Publication date: 01/27/2021
Just as poets consider the eyes to be the mirror of the soul, so doctors are accustomed to viewing the tongue as an organ that reflects the work of the body as a whole. No matter what you complain about, the doctor at the appointment will definitely ask you to stick out your tongue and carefully examine it. And at the dentist’s appointment, special attention will be paid to the tongue. And all because of glossitis. The word is beautiful, but the condition is not. Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue, one of the signs of which is the appearance of cracks.
Tongue in cracks - reasons
- Bacterial and viral infections
This doesn't just apply to infections in the mouth. Viruses and bacteria spread throughout the body, and the infection manifests itself in the tongue. Most often, cracks in the tongue are caused by the herpes virus. - Anemia
Iron deficiency can cause glossitis. Iron is transported by a special protein - myoglobin, which is responsible for the healthy state of muscle tissue. If there is not enough iron, all muscles suffer, including the tongue. - Allergic reaction
The body's response to various allergens: food, medications, sometimes even toothpaste components - can cause inflammation. - Mouth injuries
Burns, cuts, and any mechanical injuries become an environment where bacteria multiply, which means inflammation occurs. - Vitamin deficiency
It has been scientifically proven that a deficiency of B vitamins can lead to cracked tongue.
Oral diseases (glossitis)
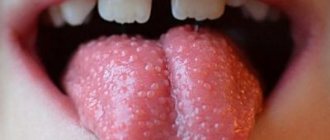
Glossitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral cavity that causes changes in the surface of the tongue. The tongue turns red and swells; A white coating, a burning sensation, and growths appear. There are more than 10 types of glossitis and only three of them are characterized by the appearance of cracks on the surface of the tongue.
Folded glossitis.
A congenital anomaly that is determined immediately after birth. Characterized by the presence of cracks of varying depths. Normally, they do not cause discomfort.
Diamond-shaped glossitis.
The affected area is diamond-shaped and has cracks in the middle of the tongue. Most often appears with gastritis with low acidity.
Desquamative glossitis.
It is sometimes called “geographical” because the lesions resemble the outlines of continents. Damaged areas can “move” on the surface of the tongue, almost always causing pain, burning, and shallow cracks. The reason for the appearance of such glossitis is still not clear. Some argue that this is an allergic reaction, others that it is a hormonal imbalance and gastrointestinal diseases.
Symptoms
Inflammation manifests itself in different ways, depending on the individual characteristics of the person and the underlying cause of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Unpleasant sensations in the mouth
- Color change
- Pain
- Edema
- Burning or itching
- Surface change
- Changes in the size and shape of the papillae
- Cracks
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chewing problems
- Gray plaque
- Difficulty speaking
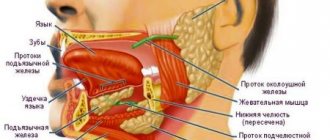
What is glossitis?
What do we know about the tongue as an organ? We know that it is located in the mouth, which helps us articulate and pronounce words correctly, helps us mix food, feel all the diversity of existing tastes, that they can be shown indignation, and in some African countries, a demonstration of it can be used to declare war.
Such a significant number of different physiological and social functions may one day be compromised. And the name of this threat is glossitis.
Despite the absolutely clear location of this organ, there are big questions about which doctor deals with its problems: a dentist, gastroenterologist, maxillofacial surgeon or otolaryngologist. This is not an easy question, and sometimes you can endlessly go from one specialist to another. But let's finally understand this intriguing matter.
Online consultation with a doctor if you are concerned about symptoms
If you are concerned about cracks in the tongue and the symptoms listed in the article: discoloration, swelling, pain, burning, difficulty swallowing and speaking due to an enlarged tongue, consult a doctor. To identify a disease with similar symptoms, in most cases, a visual examination is sufficient. An online consultation with a dentist will help you timely recognize the degree of soft tissue damage, the exact location and the appropriate treatment regimen. If you do not pay attention to cracks in the tongue, you may not notice more serious diseases and complications from them: abscesses, phlegmons. Treatment in this case will be long and more expensive.
Diagnostics
Successful therapy requires careful research. Diagnostics in dentistry include an initial consultation with a dentist, and, if necessary, specialists. It is the dentist who deals with problems related to the oral cavity. Usually, after the dentist, the patient is sent to a therapist in order to study the clinical picture. Finding out the medical history allows you to determine which specialists to refer the patient to.
A loose tongue with cracks requires inspection:
- Hematologist;
- Gastroenterologist;
- Endocrinologist;
- Infectious disease specialist;
In addition, the patient is sent for blood tests, and a scraping of epithelial tissue in the area of the furrow is taken. The condition of the gastrointestinal tract is assessed, and other studies are carried out, which make it possible to assess the state of the body. All these examinations allow us to identify the true cause of the defect.
Treatment in the clinic
Before prescribing medications and procedures, it is necessary to find out why cracks occur. After this, a plan is drawn up, which may include:
- Treatment of a common disease
- Antifungal medications
- Iron tablets
- Vitamins
- Corticosteroids
- Immunostimulants
- Antihistamines
The surface of the tongue is disinfected with antiseptic solutions. Painkillers are used to reduce pain.
If mechanical injuries occur as a result of unsuccessful prosthetics, it is recommended to replace the structure.
Forms and types of disease
Inflammation of our organ of taste occurs frequently and does not always manifest itself with symptoms, proceeding completely hidden from us.
There are several forms and types of the disease:
- According to the duration, the disease is divided into acute (develops quickly and lasts no more than a month) or chronic glossitis (lasts more than a month);
- According to the form of the lesion, the catarrhal form (proceeding with redness and swelling) and the desquamative form (proceeding with a change in appearance) are distinguished;
- purulent forms - phlegmon and abscess (a purulent focus in the thickness of the organ tissue itself);
- a separate group includes neurological diseases of the nerves innervating this organ.
Cellulitis and abscess occur acutely, they are associated with infection and require urgent surgical intervention. They manifest themselves as severe pain, chills and swelling of the lymph nodes of the neck - this form can be confused with acute inflammation of the salivary glands, so diagnosis using ultrasound and x-rays is needed. It is better not to delay these symptoms and seek medical help as an emergency.
The catarrhal form of glossitis manifests itself with a sharp blood supply - the tongue swells, becomes bright red - this can manifest itself, for example, with scarlet fever, or an allergic reaction, which, in addition to the organ of taste itself, spreads to the soft palate with the tongue. Treatment in this case is aimed at eliminating the allergic reaction and inflammation.
The largest and most heterogeneous group is desquamative glossitis. It is difficult to list the number of factors (external, internal) that can provoke this form of the disease. We will not make a mistake if we say that “the tongue is the mirror of the digestive tract.” Since it contains many nerve receptors and papillae of different shapes and purposes (filamentous, cone-shaped, mushroom-shaped, leaf-shaped, groove-shaped), a change in each link of its anatomy outwardly reveals a hidden disease. Let's take a little look at the most common diagnostic signs of these conditions.
Home Remedies
Folk remedies are not able to eliminate the cause of cracks, especially if it is a common disease. In rare cases, the body can defeat a bacterial infection on its own. Therefore, medications from a home medicine cabinet can only be considered auxiliary. These include:
- Gargling with decoctions of sage and chamomile
- Lotions with sea buckthorn or olive oil
- Propolis
- Potato juice applications
Incorrectly selected folk remedies can reduce the effect of drug treatment.
Be sure to consult your doctor.
Allergic reactions
Did cracks appear on your tongue out of nowhere? Pay attention to your personal hygiene products; perhaps the reason is unsuitable toothpaste or mouth rinse. Or maybe you recently started taking medications that led to a similar reaction.
It will be enough to stop using the product and take a course of antihistamines so that the tongue in the cracks no longer bothers you. After such manipulations, the symptoms will naturally disappear.
“I really like to eat sour fruits, I love citrus fruits. There was a time when I couldn’t live a day without them. However, something bad happened to me; one morning I felt pain and a burning sensation on my tongue. Looking in the mirror, I saw that he also looked extremely unpleasant. The doctor said that this is an allergy to citrus fruits, that in principle you can’t eat a lot of them, and they are even dangerous for the mucous membranes.”
[email protected] , from correspondence on the forums
Top five dental clinics
All clinics on the list are multidisciplinary. They are engaged in prevention, treatment, prosthetics and implantation.
| Dental center | Clinic address | General information |
| Cerecon | Moscow, Andropova Ave. 8 | Metro Technopark. Opening hours: 24 hours a day |
| ROOT | Moscow, st. Rustaveli, 14 building 9 | Metro Butyrskaya. Opening hours from 10:00 to 22:00 |
| Alpha-Dent | Moscow, Beskudnikovsky blvd., 24, bldg. 1 | Metro Petrovskoye-Razumovskoye. Open all days of the week. |
| MegaStom | Moscow, Bolshoi Kozlovsky lane, building 10, building 2 | Metro Red Gate. They don't work on Sundays |
| Denta amo | Moscow, st. Grekova, 9 | Metro Medvedkovo Open daily from 9 to 9. |
Everyone has at least once encountered such an unpleasant phenomenon as the formation of a crack in the tongue. Moreover, very often it seems that the tongue has cracked for no apparent reason, on its own. Small cracks may not bother you at all for a long time, while deep cracks cause discomfort and acute pain to the patient. However, plaque and cracks should not be ignored, since over time even the smallest cracks, if left untreated, can increase in size and begin to hurt. We will tell you why they appear and what they mean, as well as whether congenital fissures are dangerous and how to treat them.
What it is
Officially, painful cracks on the tongue and along the edge of the tongue are called glossalgia. This is a fairly common neurosomatic disease.
Most common symptoms:
- dryness in the tongue area;
- itching and burning;
- swelling;
- soreness.
The insidiousness of glossalgia is that it does not go away on its own; without appropriate treatment it is impossible to get rid of a crack in the tongue.
At an early stage of the disease, the doctor may not notice pronounced cracks in the tongue, since they are microscopic and mainly manifest themselves as burning and pain. If you do not respond to this symptom in a timely manner, over time a crack may form at the tip or in the middle of the tongue, longitudinally, as well as cracks under the tongue and on the sides. In this case, the doctor also notes swelling and swelling of the tongue, atrophy of the salivary glands and filiform papillae on the surface of the tongue. The sooner you start treatment, the easier it is to get rid of glossalgia, so if you have cracks in your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Congenital fissures
It happens that a patient has cracks in the tongue since birth or childhood, which practically do not cause him any concern. Such cracks are usually transverse and are caused by the development and formation of the tongue.
Some patients have a so-called folded tongue, a congenital feature of tongue development. It is usually considered normal and does not require any treatment. The exception is red cracks in the tongue, which form at the bottom of the folds and cause pain to the patient. This happens with insufficient oral hygiene, so those with a folded tongue must carefully clean not only their teeth and gums, but also their tongue from plaque. If the owner of a folded tongue has developed cracks, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the design features of the patient’s tongue. To prevent the formation of folds in the depths, more attention should be paid to the sanitation of the oral cavity.
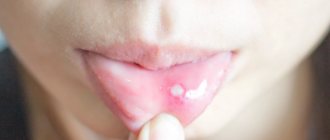
How do they look
Small cracks in the tongue can be completely invisible to the naked eye; only an experienced doctor can examine them using special instruments. The larger ones are clearly visible to the naked eye; they resemble longitudinal or transverse grooves on the tongue. Deep cracks look like crevices; sometimes the tongue appears to be cracked or split into two parts. If you notice such a problem, consult a doctor, even if nothing is bothering you at the moment. If an infection gets into the crack, the course of the disease may be complicated by the inflammatory process.
Reasons for appearance
Reasons for education:
- lack of nutrients, iron and vitamin PP in the patient’s body;
- anemia;
- lack of B vitamins;
- allergic reaction to toothpaste or medications;
- chronic fatigue and constant nervous tension;
- mechanical damage to the tongue (nervous biting, chewing);
- disruption of capillary blood flow in the tongue;
- the patient has diseases such as gastritis, enterocolitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis;
- wearing uncomfortable dentures.
The main reason why the tongue is cracked is mechanical injuries due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the patient’s body. In this case, it is enough to bite your tongue while chewing food so that a painful crack forms at its tip.
Another fairly common reason why a patient’s tongue is cracked is a malfunction in the patient’s central nervous system, which is caused by chronic fatigue, frequent stress, and lack of sleep. This is a reason to suspect a problem with the hypothalamus.
It happens that patients are perplexed: why there are cracks on the tongue, there seems to be no visible reason for their appearance. In this case, the answer to the question of why cracks appear can only be given by an experienced doctor, after a thorough diagnosis. It is necessary to do a detailed blood test to determine which microelements and vitamins are missing in the patient’s body. Quite often, correction of the nutritional system helps get rid of the disease.
Many people are probably interested in the question of what cracks mean. After all, the tongue, as is known, signals the presence of many diseases and pathological conditions of the human body. Cracks in the tongue are a sign of a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body. Quite often, cracks are caused by worms, as they deplete the human body, causing anemia and iron deficiency. They also indicate a diseased liver, since with this disease the human body does not receive many microelements important for health.
Cracks in the tongue on the side can be a sign of thyroid disease; in this case, it swells and is injured at the edges by the patient’s teeth.
Treatment
The main question that worries patients with glossalgia is how to cure cracks in the tongue. In fact, everything is not so difficult. The treatment method depends on the cause of glossalgia.
- First, it is necessary to eliminate the dental causes of tongue cracks - correct an incorrect bite, replace defective fillings, repair a prosthesis. Next, the patient should be carefully examined by a therapist, neurologist, and, if necessary, by an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist. And only after this should treatment for glossalgia be prescribed.
- Typically, treatment for fissures consists of drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment with medications is to improve blood circulation in the tissues of the oral cavity, as well as to improve general cerebral circulation. For this purpose, drugs such as trental, cavinton, nicotinic acid, and vitamin C are prescribed.
- The tone of the autonomic nervous system should also be improved; for this purpose, sedatives are prescribed - tincture of valerian, motherwort, persen.
- Additionally, the doctor may prescribe procedures such as electrical neurostimulation using a TENS device. A good effect is achieved by using electrophoresis, as well as iontophoresis of novocaine.
- If the tongue is severely painful, the doctor may prescribe local painkillers - lidocaine, dicaine.
- If the patient has cracks in the tongue, plaque and burning, it is necessary to adjust the diet. During treatment, you should completely exclude from the diet foods that irritate the surface of the tongue - such as sour juices, vegetables, pickles and marinades. You should not consume large amounts of spices, especially pepper and salt. It is advisable to quit smoking.
- After each meal, be sure to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with salted water or a decoction of medicinal herbs. Oak bark, sage, propolis, and honey have a healing effect.
Lifestyle change
If a person’s tongue is covered with cracks, then it is necessary to exclude irritating factors when eating. This means that you need to remove hot, hot and spicy foods from your diet. It is necessary to limit the intake of store-bought and homemade marinades, sauces, and fried foods.
A balanced intake of vitamins A and B will help improve your general condition, which will have a beneficial effect on the speed of the process of getting rid of cracks. To provide the body with B vitamins and carotenes, you need to eat plant foods. Vitamin A and B12 are found in high concentrations in animal liver, dairy products and fish oil. In winter, if there is a shortage of vegetables and fruits that have not undergone deep heat treatment, it is necessary to take multivitamins.
Careful oral hygiene is required. It is better to clean teeth from plaque using a soft brush to avoid physical impact on the injured surface of the tongue, especially if it hurts.
Smoking is a significant problem because nicotine contributes to the development of stomatitis and gingivitis, diseases that often accompany glossitis . If your tongue is cracked, you should not drink strong alcohol, as it will cause burns to open wounds, which will take a long time to heal.
If a patient detects cracks in the tongue, doctors talk about a serious stage of glossitis, which must be treated urgently. In most cases, the treatment prognosis is favorable, and the technique depends on the causes of the disease, the neglect of the process and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The speed and effectiveness of therapeutic measures is directly related to how the patient complies with the recommendations of doctors.
What does a healthy tongue look like?
The tongue is pale pink - absolutely healthy.
Diagnosis by the appearance of the tongue was mastered by ancient healers, who believed that a disease could not be considered cured until the patient’s tongue regained its previous appearance. The tongue of an absolutely healthy person has the following signs:
- Pale pink color;
- Small taste buds without pronounced features;
- No bad breath;
- Be moderately moist;
- The presence of a small amount of translucent bright pink coating is allowed;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
If you deviate from these signs, you should consult a general practitioner or gastroenterologist and undergo the examination prescribed by him.
Causes of glossalgia
Many patients with glossalgia associate the appearance of the symptom with trauma to the tongue from sharp edges of fillings or teeth with chipped enamel, as well as incorrectly installed crowns and dentures. More often, the disease appears after disorders of the autonomic nervous system. As the disease progresses, it becomes chronic.
This is a functional disorder that has no organic causes. Researchers associate its appearance with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often there is a combination of disorders of the nervous system, vascular lesions and diseases of the digestive system. A stimulating factor can be diseases that lead to a decrease in tissue sensitivity or change the response to mechanical stimuli.
Glossalgia can also develop against the background of the following diseases:
- ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke;
- encephalitis of any origin;
- neurosyphilis.
Aggravating factors may include hypovitaminosis, lack of iron, minerals, endocrine diseases, infections and autoimmune pathologies. The disease is also affected by taking certain medications - chemotherapy drugs, antihistamines, etc.
Research shows that the disease may be one of the signs of viscero-reflex bulbar syndrome, which affects the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. Disturbances in the transmission of nerve impulses cause glossalgia, as they lead to the appearance of false sensations. And external irritants can only intensify the symptom, which explains the high incidence of the disease in people with dentures and crowns.
Ask a Question
Is plaque on the tongue dangerous - how to treat it
An ultrasound of the stomach will help clarify the diagnosis.
Plaque itself does not pose any threat to health. As soon as the underlying disease is cured, the condition of the tongue will return to normal.
As for gastritis, long-term treatment with careful adherence to the recommendations of a gastroenterologist will help relieve its symptoms.
Perhaps the doctor will conduct research aimed at clarifying the diagnosis: FGDS, ultrasound of the stomach, laboratory tests of blood and gastric juice. The following drugs will be prescribed as treatment:
- Antibiotics of 2-4 types, taken in combination:
- Pro- and prebiotics;
- Vitamins;
- Antacids;
- Proton pump blockers.
Patients with gastritis must follow a strict diet aimed at sparing the gastric mucosa and not provoking the release of excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid. With this treatment, not only the gastric mucosa, but also the condition of the tongue will definitely return to normal.
Localization of cracks
The position of the cracks is not random. Localization is divided into three types, each of which is caused by specific problems. You can independently identify the type of localization by assessing the position of the cracks in the tongue: in the center, on the sides or at the tip.
The presence of cracks only at the tip of the tongue indicates the following causes of the problem:
- Thermal damage. Hot food first comes into contact with the tip of the tongue and causes major damage to it. Often the problem is contact with a hot metal spoon.
- Chemical damage. Occurs from contact with spicy, sour foods or corrosive substances.
- Physical impact. The tip can crack due to an incorrect bite or a cut on the sharp protruding parts of the incisors and canines.
Photo: cracks on the sides of the tongue
The formation of cracks in the tongue in the middle has a different reason, since it is almost impossible to injure this area without touching the periphery. This means that inflammation is an indicator of pathology or disease of internal organs. In addition, the formation of cracks in the center is possible when the middle area dries out, local circulation is impaired, or the immune system is weakened. There may be only one crack; upon examination, it appears as if the tongue has split into two parts.
The presence of cracks on the sides of the tongue can be caused by various reasons. If the inflammatory process is present on the side on one side, then this means physical damage from the sharp edges of small and large molars or dentures. If the tongue is cracked on both sides, it means that there are serious malfunctions in the functioning of the body , where glossitis acts only as an indicator of pathology.
Which doctor should I contact?
The answer to the question of which doctor treats glossitis is simple. When painful changes appear in the mouth, patients turn to the dentist. This specialist will help alleviate the condition, but there is a high chance that damage to the taste organ is only a symptom of changes in the body. It is not always possible to determine the disease by the tongue; additional studies are prescribed. Consultations with a hematologist, endocrinologist and gastroenterologist may be required, diagnostics including:
- external examination of damage, swelling;
- epithelial scraping examination;
- blood analysis;
- identification of concomitant chronic or acute diseases.