor.
Conservative therapy
For uncomplicated forms of the disease in women, local treatment is often sufficient. Therapeutic measures include the appointment of suppositories with antibacterial or antifungal action, which depends on the etiology of the pathogen. To eliminate discomfort, local baths with disinfectant solutions are recommended. Ointments with topical corticosteroids help relieve severe burning and itching.
For specific acute vaginitis, therapy is selected based on the sensitivity of the pathogen: gonorrheal infection is treated with penicillins, tetracyclines, chlamydial and mycoplasma - with macrolides, fluoroquinolones, trichomonas - with nitroimidazoles. For chronic candidal vaginitis, systemic antimycotics are effective. For the treatment of herpes in women, drugs from the acyclovir group are used.
Gynecological diseases are accompanied by vaginal dysbiosis, which increases burning and discomfort, so pathogenetic treatment is aimed at normalizing the microflora. Vaginal suppositories with lactobacilli, as well as oral combined probiotics, are effective. For chronic diseases, immunomodulators are recommended.
Treatment of itching after intercourse
Treatment for a symptom such as itching after sexual intercourse is prescribed by a doctor based on examination data and the cause of the disease or condition that caused it. For example, with menopausal syndrome in women, estrogen deficiency is compensated, which negatively affects the vaginal mucosa. If you are allergic to contraceptives or hygiene products, you must choose hypoallergenic products that will not cause a pathological reaction. Of course, you need to carefully monitor intimate hygiene and wear underwear made from natural fabrics.
If the cause of itching after sexual intercourse is candidiasis, local and systemic antifungal agents are prescribed; Most STDs and bacterial infections of the genitourinary system require antibiotic therapy. At the same time, the immune system is strengthened and vitamin therapy is prescribed.
Due to the availability and accuracy of diagnostic methods, identifying the cause of itching after sexual intercourse is not difficult. To increase the chances of a successful recovery and the absence of dangerous consequences, you should follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Doctor of the Private Practice clinic, dermatovenerologist, urologist Volokhov E.A. talks about itching after intercourse.