The liver is the largest and most important organ of the abdominal cavity. Provides protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
Fatty liver disease is a very common disease today. The stereotype that fatty liver disease only affects overweight people and alcoholics is misleading. This disease is caused not only by excessive alcohol consumption, but also by unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle, which characterize a large part of the population.
The average age at which fatty liver is detected is 50 years, but in general the incidence of hepatosis increases with age: from 2.6% of children to 26% of people aged 40-50 years.
What is fatty liver disease?
The content of the article
A healthy liver should contain little or no fat. With fatty degeneration or steatosis of the liver, fat drops accumulate in its cells - hepatocytes.
Hepatic steatosis develops slowly, but even in its early stages can have a negative impact on the cardiovascular system. Also, the liver is not able to effectively cleanse the body of excess cholesterol and toxins.
As the number of damaged cells increases to a critical level, the liver is no longer able to function.
Fatty liver in itself is not a big problem. But adipose tissue is not an inert formation; it secretes hormones and promotes inflammation. So some people—20% on average—develop fatty liver disease, or steatohepatitis, and that's not good.
In some, steatohepatitis progresses and over time, connective tissue and fibrosis develop instead of liver cells - the path to liver cirrhosis and the development of irreversible changes in this organ. The liver tissue is replaced by connective tissue and no longer functions. Consequently, the liver does not do its job well - it does not produce, detoxify, cleanse or metabolize. The risk of liver cancer is also higher.
If you need emergency help, contact Alco-Center
Call the hotline +7 (495) 773-03-43 and our doctors will provide emergency care for intoxication of the body with breakdown products of alcohol and narcotic substances.
from 3,200 rub.
Withdrawal from binge drinking
Emergency body detoxification procedure
from 4,000 rub.
Coding
Urgent blocking of cravings for alcoholic beverages
from 68,000 rub.
Rehabilitation
Comprehensive rehabilitation giving 100% results
Causes of fatty liver disease
Almost every third person is diagnosed with fatty degeneration or steatosis, or fatty liver hepatosis after an abdominal ultrasound. Patients with these diagnoses often do not complain, so fatty liver is discovered by chance.
The main causes of fatty liver are known:
- Alcohol abuse. The liver breaks down alcohol, produces excess energy, and the body stores it in the form of fat droplets.
- Too many calories a person consumes - unhealthy diet, excessive consumption of saturated fatty acids, such as butter and sugar. The so-called central obesity is especially bad - excess fat accumulates in the abdominal area, because more fatty acids enter the blood from the intestines and sebaceous membranes. They enter the liver and droplets of fat accumulate in it.
- One of the metabolic syndromes: overweight, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, hypertension or other symptoms.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Impaired insulin function. Insulin is a hormone that promotes the synthesis of proteins and fats in the liver and helps lower blood sugar levels after meals. In the absence of insulin, incomplete oxidation of intermediate fats in the body can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Viral hepatitis B or C. However, this is rare.
- Sometimes the main reason is regular medication use. About 99% of drugs used are metabolized directly in the liver. Therefore, any medicine could potentially harm her. Research shows that antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, statins, drugs used to treat tuberculosis, fungal diseases and mental illness are more likely to cause liver damage.
Classification
The disease is divided according to changes in the organ and severity. The following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- Small-knot.
- Large-knot.
- Mixed.
Stages of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver:
- Compensated – without pronounced symptoms.
- Subcompensated – with initial manifestations, but with preservation of functions.
- Decompensated – accompanied by partial and then complete failure of functioning.
Alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alcohol is a cause of fatty liver, especially if consumed regularly. However, if alcohol intake is stopped, fatty liver disease usually goes away. This is a significant difference between alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
The ability of alcohol to affect the liver is largely determined by the dose of the substance. A small dose - no more than 10 grams per day of red wine - even strengthens the liver. The liver is not damaged by a higher dose of alcohol, but it should not exceed 30 grams per day. But some people are very sensitive to alcohol, so it can cause liver damage in them, even if they drink it very little, but every day.
Fatty liver disease develops most quickly with regular alcohol consumption:
1) For men, if 60 g of alcohol is drunk daily, that is about 1.5 liters of beer or 0.6 liters of wine, or 120 g of rum.
2) For women, if you drink 20-40 g of alcohol daily, that is approximately 0.5-1.0 liters of beer or 0.2-0.4 liters of wine.
Content:
- How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
- Classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- How long do people live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The human liver is the main organ that protects the body from the effects of poisons. It takes the brunt of alcohol and neutralizes toxins. In this difficult and sometimes unequal struggle, it itself is gradually being destroyed. As a result, inflammation develops - hepatitis, which, with continued alcoholization and the destructive influence of alcohol, turns into alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. This complication is life-threatening and, in the absence of sobriety and adequate treatment, leads to disastrous consequences. Therefore, the sooner the patient begins to get rid of this disease, the greater his chances of regaining health. Healing pathology is included in the tasks of the main course of anti-alcohol treatment. Hepatologists deal with advanced stages.
Diagnosis of fatty liver disease
The liver doesn't hurt. Patients with fatty liver disease usually do not experience any health problems. There are only general disorders - weakness, increased fatigue, heaviness or tightness in the right upper hypochondrium of the abdomen, because the liver becomes larger when fat is deposited. Potential problems are easy to diagnose, so it's a good idea to have your liver checked and cared for periodically.
Diagnostic stages:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- Assessment of concomitant diseases – diabetes mellitus, hypertension and others;
- A blood test, paying special attention to liver enzymes - ALT, AST, GTP, other indications should be taken into account - glucose, cholesterol, LDL and HDL.
In patients with NASH, ALT is often higher than AST. But in patients with ATAS, the level of AST in the blood is twice the level of ALT.
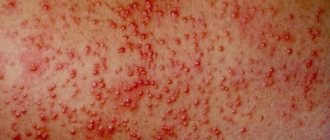
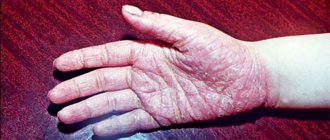
Signs of chronic alcohol use:
- skin stars most often affect the skin of the face;
- massive dilation of blood vessels in the skin and mucous membranes;
- erythema of the wrist - pink round spots on the skin of the hands;
- gynecomastia in men - enlargement of the mammary glands;
- enlarged salivary glands;
- sweating, tachycardia, hand tremors;
- increase in red blood cell volume;
- an increase in GGT, an enzyme found in the liver;
- AST concentration > than ALT.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
According to statistics, up to 80% of people who fall ill do not experience any significant changes in their health. A decrease in detoxification function provokes weakness, muscle pain and heaviness on the right side, under the lower rib after fried and fatty foods.
Undamaged cells are able to compensate for the work of dead cells up to a certain point. This condition lasts up to several years. Some patients experience dyspeptic disorders after drinking alcohol, even in small doses. Possible nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastrium, flatulence, diarrhea. Once the symptoms are eliminated, everything stops.
Doctors distinguish three stages of liver cirrhosis with characteristic signs:
Compensated
- moderate pain in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- disturbance of sleep and concentration;
- external phenomena - spider veins on the skin in the upper part of the body.
Subcompensated
- an increase in neurological symptoms - drowsiness, forgetfulness, handwriting changes, fingers trembling;
- skin manifestations - spider veins in the shoulder girdle area, itching, redness of the palms, pale nails, crimson tongue;
- baldness of the armpits and pubis;
- passing episodes of water retention, flatulence, diarrhea;
- increased bleeding;
- hormonal disorders - gynecomastia in men, menstrual irregularities in women.
Decompensated
- weight loss and loss of appetite;
- osteoporosis;
- muscle weakness;
- ascites that cannot be cured;
- darkening of urine and discoloration of feces;
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- increased body temperature;
- hepatic encephalopathy - dizziness, heaviness in the head, confusion, possible coma;
- the addition of infection and the occurrence of pneumonia, sepsis;
- varicose veins of the digestive tract.
External signs of liver cirrhosis - “stars, red palms, a bright shade of the tongue - are associated with an excess of female sex hormones. An imbalance that occurs during the breakdown of hormones is to blame for this. Therefore, they accumulate and expand the capillaries.
When palpated in the area of the right hypochondrium, in 30% of patients, an uneven, knotty surface of the deformed gland is revealed. In 70% it is enlarged, and in 50% an enlarged spleen is added. At the stage of decompensation, a decrease in size below normal is noted. This is due to the greater coverage of fibrosis.
There are active and inactive forms. The first is characterized by slow growth of connective fibers, which lasts up to several years. Sometimes - decades. The second is characterized by progression. In the presence of provoking factors - drinking alcohol, smoking, etc., it quickly passes into the decompensated phase. Concomitant HIV infection also contributes to rapid progression.
Special methods are used to detect dangerous violations.
Treatment
Treatment of fatty liver is based on eliminating its causes. If the patient drinks alcohol, it should be stopped, and if fatty liver is caused by metabolic syndrome, then blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels and weight loss should be controlled.
The main treatment is to reduce excess fat. For patients with NATAS and obesity, a 7-10% reduction in body weight is recommended. This can be achieved by reducing calorie intake and increasing physical activity to at least two to three times a week.
Some tips for reducing calories:
- the amount of animal fats and sugar in the diet should be limited;
- give up sausages and fatty meats;
- learn to drink unsweetened tea or coffee;
- do not consume milk and dairy products with high or normal fat content;
- limit the consumption of cakes and sweets;
- do not drink sugary drinks;
- do not drink alcohol;
- The liver will enjoy a Mediterranean diet based on plant foods, fish, nuts and olive oil.
If a person cannot take these measures, then it is necessary to take weight loss medications - orlistat or sibutramine. If this treatment does not help, you should stop taking the drug and consider fat reduction surgery.
The use of hepatoprotectors - essential phospholipids and silymarin - can help cleanse the liver and improve its biochemical properties. Essential phospholipids have antioxidant and antifibrotic effects. Silymarin – sea buckthorn extract. Studies have shown that silymarin reduces insulin resistance and can lead to a decrease and normalization of AST and ALT.
Diagnostic features
When identifying cirrhotic changes, the existing symptoms are taken into account. Additionally, clinical and biochemical blood tests are taken from patients.
They define:
- Anemia.
- Less commonly, leukocytosis.
- Decreased platelets.
- Increase in gamma globulins.
- Increase in AST (more) and ALT.
Ultrasound data plays an important role. They reveal a decrease in the size of the organ and foci of fibrosis. Computed tomography provides an even more accurate picture. With its help, not only the structure is assessed, but also pathological changes in nearby anatomical formations. Informative methods include elastography, and the most accurate is liver biopsy. All obtained data are examined using a special Child-Pugh scale, which allows you to accurately determine the phase of the disease: compensated, subcompensated, decompensated.
Prevention
A healthy liver loves good nutrition, and it is important that it be varied. Namely, for liver cells to function actively, they need both good unsaturated fatty acids and carbohydrates to process them. On the contrary, if a person eats homogeneous food, for example, sits on a cabbage or rice diet, some of the liver cells are lazy. The liver will “enjoy” several cups of coffee a day - coffee has been proven to reduce the risk of developing liver fibrosis.
To get rid of fat in the liver, you cannot do without regular physical activity, preferably with an increase in heart rate. Suitable for both walking and slow running, cycling, swimming, rowing, regular active walks three to five times a week for at least half an hour are recommended.
Even if weight has not decreased, fat mass will decrease as a result of physical activity. Fats are triglycerides that are broken down and passed from the liver to the muscles because they need energy to move. A physically active person has a much lower chance of developing steatohepatitis.
To maintain liver health, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and try to avoid and reduce bad habits as much as possible. Timely fight against the causes of the disease is the best solution. Prevention is definitely better than cure.
Complications of liver cirrhosis
They are the result of carelessness or lack of awareness of the seriousness of the consequences. Severe complications cannot be cured and cause death. These include:
Ascites is an accumulation of liquid substance in the peritoneum. The abdomen increases, which is noticeable even in a lying position. There is weight gain and swelling of the legs. Swelling does not go away after rest and makes movement difficult.
Bacterial peritonitis occurs when fluid in the abdominal cavity becomes infected. Body temperature rises - up to 40C, severe pain and malaise appear. In the absence of emergency assistance, death occurs.
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neurological symptom complex. Headache, dizziness, and unsteady gait are observed. Often progresses into a coma.
Acute renal failure due to dysfunction of the hepatobiliary system. In the absence of timely resuscitation, it ends in death.
Portal hypertension is accompanied by varicose veins of the gastrointestinal tract. Because of this, bleeding begins, during which the pressure drops, and vomiting with bloody elements appears. The condition often ends in death. Resuscitation does not always help save the patient.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the formation of a cancerous tumor. Occurs when the disease lasts for a long time. Provoking factors are considered to be heredity and bad habits - smoking, alcoholism. In case of single tumors and the absence of metastases, it is removed surgically. In case of extensive degeneration, transplantation will help solve the problem.
The likelihood of complications of liver cirrhosis increases significantly with an inadequate approach or late detection of problems. To protect yourself, you need to undergo a preventive examination once a year, take general and biochemical tests, and do an ultrasound scan of the body. At the slightest suspicion, it is better to consult a doctor.
To prevent liver cirrhosis, play sports or engage in other adequate physical activities. Classes should be regular, preferably in the fresh air. This will help avoid stagnation. The psycho-emotional background is of great importance. Stress causes spasm of internal organs, which affects their functioning. It is better to avoid negative emotions as much as possible.
You should not ignore problems with bile discharge and excess weight. It is important to follow healthy eating rules. Doctors advise keeping a food diary. More movement, less negative emotions - the rule for restoring strength. An active lifestyle and giving up bad habits - drinking alcohol and smoking - will help avoid serious health misunderstandings and eliminate the causes of liver cirrhosis.
Author of the article: Yakovlev Evgeniy Anatolyevich
Narcologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Establishing the severity of liver damage
According to laboratory studies, the severity of hepatocyte damage and the activity of the process are determined. Here, special attention is paid to the level of enzymes secreted by the body for detoxification. Depending on the excess level of enzymes in the blood, the severity of inflammation is determined (from weakly active to highly active hepatitis). An important point here is also to monitor the increase in signs of liver failure, by which one can judge the acute or chronic nature of the poisoning that caused toxic hepatitis.
Liver function can be impaired due to many pathologies. In total, more than a hundred liver diseases are known, caused by different reasons and having different mechanisms of development, different course and prognosis. They occur in people of any age and can be congenital, hereditary, or acquired.
Some liver diseases have a short duration and end in complete recovery, others can bother a person for years and lead to irreversible changes in the liver tissue and serious, life-threatening complications.
English synonyms
Liver disease, hepatic disease.
Symptoms
In the initial stages, symptoms of liver disease may be nonspecific. Some diseases are asymptomatic. Characteristic signs of liver dysfunction appear when a significant part of the liver tissue is damaged. Main symptoms of liver diseases:
- nausea, vomiting;
- heaviness, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera.
There are also a large number of additional symptoms, the presence and intensity of which depend on the form of liver pathology, the activity of the disease and the degree of damage to the liver tissue.
General information about the disease
The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It is located in the right hypochondrium under the diaphragm, borders the stomach, right kidney and intestinal loops and consists of two main lobes and many lobules. Blood enters it through the hepatic artery and portal vein (from the gastrointestinal tract), and flows out from it through the hepatic vein. The liver also has a system of bile ducts, through which bile enters the gallbladder and intestines.
The liver performs a number of vital functions necessary for the normal functioning of the body:
- cleansing – cleansing the blood of microorganisms, toxins, allergens, poisons that enter the liver through the portal vein from the gastrointestinal tract, removing excess hormones and toxic metabolic products;
- synthetic – the formation of blood proteins (components of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems), hormones, enzymes, cholesterol, fats and their derivatives;
- digestive - synthesis of bile, which accumulates in the gallbladder, enters the intestine through the bile ducts and is involved in the digestion of fats;
- depositing - storage of blood, glycogen (a polysaccharide formed by glucose molecules), fat-soluble hormones, vitamins and microelements.
With liver disease, it can increase in size, which causes a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. The outflow of bile, necessary for the digestion of fats, is disrupted, resulting in nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation, bloating, and bowel problems (diarrhea or constipation). The liver does not cope with the cleansing function, which leads to the penetration of poisons and toxins into the blood and causes malaise and weakness. When bile acids enter the bloodstream when liver cells are destroyed, it can cause itching. Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes is caused by an increase in bilirubin levels. It is formed during the destruction of red blood cells, binds to glucuronic acid in the liver (direct, bound bilirubin is formed) and is excreted in the bile. In liver disease, this process is disrupted, and direct bilirubin enters the blood. Violation of protein (albumin) synthesis leads to a decrease in the osmotic pressure of the blood and the release of fluid into the tissue, as a result, edema occurs. Due to a decrease in the number of clotting factors, bleeding increases.
The following factors can cause liver damage:
- inflammation of the liver tissue, for example, with viral hepatitis;
- direct destruction of liver cells by poisons, toxins or malignant tumor cells;
- impaired blood flow in the liver, for example, with cardiovascular failure, hepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrome);
- disruption of the outflow of bile, for example, when the bile duct is blocked by a stone;
- accumulation of fats and cholesterol in the liver, that is, steatosis.
Among the many liver diseases, the most common are:
- alcoholic hepatitis - inflammation of the liver as a result of many years of alcohol abuse, which has a toxic effect on liver tissue;
- cholelithiasis - the formation of stones in the gall bladder and bile duct;
- viral hepatitis A, B, C is an inflammation of the liver tissue that is caused by hepatitis viruses;
- non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - a disease that is accompanied by the accumulation of fats in the liver and can be combined with diabetes, obesity and other metabolic diseases;
- Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease in which irreversible changes occur in the liver tissue with the replacement of normal cells by fibrous connective tissue;
- liver cancer – it can also cause damage to the liver tissue by metastases from cancer of another location;
- toxic hepatitis - caused by a direct toxic effect on the liver of poisonous mushrooms, alcohol substitutes, arsenic compounds, toluene, benzene, lead and other substances.
Less common are hereditary and autoimmune liver diseases, tumors, as well as liver pathologies associated with diseases of other organs and systems of the body. The reasons for some of them are not fully understood.
Liver disease associated with other diseases and conditions
- Jaundice in pregnancy is a manifestation of severe pregnancy pathology, in which the liver can no longer cope with the increasing load.
- Sarcoidosis is a disease that affects the liver, lymph nodes, spleen, lungs and other organs with the formation of limited areas of inflammation in them - granulomas. The cause of the disease is not fully understood.
- Neonatal hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that occurs in children in the first months of life. The most common cause is intrauterine infection with hepatitis A or B viruses. In some cases, the cause of liver damage remains unclear.
- Reye's syndrome is a severe damage to the liver and brain in children after viral infections, which is based on a disruption in the functioning of liver cell enzymes. Often associated with taking medications containing acetylsalicylic acid.
- Amoebic liver abscess is the formation of a purulent focus in the liver, which is caused by a parasite - dysenteric amoeba, which enters the liver from the intestines.
- Autoimmune diseases: autoimmune hepatitis is a disease in which cells of the immune system destroy normal liver cells; the reason for the formation of a pathological immune reaction is not fully known;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis - destruction of the bile ducts by cells of the person’s own immune system; as a result, inflammation and obstruction of the bile ducts develop.
- Hereditary diseases:
- Wilson-Konovalov disease - a disorder of copper metabolism, in which it is deposited in the liver and other organs;
- deficiency of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), a protein that protects the lungs from damage, while a defective AAT enzyme accumulates in the liver, resulting in impaired lung and liver function;
- Alagille syndrome is a hereditary disease characterized by congenital heart defects, pathologies of the spine, eyes, liver and kidneys;
- Glycogen storage diseases - a violation of the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen; defective glycogen can accumulate in the liver, kidneys, intestinal walls and other organs, disrupting their function;
- galactosemia - a violation of the metabolism of galactose (sugar) and its conversion into glucose with the accumulation of its breakdown products, toxic to the liver and other organs;
- hemochromatosis is a disease in which the absorption of iron in the intestine increases and it is deposited in the tissues of the body.
Who is at risk?
- People who require long-term use of medications that are toxic to the liver.
- Drug users.
- Alcohol abusers.
- Not vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Frequently in contact with high doses of toxic chemicals - pesticides, insecticides, household chemicals - without appropriate protective equipment (masks, gloves).
- Pregnant women.
- Obese people.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of liver diseases is aimed at determining the immediate cause of the pathological process and the degree of damage to the liver tissue. A number of studies are also necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the therapy. Some diagnostic methods can detect the disease in the initial stages, when symptoms are absent or mild.
Laboratory diagnostics
- General blood analysis. The level of leukocytes may be increased, which is caused by insufficient purification of the blood from microorganisms or an infectious cause of liver damage. A lack of platelets may also be detected due to a decrease in the concentration of thrombopoietin, an active substance that is synthesized by the liver and stimulates the formation of platelets.
- AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase). Liver enzymes that enter the bloodstream when liver tissue is damaged. With liver disease, their increase is likely.
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT). A liver enzyme, the amount of which increases with damage to the liver and bile ducts. This is especially true for alcoholic hepatitis.
- Prothrombin index. Prothrombin is a precursor of thrombin and is involved in blood clotting. The test is used to assess the rate of blood clotting. In liver diseases, the prothrombin index may be reduced.
- Fibrinogen is a blood clotting factor that is synthesized by liver cells. When liver tissue is damaged, it may be reduced.
- Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is found in all tissues of the body, but mainly in the bones, kidneys and liver. In case of liver diseases, it may be increased.
- Total bilirubin. In liver cirrhosis, it is increased mainly due to the direct (bound) fraction.
- Total whey protein. In liver disease, the level of total protein can be reduced by reducing the amount of albumin. Albumins are the main proteins in blood plasma that are synthesized in the liver.
- Total cholesterol is a substance that is synthesized in the liver and is an element of cell membranes, a precursor of bile acids and some hormones. In case of liver diseases, it may be lowered.
- Tests for hepatitis B, C, D. The presence of hepatitis viruses and antibodies to them in the body is determined.
- Ferritin, transferrin. Ferritin is a protein that binds iron in the liver, and transferrin is a protein that transports iron from the intestines to the liver. Their levels may also be elevated in hemochromatosis.
- Copper, ceruloplasmin. The level of these substances is examined if Wilson's disease is suspected, in which there is a decrease in the level of ceruloplasmin and an increase in the amount of copper in the body.
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin. A decrease in the level of this enzyme may indicate congenital alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- Alpha fetoprotein. This is a protein that is produced in the liver and gastrointestinal tract of the fetus. The maximum level of alpha-fetoprotein is observed in the fetal blood at the 13th week of pregnancy, which causes an increase in the amount of this protein in the mother's blood. Normally, men and non-pregnant women have very low levels of alpha-fetoprotein - less than 1% of the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the fetal blood. However, in diseases that are accompanied by active cell division (proliferation), its amount may increase. In particular, an increase in alpha-fetoprotein levels is a marker for testicular cancer in men or liver cancer.
- Antimitochondrial antibodies are proteins that destroy the membranes of mitochondria (cell components necessary for energy production). Their level may increase in primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Screening study for the presence of narcotic, psychotropic and potent substances. Determination of compounds that could cause liver cell destruction.
Additional research:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Used to determine the size and structure of the liver. It also allows you to identify abscesses, granulomas and other pathological elements in the liver tissue.
- Radiography. Used to determine the size and structure of the liver, and to exclude other liver diseases. With cirrhosis, the liver can be enlarged or reduced, the liver tissue is heterogeneous, with areas of compaction.
- Angiography is of great importance in diagnosis - an x-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the liver vessels, which is clearly visible in the pictures. Used to assess hepatic blood flow.
- Cholangiography. X-ray examination, which is carried out after the injection of a contrast agent into the bile ducts. Allows you to assess the patency of the bile ducts.
- CT, MRI. Methods that resemble radiography, but provide more detailed and clear information about the structure of the liver.
- Radionuclide scintigraphy. This test involves injecting a special short-lived radioactive substance into the body, which is absorbed by liver cells, and then obtaining an image by recording the radiation it emits. Allows you to assess the condition of liver cells and the patency of the bile ducts.
- Fibroelastometry. A method reminiscent of ultrasound. A sensor is used that generates oscillations of a certain frequency. Used for liver cirrhosis to determine the percentage of connective tissue in the liver.
- Liver biopsy. The procedure for taking a sample of liver tissue is carried out using a thin hollow needle, which is inserted through the skin of the abdominal wall after preliminary anesthesia.
Treatment
Treatment of liver diseases is directly determined by the cause of the development of the pathological process. For example, antiviral and antibacterial drugs can be used to treat infectious liver lesions. The treatment regimen also depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of damage to the liver tissue.
Many liver diseases require long-term, complex treatment, which, in addition to treating the immediate cause of the disease, includes monitoring the main symptoms of liver pathology, diet, and general health procedures. In Russia, so-called hepatoprotectors are also used, that is, medications that protect liver tissue. However, there is still no reliable evidence of the effectiveness of these drugs, and they are not used in other countries.
In certain cases, surgical treatment is effective, for example, for cholelithiasis, portal hypertension. Some patients with severe liver disease that cannot be treated with medication may require a liver transplant.
Prevention
- Timely vaccination against hepatitis A and B
- Use of personal hygiene products
- Quitting alcohol and drugs
Recommended tests
- General blood analysis
- Coagulogram No. 2 (PI, INR, fibrinogen)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Alkaline total phosphatase
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Total protein in whey
- Serum albumin
- Total cholesterol
- Transferrin
- Ferritin
- Ceruloplasmin
- Copper in the blood
- Alpha 1-antitrypsin
- α-fetoprotein (alpha-FP)
- HBsAg
- Anti-HCV
- Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
- Screening study for the presence of narcotic, psychotropic and potent substances
- Cytological examination of punctates, scrapings of other organs and tissues
Treatment at the clinical hospital on Yauza
As soon as the patient is given an accurate diagnosis, our specialists immediately prescribe treatment, which is carried out in several stages:
- eliminating the influence of the toxin;
- prescribing a special “liver” diet, the observance of which “spares” the liver
- detoxification of the body and administration of antidotes;
- prescribing drugs to restore liver function.
The first priority, of course, is to eliminate the influence of the substance that caused liver damage. If the reason lies in the use of any medication that the patient cannot do without, the doctor replaces it with another, less toxic drug, or reduces the dose to a minimum. In this case, it may be necessary to work together with hepatologists and specialists from other areas of medicine to select a drug that performs its task, but does not cause drug-induced liver damage, the symptoms of which must be relieved. The capabilities of our hospital allow specialists from different fields to consult with each other and jointly select treatment.
Advantages of treatment in our hospital
- Doctors. Diagnosis and treatment of liver lesions at the hospital on Yauza are carried out by highly qualified specialists with extensive practical experience in the field of hepatology and gastroenterology.
- Diagnostic accuracy. The latest laboratory and instrumental equipment used in our hospital is highly accurate, which allows us to accurately make diagnoses.
- Individual approach. We take into account the characteristics of each clinical case and patient when selecting diagnostic methods, drug treatment, herbal medicine, diet, etc.
- Efficiency. We value your time and know how important it is to be able to begin treatment without delay, so we try to serve patients as quickly as possible.
- High quality of service provision. The quality of our services fully meets the high requirements of international standards.
- Comprehensive support. By contacting us, patients can count on comprehensive support: our specialists will answer any questions, give recommendations, and, if necessary, provide psychological assistance.
What is hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammatory process in the liver under the influence of a provoking (in most cases viral) agent, causing damage to its tissues.
Today, hepatitis is considered one of the most common infectious diseases after ARVI, influenza and chickenpox. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in young people aged 15-30 years (especially those prone to unprotected sex and drug use), another “risk group” is usually represented by medical specialists who have direct contact with blood (including infected people).
Types of liver damage
Based on the reasons that led to pathological changes in the liver tissue, several types of lesions of this organ are distinguished:
- toxic;
- medicinal;
- immune;
- infectious;
- dystrophic;
- oncological;
- metabolic
Of all the above types, drug-induced and toxic liver damage is the most common. Drug-induced damage develops due to long-term use of certain types of medications. Children under three years of age and people over forty are at increased risk.
As for toxic damage, it is provoked by exposure to toxic substances on the body, the main of which is alcohol and its breakdown products. According to recent data, about a third of people suffering from alcoholism have some kind of liver problems.