Causes of candidal dermatitis
Candida inflammation of the skin occurs when conditions are created for the active growth of these fungi:
- Warm and humid weather,
- Tight clothes,
- Insufficient personal hygiene,
- Rare change of underwear,
- Skin injuries
- Obesity, in which a large number of skin folds are formed, where the environment is favorable for candidal infection,
- Antibiotics that destroy beneficial bacteria on the surface of the skin, inhibit the division of fungi,
- Treatment with glucocorticoids or other drugs that affect the immune system,
- Diabetes mellitus, in which, in addition to reduced immunity, the fact that skin secretions contain a large amount of glucose also plays a role. This is a breeding ground for fungi. In case of candidal dermatitis, the doctor will definitely prescribe a blood test for glucose, so often this condition accompanies diabetes,
- Pregnancy, which changes the balance in the immune system and may impair glucose tolerance
- Diseases that reduce the immune response
- Moist skin, especially in skin folds. For example, when a person does not dry himself well enough after a shower and puts on shoes on wet feet.
Candida fungi grow and thrive in moist, warm environments. This is why this condition usually affects the skin fold area. Candidiasis is not a contagious disease. However, to people with a weakened immune system, it can be transmitted by touching the affected area of another person's skin.
Symptoms of candidal dermatitis
Symptoms usually vary depending on the area affected, but candidiasis often includes the following:
- Unbearable itching
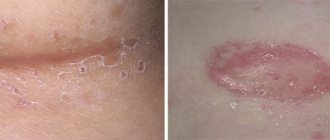
- Pink or purple-tinged spots in the affected area,
- Discharge from the affected area that appears as a white, patchy, curd-like coating that comes off easily,
- Peeling and flaking of flakes of dead epithelium,
- Skin irritation and sensitivity,
- Persistent redness
- Maceration is a change that occurs to the skin from prolonged exposure to liquid. The epithelium becomes saturated, swells and becomes loose, light and soft in appearance,
- Around the affected area, pustules and pimples are formed, filled with cheesy purulent discharge,
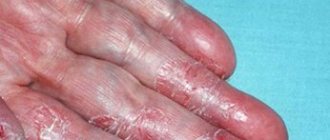
- Cracks in the epithelium, especially pronounced if the areas between the fingers are affected,
- In rare cases, deep subcutaneous ulcers develop, from which a fungal culture is cultured.
Candidal dermatitis is often accompanied by the spread of infection to the mucous membranes. It is characterized by the appearance of painful jams in the corners of the mouth, which are very difficult to cure. The mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue may be affected, on which a white, cheesy coating forms.
Inflammation of the nail bed is also often caused by these microorganisms. Typically, the microflora combines fungi and bacteria. This is a chronic infection in which the area around the nail becomes swollen, red and painful, the color of the nail changes, and the nail may become deformed and peel off. As a result of chronic paronychia caused by Candida, the nails take on strange shapes and can change color, as well as become dystrophic, thinner or, conversely, thicken. Conditions predisposing to candidiasis paronychia include an excess of adrenal hormones and Raynaud's syndrome, a disease manifested by impaired blood flow in the fingers.
There are also several rare forms of candidal dermatitis, which occur in adults and children and are usually severe and less treatable than ordinary candidiasis.
- Common cutaneous candidiasis is a disease in which, spreading from one focus, fungal inflammation covers large areas of the skin, perineum, arms and legs, including hands and feet, as well as the entire surface of the body.
- Candidal granulomas are large, dry, wart-like rashes that form in chronic dermatitis. When examined under a microscope, Candida fungi are found in keratinized epithelial cells.
- Disseminated candidiasis is a condition in which an infection located inside the body, when it weakens, spreads to the skin, forming candidal dermatitis. Candida spreads hematogenously, that is, through the blood to the skin.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor conducts an examination, takes a smear from the site of the lesion, which is treated with potassium hydroxide, stained and examined under a microscope - Candida yeast fungi will be visible in it.
Candidal dermatitis in a child
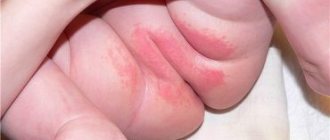
Candidal dermatitis occurs in childhood, is especially common in infants, has a characteristic localization (see photo), and when it appears, immediate treatment is required. At an early age, candidal dermatitis affects the inguinal folds and the area between the buttocks, especially when using reusable diapers and when the child rarely changes them, constant humidity and heat in this area are the causes of fungal growth and inflammation (as shown in the photo), and treatment is carried out first It’s all about following the rules of hygiene.
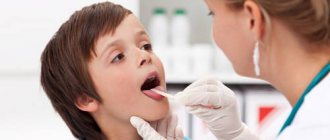
In addition to the complication of diaper dermatitis, this fungus often affects the tongue, cheeks, and can spread to the esophagus. A cheesy white coating forms against the background of reddened mucous membrane, which is easily removed with a spatula. Erosions and ulcers may form. This inflammation can be very painful. This leads to a disruption in general well-being, the baby has difficulty swallowing, he worries, cries, loses appetite and sleeps poorly.
Also, children sometimes experience sinusitis caused by candidiasis. Lesions of the external auditory canal with the release of a cheesy discharge from the ear are also common.
In rare cases, congenital candidiasis occurs - this condition is accompanied by a rash throughout the body, enlarged liver, sepsis, and respiratory distress.
Symptoms in infants include:
- Severe and persistent diaper dermatitis,
- Skin rash that resembles eczema
- White or yellow spots on the tongue or the inside of the mouth and cheeks,
- Colic and abdominal pain for longer than one month,
- Recurrent ear infections
- Symptoms are worse in wet weather.
In older children, signs of chronic candidal infection include:
- Constant craving for sweets
- School skills disorders
- Frequent irritability and bad mood,
- Frequent ear diseases
- High indoor humidity or humid weather worsens the condition.
Candidal dermatitis in an adult
Candidal dermatitis in adults, unlike children, develops more often in the armpits, inguinal folds, under the mammary glands, less often between the fingers and in the folds of the skin in obesity (as shown in the photo), and in this case, treatment also consists of eliminating provoking factors and the use of antifungal drugs.
In bedridden patients, dermatitis caused by these fungi develops on the back.
Cases have been described in which candidiasis developed under the ring on the finger in patients with reduced immune system function.
In young mothers who are breastfeeding, an inflamed nipple with very severe soreness can also be caused by candidiasis. This makes feeding the baby much more difficult. The infection is most often transmitted from the baby's mouth, especially if he has candidiasis of the oral mucosa. Some researchers believe that cutaneous candidiasis is the main cause of nipple pain associated with breastfeeding.
The mechanism of development and features of candidiasis in infants
Candidiasis manifests itself as a white coating
As noted earlier, no one is immune from thrush or, scientifically, candidiasis. This state of affairs is not difficult to explain, because the provocateurs of this pathology can exist quite peacefully in the body of any person.
Why? All because of their conditional pathogenicity. If the human body is in good shape and is able to organize its high-quality defense, then the activation of Candida fungi will not occur. But as soon as it gives the slightest glitch, the unfavorable microflora is activated, begins to actively multiply and literally “eat” healthy tissue.
Fungal microorganisms can and often do live in all parts of the human body. The largest accumulation of candida microflora can be found in:
- oral cavity;
- intestines;
- genital area.
As a rule, the activation of fungi in one area entails the unfavorable activity of their “brothers” in another part of the body. In infants, candidiasis is an inflammatory disease that develops either in the mouth, or in the groin area, or both.
Many parents are interested in “Where could their child, seemingly born quite recently, pick up fungal microflora?” In fact, anywhere. Often, Candida fungi are transmitted to children at birth and live in their bodies for the rest of their lives.
Naturally, only with the activation of unfavorable microflora does the development of pathology and its accompanying manifestations take place.
Treatment of candidal dermatitis
Treatment for candida skin infections is usually quite simple. If the immune system works well and the infection does not spread to internal organs, hospitalization is not required. The doctor will usually prescribe a drying agent along with antifungal creams, ointments, or lotions to apply to the affected skin. Sometimes medications in tablets are needed.
Treatment of candidal dermatitis with medications
- The topical antifungals most often prescribed to treat candidal dermatitis are ketoconazole or clotrimazole. They are used topically and have very few side effects.
- Fluconazole is an oral tablet that is used when topical treatments are ineffective. It is quite safe, there are few adverse reactions to it, and sometimes one dose is enough to fight the infection.
- Nystatin and amphotericin B are more powerful drugs that are used intravenously for a common infection in a hospital setting.
Most medications are used twice daily. Some medications (such as miconazole and clotrimazole) are safe in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Side effects include:
- Itching at the application site,
- Redness and burning sensation in the area of application,
- Headache,
- Upset stomach and indigestion,
- Skin rash.
Intravenous antifungals cause more severe effects:
- Loss of appetite,
- General weakness
- Stool disorder
- Pain in muscles and joints,
- Various types of rashes.
In rare cases, these drugs cause dangerous allergic reactions or severe skin damage with the death of the epithelium and the formation of blisters like a burn.
Patients with liver disease should not use antifungal agents without medical supervision. They cause liver damage and, if used uncontrolled, can lead to liver failure.
Medicines that, when used simultaneously, can react with antifungals and change their activity:
- Rifampin, an antibiotic
- Benzodiazepines, which are prescribed to improve sleep and reduce anxiety,
- Estrogens and progesterones, which are contained in oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy,
- Phenytoin, which is sometimes prescribed for epilepsy.
- Among drying agents, the most effective and inexpensive is zinc oxide, which has virtually no contraindications or adverse effects. This remedy can even be used in infants with diaper dermatitis caused by fungi.
- Fukortsin is another drug that has a drying, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. This is an aqueous solution of fuchsin, it has a bright pink color, it is recommended for use in acute cases of the disease. It is not advisable to use it in children due to some toxicity.
- A weak solution of apple cider vinegar may be useful as an additional remedy for acute dermatitis in adults.
- Benzoyl peroxide has shown effectiveness in subacute cutaneous candidiasis.
- It is also recommended to cover the affected area with bandages as little as possible, try to keep it open, and ensure that there is no weeping or rubbing of the skin.
How to treat diaper dermatitis and what are the methods of prevention
How to treat diaper dermatitis and how to minimize the risk of their occurrence? The methods are the same - adhere to the following rules:
- Change your diaper regularly.
A wet or dirty diaper should be changed as quickly as possible. Too much contact with urine and feces irritates the skin. Regular diaper changing is a key condition for the treatment and prevention of diaper rash.
- Use diaper cream.
Consult your pediatrician about which cream he recommends using. Diaper cream creates a protective barrier against moisture and helps prevent diaper rash. Apply the cream in a thick layer.
- Clean the skin under the diaper thoroughly with mild products.
Use fragrance-free and alcohol-free wet wipes. You can also wash your baby with water and baby detergent (not containing soap). If diaper dermatitis has already appeared, then wash the baby with running water without using special products. Don't rub diaper rash. After completing the hygiene procedures, pat the skin dry with a towel and give your baby an air bath. Before putting on a clean diaper, apply a thick layer of barrier cream to your baby's skin.
- Use
the correct size diapers .
A diaper that is too tight does not allow the skin to breathe and can also cause chafing. If the diaper fits correctly and your baby has a diaper rash that you are treating, try using looser diapers until the diaper rash goes away. - Arrange air baths.
When possible, let the baby lie down with his bottom bare. For example, you can use an absorbent diaper or towel when placing your baby on his tummy.
For your convenience, we have made a reminder about diaper dermatitis:
When to see a doctor
Contact your doctor if:
- After two or three days of treatment, the baby's diaper rash did not improve.
- In addition to diaper rash, there are also pimples, blisters, and pus-filled sores that become weepy or crusty.
- The child is treated with antibiotics and develops a bright pink or red rash with red dots around the edges.
- The rash is very painful (if you touch it).
- In addition to the rash, the child has a fever.
What can a doctor recommend?
If diaper rash does not go away or gets worse, your doctor may prescribe a special ointment or cream, such as:
- topical preparation based on hydrocortisone or steroids;
- a topical agent with an antifungal effect (in case of fungal infection);
- oral antibiotics or topical antibacterial ointment (in case of bacterial infection).
Treating diaper dermatitis with home remedies
Some studies have shown that the following may be effective for treating diaper rash:
- zinc cream;
- aloe vera;
- calendula.
If you want to try treating baby diaper rash with home remedies, consult your doctor first.
| In brief The first and most important rule for preventing diaper rash is to change the diaper as soon as the baby poops. Clean the diaper area thoroughly but gently and use barrier cream every time you change the diaper. Use high-quality, absorbent diapers and let your baby go naked whenever possible. If you follow these measures, but diaper rash still appears and does not go away, consult your pediatrician. |
FAQ
- In most cases, mild diaper rash in a baby will go away within a few days if:
- change the diaper regularly;
arrange air baths for the area under the diaper;
- use protective cream under the diaper.
Prevention of candidal dermatitis
Tips to help prevent candida dermatitis include the following:
- Wear clothing made from athletic material that wicks moisture away from the body and helps keep skin dry.
- Keep your armpits, groin folds and other parts of the body that are prone to candida infections dry.
- Always shower and dry thoroughly after exercise or if you become sweaty.
- If you are overweight or obese, always keep your skin folds dry, wipe them often, use powder,
- In warm weather, it is preferable to wear open shoes rather than sneakers.
- Change your socks and underwear regularly
- If you have diabetes, it is important to control your blood sugar levels very closely. Hyperglycemia, in addition to other complications, leads to cutaneous candidiasis,
- Losing weight and maintaining optimal body weight is an important measure in the prevention of candidiasis. A person with normal nutrition has a reduced number of skin folds and areas of friction between skin areas. These people are also less likely to develop diabetes, an important underlying condition for thrush.
What is diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis occurs when your baby's delicate diaper skin comes into contact with urine or feces for too long. As a result, diaper rash appears. Diaper rash in children looks like red, inflamed, flaky areas of skin. With proper treatment, diaper dermatitis resolves within three to four days. But if newborn diaper rash does not go away within a few days or gets worse, consult a doctor. The main rule for preventing film dermatitis is to change the diaper regularly.
| In Brief Diaper dermatitis is common. Sooner or later, all parents encounter them. Diaper rash in children is inflamed areas of skin under the diaper. After the baby has pooped, you need to change the diaper immediately - this reduces the likelihood of diaper rash. If your baby's diaper rash does not go away, consult your pediatrician. |