Everyone knows that the sun's rays that fall on unprotected skin are a direct threat to the body. Ultraviolet radiation provokes the development of pathological processes in the skin, which can significantly cause harm. Insolation and ultraviolet rays can cause a problem such as hypomelanosis - the appearance of white spots on the skin.
The disease is characterized by a violation of the formation of melanin pigment in the skin and is a pronounced aesthetic defect. Today on estet-portal.com read about why hypomelanosis occurs and how it is effectively treated.
Risks of occurrence
Predisposing factors play one of the key roles in the development of skin cancer. Among them are:
- prolonged exposure to the sun and frequent sunburn;
- hereditary predisposition. If there have been cases of tumor formations on the skin in the family, this increases the risk of their development in subsequent generations;
- fair skin with a lot of moles and freckles, red hair color. This dermis is characterized by a low content of melanin in the cells;
- elderly age. It is believed that with age, the chance of developing skin tumors increases. Despite this, oncologists note an increase in the detection of pathology among young people;
- occupational hazards. Some professions involve constant contact with carcinogenic substances. Prolonged interaction of toxins with the skin increases the risk of tumor development.
The presence of at least one of the listed risk factors requires regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations.
State Budgetary Institution of Health Care of Sevastopol “Dermatovenerologic Dispensary”
Solar radiation and its effects on the skin
The main damaging effect on the skin, leading to the appearance of the first signs of aging and their progression, is ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It initiates a degenerative process in the skin, as a result of which it becomes drier and rougher, gradually loses its tone, and wrinkles and age spots appear on it. Changes caused by exposure to UV radiation are called photoaging. The source of ultraviolet radiation is the sun.
Depending on the length of electromagnetic waves, UV radiation is conventionally divided into UVA, UVB and UVC ranges. UVC rays, the rays with the shortest wavelength (200-290 nm), are the most dangerous because they have the highest energy. Fortunately, all UVC rays are blocked by the ozone layer of the earth's atmosphere.
UVB rays with a wavelength of 290 to 320 nm are only partially blocked by the ozone layer and reach the Earth's surface, although they practically do not penetrate glass. A significant part of them (more than 70%) is reflected by the stratum corneum of human skin, and yet some of the UVB rays penetrate into the epidermis, and about 10% even into the uppermost layers of the dermis. These rays have a strong damaging effect. They cause erythema (redness of the skin or sunburn) and tanning, and are responsible for many of the acute and chronic side effects associated with exposure to sunlight.
The wavelengths of UVA rays range from 320 to 400 nm. Of the entire UV spectrum, these rays have the lowest energy, but at the same time the highest penetrating ability. They are not retained by the ozone layer and pass through glass and the stratum corneum of the skin. In human skin, UVA rays reach the middle layers of the dermis and, although they do not cause sunburn, play a leading role in the development of actinic skin damage.
It has now been reliably established that both UV radiation spectra—both UVA and UVB—play an active role in the process of photoaging.
UV radiation triggers photochemical reactions in the skin, the products of which are free radicals and reactive oxygen species. By reacting with other biological molecules - protein, lipid or DNA molecules - they transfer their activity to them. Having thus turned into free and aggressive radicals, they, in turn, begin to react with the molecules surrounding them. In this case, proteins cross-link with each other, lipids of biological membranes are oxidized, and mutations occur in the genetic apparatus of the cell. Free radicals damage the connective tissue of the dermis, keratinocytes, have a negative effect on the vascular system of the skin, and enhance all manifestations of photoaging.
SIGNS OF PHOTOAGING
Premature skin aging begins with connective tissue, where collagen and elastin fibers are located. Collagen provides skin elasticity, and in young people its threads are constantly renewed. The enzyme collagenase destroys old threads, and new ones are synthesized in fibroblasts. Over time, under the influence of UV radiation, collagen synthesis in fibroblasts decreases and cross-linking of collagen filaments occurs. Collagen dimers are inaccessible to collagenase, so they gradually accumulate in the skin. Cross-linking of collagen fibers occurs after each free radical attack, while elastin synthesis increases, which together leads to a decrease in skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles.
Signs of photoaging can be divided into physiological, clinical, anatomical and histological.
MAIN MANIFESTATIONS OF PHOTOAGING
With intense exposure to UV radiation, already at the age of 35-40 years, people develop signs of skin photoaging. It becomes drier, light wrinkles, pigment spots, and isolated telangiectasias appear. With age, these phenomena steadily progress. Degenerative changes, atrophy, keratosis begin to develop, spots of hypomelanosis (with partially lost pigment), yellow nodules and plaques appear. The listed clinical signs are combined into the concept of dermatoheliosis.
SOLAR ELASTOSIS
The main manifestation of dermatoheliosis is solar elastosis, which develops at the age of 40-50 years and clinically manifests itself as Milian lemon skin, characterized by reticular striations in the form of diamond-shaped slits and grooves against the background of thickened pale yellow skin). The process is usually localized on the face, neck, hands and forearms. As for other parts of the body, solar elastosis can only manifest itself as a yellowish tint to the skin. The disease is steadily progressive and, although not malignant in itself, serves as a marker for other more serious sun-induced skin lesions such as solar keratoses and squamous cell skin cancer.
Simultaneously with solar elastosis, other skin lesions develop as a result of UV irradiation, the number and nature of which may vary depending on the location of the affected area on the body. Such skin lesions include:
- • diamond-shaped skin of the neck;
- • Favre-Rakucho disease;
- • diffuse Dubreuil elastoma;
- • senile hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands;
- • Bateman's solar purpura;
- • O'Brien's actinic granuloma;
- • actinic comedonal plaques;
- • venous lakes;
- • lentigo solar;
- • idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis.
DIAMONDS NECK SKIN
Diamond-shaped skin of the neck (Cutis rhomhoidalis nuchae) clinically manifests itself as thickened, deeply diamond-shaped skin on the back of the neck, as well as yellow plaques. When stretched, this skin is no different from the lemon Milian skin on the face, that is, such a lesion is essentially a pronounced manifestation of solar elastosis in the neck area. Diamond neck skin occurs predominantly in men because women's neck skin is usually protected by hair.
FAVRE-RACOUCHO DISEASE
Intense insolation and wind contribute to the development of Favre-Racouchot disease in men over 50 years of age, which affects the skin of the face, especially the temporal areas and around the ears, as well as the back of the neck. In the lesions, against the background of thickened and compacted skin of a yellowish-red hue, collected in rough folds (phenomena of pronounced solar elastosis), nodular elements with a diameter of 0.5-1.0 cm, cysts with whitish contents with a diameter of 0.1-0.5 are visible cm and comedones, located in the central part of most nodules and cysts. In severe cases of the disease, cysts can merge, forming thickened yellowish plaques with many large comedones.
DIFFUSE ELASTOMA OF DUBREUL
A milder variant of Favre-Racouchot disease, diffuse Dubreuil elastoma, is characterized by the presence of well-defined yellowish plaques in the forehead, cheeks and lateral neck. Sometimes the disease manifests itself as a solitary papule or plaque in the area of the nose or back of the head, consisting of papule-like elements that resemble cobblestones. The skin in the area of the plaque is yellowish, wrinkled, soft, and gradually undergoes atrophy.
SENILE HYPERPLASIA OF THE SEBABY GLANDS
After prolonged intense sun exposure, senile hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands develops, characterized by the appearance of small light yellow papules in the forehead, lower eyelids, cheeks, nose and forearms, which over time acquire a darker yellow tint, a dome-shaped shape and umbilical depressions in the center. When the elements are squeezed, droplets of sebaceous secretion are released from them.
BATEMAN'S SOLAR PURPLE
Long-term exposure to sunlight, which damages fibroblasts around blood vessels and leads to loss of collagen and vascular fragility, is a major predisposing factor in the development of solar Bateman's purpura in people over 60 years of age. The immediate cause of purpura is mechanical trauma, leading to rupture of dilated vessels of the subpapillary venous plexus. Clinically, the disease is characterized by the sudden appearance of hemorrhagic spots of red or purple color with a diameter of 1.0-5.0 cm with clear rugged contours on the back of the hands, extensor surfaces of the shoulders and forearms, and very rarely on the lower extremities or face. The surrounding skin is thin and has reduced elasticity. Due to the presence of hemosiderin in the elements and a decrease in the activity of macrophages, the lesions slowly evolve into pigment spots.
O'BRIEN'S ACTINIC GRANULOMA
O'Brien's actinic granuloma is formed as a result of an inflammatory reaction with a giant cell infiltrate that develops in the dermis in areas of solar elastosis. It most often occurs on the extensor surface of the forearms and upper back in people with fair skin color and the presence of freckles. It begins with the appearance of translucent reddish-brown papules, which gradually enlarge, lighten and turn into ring-shaped elements with a diameter of 1.0-3.0 cm. The skin over them is compacted and smooth. The center of the element is atrophic and depigmented. The elements are usually asymptomatic, but sunburn can cause severe erythema and irritation.
ACTINIC COMEDONA PLACLES
Actinic comedo plaques are single or multiple nodules or plaques localized on the extensor surface of the forearms and face, especially around the eyes and on the upper cheeks. The color of the plaques varies from pink to blue, and comedone-like elements may form against their background.
VENOUS LAKES
Venous lakes are clinically expressed in the appearance of soft blue or purple papules with a diameter of 0.5 cm, disappearing with diascopy. Single or multiple elements are usually located on the lower lip or in the helix area of the auricle, less often on other areas of the skin exposed to sunlight.
LENTIGO SOLAR
Lentigo solaris is the result of local proliferation of melanocytes in the area of the dermoepidermal junction. Clinically, it manifests itself as multiple pigment spots of a uniform light or dark brown, and sometimes black color, located on open areas of the skin and especially noticeable on the face (temples, forehead), the back of the hands and the extensor surface of the forearms. The spots are usually quite large - more than 1.0 cm in diameter, have a round shape and unclear boundaries. Although solar lentigo is the result of cumulative sun exposure, it, unlike freckles, does not darken with exposure to the sun.
According to some authors, the focus of solar lentigo, when basaloid cells spread into the lower layers of the dermis, can turn into a plaque of solar keratosis of the reticular type. In addition, lesions of solar lentigo can become inflamed, becoming the precursors of benign lichenoid keratosis. In very rare cases, long-standing solar lentigo progresses to Dubreuil's limited melanosis, a disease that transforms into melanoma.
TEAR-shaped IDIOPATHIC HYPOMELANOSIS
Guttate idiopathic hypomelanosis is characterized by the appearance of hundreds of asymptomatic depigmented porcelain-white spots with clear edges of a round or star-shaped shape measuring 0.2-0.5 cm, scattered like confetti on the anterior surface of the legs and forearms. The development of the disease is associated with prolonged UV irradiation, leading to a decrease in the number of melanosomes and melanin granules.
One of the dangerous consequences of photodamage to the skin is photocarcinogenesis—malignant degeneration of cells that occurs under the influence of UV radiation. Under the influence of UV radiation, the expression of genes encoding both suppressor proteins and proteins that promote tumor development is disrupted. UV radiation stimulates the production of the protein c-fos, which stimulates cell proliferation. At the same time, constant long-term UV irradiation can cause mutations in the gene encoding the tumor suppressor protein p53. As a result, a discrepancy between cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis occurs. With age, the imbalance of these processes worsens, which gradually leads to the development of skin tumors.
MODERN WAYS TO COMBAT PHOTO-AGING OF SKIN
The initial manifestations of photoaging are reversible and with skillful handling of the sun and rational skin care, their regression can be achieved.
To eliminate the phenomena of dermatoheliosis, more active therapeutic measures are needed (the use of systemic and topical aromatic retinoids, peelings, cryotherapy, laser therapy, dermabrasion, surgical excision). Treatment is usually lengthy and in some cases traumatic. In addition, it requires certain financial costs. Unfortunately, especially with already widespread processes, it is not always possible to achieve the desired result. At the same time, with the right and rational approach to insolation, photoaging can be prevented, prolonging the youth of the skin for many years.
The most effective way to combat photoaging in the modern world is its active prevention .
First of all, it is necessary to inform the general public about scientific data confirming the damaging effects of UV radiation on the skin and the body as a whole, and to form a critical attitude towards excessive insolation and the fashion for tanning. In order to prevent photoaging, a set of measures should be used aimed at protecting the skin from damaging solar radiation. To do this, you should, if possible, avoid direct sunlight , use clothing that protects your skin from the sun, and sunbathe only during the period of minimal summer sun activity.
It must be remembered that not only UV radiation from direct sunlight has a damaging effect, but also UV radiation reflected from the ground and surrounding objects, passing through clouds, water and even light clothing. In this regard, the leading element of prevention is the use of sunscreens that prevent skin damage from sunlight.
Causes
The exact causes of this type of cancer are unknown. The study of melanoma is also complicated by the fact that it is usually asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. It attracts attention after a mole changes color to a darker color or due to tumor growth. Malignancy of moles and birthmarks occurs due to the following factors:
- excessive ultraviolet irradiation - sunburn, trips to the solarium - all this negatively affects not only the general condition of the skin, but also increases the risk of malignancy of moles;
- congenital nevi;
- hereditary predisposition (cases of melanoma in the family);
- thyroid diseases;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- injury to the skin, birthmarks and moles;
- increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- skin cancer (even in remission);
- age factor;
- Skin phenotypes 1 and 2 – people with fair skin, blond or red hair, blue or gray eyes and freckles are most susceptible to melanoma due to genetic predisposition.
It is important to understand that if you have at least 3 risk factors listed above, you should undergo regular examinations with a dermatologist, checking all newly formed moles and freckles. Timely removal of malignant tumors increases the chances of stable long-term remission and relieves the patient from secondary complications.
Expert opinion
Author:
Milana Khanlarovna Mustafaeva
Head of the oncology department, oncologist, chemotherapist
It has been clinically proven that melanoma is the most aggressive type of malignant neoplasm. In the mortality structure, skin cancer accounts for 40% of cases. Each year, an increase in the onset of the disease is determined. Failure to seek medical help in a timely manner leads to the development of severe forms of the disease. As a result, diagnosis is carried out at stages 3–4, when treatment is ineffective.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists pay special attention to the diagnosis and treatment of skin melanoma. If suspicious lesions appear on the skin, you should consult a doctor. This will allow cancer to be diagnosed in the early stages, when the prognosis for recovery is considered favorable.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors conduct a full course of examination, which is necessary to determine the stage of development of skin cancer and all related criteria. For this purpose, a CT scan with the possible use of a contrast agent, dermatoscopy, and biopsy are prescribed. The laboratory determines cancer markers in a blood test. After diagnosis, oncologists develop an individual treatment plan. The drugs are selected according to the latest European recommendations for the treatment of skin tumors.
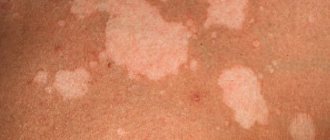
Causes of hypomelanosis: why white spots appear on the skin
The main cause of the disease must be sought in the human genetic apparatus. There is a connection between the development of hypomelanosis in parents and their children - the hereditary nature of skin pigmentation disorders. The disease is inherited in a recessive manner, and the carrier of the hypomelanosis gene can be identified by white spots on the skin, freckles and areas of gray hair on the head that have clear boundaries.
The formation of spots on new areas of the skin and the progression of hypopigmentation on already affected areas is provoked by excessive sun exposure.
First symptoms and signs
Among the main clinical signs of skin cancer are:
- pain syndrome. The degree of its severity depends on the stage of development of melanoma. This may include tingling, burning, itching. The symptom is caused by rapid cell division within the tumor;
- alopecia in the area of tumor growth. As melanoma grows, the hair follicle is damaged. As a result, hair falls out;
- change in the color and contours of the mole. After trauma, the nevus may darken or lighten. The color depends on the degree of melanocyte damage;
- rapid growth of the tumor. Melanoma is characterized by rapid growth. This is due to the high aggressiveness of the tumor;
- changes in the skin in the area of cancer formation. This symptom is characteristic of the later stages of melanoma development. The skin becomes deformed due to damage to healthy cells;
- hyperemia of the tumor contours. The symptom is caused by an inflammatory process. The appearance of this symptom indicates an immune response to the changes taking place;
- damage to neighboring organs. Melanoma metastasizes early. Depending on their location, certain symptoms appear. The liver, bones, brain, lungs and gastrointestinal organs are most often affected;
- lymphadenopathy. As the tumor process grows, nearby lymph nodes are affected;
- lack of appetite. The result is sudden weight loss. As the tumor process spreads, cachexia develops;
- intoxication syndrome. It is characterized by weakness, a sharp loss of strength, fluctuations in body temperature, headache and dizziness.
Differences between melanoma and mole
There are a number of characteristic signs of melanoma that are characteristic of a malignant tumor. During degeneration, the mole changes its shape and loses its symmetry. To check whether melanoma can be benign, draw a conditional line in the middle of the nevus. Benign tumors are completely symmetrical.
The difference between a mole and melanoma is that healthy nevi have clear, even edges. This is due to the local location of melanocytes. If the process of transformation of a mole into melanoma begins, melanocytes begin to spread into neighboring tissues. This leads to a kind of “blurring” of the contour.
Normally, the nevus is uniformly colored with pigment. Birthmarks may contain areas of different shades of the same color, but this is the exception rather than the rule. Usually, due to the uniform distribution of melanocytes in the neoplasm tissue, nevi are colored evenly over the entire area. During degeneration, the cells begin to be distributed unevenly. This leads to the appearance of areas with different colors.
Regular moles do not increase in size. Slight growth may occur during puberty and between the ages of 20 and 30. If a mole begins to grow rapidly, this is an alarming symptom that may appear as it degenerates into melanoma. If you have a mole with a diameter greater than 6 mm, you should immediately undergo examination by a dermatologist.
Symptoms of hypomelanosis: clinical picture of pathology
Hypomelanosis is a genetic pathology characterized by impaired production of the melanin pigment. The first symptoms of the disease can be observed from the birth of the child, but the pathology can progress at a later age. The clinical picture of the disease is characterized by the formation of white areas on the skin, which have clear boundaries and differ in their shade from other areas of the skin.
The size and number of spots with hypomelanosis can be completely different and tend to increase over time.
Diagnostics
Among the main methods for studying skin melanoma are:
- Collecting anamnesis of illness and life. The doctor finds out the time of appearance of the pathological formation and accompanying symptoms. Presumable causes and predisposing factors are determined. The presence or absence of a hereditary predisposition to tumor diseases is clarified.
- Skin examination. The doctor conducts an objective examination of the tumor. Experts identify the so-called alphabet of melanoma. It is designed specifically to characterize pathological formations:
- A (asymmetry) - asymmetry of the shape of the mole;
- B (border irregularity) - uneven borders of the nevus;
- C (color) - change in pigmentation of the mole;
- D (diameter) — increase in nevus diameter;
- E (evolving) - a combination of the above changes.
Dermatoscopy. It is carried out using a dermatoscope. Thanks to it, it is possible to increase the size of the pathological formation several times. This allows you to examine the structure of the tumor in detail.
Biopsy. The most reliable way to confirm skin cancer. The material selected during diagnosis is sent for histological examination. The danger of manipulation is that additional damage to melanoma can provoke an acceleration of the growth of the tumor process. Therefore, it is important to contact experienced doctors.
Treatment
Treatment of melanoma requires an integrated approach. For this purpose the following activities are prescribed:
1. Surgery.
It is the main treatment method for skin melanoma. Surgery becomes the only way to treat cancer if it is diagnosed at stages 1–2 of development. In order to reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence, surgery removes the tumor along with healthy cells.
2. Chemotherapy.
Prescribed to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells. Due to the aggressiveness of the tumor and the early appearance of metastases, unified chemotherapy regimens for melanoma have not yet been developed. Doctors select medications and their dosages individually depending on the stage of cancer development. When melanoma is detected in late stages, chemotherapy is palliative.
3. Radiation therapy.
High doses of radiation help destroy cancer cells. In this way, it is possible to improve the prognosis for further treatment and recovery. Radiation therapy may be given in combination with surgery and chemotherapy. For inoperable melanoma, radiation therapy is palliative.
4. Immunotherapy.
Drugs that enhance the body's protective functions are necessary to activate the antitumor immune response. As a result, the immune system begins to fight cancer cells on its own. Drugs used during immunotherapy include:
- interferon-alpha;
- interleukin-2;
- reaferon;
- ipilimumab.
Thanks to immunotherapy, it is possible to reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
5. Diet food.
The diet prescribed as part of the complex treatment of melanoma requires the exclusion of the following products:
- canned food;
- spices;
- smoked products;
- spicy and fatty foods.
The daily menu should contain a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, cereals, lean meats and fish, poultry, and dairy products. Thanks to such a diet, the body receives vitamins, minerals, micro- and macroelements. They are necessary during the period of treatment and recovery.
Stages and prognosis
Determining the stage of the tumor process is necessary to prescribe appropriate treatment. Depending on the stage at which skin cancer was diagnosed, the further prognosis is determined. The later the tumor is detected, the more unfavorable it is. In accordance with the size of the formation, its localization, the degree of germination into surrounding tissues and metastasis, the following stages of melanoma are distinguished:
- first. Characterized by shallow penetration into the thickness of the skin. At this stage, the thickness of melanoma does not exceed 1 mm. The pathological process does not spread to nearby lymph nodes. The tumor does not bleed or form ulcers;
- second. Accompanied by a more rapid spread of the tumor process. Cancer grows into the skin to a depth of 2 mm. The changes are characterized by a corresponding clinical picture. The tumor formation becomes covered with ulcers, bleeds and peels off. At the second stage of melanoma, regional lymph nodes are not affected;
- third. The tumor process spreads to nearby lymph nodes. This worsens the prognosis for further therapy and survival. At this stage, complex treatment is required, including surgery and chemotherapy;
- fourth. The last and most severe stage of melanoma. Characterized by the presence of multiple foci of metastases. They spread through the blood and lymph flow. Melanoma at this stage of development has an unfavorable prognosis in terms of recovery. Treatment may be ineffective. In some cases, only palliative therapy is prescribed.
Features of the treatment of hypomelanosis: an effective treatment regimen
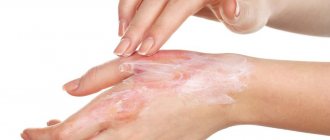
Hypomelanosis is a pathology that spreads at the genetic level, so there is currently no pathogenetic treatment for the disease. Symptomatic therapy is used:
- Correct and active sun protection
- Clothing that covers exposed skin
- Corticosteroids are also used locally in the form of ointments.
- Retinoids: local and systemic use
- Elidel 1% cream 2 times a day - until hypopigmentation decreases or completely disappears.
The development of hypomelanosis is provoked by excessive sun exposure, so the best prevention of pathology is to avoid direct sunlight on unprotected skin.
Read more articles on skin diseases in the “Dermatology” section on estet-portal.com. Thank you for staying with us!
Share:
Relapse and treatment tactics
The risk of relapse depends on the degree of tumor germination and the presence of metastases. Most often, recurrent melanoma is localized near the previous lesion. In order to reduce the risk of tumor recurrence, doctors recommend following the following preventive measures:
- limit the time spent under ultraviolet rays;
- Conduct regular self-examination of moles;
- use protective clothing when in contact with toxic substances;
- undergo a preventive examination by a dermatologist.
If you suspect the presence of skin tumors, we recommend that you contact the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic’s specialists use modern equipment to diagnose diseases. Therapy is carried out in accordance with the latest global oncological recommendations. You can make an appointment by phone.