A boil in a child is not only an unpleasant occurrence, but also a rather dangerous disease. The appearance of boils indicates a deterioration in the general physical condition of the child. In addition, lack of timely medical care can lead to serious complications. That is why and for a number of other reasons, a boil in a child requires close attention and a responsible attitude of parents. Self-treatment of boils in children is excluded, since the effectiveness of the measures taken directly depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. Not all medical techniques and methods can be used to treat children. Contacting a pediatrician will help you avoid many problems and complications.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for the appearance of boils on the body in children are very different. Doctors identify several common causes of this pathology. In order for boils to occur in a child, the reasons may be as follows:
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine disorders;
- frequent colds and ARVI;
- weakened immunity;
- malnutrition;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- lack of fresh air;
- overheating or hypothermia.
Doctors divide the causes into external and internal. External reasons include:
- untreated wounds or cuts on the body;
- dirt on hands and body;
- allergic reactions with rashes;
- clogged pores due to excessive sweating.
In order to avoid the appearance of boils for external reasons, it is enough to maintain hygiene and treat scratches in a timely manner.
The answer to the question of why a child has boils is more difficult to give if the reasons are internal. Internal reasons include:
- low hemoglobin level;
- frequent stress and problems with the nervous system;
- metabolic disorders;
- weakened immunity;
- frequent illnesses (for example, a boil on a child’s abdomen may appear after a serious illness);
- diseases of the endocrine system, in particular diabetes;
- mental or physical fatigue.
Boils can occur in a child, the causes of which are very different, and can occur at any time, regardless of the external temperature and time of year. Boils can also be caused by a lack of vitamins, skin damage from friction, diseases of the digestive system, and frequent hypothermia.
Experienced doctors at the Pediatric Department of JSC Medicine (academician Roitberg’s clinic) in Moscow will help you accurately determine the cause of the disease. Our clinic’s specialists use certified safe medications and effective technologies, which is one of the conditions for the complete recovery of young patients.
What's really going on?
Barley is an acute, purulent clinical, infectious inflammatory process in origin. From this exhaustive definition, the reasons for its appearance, patterns of development, and the choice of adequate treatment and preventive measures clearly follow.
In the vast majority of cases, hordeolum is caused by the introduction of a bacterial (more precisely, Staphylococcal aureus) infection with subsequent rapid proliferation of the pathogen in the hair follicles, glands of Moll and/or Zeiss, less often in the meibomian glands (in this case, the “internal” barley is turned by the fistula canal towards the conjunctiva ).
Constant, often recurrent styes in a child always indicate the presence of some hidden or obvious systemic pathology. Usually this is a decrease in immunity due to an incorrect, unnatural lifestyle for children (physical inactivity, lack of sunlight, fresh air, etc.), hypovitaminosis, endocrine or gastroenterological disorders, recent diseases or operations, and the presence of worms.
Hypothermia and overheating, untreated or undertreated infectious foci, for example, in the oral cavity or nasopharynx (caries, tonsillitis, etc.) contribute to the development of stye.
But the main factor that makes styes a global problem and an almost inevitable companion to childhood is children's curiosity, combined with unwashed hands and a lack of strong sanitation and hygiene skills.
The crowding of children's preschool and school groups, the use of common towels or pillows, the habit of examining everything, so to speak, by palpation, the reflexive impulse to intensively rub the eyes in case of any discomfort - all this creates extremely favorable conditions for the spread of staphylococcal infection.
In addition, adults make a significant contribution to increasing the adaptability and survival of staphylococcus: uncontrolled and inadequate use of antibiotics leads to mutations and the formation of drug-resistant bacterial strains.
Symptoms
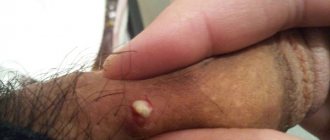
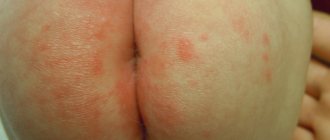
The most obvious symptom is the appearance of an area of inflammation with purulent contents. Symptoms depend on several factors, including the location of the boil:
- a boil on a child’s hand interferes with movements and can lead to the formation of a wound;
- You can notice a boil on a child’s head while washing his hair or while combing his hair;
- a boil on a child’s lip is visually noticeable and interferes with speaking and eating;
- a boil on the child’s bottom makes it difficult to sit;
- a boil on a child’s face is visually noticeable and can cause swelling;
- a boil in the child’s nose interferes with breathing and is painful;
- a boil in a child’s ear can cause ear pain and hearing impairment;
- a boil on a child’s knee complicates movement;
- A boil on a child’s neck can cause enlarged lymph nodes.
Common symptoms of a boil are:
- general malaise;
- painful sensations in the area where the boil is located;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- headache;
- intoxication, nausea, vomiting;
- lack of appetite, drowsiness;
- dizziness.
In order for the elimination of pathology to be effective, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the boil. Only a doctor can accurately indicate the cause after a thorough examination, so the only correct decision is to contact a pediatrician. The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) in Moscow offers the services of qualified pediatricians with considerable experience in the diagnosis and treatment of childhood diseases.
If symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Independent use of lotions, ointments and traditional medicine is strictly not recommended, especially squeezing pus out of a boil.
Which doctor should I contact?
Diagnosis of boils, provided they are superficial, is not difficult. It is much more difficult to correctly determine the cause of purulent inflammation. A thorough examination is carried out in the following cases:
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- complications caused by pathology;
- when the boil is located internally (in the ear, nose).
The diagnosis of boils and treatment of pathology at the Pediatric Department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in Moscow is carried out by pediatricians, who, based on the results of the examination, can refer the little patient to a dermatologist or other specialist.
When conducting a comprehensive examination, the doctor can give the patient a direction:
- for a blood test;
- for bacterial inoculation from the skin;
- for immunodiagnostics;
- for a complete blood test.
You should urgently contact the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) if:
- the boil is located on the child’s face or in the spine;
- the child feels unwell, the temperature has risen;
- When the size of the boil is from 3 to 10 cm, the abscess does not burst.
Recurrent furunculosis in children and adults
Authors : Shcherbina E. A.
Furunculosis is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding connective tissue caused by pyogenic bacteria. Boils are most often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Recurrent furunculosis is said to occur when the disease recurs 3 times in a year or more.
How can you or your child get Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus is quite common among the world's population. Staphylococcus colonization of the skin and mucous membranes can occur in the following cases:
- constant contact with a person who is a carrier of this bacterium (especially during the active phase of the infection);
- constant contact with objects belonging to a person who is a carrier of Staphylococcus aureus.
Carrying Staphylococcus aureus does not mean that you or your child have something wrong with their immune system! Absolutely healthy people can be carriers of this pathogen!
What is "decolonization"?
Most cases of Staphylococcus aureus disease can be cured with antibiotics and proper skin care. To reduce the likelihood of developing repeated boils, it is necessary to reduce the number of these bacteria on the skin and mucous membranes of all family members who are carriers of Staphylococcus aureus. This procedure is called "decolonization".
There are many ways to decolonize, but there are mandatory ones that absolutely everyone must follow. If an adult or child has boils for the first time in their life, then usually to treat them it is enough to carry out the measures described below. If anyone in your family has recurrent boils, you may need to take additional steps.
Mandatory activities during decolonization:
- Keep your nails short.
- Change your underwear, towels and pajamas daily. Wash them thoroughly.
- Wash bedding weekly in hot water. The ideal option is at a water temperature of 70 °C and above.
- Try to keep all wounds and scrapes on the skin clean and dry, and cover them with a bandage until they heal. Already formed boils must also be covered with a plaster or bandage to prevent further spread of infection.
- Each family member should have their own bath sponge, which should also be washed frequently.
Additional activities that your doctor may prescribe:
Staphylococcus aureus is very easily transmitted from one person to another in case of close contact between them. This bacterium is very difficult to get rid of, especially if there are carriers in the family who constantly infect others. If your child or any other family member suffers from recurrent furunculosis, your doctor may prescribe the following:
- Nasal antibacterial ointments. This group of drugs includes, for example, nasal ointment with 2% mupirocin (Bactroban). When used correctly, this ointment is quite effective in killing Staphylococcus aureus living on the nasal mucosa. The use of this method in itself significantly reduces the likelihood of relapse of furunculosis, but it is much more effective to combine it with other measures. The ointment is administered into the nasal cavity 2 times a day. A small amount of the drug, the size of a match head, is taken on the little finger and injected into one nostril. The drug is also injected into the other nostril. Then the nostrils are closed on both sides, while the ointment is distributed in the nasal passages. The duration of treatment is 5–10 days, once a month for 3 months in a row.
- Rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine solution. In parallel with treating the nasal cavity with antibacterial ointment, rinse the mouth with a 0.2% chlorhexidine solution 3 times a day.
- Bleach baths. To destroy Staphylococcus aureus located on the surface of the skin, you can take special baths with regular bleach. It is advisable that there are no open wounds or manifestations of eczema on the skin. To prepare a bath, you will need any bleach that contains sodium hypochlorite 2.63%. Just add 1 teaspoon of liquid per ~4 liters of clean warm water. In the vastness of the CIS countries, you can most often find bleaches containing 5% sodium hypochlorite - in this case, you will need to add one teaspoon of solution not per 4 liters, but per 8 liters. You need to take baths 2 times a week for 15 minutes for 3 months. After the cleansing bath, it is necessary to rinse off the bleach with clean water and treat the skin with any emollient, since sodium hypochlorite makes it very dry.
- To cleanse the skin, soap with 1% triclosan and a 4% chlorhexidine solution (as an option - special wipes containing the same concentration of chlorhexidine) can also be used, which are used to treat the entire surface of the body and scalp. These antiseptics should be used daily and should be in contact with the skin/hair for at least 5 minutes before being rinsed off with water. This treatment is carried out first for 7 days daily, then 2 times a week, and after decolonization is achieved - 1 time a week for several months.
- Systemic antibiotics. If the above methods do not work, your doctor may prescribe an additional course of oral antibiotics to provide a stronger effect. Antibiotic regimens are different; one universal protocol for the treatment of furunculosis has not yet been developed. What specific dosage of antibiotic to use, for how long and in what combination - only the doctor decides!
We must not forget that conditions such as iron deficiency, diabetes mellitus, chronic skin diseases (especially atopic dermatitis), HIV infection, alcoholism and obesity are also risk factors for the development of recurrent furunculosis. Treatment of these diseases should be carried out simultaneously with decolonization of Staphylococcus aureus.
Page of Shcherbina E.A. in ClubCom
published 12/08/2015 12:00 updated 21/08/2015 — Infectious diseases, Popular medicine
Danger of boils
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner can lead to dire consequences, since this pathology belongs to the category of dangerous diseases:
- a boil on a child’s head can cause meningitis;
- a boil on a child’s lip can cause inflammation of the nerves of the nasolabial triangle;
- a boil on the child’s bottom makes it difficult to sit;
- a boil on a child’s face can lead to meningitis;
- a boil in a child’s nose can cause inflammation of the respiratory system;
- a boil in a child’s ear can cause inflammation of the hearing organ;
- A boil on a child’s neck can lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes and severe intoxication.
In the absence of timely medical care, a carbuncle, which is a collection of boils, may develop. Possible consequences are also:
- infection of the deep layers of skin tissue;
- scar formation after healing;
- sepsis.
The appearance of multiple boils causes discomfort in the child, increased temperature, and deterioration of well-being.
The consequences of the formation of a boil can be prevented if you promptly contact the pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg), which offers the services of qualified experienced specialists in various fields of medicine.
Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Diagnostics
You can suspect a boil at the first visual examination of the affected area of skin. The following laboratory and instrumental research methods can be used to distinguish it from other similar skin diseases, such as erythema, anthrax, and skin tuberculosis:
- Clinical blood test.
- Blood chemistry.
- General urine analysis.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Bacterial culture of purulent contents for flora and sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- Fluorography.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- MRI of the brain.
- Spinal tap.
The appropriateness of each of these methods is determined by the attending physician. In addition to all of the above, there may be a need for consultations with several specialists at once. Depending on the location of the boil and the complications that arise, the child can be examined by a dermatologist, surgeon, immunologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, and in some cases, a gynecologist, urologist and endocrinologist.
Treatment
If a boil appears in a child, treatment should be started immediately. Based on the examination and examination of a small patient and taking an anamnesis, the doctor will draw up an effective treatment program. Consultation with a pediatrician is required if internal boils are present. If a boil on a child’s leg does not cause any particular concern, then treatment can be medicinal, using antiseptic and painkillers.
Modern techniques include the use of local ultraviolet irradiation. The pediatrician of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) can also prescribe physical therapy (UHF therapy, electrophoresis with antimicrobial drugs).
Drug treatment
When a boil is diagnosed in children, treatment is prescribed taking into account the stage of the disease and the level of immunity. Antibiotics may be prescribed under the following conditions:
- a carbuncle has formed;
- high temperature rose;
- a boil has formed on the face;
- the infection has penetrated into the deep layers of the skin;
- there is severe pain.
Medicines are prescribed exclusively by a doctor based on the results of the examination.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of pathology is rarely used under local anesthesia. If the boil in children, the treatment of which is selected individually, does not rupture on its own, the surgeon pierces it with a sterile needle or makes a small incision through which the pus is removed.
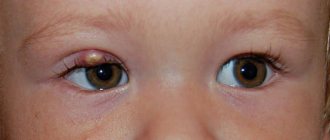
Stye on a child’s eye – causes and how to treat
The natural protection of the eye, the eyelid, consists of five main elements: the anterior (external) skin, muscle fibers, cartilage tissue, the posterior (internal) mucous membrane-conjunctiva and the ciliary row along the edge.
In addition, evolution has provided a system of small glands, which are located partly in the conjunctiva (additional lacrimal glands), partly in the inner space of the eyelid (sweat and sebaceous glands). Moll's sweat glands and Zeiss' sebaceous glands emerge between the eyelashes or communicate with each other; Meibom's sebaceous glands are located deeper and open from the conjunctiva. In general, the secretion of the glands serves to hydroregulate the skin and ciliary roots, as well as to reduce friction during blinking.
Despite the fairly simple structure of the eyelid, each of its structural elements is susceptible to many pathological processes and conditions. Most of them are infectious and inflammatory in nature and are caused by viral, bacterial or fungal pathogens, as well as a skin parasite - the smallest Demodex mite, which settles at the base of the eyelashes, in the hair follicles and glands.
Thus, patients constantly turn to ophthalmologists with all kinds of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, as well as various combinations thereof. Such inflammations occur with varying frequencies, which depend on many factors - regional, age, etc. However, among these diseases there are undisputed leaders: conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane) and hordeolum, or barley.
Both diseases are so widespread that, probably, any earthling will encounter them at least once during his life - if not in himself, then in his closest relatives. And when a child with barley appears at the reception, one can often only be surprised at how little parents know about the causes and patterns of this “national” pathology, and what strange and sometimes dangerous methods they try to cope with it.
Consultations with other specialists
Contacting specialists in various fields of medicine is necessary, since boils of bacterial origin (staphylococcus) can provoke:
- formation of a focus of chronic infection (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- diseases and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, dysbacteriosis, etc.).
The formation of boils may indicate a urinary tract infection, iron deficiency anemia, immune diseases, or the presence of a latent infection (herpes, cytomegalovirus infection).
How to make an appointment with a doctor
The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in Moscow offers European-level services for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of boils in children. To receive highly qualified medical care, you must make an appointment with a pediatrician who will conduct an examination and comprehensive medical examination of the child. If necessary, the pediatrician will consult with or refer other specialists.
To make an appointment with a specialist in the pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), use one of the following methods:
- quick registration form on the website;
- by telephone 24/7;
- using a mobile application.
Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station, as well as not far from the Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Novoslobodskaya metro stations.