Types of allergies in children
There are many types of allergic reactions, depending on the clinical picture and the group of substances that cause the pathology. The most common of them:
- respiratory (breathing) allergies;
- contact (skin) allergies;
- food allergies;
- insect allergy (reaction to contact with insects and their bites);
- drug allergies;
- infectious allergy;
Every year there are more and more children with allergic manifestations. Currently, the pathology is diagnosed in 25-30% of the population. If allergies are not treated, the child may experience serious complications: asthma, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock, loss of consciousness, etc.
Symptoms of allergic reactions
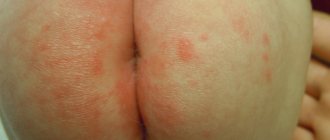
- Skin rashes or irritations. Manifest in the form of redness, itching, spots, peeling. Rashes from food or contact allergies often resemble insect bites or nettle stings.
- Difficulty breathing. A runny nose, coughing, and sneezing are the most common allergic reactions to dust, pollen, and animal dander. Allergens cause irritation of the nasal or bronchial mucosa.
- Conjunctivitis. Redness, itching, and watery eyes often occur upon contact with household chemicals, cosmetics, pollen, dust, and wool.
- Difficulty in digestion. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting - a reaction to food allergens.
- Anaphylactic shock. The most dangerous manifestation of allergies. Shock can be caused by insect bites, medications, and certain foods (for example, nuts). An allergy sufferer's skin turns red, breathing becomes difficult and the heart rate increases. Loss of consciousness and convulsions are possible. You must call an ambulance immediately!
Symptoms similar to allergies can hide various diseases, so professional diagnosis is indispensable. The presence of allergies is confirmed by skin tests or blood tests. Do not delay your visit to the doctor in order to prescribe a course of treatment as soon as possible and avoid complications.
Allergy symptoms
The clinical picture of an allergic reaction directly depends on the type of pathology and the location of the pathological process.
Manifestations of skin allergies in a child include various types of rashes:
- redness of skin areas;
- the appearance of a rash;
- peeling of the skin;
- itching
This type of allergy is most common in infancy, but can persist into adulthood.
Manifestations of allergic rhinitis and hay fever:
- impaired nasal breathing, nasal congestion;
- watery nasal discharge;
- sneezing;
- itching in the nose area;
- lacrimation.
Manifestations of allergic conjunctivitis:
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- redness of the whites of the eyes;
- profuse lacrimation;
- a feeling of stinging in the eyes (or a feeling of “sand”);
- photophobia.
At what age can a child develop allergies?
A common manifestation of allergies in children under 2 years of age is atopic dermatitis, which is called “infantile” dermatitis. Often, after 2 years of age, children “outgrow” this disease and the problem goes away.
Asthma can be diagnosed at any age. If asthma is atopic in nature, then allergy testing and exclusion of contact with allergens is very important. If the trigger for asthma is an infectious process, then the possibility of such a child continuing to attend kindergarten must be considered, and an immunological examination is carried out.
In children 4-5 years of age and older, allergies are often expressed in the form of allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis.
This is especially true if parents or older children in the family have a similar problem, i.e., a hereditary predisposition. It is important for parents to know that experts always consider allergic rhinitis as asthma.
Sometimes allergies can manifest as recurrent bronchitis. If a child has more than 3 bronchitis during the year, then it makes sense to visit an allergist. The specialist will prescribe the necessary examination and, if necessary, select the optimal treatment regimen.
Food allergies can occur at different ages. Most often, provocateurs are foods such as milk, eggs, fish, and nuts. The disease can be very dangerous. With an acute systemic allergic reaction, children are often admitted to the hospital.
In case of food allergies, consultation with an allergist-immunologist, thorough diagnosis and selection of nutrition are required. Parents of such children in emergency situations should be able to provide emergency assistance. Abroad, the drug Epipen in syringe pens is used to relieve severe allergic reactions. It has not yet been registered in our country.
Acute allergic reactions in children
Parents also need to know the signs of serious conditions that occur as a result of allergies in a child: Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock and bronchial asthma.
With Quincke's edema, swelling of the skin and mucous membranes suddenly develops. The most dangerous is swelling of the throat mucosa, which is manifested by difficulty breathing, hoarseness of the voice, a strong barking cough and clouding of consciousness (due to lack of oxygen). Anaphylactic shock can be identified by a drop in blood pressure, pale or bluish skin, bronchospasm, and loss of consciousness. Bronchial asthma is diagnosed based on the following symptoms: cough with difficult to separate sputum, whistling or wheezing when breathing, shortness of breath (predominantly exhalation is difficult), oxygen starvation of the body, attacks of suffocation.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of allergic reactions, it is necessary to closely monitor the child’s diet and his household environment.
- If a nursing mother has any allergy symptoms, it is important to regularly visit a doctor and follow a diet. It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that are potential allergens, for example: milk, honey, chocolate, nuts, seafood, citrus fruits, cereals, as well as products with flavorings and flavor enhancers.
- If breastfeeding is not possible, you should entrust the choice of infant formula to a specialist.
- If a child’s allergy has already been identified, limit contact with the allergen and eliminate potentially dangerous foods from the diet.
- Regularly carry out wet cleaning, vacuum the furniture and prevent the formation of mold.
- Do not skimp on hygiene products for children and household chemicals. Choose products marked “hypoallergenic”.
- Get rid of excess dust “accumulators”: carpets, soft toys, heavy curtains.
- Replace synthetic bedding with natural cotton. Pillows, mattress and blanket should be hypoallergenic.
- Maintain room humidity at least 50%.
- Don't smoke in front of your child!
- In case of seasonal allergies to pollen or tree fluff, it is recommended to ventilate the room only after rain. A good solution would be to install an air conditioner.
- Be careful when letting your child try new foods. Update your diet gradually, in small portions.
Be sure to keep antihistamines in your medicine cabinet, but refrain from choosing your own medication! Entrust this important task to your doctor.
Take care of your child’s health, but don’t worry if an allergy does show up. This diagnosis does not interfere with comfortable development - just avoid allergens and follow the recommendations of a specialist!
Causes of allergies in children
The reason for the development of allergic reactions is the penetration of allergens (irritant substances) into the child's body. Substances can enter the body in three ways:
- Oral – when consuming food, various drinks.
- Respiratory - when inhaling an allergen in the air (for example, plant pollen).
- Contact – in direct contact with the allergen.
In childhood, allergies most often occur when the body comes into contact with pollen, animal hair, certain medications, insects, cleaning and detergent chemicals, as well as highly allergenic foods (whole cow's milk, eggs, nuts, chocolate, honey, etc. ).
Why exactly allergies develop is still unknown to scientists. However, there are factors that significantly increase the risk of this pathology:
- Hereditary factor.
- Exposure to frequent infectious diseases.
- Poor environmental conditions in the region of residence.
- The desire of parents to create “sterile conditions” for their child to live.
- Too early introduction of complementary foods, early refusal of the mother to breastfeed.
How to distinguish symptoms of food allergies in infants from signs of other diseases
There was an allergy, but now it is gone... How to find out if a baby has a food allergy - after all, it can easily be mistaken for another disease - and what can be done to prevent the disease from returning? Alla Anatolyevna Shcherbakova, pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category and deputy head of the children's hospital on Savelovskaya, talks about the treatment of children with allergies, the unobvious danger of red cheeks and how to avoid chronic allergies.
— Alla Anatolyevna, what is a food allergy?
— Food allergy is intolerance to a food product. It manifests itself as a pathological reaction with immune mechanisms at its core. In children of the first year of life, allergies are often caused by cow's milk protein and complementary foods. The onset of food allergies usually occurs in the first weeks and months of life.
— What do the manifestations of food allergies look like in infants and what are the symptoms of the skin form?
— The cutaneous form (atopic dermatitis or diathesis) is the most common manifestation of food allergies in young children. It is expressed in the form of dryness, redness, and weeping. Localized on the cheeks, extensor surface of the elbow joints, knees, shins, and other external surfaces. An experienced doctor, based on just one examination, can say that a child has a food allergy.
Children in the first months of life with diathesis do not experience itching and the skin does not itch. In children of the second half of life and older, atopic dermatitis is manifested by itchy skin.
— Small pimples and peeling on the face of a baby - is this a food allergy or not?
— It’s a rather difficult question; it’s often asked by mothers at receptions. For children in the first days and first weeks of life, it is possible that such manifestations are not allergies. In the first month, the skin is populated by microbes, a microbiota different from the mother’s. And if isolated rashes are noticeable around the nose and mouth in the nasolabial triangle, this could be newborn acne or the so-called “bloom”. It is quite difficult to distinguish it from a food allergy. And since allergies are so common, doctors are very wary of food allergies. With skin rashes, a small patient should be given a second appointment, monitor them dynamically and track the problem - what it really is.
— How else do allergies manifest themselves in children?
— The gastrointestinal form of food allergy manifests itself in the gastrointestinal tract. This is an allergic, non-bacterial inflammation, which is accompanied by vomiting, regurgitation, insufficient weight gain, rumbling in the stomach, mucus and blood in the stool, flatulence, and pain during feeding. Some researchers believe that infant colic in children in the first weeks of life is a manifestation of food allergy.
- “Accumulative allergy” - what is this phenomenon?
- In adults, allergies are usually of the immediate type - they ate something, and immediately there was a reaction - hives, itching, Quincke's edema, swelling of the face or mucous membranes.
In children, allergies are often cumulative, of a delayed type, which do not appear immediately. Some doctors call such an allergy false, because it is “silent” until the moment when the number of allergens in the body becomes critical, and it fails with pronounced symptoms. Cumulative allergies appear more often from birth, but which allergen caused it is difficult to determine, because there is no clear connection.
— What to do if there is an allergic reaction?
— If you have any complaints, it is better to consult a doctor. Food allergies in infants are the same disease as others, so patients with food allergies should be monitored and treated by a specialist.
The main method of treating food allergies is an elimination diet with the exclusion of a fundamentally possible allergen - cow's milk protein - from the child's diet.
When artificially feeding a child with signs of food allergies, a medicinal mixture is prescribed. When breastfeeding, the mother is prescribed a dairy-free diet. The result of an elimination diet is not immediately noticeable - to remove the allergen from the body, mother and child need time, so the duration of a dairy-free diet is 1-1.5 months. If during this period the child continues to have complaints, the question of continuing breastfeeding and prescribing special therapeutic nutrition is raised. A child with a food allergy should not be given complementary dairy products until one year of age.
— How does food allergy go away in infants? How long does it take?
- Differently. For some infants, after a month of following the diet by the nursing mother. It happens that food allergies go away at 13-14 years of age or earlier, at 6-7 years of age, when the child begins to attend school. It all depends on the patient and the type of allergy, but when examining a child, it is very difficult to make a prognosis.
— Alla Anatolyevna, how to distinguish food allergies from other types of childhood allergies?
— In children of the first year of life, the lion's share of allergies is food. Contact dermatitis is noticeable on the skin. For example, put a T-shirt on the baby powder that mom used to wash her clothes, and redness will appear in the area of the T-shirt. If a child in the second half of life has itching and rashes on the cheeks and elbows, then most likely he has a food allergy.
— What diseases can food allergies be confused with?
— It all depends on the form of the allergy. Skin allergies can be confused with newborn acne, and in older children, an itchy rash can be mistaken for scabies. The gastrointestinal form of allergy can be confused with intestinal infection and rare forms of gastrointestinal diseases (celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, antibiotic-associated diarrhea). Therefore, in some cases, differential diagnosis of diseases should be carried out.
— How quickly does a child’s body “adapt” to an allergen and when should you start helping him?
— If your child has any complaints, it is better to consult a doctor. There is no need to wait: the longer a child is in an exacerbation of food allergies, the higher the risk of developing long-term long-term manifestations. Chronic inflammatory allergies will not go away unless the intake of the allergen from food stops. The so-called “atopic march” will occur - when the allergy begins in infancy as an atopic reaction, but over time its place is taken by “adult” manifestations of the disease - bronchial asthma, neurodermatitis, eczema, hay fever, seasonal runny nose, intolerance to animal hair. And it is much more difficult to fight them.
The longer the child is in good condition, with clear skin, without exacerbation and manifestations of food allergies, the more favorable the prognosis - the child will have a way out of food allergies, and provocations may go better.
Food allergies are common in young children. Skin rashes, vomiting, regurgitation, insufficient weight gain are reasons to consult a doctor. Such symptoms indicate a food intolerance, and the child will most likely be prescribed food allergy treatment. Treatment can be lengthy and depends on how timely and correctly the baby’s nutrition is selected.
Pediatrician Alla Anatolyevna Shcherbakova
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
Diagnosis of allergies
If a child is suspected of having an allergy, parents should definitely show the child to an allergist.
The purpose of diagnosis is not only to identify pathology, but also to determine the cause of its development, i.e. identify the allergen that causes an increased immune response. To do this, the doctor examines the small patient, talks with him and his parents, collecting an anamnesis (medical history). Then the child is sent to undergo various studies:
- Blood test - to measure the amount of antibodies (allergies are indicated by a significant increase in the concentration of class E immunoglobulins).
- Skin allergy tests to determine irritant allergens (prick test, scarification test, patch test, provocative test).
- Determination of external respiratory function (to exclude bronchial asthma or allergic bronchitis).
In accordance with the data obtained during the diagnosis, the specialist selects the most suitable treatment tactics for each child.
Allergy treatment
The most effective way to combat allergies is to exclude your child from contact with allergens. The child should be protected as much as possible from exposure to irritating factors (contacts with chemicals, dust, tobacco smoke, etc.).
In the acute period, children are prescribed treatment depending on the type of allergy, its causes and main symptoms:
- Taking antihistamines to relieve manifestations of pathology.
- Applying anti-inflammatory and antipruritic ointments, creams or gels to the skin to relieve irritation, itching and burning.
- The use of hormone-containing drugs for pronounced manifestations of allergies (usually in the form of creams or ointments).
The SM-Doctor clinic for children and adolescents actively uses a modern method of treating allergies - allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT). The essence of this technique is to administer to the child a special allergy vaccine containing microdoses of an allergen substance. Over time, the volume of the drug is gradually increased, thereby training the immune system to correctly respond to the irritant substance. By the end of the course of treatment, the child’s body tolerates contact with allergens much more easily. And in 90% of cases, therapy helps to completely get rid of allergy symptoms.
Clinical researches
TM La-Cri products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. Clinical studies conducted by specialists have proven the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products, including for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Sources:
- Fokina R.A., Atopic dermatitis: stages of development of classification forms, Siberian Medical Journal, 2007
- A.N. Pampura, A.A. Chuslyaeva, Modern approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
- N.L. Rybkina, Modern approaches to newborn skin care: pediatrician tactics, journal Bulletin of Modern Clinical Medicine, 2014
- I.I. Ryumina, V.V. Zubkov, Newborn skin care, Healthy Child magazine, 2017
Photos of allergies in children
Photo album on the disease
Allergy prevention
The modern world is considered very allergenic.
Therefore, parents must adhere to a number of rules that can prevent the development of an inadequate response of the child’s immune system to external or internal environmental factors. This is especially true for children with a family history. Prevention measures are:
- long-term continuation of breastfeeding, refusal to use infant formula;
- correct introduction of complementary foods;
- refusal to consume products containing preservatives, dyes, flavors and other synthetic substitutes;
- eating simple natural foods (meat, seasonal vegetables and fruits, cereals), avoiding complex multi-ingredient foods (sausages, industrial sauces, cakes, etc.);
- use of hypoallergenic personal hygiene products.
Complications of allergies in children
In the absence of medical care and preventive measures, the allergic process can cause unpleasant complications. Most often, parents of young patients face the following problems:
- frequent headaches associated with constant nasal congestion;
- fatigue, drowsiness, deterioration in school performance;
- scratches on the skin that can become infected;
- eye infections due to allergic conjunctivitis;
- life-threatening conditions (acute reactions): angioedema, anaphylactic shock, etc.
If you keep the process under control, minimize contact with allergens and take medications prescribed by your doctor in a timely manner, these complications can be avoided.
Atopic dermatitis in children
Unfortunately, many children experience the first manifestations of skin allergies at an early age. It's not always possible to understand why. It seems that the parents are doing everything right: they don’t let them eat “chemicals”, they take care of the skin, they bathe the baby, they introduce complementary foods correctly, but the child has itching and rashes.
So what is “atopic dermatitis” or, as it is often called in older children, “neurodermatitis”. How to defeat him?
What is atopic dermatitis? Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease caused by various factors, in which the child is bothered by itching.
Typically, atopic dermatitis begins in early childhood, can continue or recur in adulthood, and significantly affects the quality of life of the patient and his family members.
Most often, if a child has allergies, then someone in the family has allergies. If both parents suffer from allergies, then, unfortunately, in 82% of cases the child will also have atopic dermatitis.
What happens in the skin during atopic dermatitis: With atopic dermatitis, immune inflammation occurs in the child’s skin, which is accompanied by an increase in its sensitivity to external and internal factors affecting the skin.
Also, with this disease, the protective barrier of the skin is disrupted, which leads to the penetration of allergens through the skin. The amount of fats (lipids) in the skin decreases, which leads to dry skin and itching.
How do doctors diagnose Atopic Dermatitis?
First of all, when examining the child and asking the parents in detail, and only then, based on the results of an allergological examination.
Unfortunately, objective diagnostic tests that can confirm the diagnosis 100% do not currently exist.
Signs of atopic dermatitis:
- Itchy skin
- Typical rashes and their location:
- children of the first two years of life: red spots, spots, weeping skin, most often on the face and less often on the legs and thighs. - older children (2-12 years): severe dry skin, thickening of skin folds, scratching on symmetrical areas of the skin, more often on the flexor surfaces of the limbs, for example, in the elbows or under the knees.
- Early age of onset of allergic rash, most often before one year
- Usually, someone in the family has or has had allergies
- Once allergic rashes appear, they do not go away for a long time
There is also such a non-obvious symptom as “white dermographism”. If you run your finger over the skin of a child’s abdomen, after a while white stripes will appear in the place where the finger touched the child’s skin, which do not immediately disappear.
And yet, what tests can be taken to understand the causes of allergies in a child?
- Clinical blood test
- Skin tests with standardized allergens (they are also called prick tests, skin prick tests). Skin testing is carried out by an allergist when there is no exacerbation of atopic dermatitis in a child, that is, there are no skin rashes and the child is not itching. If a child is taking antihistamines, they must be discontinued at least three days before the test, otherwise the result may be unreliable.
- It is recommended to determine allergen-specific immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE antibodies) in blood serum. They are also called “allergens”. Using them, you can understand what foods or household factors your child is allergic to, but, unfortunately, they are not always 100% accurate.
What are the manifestations of atopic dermatitis in children like:
There are many skin diseases that allergy rashes in a child may resemble. Here are some of them:
- scabies
- seborrheic dermatitis
- allergic contact dermatitis
- ichthyosis
- psoriasis
All diseases are different and are treated differently.
Therefore, in addition to an allergist, children with regular manifestations of skin allergies should be consulted by a dermatologist.
Treatment There is an opinion that following a low-allergen diet will clear the skin and the itching will go away. This is not entirely true. Treatment must be comprehensive.
There are several areas of treatment and they are all important:
1. Elimination diet 2. Hypoallergenic regimen 3. Proper skin care 4. Taking antihistamines and antibacterial drugs 5. Psychotherapy
Elimination (hypoallergenic) diet
Of course, it is important to identify what foods your child is allergic to. And then, by removing these foods from the diet, you can reduce the manifestations of atopic dermatitis. Please note that it is precisely to reduce, and not to stop altogether, the manifestations of allergies, since a low-allergen diet is important not on its own, but always in combination with proper skin care, which we will discuss below.
But identifying what you are allergic to is often very difficult. Both from laboratory tests and from observing what foods a child eats, it can be difficult to understand what the child is allergic to. In such cases, a so-called hypoallergenic diet is recommended. Foods that can cause an exacerbation of allergies in most people with allergies are excluded from the diet.
Not recommended for use:
- Citrus
- Seafood
- Rich broths
- Processed meat products
- Mayonnaise, vinegar, mustard
- Radish, horseradish, radish
- Spices
- Whole milk
- Honey
- Strawberry
- A pineapple,
- Melon,
- Sweet carbonated drinks,
- Nuts
Hypoallergenic mode
Reducing a child’s contact with an allergen can hardly be overestimated, which is why it is so important to follow household rules. In most cases, it is impossible to completely eliminate contact with the allergen, but as a result of following the recommendations, contact with it is significantly limited, which means that the course of the disease is alleviated and the need for medications is reduced.
Here's what you need to do - the information below is presented by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, that is, it is official and truthful:
1. regularly wash bedding (1-2 times a week) at a temperature above 56°C to kill mites (washing with cold water reduces mite allergens by 90%, and washing with hot water destroys mites) 2. wash pillows and blankets with hot water more than 56°C and mattress covers (covers) made of mite-proof fabric 3. remember that good ventilation of the home reduces humidity, reducing the humidity in the house to 40% is important for controlling the number of mites and fungi
Additionally:
1. use vacuum cleaners to clean your home (preferably with a HEPA filter) 2. use special napkins to remove dust 3. to ensure better conditions for cleaning, it is advisable to replace carpets and rugs with linoleum or parquet 4. it is better to change curtains in the bedroom with washable blinds 5. replace fabric-covered furniture with leather or vinyl 6. remove soft toys from the bedroom; if necessary, they can be washed in hot water (over 56°C) or frozen in the freezer of a home refrigerator to kill ticks 7. considering, that house dust mites are sensitive to direct exposure to sunlight, you can dry mattresses, carpets, rugs in the sun for at least 3 hours (taking into account regional characteristics) 8. In addition, special means can be used to destroy house dust mites - cleaning wipes, aerosols, anti-mite bedding, sprays, washing powders, anti-mite carpet cleaners (based on benzyl benzoate - acaricides), anti-mite cleaners for cleaning vacuum cleaners, etc. 9. To achieve the desired result, an integrated approach is important, since most elimination measures applied individually turn out to be unprofitable and ineffective 10. Important! It must be remembered that allergen-free animals do not exist. It is better to take radical measures - part with pets and not get new ones. After removing the animal from the apartment, it is necessary to carry out repeated thorough cleaning of the room to completely remove traces of saliva, excrement, dander, and animal hair. Cat allergens persist in the living room even after the animal is removed for a long time (about 6 months)
Besides:
1. Carpets, mattresses and coverings should be subjected to regular vacuum cleaning; change clothes when leaving home if there was contact with a pet 2. do not visit the circus, zoo and houses where there are animals 3. do not wear clothes made of wool or animal fur
It is also necessary:
1. limit as much as possible contact with environmental factors that cause exacerbation of the disease 2. ensure optimal room humidity (40%) 3. maintain a comfortable air temperature 4. use indoor air conditioning in hot weather 5. do not use synthetic fabrics or wool clothing , preference is for cotton fabrics 6. ensure a calm environment at school and at home 7. cut your nails short 8. during an exacerbation, sleep in cotton socks and gloves 9. do not prohibit bathing! do not use hot water for showers and/or baths; water procedures should be short-term (5-10 minutes) using warm water (32-35°C) 10. use special skin care products for atopic dermatitis (so-called emollients) constantly, even when the skin is “good” 11. for when washing, use liquid rather than powder detergents 12. minimize contact with allergens that cause aggravation of the disease, as well as irritating substances 13. in sunny weather, use sunscreens that do not cause contact irritation of the skin 14. after swimming in the pool, you must take a shower and apply moisturizer 15. completely follow the doctor’s instructions
Not worth it:
1. use alcohol-containing hygiene products 2. use products with antimicrobial components without the recommendation of the attending physician 3. participate in sports, as this causes intense sweating and is accompanied by close contact of the skin with clothing 4. take water procedures too often 5. intensively while washing rub the skin and use tools for washing that are harsher than a terry cloth washcloth
To achieve the desired result, an integrated approach is important, since most elimination measures applied individually turn out to be unprofitable and ineffective.
Proper skin care
The goal of proper skin care is to relieve itching by restoring the water-lipid layer and barrier function of the skin.
1. Local glucocorticosteroids
In case of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, to quickly alleviate the child’s condition, it is recommended to apply so-called local glucocorticosteroids to the areas of allergy.
2. Calcineurin inhibitors These drugs are recommended to be applied to the skin of a child when atopic dermatitis often worsens, the exacerbations do not subside for a long time, and the child is constantly bothered by itching and irritation of the skin. These drugs are prescribed only by a doctor.
3. Moisturizers and emollients
They are called "emollients". They do not contain hormones or parabens. These products nourish and moisturize the skin, reduce dryness and reduce itching.
It is important to apply them to the skin daily, at least twice a day, even when the skin is smooth, without allergies and without itching.
Emollients are selected individually by parents, on the recommendation of a doctor, so that the child finds their texture pleasant; for some children, it is important that the emollient does not have any odor.
To cleanse the skin, it is advisable to use daily short cool baths (10 minutes) with a soft detergent base with pH 5.5, which does not contain alkali. When cleansing the skin, do not rub it. After bathing, it is recommended to only blot the surface of the skin without wiping it dry.
And it is more effective to use bathing products of the same brand as the emollient. Then they reinforce each other.
Taking antihistamines and antibacterial drugs
1. Antihistamines, or as they are also called, antiallergic drugs, reduce itching. They are prescribed by a doctor.
2. Taking antibacterial drugs Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) often grows on the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, which increases the manifestations of allergies. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs in the form of cream/ointment or in the form of syrup, which the child takes orally.
Psychotherapy
Working with a psychotherapist and a psychologist is also important. These specialists teach the child techniques for relaxation, stress relief and behavior modification. But these methods are only suitable for older children.
What's next?
Atopic dermatitis has a wavy, relapsing course: unfortunately, 60% return throughout life. Therefore, a hypoallergenic lifestyle, proper skin care (constant use of emollients), and a hypoallergenic diet are important throughout the life of a child with atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease that significantly reduces a child’s quality of life due to constant itching and dry skin, but it can be managed thanks to the achievements of modern medicine. It is important to find a doctor you trust and follow his recommendations.
Prognosis for allergies in children
When a child first experiences allergies, it is difficult to say how the pathology will manifest itself in the future, what symptoms will occur and how often they will occur.
Some children successfully outgrow the disease and do not encounter it in the future, while others remain diagnosed throughout their lives. The main thing is not to let the process take its course, act as a team with doctors and, over time, explain to the child the importance of constant monitoring of health. Every child can receive qualified medical care. Our specialists carry out high-quality diagnostics, identify the causative allergen and draw up a personalized treatment program. Contact the best allergists to give your child health!