Pathology is included in the list of neoplasms that arise in the area of the pilosebaceous apparatus of the dermis. Atheroma is a capsule filled with a thick whitish-yellowish secretion with an unpleasant odor. The outer shell of the tumor-like formation is formed from connective tissues covered with flat epithelial cells in several rows.
What is atheroma
Despite the fact that the pathology looks similar to a skin tumor, it is a sebaceous cyst. The appearance of a lump is associated with a violation of the outflow of glandular secretions and its deposition under the skin layer. The secretion usually accumulates in the duct; it is not removed from the gland and makes its walls stretchable. The greasy contents gradually mix with dead organic substances, cholesterol inclusions, drops of fat, and dead keratinized epidermis. The inside of the neoplasm is lined with flat epithelium.
The structure of skin atheroma can be divided into several elements:
- cavity with contents;
- capsule;
- hole (does not always happen);
- leather;
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
The disease is equally common in men and women. It is a common pathology in skin appendage surgery. Most often, a lump is found on the head due to the presence of a large number of sebaceous glands there.
Dangerous signs of complications after surgery
- Addition of inflammation after removal of an uncomplicated form of the cyst, appearance of pus;
- An increase in temperature indicates tissue infection; normally, hyperthermia disappears within 2-3 days;
- Dehiscence of wound edges – discovered during dressing;
- Leakage of blood through the bandage - increased bleeding is diagnosed in hepatitis, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, enlarged spleen, as well as in patients using anticoagulants (Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Heparin, Thromboass).
The appearance of any of the above signs is a reason to consult a doctor, who will assess the risk of complications and carry out therapeutic measures.
Causes of atheroma
The specific reason for the appearance of atheroma is the disruption of the sebaceous glands, but a number of predisposing factors lead to this. They are the ones who provoke problems with the separation of sebum, its increased production and blockage of the duct to the outside, which can lead to the appearance of skin atheroma. Factors in the development of the disease include:
- heredity;
- hormonal imbalance (especially in adolescence, when taking hormonal drugs, etc.);
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- untimely exfoliation of dead skin;
- high viscosity of sebum (individual feature);
- problems with excretory function;
- increased skin contamination;
- narrowness of the gland ducts;
- insufficient hygiene;
- chronic skin trauma;
- negative impact of the environment;
- the use of antiperspirants, which narrow the ducts and clog the gland.
Classification
In practical dermatology, two classifications are used: according to the type of structure of capsule cells (histological) and according to the type of formation. Practitioners mainly use the second one. There are:
- Congenital (or primary) atheromas, the formation of which is caused by congenital changes in the ducts. The size of such formations is up to 0.5 cm, they are multiple and are detected soon after the birth of the child.
- Acquired (or secondary) atheromas develop in initially unchanged gland ducts in people with skin damage or impaired sebum production. The size of cysts can reach several centimeters. As a rule, they are single.
Symptoms and localization
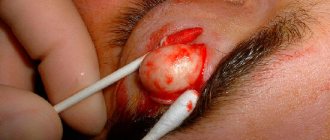
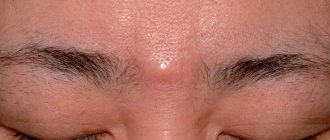
It is not difficult to recognize atheroma by visual examination; additional diagnostics, as a rule, are not required. It looks like a neoplasm located under the skin and comes in various sizes - from a button to a chicken egg. When palpated, the lump is dense, covered with skin, since it is fixed in the area of the gland and does not move freely during palpation. A black dot can be found on the surface - this is a clogged duct of the sebaceous gland. When pressed, fat masses come out.
When palpated, the neoplasm is dense and painless if there is no inflammatory process. Sometimes, in places where visibility is difficult, patients cannot even assume the presence of pathology. When the cyst is small, it does not cause discomfort, and its enlargement occurs quite slowly. For tumors 3–4 cm in diameter, the neoplasm causes discomfort and is a significant cosmetic defect. If we talk about the face, where the skin is thin, patients prefer to remove even small tumors up to 1 cm in diameter, since the lump becomes noticeable.
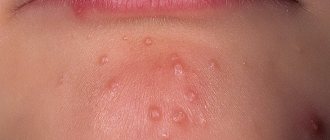
Atheroma is located in places where sebaceous glands accumulate, actively secreting secretions. Most often, a tumor appears in the head area, growing to large lumps. Skin atheromas are also diagnosed on the back between the shoulder blades, in the neck, on the face, near the tailbone and even on the genitals. They can become encysted with connective tissue, remaining the same painless bumps for a long time.
Symptoms of skin atheroma become more obvious if it suppurates. This usually happens with long-existing large tumors. Typical signs of an inflamed cyst:
- pain at the site of the tumor;
- redness and local hyperthermia;
- subcutaneous abscess;
- swelling of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- involvement of surrounding structures, such as lymph nodes, in the inflammatory process.
Atheroma during inflammation can open on its own, especially if there was a blocked duct. Purulent discharge and the contents of the gland are released through it. It is better to remove the cyst in a timely manner so as not to worsen the situation. The transformation of pathology into a malignant neoplasm occurs extremely rarely.
Clinical picture
When consulting a dermatologist, the patient undergoes a standard examination. Visually, the doctor determines the presence of a neoplasm with high mobility and absence of painful sensations during pressing. In the absence of complications, the skin over the cyst remains unchanged; sometimes an enlarged sebaceous duct is clearly visible in this area of the dermis.
If atheroma is characterized by rapid development, then small ulcerations may appear on the dermis. When an infection occurs and the subsequent development of the inflammatory process, the skin becomes red.
Atheroma without inflammation and secondary complications does not affect the life and health of the patient. Most patients seek professional help for aesthetic purposes. In other cases, surgical intervention becomes a necessary measure to stop developing inflammatory processes with the accumulation of purulent contents.
Treatment
Treatment of skin atheroma is not required if it is small in size and not inflamed. In this case, it is enough to observe the neoplasm. As the size of the tumor increases, if it causes discomfort and is a cosmetic defect, it is removed surgically. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. There is no conservative treatment for the disease.
The intervention is performed in a clinic and does not require hospitalization if the skin atheroma is small and located in a place convenient for the intervention. The tumor is excised along with the capsule, as this gives a better effect and reduces the risk of relapse in the same place. An uncomplicated tumor is operated on in one of the following ways:
- an incision is made at the site of the neoplasm in its center, the contents are removed, and then the capsule is excised;
- an incision is made along the edge, the cyst is moved along with the intact capsule and removed with a surgical spoon;
- enucleation using two incisions and jaws, which remove the neoplasm along with the capsule.
The latter method of surgical intervention is the most effective. After removal, self-absorbing internal sutures and atraumatic thread sutures are applied, which must be removed after a week.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist, surgeon or general practitioner. Most often, a general examination is sufficient for diagnosis, since the appearance of the formation has characteristic features.
In rare cases, for differential diagnosis with other benign formations - fibroma, lipoma, hygroma - ultrasound is recommended. This reveals a dense capsule and liquid contents of the cyst.
Since the risk of atheroma degenerating into a malignant tumor is extremely low, a biopsy is usually not recommended. After its removal, a histological examination of the capsule can be performed. The result takes 10-14 days to prepare.
Prevention
There are no effective methods of prevention. If there is increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, atheromas may appear in places near removed bumps or in new locations. As a preventative measure, you can eat less fatty and high-carbohydrate foods so as not to stimulate the glandular apparatus. Use antiperspirants as little as possible; your skin is oily. Use the right skincare products for your skin type to ensure that your pores are free of sebum.
Advantages of visiting our clinic
If you need removal of atheroma using the radio wave method in a clinic in St. Petersburg, then you can safely contact us. Our clinic employs highly qualified specialists with extensive experience who can competently diagnose and prescribe effective treatment. During their work, our ENT doctors use the most modern equipment to treat atheroma. We try to find an individual approach to each patient in order to take into account the characteristics of his body as much as possible. Our center employs highly qualified surgeons who can successfully remove atheromas without the risk of relapse. So, by contacting us, you can enjoy the following benefits:
- Consultation with a doctor with extensive experience.
- Competent diagnostics.
- Correct prescription of treatment.
- Treatment of atheroma is carried out using the most advanced technologies and modern equipment.
- Individual approach to each client and polite treatment.
- Favorable prices.
In addition, our center also employs pediatric ENT doctors , during whose appointments your children will not be afraid. You can find out more detailed information about how atheroma is removed using the radio wave method, prices and much more by contacting our employees by phone.
Answers to frequently asked questions
- Is there a risk of atheroma reappearing?
Yes, even a small number of surviving cells can give rise to the appearance of a new cyst.
- What does a postoperative scar look like? Is it possible to avoid it?
Minimal scars are formed after surgery using radio wave radiation. In second place is the argon plasma method. After these interventions, there may be no scars at all. Traditional surgery leaves noticeable scars.
- How to prevent atheroma?
There are no specific methods of prevention. It is important to control hormonal levels, maintain hygiene, and avoid skin injury.
- What is the difference between atheroma and lipoma?
Lipoma is located in the thickness of the fatty tissue, it is caused by excessive growth of connective tissue and is a benign tumor.
- Can the process become malignant?
No, such cases are excluded, this is not a precancerous disease.
- Can cyst destruction occur on its own?
No, this is impossible, atheroma cannot resolve, it remains unchanged for a long time.
- Is a surgeon required to operate on non-inflammatory atheroma?
Services under the compulsory medical insurance policy may not provide for the removal of non-inflammatory atheroma. The solution is to undergo surgery in a private clinic or wait for inflammation to develop, which does not guarantee the absence of a cosmetic defect after the intervention.
- What are the consequences of self-squeezing atheroma?
The cyst is usually located in areas of intense blood circulation, so there is a high risk of infection spreading to the brain through the blood vessels if bacteria gets into the wound. You cannot squeeze out the cyst - you need to seek qualified medical help.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors