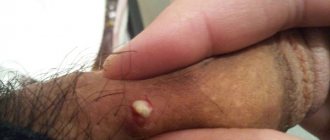
A groin rash can appear due to a number of reasons. For example, we can talk about inflammatory processes, dermatological problems, infectious and even sexually transmitted diseases. After all, there are even cancer diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of a rash on the male genital organ.
A qualified dermatologist knows that the nature of the rash can also be very different. These can be various pustules, small spots, ordinary redness, other irritations and spots. The surface of the elements can be smooth or, conversely, rough. Sometimes blisters appear containing pus and other clear fluid.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Demodicosis | Rash on shoulders | Dermatologist at home |
Causes of groin rash
The appearance of a groin rash can be influenced by various factors. The symptoms are characteristic of both acute infectious diseases and ordinary allergic reactions to intimate hygiene products used.
The main reasons for the formation of uncharacteristic rashes in the groin area include:
- underwear that is too tight or made from rough fabrics;
- non-compliance with generally accepted rules for caring for the genitals;
- increased sweating, especially in the hot season;
- overweight;
- dermatological diseases, such as candidiasis or psoriasis;
- decreased immunity;
- venereal diseases;
- diabetes;
- long-term use of medications that can affect the reproductive system.
If characteristic symptoms are detected, you should not self-medicate using a variety of creams and ointments that temporarily relieve swelling and discomfort.
Timely diagnosis of the cause of a groin rash facilitates the completion of an appropriate therapeutic course in the early stages of the disease, which helps to avoid possible complications.
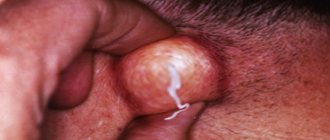
Blisters in the groin due to scabies
The risk group for groin scabies is men.
The most common location of scabies is the hands, from there it spreads to the penis.
Normally, blisters do not form with scabies.
The rash consists of blisters and papules.
The bullous form with blistering is rare.
The severity of scabies is not related to the number of mites.
It depends only on individual allergic reactions to pathogens.
A more common cause of the development of blisters is the addition of a secondary infection.
It occurs against the background of scratching in the groin.
Scabies causes severe itching.
The genital area contains a large number of bacteria.
Secondary infection develops relatively often.
The main therapy for scabies is carried out with antiscabiosis drugs.
Previously, special talkers were used for this.
The treatment took up to a week.
Now there are modern means.
They get rid of parasites in 1 – 2 applications.
Secondary infection, if present, requires additional therapy.
What tests should be taken for a groin rash?
There are many factors influencing the formation of a rash in the groin area. It is impossible to determine the causative agent of unnatural manifestations on the skin by external signs. Therefore, to identify the cause of the pathology, certain types of laboratory tests may be prescribed:
- a general smear from the urethra is taken for subsequent examination under a microscope to determine an increased level of leukocytes, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the genital organs;
- collection of secretions from the urethra is taken if the presence of an infectious disease is suspected;
- general tests for STDs;
- blood for diagnosing sugar levels;
- flushing from the area of the rash onto the seeding tank.
To obtain more accurate test results, you must follow all doctor's recommendations. In preparation for diagnostic measures, it is required to abstain from sexual contact and avoid drinking alcoholic beverages.
Skin rashes in the groin area should not be lubricated with creams or other means; on the day of washing, taking a shower is excluded.
Yellow discharge in women and purulent rash
Purulent rashes may appear on the labia and mucous membranes of the vulva. This is a sign of a bacterial infection. The clinical picture is usually complemented by yellow vaginal discharge. Gradually, acne spreads to the pubic area, causing folliculitis (ulcers on the hair follicles).
The pathology is easily treated - antibiotics, local antiseptics, drugs for immunity. However, the disease is dangerous because the infection spreads to the deeper layers of the skin. A boil forms at the site of damage to the fatty tissue. The formation is dense and painful. The pain radiates to the abdomen and rectum.
Often the formation of a subcutaneous boil ends in bartholinitis. This is an inflammation of the reproductive gland in the vestibule of the vagina. With bartholinitis, a large formation appears at the vaginal vault, which hurts and interferes with movement. Bartholinitis is treated surgically - the formation is opened, the pus is removed and washed with an antiseptic.
Rash in the groin in men
In the male half of the population, the lesion in the groin area differs from healthy skin in its unnatural color, structure and rashes of various structures.
It can often be accompanied by itching in the external genitalia and acute pain when in contact with underwear. The formation of a groin rash in men may indicate a certain number of pathological conditions:
- seborrheic dermatitis in chronic form, which during exacerbation causes small pinpoint rashes in the groin;
- candidiasis manifests itself in the form of small papules with serous filling;
- epidermophytosis, accompanied by a rash in the groin in the form of rings, the edges of which are covered with small blisters; the formation is caused by a fungus;
- psoriasis causes the formation of plaques on the skin in the groin, similar to fish scales with gradual enlargement and falling off of crusts;
- syphilis is often transmitted through sexual contact and is of infectious origin.
The most dangerous pathology when a rash appears is pemphigus. Rashes form between the legs and in the folds of the groin area, often affecting the testicles, and erosions appear at the site of formation. The disease is accompanied by elevated body temperature and rapid dehydration of the entire body.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure
Hepatitis C rash in men
Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver of a viral nature. The disease can occur in mild or severe form. However, the main symptom of any form of the disease is a rash on the skin with itchy patches. Over time, the rash may spread to the mucous membranes.
With hepatitis C, the rash on the skin of the genital organs in men can have a different character. With this disease, the following types of rashes are observed:
- urticaria - small nodular rash;
- pink spots with pinpoint hemorrhage;
- bluish spots in which the capillary network is clearly visible;
- acne with pus.
The affected areas are constantly itching, so scratching may appear in the perineum. This brings additional discomfort because the wounds bleed and hurt. In this case, a secondary infection may enter the wound.
A rash on the penis in the form of urticaria as an isolated symptom cannot be considered a sign of hepatitis. This disease is also accompanied by other specific symptoms:
- chronic fatigue;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- temperature increase;
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- bad breath;
- sleep disorder;
- fainting, headache.
Rash in the groin in women
Rashes in the groin area in women may be evidence of a pathological abnormality in physiology, the presence of an infectious disease, or the development of a neoplasm of varying quality. In normal condition, the outer covering of the genital organs should be smooth, so the presence of a rash in any form is a reason to urgently consult a doctor.
At first glance, harmless changes in the structure and color of the epidermis can seriously threaten the health of the entire body, hiding dangerous pathological processes that gradually destroy the normal functioning of the reproductive system. As a rule, rashes appear suddenly and in large quantities.
There are the following types of groin rash in women:
- ordinary pimples, filled with liquid of various colors and appearing in the form of bubbles, blisters or bumps;
- purulent formations of various diameters and a liquid filling of a cloudy color, which is purulent exudate;
- condylomas are inflammatory branches of the papillary seals of the epidermis;
- erythema is characterized by bulges of pinkish or bright burgundy color;
- nodes are subcutaneous compactions in the form of neoplasms.
Any type of groin rash in women is a symptom of the development of another pathology directly related to the reproductive system. Also, a rash is a kind of signal about a violation of the rules for caring for the intimate area, an allergy to cosmetics or poor-quality depilation. Only a doctor can identify a more accurate cause of external manifestations based on the results of diagnostic measures.
Rash due to hormonal imbalance in women
Hormonal imbalance is dangerous for a woman’s health. Reproductive function, metabolism, hair, nails, and skin suffer from improper hormone production. Active acne that is difficult to treat is a clear sign of hormonal imbalance.
Hormonal rash in a woman manifests itself in the form of acne and pimples, characteristic of adolescence. The formation of acne is promoted by clogging of the sebaceous glands with dead epithelium. Moreover, in case of hormonal imbalance, sebum is produced more actively. This provokes the appearance of new acne. The clogged ducts begin to fester. Often, ulcers are accompanied by a secondary infection, which further complicates treatment.
Hormonal acne occurs throughout a woman's body. But more often acne is observed on the face, back, and back of the head. Sometimes acne appears in the pubic area in women. This happens due to blockage of the pubic hair follicles. Hormonal rash spreading to the intimate area requires a comprehensive diagnosis. Unlike adolescence, hormonal acne in an adult woman does not go away on its own. It is necessary to start treatment.
Rash in the groin of a child
The appearance of rashes of various shapes and structures in the groin area of a child indicates the occurrence of a pathological process. This phenomenon can occur for various reasons. Parents are required to understand that the presence of a rash can be associated not only with dermatology, but also with other more dangerous diseases.
The skin of children is most sensitive to extraneous irritants that affect the body, both from the outside and from the inside. Groin rashes are common in the first twelve months of a baby's life and can often be resolved with better personal hygiene and the use of specialized creams.
Other causes of rashes include:
- allergic reaction;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- prickly heat or scabies;
- fungal infection of the skin in the groin;
- eczema;
- diaper dermatitis.
Such manifestations can be a sign of more serious pathologies. Therefore, if the rash is localized in the groin of a child, you should undergo a more thorough examination, which will be prescribed when you consult a doctor.
Answers to frequently asked questions about skin rashes:
- Which doctor should you contact for a skin rash?
- Is the skin rash contagious?
- What diet is necessary for skin rashes?
- What diagnosis is needed for a skin rash?
- Why is a skin rash dangerous?
- Why is it necessary to get tested for a skin rash?
- What diseases does a skin rash indicate?
- What examination is necessary for a skin rash?
- Which skin rash is dangerous?
- How to distinguish an allergic rash from an infectious one
- How to get rid of skin rashes?
- How to get rid of itching skin rash?
- What organs are affected by a skin rash?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a dermatologist?
- How to get checked for skin diseases?
- What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
- What tests should be taken by a dermatologist?
- What diagnostics can a dermatologist perform in the clinic?
- Where to go with a skin disease?
Blisters in the groin with herpes type 2
Herpes can cause pathology not only on the lips, but also on the genitals.
The disease is transmitted through unprotected sexual contact.
Infection of a partner occurs both during active disease and when there are no manifestations.
Symptoms begin with the appearance of grouped blisters containing cloudy liquid in the genital area.
Then they rupture, and erosions and ulcers appear on the damaged area.
A little later they dry out and become crusty.
All periods of rash are characterized by painful sensations.
It is important to remember that the body is never completely free of the herpes virus.
A complete cure will not occur even with complete and competent therapy.
Therefore, a single appearance of herpetic blisters in the groin always leaves a risk of repeated rashes.
Recurrences of herpes infection are possible under the following conditions:
- other infectious diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- decreased level of immunity;
- hypovitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- dysbacteriosis.
In each case of exacerbation, the best way out of the situation is to consult a doctor.
You should not be treated without prior consultation.
What diseases can cause a groin rash?
With proper skin care in the intimate area and timely, regular changes of underwear, the appearance of a rash in the groin area indicates a variety of pathological disorders.
Without a timely visit to a doctor to diagnose the cause of skin disorders and subsequent treatment, serious complications may arise that adversely affect the functioning of the body as a whole.
There are a number of diseases that are accompanied by similar manifestations, here are the main ones:
- perianal dermatitis, which is initially localized around the anus and later spreads throughout the groin area;
- infectious lesions, which may be caused by unprotected sexual intercourse with a casual partner;
- lichen planus, which appears in men as pinkish shiny nodules with a depression in the center;
- psoriasis and syphilis cause accelerated cell death, which is accompanied by smooth plaques on the skin in the groin and causing acute pain;
- scabies is a contagious disease caused by the scabies mite, accompanied by small reddish rashes with severe itching;
- inguinal epidermophytosis, formed as a result of skin damage in the intimate area by a fungus.
The presence of erosions or ulcers that do not heal for a long time and deform the tissues of the external genital organs with the appearance of actively increasing pigment spots is evidence of an oncological process and the development of malignant neoplasms.
Causes of irritation in the bikini area
- External factors
Irritation in the bikini area is often caused by mechanical damage to the skin. After shaving the intimate area, redness, pimples, and itching often appear - the skin becomes especially inflamed in the summer, when sweating increases. When depilating with a razor, the top layer of skin is damaged, which can lead to dryness and flaking, and growing short hairs cause itching and, accordingly, redness and scratches on the skin.
Expert opinion
Depilation using wax, sugar paste and tweezers damages the top layer of skin to a lesser extent, but more often provokes ingrown hairs. As a result, painful pimples form in the bikini area, the opening of which is fraught with the penetration of pathogenic agents into the deeper layers of the skin (especially in the hot season).
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Violation of the temperature regime that is comfortable for the skin - too high or, conversely, low temperature - can also cause discomfort in the vagina. Of course, external contamination of delicate areas may not be the last cause of irritation.
In addition, discomfort may occur from inappropriate intimate cosmetics. For example, hypoallergenic baby soap, which many women still use as an intimate care product, greatly dries out the delicate skin of the vagina, since the production of sebum by baby skin and the delicate skin of the intimate area occurs in different volumes. It is important to use special products for intimate hygiene - for example, GINOCOMFORT Soothing washing gel consists of natural ingredients that not only delicately cleanse the vaginal mucosa and skin of the labia, but also regulate the acid-base balance that is comfortable for this area.
- Microflora disturbance
One of the most common causes of severe irritation in the intimate area is diseases associated with disruption of the natural bacterial and acid-base balance: thrush (candidiasis), bacterial vaginosis (dysbacteriosis).
These diseases can be caused by a general decrease in immunity, poor diet, sleep, hygiene, frequent stress, taking antibiotics, promiscuity, etc.
Characteristic symptoms include severe irritation in the intimate area after sex, thick atypical discharge with a pronounced unpleasant odor, severe itching and burning. Any of these diseases is treated with special regimens using antibacterial drugs, pro and prebiotics. Self-medication can cause irreversible complications or make the process critical, so it is better to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist to clarify the diagnosis and develop treatment tactics.
- Allergic reactions
Often, intimate itching can occur with contact dermatitis - a manifestation of allergies in a delicate area. One of the most common reasons is scented hygiene products. Fragrance in pads, tampons, and toilet paper is a strong allergen and can cause itching. If you experience irritation in your intimate area, especially during menstruation, try changing your pads - this may solve your problem. In some cases, allergies can be caused by contraception (latex condoms) and lubricants. Most condoms are made from latex.
- Hormonal background
Irritation in the intimate area in women often occurs before hormonal changes: menstruation, pregnancy. Many women are familiar with the sensation of dryness, burning, and severe itching. Irritation in the perineum can be an external sign of hormonal disorders such as hypo- or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, ovaries, and adrenal glands. To establish an accurate diagnosis, a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and tests for hormone levels are necessary.
Expert opinion
Changes in hormonal levels and the resulting irritation in the intimate area can be triggered by taking oral contraceptives. This situation is especially common if a woman takes OCs, chosen independently or on the advice of a friend, without consulting a gynecologist.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
- Poor intimate hygiene
It is obvious that irregular showering, especially during menstruation, hot weather or after visiting the gym, leads to an increased proliferation of harmful bacteria and fungi, causing rashes and itching in the intimate area in women. Wearing synthetic underwear also has a negative effect - panties made of artificial fabrics do not allow air to pass through, creating a greenhouse effect - an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microbes. It is important to know that thongs, thongs and similar models are a “bridge” for bacteria from the anus, so if discomfort occurs, it is better to refrain from wearing them.
- Diseases of internal organs
Endocrinologists warn: severe itching and dryness in the genital area is one of the indirect signs of diabetes. Sometimes irritation in the intimate area can indicate anemia, leukemia, immunodeficiency conditions, inflammation in the urinary system, gastrointestinal tract, and cancer. Redness, spots and rashes on the external genitalia occur with eczema (eczematis) and psoriasis (psoriasis).
Of course, you can’t rely only on vaginal itching to make an accurate diagnosis, but this unpleasant symptom can indicate serious health problems, so it’s better not to delay visiting a specialist.
- Sexual infections
Itching, burning and unpleasant discharge after sexual intercourse (especially unprotected with a new man) are accompanying sexually transmitted diseases. They are especially characteristic of gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea), chlamydia and trichomoniasis (trichomoniasis). In addition to discomfort in the intimate area, sharp pain during urination, pain during sexual intercourse and foul-smelling discharge may be added - if these signs appear, you should urgently get tested and visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. Most sexually transmitted infections in the early stages can be quickly and successfully treated, so timely consultation with a doctor can save you from unpleasant consequences and complications.
- Stress
The female genital organs are very susceptible to psychological conditions: emotional instability, stress and frequent anxiety can cause itching in intimate places.
It is important to monitor your stress levels whenever possible and use sedative therapy if necessary to improve your quality of life.
The causes of irritation in intimate areas are varied and may depend on completely different factors. If you feel that self-treatment does not lead to an improvement in the situation, do not hesitate to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist, this way you will quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and get rid of it.
The causes of irritation in intimate areas are varied and may depend on completely different factors. If you feel that home treatment does not lead to an improvement in the situation, do not hesitate to visit a gynecologist, this way you will quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and get rid of it.
Is a groin rash contagious?
Depending on the cause of the groin rash, it can be transmitted from an infected patient to a healthy person through direct contact with the patient or his personal hygiene items. The most common places where there is a high risk of infection are public baths, swimming pools, beaches and saunas.
If you have inguinal athlete's foot, you must adhere to certain rules of personal hygiene and use intimate area care products only for your own purposes. After the patient has suffered from this disease, it is necessary to completely change all household items, and thoroughly disinfect underwear and clothing.
If the rash is associated with allergic manifestations or the inconvenience of underwear, then the risk of infection of others is excluded.
Pimples and irritation after shaving in the intimate area in women: how to properly remove hair with a razor?
Hair removal in intimate areas is a recent trend. How to avoid irritation after depilation?
- Be sure to apply shaving cream or foam to your skin before depilation.
- If you are removing hair with a reusable machine, treat it with a disinfectant such as alcohol or chlorhexidine.
- Use only a very sharp razor; a dull razor can damage delicate skin.
- Do not press the razor too tightly against the skin or run over one area several times in a row.
- After depilation, treat the skin with a septic cream and do not wear underwear until it dries to allow the area to calm down and not cause irritation.
Which doctor treats groin rash
A dermatologist is involved in the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as a rash localized in the groin area. When contacting our clinic, the doctor will conduct an initial examination and prescribe the necessary tests, based on the results of which the most appropriate course of treatment will be formed.
Not everyone has the opportunity to personally visit a medical center for characteristic rashes in the groin. In such situations, it is possible to call a dermatologist at home.
It is especially recommended for patients who fall into certain categories to use this service:
- elderly people who have difficulty moving independently on public transport;
- people with disabilities resulting from mechanical injuries or recent surgery;
- bedridden patients who are unable to move without assistance;
- people with limited free time in order to save it.
If you identify characteristic groin rashes, do not hesitate to contact our clinic and see a dermatologist. An advanced form of any pathology is much less responsive to therapy and can cause serious complications that have an adverse effect on the reproductive system.
Where to go with a groin rash
An experienced dermatologist from our clinic is ready to see a patient on the most convenient day for him, excluding holidays and weekends. At the first appointment, a history will be taken and an examination will be carried out, following which a referral will be issued for subsequent pathology diagnostics in order to identify the pathogen and make the most accurate diagnosis.
Based on all the research activities carried out, a conclusion is drawn and a therapeutic course is drawn up, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Symptoms that require immediate medical attention:
- pinkish rashes that are constantly increasing in size;
- simultaneous localization on the inguinal folds, perineal area and around the anus;
- the rashes flake, itch and cause severe discomfort when walking;
- acute itching of the affected areas of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- the rash does not go away for a long time.
People facing problems caused by the formation of a groin rash are exposed to an additional stressful situation. Our clinic offers anonymous treatment, with complete confidentiality of all information provided by the patient.
| Appointment with a dermatologist at the clinic. Call a dermatologist at home. | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
Treatment of groin rash
The determination of the treatment method in the presence of pathological rashes in the intimate area is formed on the basis of an initial examination, medical history and the results of diagnostic measures. If an allergic reaction is detected, the diet is analyzed in order to adjust it and identify the product that contributes to the development of a rash in the groin.
It is also recommended not to use tight underwear and give preference to natural fabrics.
Certain methods of therapy are distinguished when identifying diseases not related to problems of personal hygiene and allergies:
- if a viral or bacteriological rash is detected, antifungal agents are used to treat the affected areas;
- special lotions based on a weak iodine solution are applied;
- certain ointments and gels are used to treat the groin area in places where rashes appear;
- Special vitamin complexes are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
For patients suffering from excessive sweating, it is recommended to use baby powders and hygienic infusions of chamomile or oak bark. The use of any medications without a doctor's prescription may contribute to the development of additional complications.
Causes of rashes in the intimate area
The content of the article
In women, rashes of various types most often appear on the pubis, genitals, and perineum. These can be ulcers, spots, pimples and other visually noticeable skin lesions. These manifestations may be associated with frequent shaving, mild allergies, and poor hygiene. However, quite often rashes in the intimate area require medical attention, as they become a response to infection.
The appearance of an unpleasant rash in the intimate area is associated with the following factors:
- Infection
. The nature of the rash depends on the type of infection that is actively multiplying in the body. Infection with a sexually transmitted infection is usually accompanied by additional symptoms. This may include purulent discharge, itching in the groin, and menstrual irregularities. - Weakening of the immune system
. This factor allows opportunistic flora to actively reproduce. Chronic diseases, antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy, childbearing, and hypothermia seriously weaken the immune system. - Chemical burn
. Aggressive substances destroy the upper layers of the epidermis. The body responds to this with the appearance of small, painful pimples. - Synthetic underwear
. Sometimes it causes genital allergies. Poor quality fabric does not allow the skin to “breathe”, which leads to the proliferation of pathogenic flora; - Ignoring hygiene rules
. This creates favorable conditions for viruses and bacteria to enter the body. It is especially important to carefully observe intimate hygiene during menstruation.
Ointments used for groin rash
When forming a course of therapy, the dermatologist is guided by the cause that provoked the manifestation of the rash in the groin and the form of development of the pathology. When prescribing research activities, certain factors are taken into account, such as damage to certain areas of the skin, the type and nature of the rash.
Based on the test results, the following ointments may be prescribed:
- "Bepantol" promotes rapid restoration of damaged skin, drying wounds and abrasions;
- “Desitin” forms an enveloping protective film over the affected areas, which speeds up the process of restoration of structural tissues, and also protects against the effects of sweat and urine on the localization of the rash;
- "Lamisil" is used against infectious fungi;
- "Drapolene" is used as an antiseptic to soften and relieve skin irritation;
- "Pantestin" prevents infectious spread to neighboring areas.
Quite often, an ointment based on the zinc component is prescribed. Its use helps relieve itching and swelling, followed by drying of the skin in areas where the rash is localized.
Calling a dermatologist at home for a rash in the groin
Not everyone has the opportunity to personally visit a doctor in our clinic if they develop rashes in the groin area. In such situations, a dermatologist is called to your home.
You can use the service in any of the most convenient ways:
- Call one of the specified clinic phone numbers with a brief description of the symptoms of the disease that has arisen. The dermatologist will visit the patient on the same day of treatment, excluding holidays and weekends.
- Filling out an electronic application on the official website of our medical center. To do this, you need to provide all the necessary information in special fields in the online application form. The dispatcher will contact the patient as soon as possible using the phone number provided to confirm the most convenient time for the doctor’s visit.
- Registration entry. This calling method may be required by patients who have a follow-up appointment but no longer wish to attend the clinic due to lack of time or other personal reasons. By contacting the registrar, you will need to briefly describe the situation and agree on the date, address and time of the dermatologist’s visit.
When choosing any type of treatment, you should be prepared to provide certain personal information. All personal data of patients is kept in strict confidentiality.
Groin rash and itching
If the groin rash is accompanied by itching in the area of the skin disorder, the rash increases in size and does not go away for a long time, then this is evidence of the development of serious pathologies.
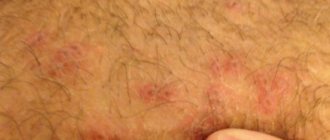
The most common types of manifestations that cause painful discomfort and a desire to scratch the affected areas:
- small red pimples that quickly spread to neighboring areas; over time, the structure changes and the skin begins to peel off;
- small blisters with purulent filling, cloudy or white;
- dark lumps that dry out the skin and indicate the development of diseases associated with the reproductive system;
- burgundy pigment spots exceeding one centimeter in diameter; small clusters of bubbles with liquid filling may form along the edges.
If such symptoms occur, an urgent visit to a dermatologist is required for subsequent diagnostic measures and an appropriate therapeutic course. In certain cases, the appearance of a groin rash with itching is an indicator of the development of cancer.
Epidermodermal mycoses of the skin in the practice of a dermatologist
Athlete's foot (synonym: "fringed eczema", true epidermophytosis) is a mycosis caused by the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum (flaky epidermophyton). The term "athlete's foot" is justified, in the strict sense, in relation only to this nosology.
The share of this fungus in the spectrum of fungal pathology is currently small - no more than 1.2–1.8%. Men get sick somewhat more often. Most of the primary diagnoses of athlete's foot upon further cultural examination turned out to be rubromycosis and were combined with onychomycosis [1, 4].
Infection with this fungus most often occurs indirectly, through objects that have been used by the patient (in baths, showers, etc.).
Clinic. Typical localization of lesions is the skin of large folds (inguinal, under the mammary glands, intergluteal). The formed lesion may contain spotted, papular, vesicular, pustular elements, i.e., there is a true polymorphism of elements within the lesion, bordered by a continuous, slightly edematous peripheral ridge. The severity of the allergic reaction to the presence of the fungus is characterized by the above sequence of primary elements: from the smallest with a predominance of spots to the maximum with abundant vesiculation, weeping and erosion.
In the center, resolution of the pathological process may begin, while acute phenomena still persist in the periphery. Subjectively, quite intense itching is noted [1, 7].
Diagnostics. In scrapings, as a rule, the mycelium of a pathogenic fungus is easily detected, except for cases when the material is taken from a lesion with a pronounced exudative component and oozing: in this case, difficulties arise in detecting the fungus, as noted by most laboratory technicians. This rule also applies to foot mycoses caused by other fungi [3, 7].
Inguinal athlete's foot should be differentiated primarily from candidiasis of large folds, which develops in obese individuals suffering from diabetes mellitus; In children, inguinal athlete's foot can mimic diaper dermatitis, which is also essentially candidiasis of large folds. Erythrasma rarely produces such pronounced inflammatory phenomena; in the rays of a Wood's lamp one can observe a “beautiful” coral-red glow. Eczema, including seborrheic, when localized in large folds, sometimes forms lesions similar to inguinal epidermophytosis [1, 2, 7]. Rubromycosis differs from inguinal athlete's foot by the presence of an intermittent peripheral ridge (N. S. Potekaev et al., 1972).
Athlete's foot is a chronic fungal disease. The lesions are localized on the skin of the arch and interdigital folds of the feet, and the nail plates are often affected.
The causative agent is Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale. Trichophyton interdigitale accounts for 5–10% of all causative agents of foot mycosis in cities and 40–50% in rural areas [10].
Clinical picture. The incubation period has not been precisely established. There are several forms of mycosis: squamous, intertriginous, dyshidrotic, acute (described by O. N. Podvysotskaya in 1937) and onychomycosis. Secondary skin rashes are possible - epidermophytids (mycids), associated with the allergic properties of the fungus [2, 7].
The squamous form is manifested by peeling of the skin of the arch of the feet, sometimes against a hyperemic background. The process can spread to the lateral and flexor surfaces of the toes. With the squamous-hyperkeratotic type of athlete's foot, areas of diffuse thickening of the skin can form, similar to callus, with lamellar peeling. With erased forms, there are no subjective sensations.
The intertriginous form begins with subtle peeling of the skin in the third or fourth interdigital folds of the feet. Then the process takes on the appearance of diaper rash with a crack in the depths of the fold, surrounded by a peeling, whitish stratum corneum of the epidermis, accompanied by itching and sometimes burning. With prolonged walking, cracks can transform into erosions with a wet surface. Due to the addition of pyococcal and yeast flora, hyperemia and swelling of the skin develop, itching intensifies, and pain appears. The course is chronic, exacerbations are observed in the summer season [7].
The dyshidrotic form is characterized by the presence of vesicles with a thick horny covering, transparent or opalescent content (“sago grains”) on the arches, lower lateral surface and on the contacting surfaces of the toes. Bubbles are usually located in groups, prone to merging, forming multi-chamber, sometimes large bubbles with a tense tire. After their opening, erosions are formed, surrounded by a peripheral ridge of exfoliating epidermis. The contents of the vesicles (blisters) may be purulent if a pyococcal infection is associated. Some patients experience lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, accompanied by pain, general malaise, and increased body temperature.
Acute epidermophytosis occurs due to a sharp exacerbation of dyshidrotic and intertriginous forms. It is characterized by the rash of a large number of vesicular-bullous elements against the background of skin edema, sometimes significant; rashes may be accompanied by lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, fever, the addition of pyodermic complications, and disability [2, 7, 8].
Damage to the nails, most often the 1st and 5th toes of both feet, occurs in 20–25% of cases: the nails are thickened, yellow-gray, but, unlike rubromycosis of the nails, their loosening and fragility develop more slowly. In the initial stages of onychomycosis caused by interdigital trichophyton, lesions of the nail plate in the form of ocher-yellow stripes are characteristic.
In more than 2/3 of patients with athlete's foot, the disease occurs with mycids - toxic-allergic rashes in areas both bordering the lesion and distant, which also distinguishes this mycosis from rubromycosis, for which, in general, allergic reactions and the exudative component are much less characteristic. This is obviously explained by the antigenic composition of the cell wall of the interdigital trichophyton, to the presence of which a violent reaction develops.
Children are especially characterized by a condition called eczema by O. N. Podvysotskaya in the literature: after full antifungal treatment and the elimination of exudative manifestations of mycosis, the process suddenly worsens with renewed vigor. In this case, fungal elements are not detected in the lesions. Pyoderma complications quickly appear.
Diagnostics. The leading role in establishing a diagnosis in the acute period belongs to clinical symptoms, since fungi cannot always be detected from exudative foci. After the elimination of inflammation, the diagnosis in some cases is confirmed by the detection of a fungus from dry hyperkeratotic areas.
| Rice. 1. Mycosis of the skin of the chest |
Differential diagnosis. The dishidrotic form of mycosis should be differentiated from rubromycosis (Fig. 1), true epidermophytosis, superficial pyoderma, contact dermatitis; intertriginous form - from candidiasis, diaper rash [3, 5].
Rubromycosis (synonym: rubrophytosis) is mycosis of the skin and nails caused by red trichophyton (Trichophyton rubrum). The mushroom is named red because of its ability to deposit red pigment at the base of the colony when grown on Sabouraud's nutrient medium. This is a fungal disease prone to exacerbations and chronicity with a predominant localization of lesions on the skin of the feet, frequent damage to the nail plates of the toes and hands, large folds, skin of the torso and limbs, less often - the face, neck and scalp [2, 7, 8] .
Only people get sick; the fungus is a true anthropophile [5]. Infection occurs through prolonged contact with a patient with rubrophytia and the use of various things of the patient (loofah, pumice stone, scissors, shoes, etc.; when visiting bathhouses, showers, swimming pools, where infected people can remain for a long time on the floor, rugs, benches, floorings, and in wastewater fungus skin flakes and particles of destroyed nails). Rubrophytosis is often called a familial infection.
In Russia, there are more than 5 million patients with this mycosis (Yu. V. Sergeev, 2008). Onychomycosis accounts for more than 24% of all mycologist visits. The intensive growth rate of onychomycosis is about 5% per year.
The main source of infection is the family!
The incubation period has not been established. The development of mycosis is facilitated by various exogenous (excessive sweating or excessive dryness of the skin of the feet, injury to them by shoes, non-compliance with hygiene rules) and endogenous (endocrinopathies, immunodeficiency state, metabolic disorders, reduction of the body’s natural resistance due to the use of corticosteroids, cytostatics, antibiotics, etc.) factors [9].
Clinic. Men and women get sick with the same frequency [2, 7, 10].
Based on localization, rubromycosis is distinguished between smooth skin, palms and soles, and nails.
| Rice. 2. Mycosis of the skin of the leg |
On smooth skin, the disease exists in two forms - erythematosquamous and follicular-nodular. The erythematosquamous form is characterized by the formation of large lesions on the skin, consisting of spotted, papular and vesicular (rarely pyodermic) elements, as well as scales, crusts, and sometimes excoriations. In the center of long-existing lesions, spontaneous resolution of the process of the appearance of areas of atrophy and telangiectasia is sometimes observed, which gives the lesion a poikilodermic appearance (Fig. 2). Along the periphery there is an intermittent ridge of papules, vesicles and crusts. The appearance of diffuse erythema within the lesions is a clinical sign of long-term treatment with corticosteroid ointments; erythema develops even if these ointments contained an antifungal additive.
The follicular nodular form is essentially a trichophytosis granuloma (gumma Majocchi). This form usually characterizes the prolonged existence of the previous form without treatment. The process develops in the dermis, deep in the hair follicles and resembles zoonotic trichophytosis in the infiltration stage (formally, rubromycosis is the same trichophytosis, as it is caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton) [5, 9].
| Rice. 3. Mycosis of the skin of the trunk |
Mycosis of the feet and hands can be represented by the following forms: intertriginous - characterized by cracks, maceration of the epidermis, single vesiculations in the interdigital folds of the feet, most often between the 4th and 5th fingers, rarely found on the hands; squamous - most often, as a rule, accompanies onychomycosis, is represented by hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles with a peculiar increase in the skin pattern, deepening of the furrows and “sprinkling” of these furrows with “flour” (floury peeling); when an exudative component is attached, the peeling becomes lamellar in nature; dyshidrotic - reminiscent of those affected by interdigital trichophyton: areas of “dry” mycosis alternate with vesiculations, sometimes with pustules, patients are bothered by severe itching [10].
Differential diagnosis. Other epidermodermal mycoses (athlete's foot inguinal), trichophytosis (Fig. 3), candidiasis of large folds, psoriasis; onychomycosis should be differentiated from damage caused by other fungi (candidal onychia, mold mycosis), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as well as onychodystrophies of non-infectious etiology (psoriasis, especially pustular, lichen planus, acrodermatitis enteropathic, etc.).
Treatment of superficial mycoses
In this article we will consider only the principles of external therapy of superficial mycoses.
For acute inflammatory phenomena, lotions are prescribed from 1–2% resorcinol solution, 0.1% ethacridine lactate solution, 0.05–0.1% chlorhexidine digluconate solution, potassium permanganate solution 1:6000–1:8000. The cover of the vesicles (bubbles) is pierced with a needle (but not cut off with scissors!) in compliance with the rules of asepsis. To eliminate acute inflammatory phenomena, aerosols containing corticosteroids and antibiotics can be used. Subsequently, solutions of aniline dyes, pastes and ointments with antimycotics (tar 2–3%, sulfur 3–10%, salicylic acid 2–3%, tincture of iodine 2%), patented antimycotic drugs naftifine, terbinafine, oxiconazole, ketoconazole, bifonazole are used etc. It is also necessary to prescribe (especially in the presence of mycids) desensitizing agents and antihistamines, sometimes sedatives. In case of secondary pyococcal infection, short-term courses of broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated [4–6].
For the erythematosquamous form of mycosis on smooth skin, it is recommended to start treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs (Mikozolon), 2% boron-tar paste, ASD paste. After the acute phenomena have subsided, you can use drugs with a mild disinfectant and non-irritating effect on the skin (Fukortsin). Usually, within a week, acute symptoms disappear, the process is transferred to a “dry” form. At this stage, you can begin to use more active antifungal therapy: 2% iodine in combination with 10% sulfur-3% salicylic ointment [4].
The follicular nodular form responds well to treatment using 2% iodine on the lesions in combination with sulfur-salicylic-tar ointment; It is advisable to prepare the latter on the basis of zinc ointment at the beginning of treatment, and later switch to a vaseline base.
The principles of treatment of dyshidrotic and intertriginous forms of skin lesions of the soles generally coincide with those for smooth skin; salicylic acid in ointments can be used in a 5% concentration. The principle of a step-by-step transition from anti-inflammatory drugs to active antifungal drugs is preserved [4].
In case of squamous-hyperkeratotic form of rubromycosis of the palms and soles, it is recommended to perform detachments of the stratum corneum according to G. K. Andriasyan under the supervision of a specialist dermatologist. After completing a series of detachments, you can prescribe one of the modern creams or Lamisil Uno solution.
Classification of modern antimycotics (means for external and internal use)
- Iodine preparations: potassium iodide - for internal use, iodine solutions - for external use.
- Antifungal antibiotics:
- griseofulvin;
- polyene antibiotics: Amphoglucamine, Amphotericin B, Levoridon, Levorin, Mycoheptin, Nystatin, Pimafucin.
- Azoles: isoconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, metronidazole, miconazole, oxyconazole, fluconazole, econazole.
- Allylamines (from the Latin Allium sativum - garlic, Allium cepa - onion): naftifine, terbinafine.
- Morpholines: amorolfine (Loceryl).
- Flucytosine (Ancotil).
- Cyclopiroxolamine (Batrafen).
- Medicines of various chemical groups (others): preparations of undecylenic acid (Undecin, Zincundan), quinosol, urea; salicylic, lactic, acetic, benzoic acids; Octicyl, Anmarin, Decamine, aniline dyes, Nitrofungin.
- Combined antifungal ointments and creams: Mikozolon, Mikospor - cream in a set, Pimafucort, Travocort, Triderm.
Based on the type of action, antimycotics are divided into fungicidal and fungistatic (although many, such as allylamines, have a combined effect). Based on the method of obtaining these compounds, natural and synthetic ones are distinguished.
There are antimycotics of a narrow (griseofulvin) and broad (itraconazole - Orungal) spectrum of action.
Literature
- Kashkin P. N., Sheklakov N. D. Guide to medical mycology. M., 1978. 328 p.
- Leshchenko V. M. Fungal skin diseases. In the book: Skin and venereal diseases (a guide for doctors). Ed. Yu. K. Skripkina, V. N. Mordovtseva. M., 1999. T. 1. P. 257–311.
- Leshchenko V. M. Laboratory diagnosis of fungal diseases. M., 1982. 142 p.
- Rational pharmacotherapy of skin diseases and sexually transmitted infections: A guide for practitioners. Under general ed. A. A. Kubanova, V. I. Kisina. M.: Litera, 2005. pp. 312–346.
- Rukavishnikova V. M. Mycoses of the feet. M., 2003. 330 p.
- Guide to laboratory diagnosis of onychomycosis. Ed. A. Yu. Sergeeva. M.: GEOTAR Medicine, 2000. 154 p.
- Sergeev A. Yu., Sergeev Yu. V. Fungal infections (a guide for doctors). M., 2003. 185–193.
- Suvorova K. N., Kuklin V. T., Rukavishnikova V. M. Pediatric dermatovenereology: A guide for postgraduate medical students. Kazan, 1996. pp. 192–312.
- Fitzpatrick T., Johnson R., Wolfe K. et al. Dermatology: a reference atlas. M.: Praktika, 1999. pp. 696–740.
- Richardson MD, Warnock DW Fungal infection: Diagnosis and Management. 2nd edit. Blackwell Science Ltd., 1997. 249 p.
A. B. Yakovlev, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor
GBOU DPO RMAPO Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia , Moscow
Contact information about the author for correspondence
Diagnosis of a rash in the groin
The variety of pathologies, which are characterized by external symptoms in the groin area on the patient’s skin, does not allow an accurate identification of the pathogen without certain types of examination.
The main types of diagnostic tests prescribed by a dermatologist include:
- scraping the top layer of skin in places where the rash is localized;
- puncture with a thin needle;
- a smear from the affected areas for subsequent microscopic examination;
- inspection of rashes using an ultraviolet lamp;
- bacterioscopy.
To obtain further information, general blood and urine tests may be required. Based on the information received, the doctor makes a diagnosis followed by a course of therapy, based on the individual indicators and characteristics of the patient.
Types of groin rash
The skin in the human groin area is a fairly sensitive area to any changes. Malfunctions in the functioning of certain organs or the reproductive system can provoke the formation of rashes of various shapes and structures.
At the diagnostic stage, an important step is to determine the type of rash:
- allergic, with redness and swelling, caused by the body’s reaction to personal hygiene products or uncomfortable underwear;
- infectious, which is accompanied by itching in localized areas and fever;
- syphilitic, can manifest itself in the groin area already in the later stages of the development of syphilis in the form of tubercles and compactions under the skin with purulent filling;
- fungal, characterized by small rashes with a white coating around the edges and swelling;
- oncological, manifests itself in the form of malignant tumors in the groin area with permanent wounds and ulcers;
- herpes, characterized by the appearance of blisters, itching and pain.
The manifestation of such symptoms should be taken extremely seriously and seek medical help without delay.
Prevention for groin rash
The best way to combat a groin rash is to prevent such manifestations. There are a number of general recommendations that are designed to reduce the risks of such a pathological process:
- regular change of underwear, which should be made from natural materials;
- compliance with generally accepted rules for maintaining intimate hygiene, which are based on daily washing of the groin area;
- do not use other people's towels and other personal items in common areas;
- do not use condoms that cause skin irritation;
- Constantly visiting a dermatologist for preventive purposes.
If you notice acne, redness or swelling in the groin, you should not hesitate to contact our clinic for the necessary diagnosis and subsequent treatment. During the period of therapy, you are required to abstain from sexual intercourse and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Cream or soap: how to properly care for the skin in intimate places?
- Use only special cosmetics for delicate intimate care. It contains natural ingredients, does not cause allergic reactions and is suitable for gentle cleansing of delicate areas. The composition of GINOCOMFORT washing gels corresponds to modern recommendations of gynecologists - GINOCOMFORT intimate cosmetics are not only suitable for daily care, but also help to maintain the cleanliness of the genitals during menstruation and during the treatment of gynecological diseases, when the body is especially vulnerable.
- If possible, wear comfortable underwear made from natural fabrics. If you want to wear erotic panties, be sure to take a shower before putting on such panties, and also change your underwear before going to bed - sleeping in thongs can increase the level of pathogenic bacteria in the vagina.
- Maintain personal hygiene: obstetricians-gynecologists recommend washing yourself 1-2 times a day, during menstruation up to 4 times a day, if possible, with each pad change.
Pads and tampons should be changed every 3-4 hours, regardless of the amount of discharge. - Pay attention to contraception: if you are allergic to latex, choose condoms made from other materials.
- Visit your obstetrician-gynecologist at least 2 times a year to rule out the development of diseases.
And remember: irritation in the intimate area, even if it just “itches” and there are no other more serious symptoms, is not the norm, and this condition is most often easy to eliminate.
There is no need to avoid the possibility of solving an unpleasant problem. The right cosmetics and treatment selected by an obstetrician-gynecologist will allow you to regain confidence in your beauty, comfort, feeling of freshness and good mood every day. Sources:
- Inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. Modern perinatal technologies in strengthening the reproductive health of patients. Naumov I.A. // Monograph. Saarbrucken: LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing GmbH end Co. KG. — 2011. — pp. 18–21.
- Microbiological characteristics of biotopes of the reproductive tract with endometritis. Glukhova E.V., Shakhovskaya I.N. // Togliatti honey. consultation – 2008. – 1 (2): pp. 38–44.
- Medical and social characteristics and forecasting of reproductive health of young women at the present stage. Torubarov S.F. // Social aspects of public health. – 2013. – 5 (33): P. 7.
- https://ciplamed.com/content/important-tips-to-maintain-intimate-hygiene
- https://www.lactacyd.eu/your-intimate-zone/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321537.php
Rash in the groin in pregnant women
During pregnancy, hormonal imbalances are observed, which contributes to the formation of rashes of various types in the intimate area of women. Such manifestations include:
- prickly heat, which is formed as a result of excessive sweating and moisturizing of the skin in the groin area;
- rashes in the form of red spots, plaques and papules, often accompanied by itching, usually go away on their own after childbirth;
- infectious manifestations in the form of purulent formations, if there is a hidden sexually transmitted disease;
- small pimples that do not cause any discomfort and are not harmful to the pregnant woman or child.
Diaper rash can also form due to increased body weight in the most sweaty areas of the body, including the groin. In such cases, a fungus may appear, which will subsequently lead to an infection followed by an inflammatory process.
Any changes or concerns should be reported at regular examinations with a gynecologist, which must be regularly attended throughout the entire pregnancy.
Rash between the legs in women: sexually transmitted infections
Sexual diseases often cause an alarming symptom - rashes in the intimate area. Pimples, vesicles, ulcers, and erythemas accompany the progression of the following sexually transmitted infections:
- Genital herpes
. This virus is present in the body of 99% of women. When the immune system is weakened, herpes type 2 actively affects the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. The woman's groin becomes covered with small whitish blisters filled with liquid. On the 2-3rd day of illness, the pimples burst, and in their place weeping ulcers form. The rash from genital herpes can last for months. Therapy helps achieve remission, but it is impossible to cure the disease. - Gonorrhea .
Affects the internal and external genitourinary tract. When infected with gonorrhea, women develop small ulcers on the mucous membranes. Often the first ulcers form on the labia minora. An ulcerative rash is accompanied by purulent vaginal discharge, itching and burning in the perineum. Sometimes a woman develops a fever. The gonorrhea rash is red and hurts when in contact with clothing; - Gardnerellosis
. This is a bacterial infection of the vulvar mucosa. The disease is accompanied by ulcerative rashes on the mucous membranes of the groin. Small ulcers cover the labia, vulva, and sometimes spread to the anus. Additional symptoms are itching, burning, swelling of the external genitalia, watery vaginal discharge. - Molluscum contagiosum
. This is a viral skin disease. Appears after infection with the smallpox virus. In this case, small nodules and compactions form on the pubic part of women, which are located singly or in groups. The skin of the genitals takes on a pink color. Seals and nodules are practically not felt to the touch. When pressing on the rash, a white liquid appears. The rash does not hurt or itch. With this disease, rashes affect the pubis, genitals, inner thighs, and anus.
Why is a groin rash dangerous?
Often, the resulting redness and other changes in the skin are symptoms of allergic reactions or infectious diseases. But in certain cases, a groin rash may indicate the development of cancer.
If the rash is accompanied by pain, itching, purulent abscesses and elevated body temperature, you should urgently seek medical help.
In our clinic, a dermatologist will perform all the required diagnostic procedures and prescribe the necessary tests in order to determine the causative agent of the pathological condition and subsequently formulate the most appropriate course of therapy.
Publication date: 2019-12-10
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Skin scraping
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Popular questions
Irritation on the pubic area under the hair.
What to do? You need to understand what caused this: an allergic reaction, a bacterial, fungal or viral infection, or an injury during depilation. For this, a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, and in some cases a dermatologist, is required. Only then will it be possible to recommend suitable treatment.
Severe itching on the labia, irritation. There is nothing to worry about in the vagina itself. What could it be?
This may result in an allergic reaction or inflammation. I recommend using Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, applying it once a day to the discomfort zone for 7 days. If you do not notice relief, consult a doctor.
I am 69 years old. I am concerned about vaginal irritation and dryness. I was treated once with Triozhinal suppositories. The result was positive for 1.5 years. Now this problem has arisen again. But now these candles cause a strong burning sensation. Today I am flying to the sea, and I am afraid that I will not be able to swim, since the salt water is making the problem worse. Please advise what I can do. Thank you! Hello! During the postmenopausal period, inflammatory processes develop in the genital tract against the background of atrophic changes in the mucosa caused by hormone deficiency. Its layers become thinner, elasticity decreases, and the number of lactobacilli decreases. In this situation, a study is required: a smear for flora, oncocytology. The first step is to prescribe drugs with anti-inflammatory activity, and the second step is to moisturize, restore microflora, and, in the absence of contraindications, local hormone-containing suppositories. A feature of treatment in this age group is continuous maintenance therapy. At this stage, before receiving the results of the study, you can use Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, which will have anti-inflammatory and moisturizing effects. The gel is applied in 1 dose 1 time per day for 10-14 days.
Hello! Is it possible to feel a burning sensation and irritation when using Gynocomfort?
Hello!
A slight tingling sensation may be felt immediately after administration, but will quickly subside on its own. If this happens, then you should continue to use the gel. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist