According to statistics, even many absolutely healthy people experience the unpleasant phenomenon of peeling and the formation of skin crusts in the ears for no obvious reason.
In a healthy person, this phenomenon does not require special treatment, but if peeling causes discomfort in the form of itching and the separation of a sufficiently large number of skin flakes, most likely there is a problem in the body.
When everything is in order in the body, skin cells fall off quietly, but if they are infected with fungus, they stick together and turn into dandruff.
Causes of ear dermatitis
There are several different conditions that can cause dermatitis of the auricle or ear canal. All these pathological processes have their own provoking factors and trigger conditions.
- Atopic eczema is quite often localized in the parotid area. If ear dermatitis appears in a child, as a rule, it is based on an atopic process. The disease is caused by hereditarily caused defects in the functioning of the immune system in combination with environmental factors. This leads to a breakdown of the protective barrier of the epidermis, making it vulnerable to infections and allergies.
- A contact reaction is an inflammation of the skin in response to direct contact with an irritating or allergenic substance.
- Seborrheic lesion is a condition associated with improper functioning of the sebaceous glands, which often causes ear dermatitis in infants.
- Otitis externa is a bacterial process when, with prolonged inflammation and poor hygiene, an infection occurs. This process can be both acute and chronic.
Main provoking factors:
- Soap, detergents, wet wipes,
- Food allergens such as soy, milk, nuts, seafood, wheat,
- Some metals: nickel, chromium,
- Perfumed care cosmetics, soaps, perfumes,
- Rough fabrics that come into contact with the body: wool, synthetics,
- Antiseptic products, disinfectants,
- Cigarette smoke
- Psycho-emotional stress,
- Dry air
- Hot climate,
- Infections.
Diagnostics
If a serious illness is suspected, the doctor may suggest several types of examinations. Which ones exactly depends on the collected history and actual symptoms. Usually the doctor acts according to the following scheme:
- visual inspection,
- dermatoscopy,
- laboratory, microscopic examination,
- blood test (or other biological material) for vitamins.
If the question arises as to why the earlobes itch, and a specialist wants to rule out allergies, then there is a need to conduct allergy tests. A needle test is performed, and the result can be assessed almost immediately after 15-20 minutes. There is also a method that uses a patch with substances applied to it that cause suspicion.
Symptoms of ear dermatitis
Auricular eczema causes symptoms similar to eczema on any other part of the body. Patients may have:
- Dry, flaky skin around the external auditory canal, on the concha and in the parotid area,
- The same changes can affect the external canal of the auditory organ,
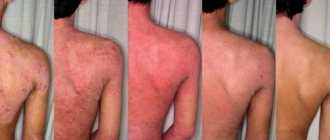
- Redness and swelling of the ear and parotid area,
- Itching around and inside the ear canal,
- Clear discharge from the ear.
Often these changes extend to the area behind the ear and affect the fold where the ear joins the head.
For most people, symptoms of eczema are mild or moderate. But in some cases the itching is very pronounced, and then the following symptoms also appear:
- The skin becomes bright red or dark,
- Severe swelling appears,
- There are areas of very dry and sensitive skin,
- The flaky areas take on a rough, leathery appearance,
- Inflamed skin becomes wet, bleeds and becomes covered with drying yellowish crusts,
- An infection of the external auditory canal occurs.
Infectious inflammations are a special group of ear diseases that require a careful approach to treatment, so these conditions must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. The infection can be primary, when microorganisms infect a healthy ear, or secondary, when it develops against the background of some kind of skin disease. Otitis externa often affects swimmers. Pool water entering the ear washes away protective wax and causes dryness.
Symptoms of infectious external otitis:
- Ear pain, which can be very intense,
- Itching of the ear canal,
- Discharge of fluid or pus from the ear,
- There may be some degree of mild hearing loss,
- The temperature may rise.
If these manifestations appear, you cannot self-medicate; you need a doctor to select medications.
Ear dermatitis in an adult
Ear dermatitis is common in older people, and in adults it is usually contact eczema or bacterial inflammation. Contact eczema is caused by metal jewelry, glasses, headphones, earplugs, as well as hair dye, some care products, and perfume, which is sometimes applied to the earlobes. Bacteria can enter the outer ear canal through bathing, swimming in pools and especially in open water, and when the skin inside the ear is damaged, such as by scratching or cleaning the ears.
...and what to do
Folk remedies help a lot in the fight against beard dandruff - you can try them if you are not yet ready to consult a doctor. If you have a brush, apply a mixture of castor, flaxseed and camphor oils to it and gently massage your beard. Oils will provide all the necessary substances for rapid healing of the skin. You can also add Vaseline - it moisturizes the skin well, but a modern man is better off giving preference to professional care products.
If you are sure that the problem is poor nutrition and digestive problems, try drinking an infusion of burdock, St. John's wort and string mixed with chamomile infusion. Of course, before this you should adjust your diet. Remember that beautiful skin and hair are, first of all, a reflection of the owner’s health!
If simple methods do not help, you should consult a doctor - a dermatologist or trichologist. He will prescribe appropriate treatment. Remember that buying medications on your own is very dangerous - you can not only aggravate the problem, but also harm yourself.
Ear dermatitis in a child
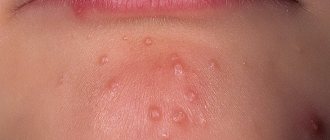
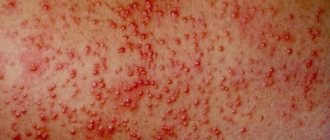
Ear dermatitis in the form of seborrheic and atopic (as shown in the photo) are the most common causes of skin lesions in the ear area in children. Seborrhea affects the area behind the ears, the postauricular fold and the concha itself. Peeling appears and yellowish greasy crusts accumulate. The itching is not very pronounced. In this case, the scalp is also significantly affected. Sometimes parents notice a connection between pathology and errors in diet. Treatment consists of mechanical removal of the crusts after softening with almond oil. Children outgrow this problem; in adulthood, the ears are affected much less frequently.
Atopic eczema manifests itself as intense itching with peeling and weeping, and is often localized in the ear canal. Atopy is often common when eczema is located in a baby on the cheeks, neck, skin folds, and is combined with bronchial asthma and seasonal pollen allergies.
Before visiting the doctor
In case of allergic itching, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the possible allergen; in case of a severe reaction, you can take an antihistamine tablet, which should be reported to your doctor. Self-medication of skin diseases or fungus is unacceptable: without accurately establishing the nature of the skin lesion, they become chronic and increase the treatment time. Before visiting a doctor, you can reduce itching and flaking by cleaning your ears with an alcohol solution, vegetable oil, or petroleum jelly.
httpss://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iEmtM62GQkw
Treatment of ear dermatitis
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment for inflammation of the skin around the ear may vary. However, in most cases it begins with general home measures and changes in routine. This approach includes:
- Rinse your ears with warm (but not hot) water every evening,
- Using a gentle, hypoallergenic moisturizer immediately after water treatments to “lock in” moisture and prevent skin dehydration,
- Eliminating all triggers that come into contact with the skin. Thus, the condition is often provoked by metal earrings, which contain nickel. They need to be replaced with hypoallergenic gold-plated or silver ones,
- Wearing a hat that covers the ears during the cold season, since cold can serve as a provoking factor for the development of the described pathology,
- Switching to the use of hypoallergenic skin care products that do not contain dyes, fragrances, ethyl alcohol and harsh surfactants,
In any case, before starting treatment of any skin lesion in the parotid area, you should consult your doctor. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose and select the right treatment, even if therapy can be carried out with home remedies.
Treatment of ear dermatitis with medications
In some cases, ear dermatitis does not respond to methods such as changing the regime and caring for the skin of the ears, in such cases it must be treated with pharmaceutical products.
Sometimes you have to choose the right remedy. If the first prescribed treatment does not show the expected effect, the doctor will prescribe an alternative method or a new combination of drugs.
Treatment may include various combinations of the following:
- Steroid hormones in the form of ointments are applied to the affected areas, which are itchy and weepy. Often ear dermatitis is located in the fold behind the ear, in this case glucocorticoid ointment is especially indicated, and patients leave good reviews about its effectiveness. Drugs from this group relieve inflammation, eliminate itching, swelling, peeling and other symptoms. If the skin lesion is located inside the canal, steroids are applied in the form of drops.
- Antihistamines are drugs in tablets whose main effect is antipruritic.
- Antifungal agents are effective in the seborrheic process, in the development of which, as scientists suggest, a microscopic fungus plays a role. Often these drugs are prescribed simultaneously with other groups of drugs.
- Antibiotics are indicated for bacterial dermatitis, or otitis externa.
- Non-hormonal ointments and drops have different directions of action. Compositions with moisturizing additives help retain moisture in the dermis and affect dryness and flaking. Salicylic emulsion exfoliates and eliminates dead epithelial cells. Herbal extracts and naftalan oil soothe and fight inflammation. Natural oils (coconut, shea, almond) effectively soften and “lock in” moisture. Olive oil, on the contrary, is not recommended, since studies have confirmed that it disrupts the barrier functions of the epithelium.
Precautionary measures
If you have just managed to get rid of the unfortunate crust in your ears, then you are still at risk. To prevent the disease from appearing again, follow the recommendations of experienced dermatologists:
- observe personal hygiene rules, do not use other people’s accessories (for example, headphones or earplugs) and wash your ears regularly;
- Otolaryngologists prohibit the use of cotton swabs to clean the ears, because they destroy epithelial cells and eliminate the protective lubricant formed in the ear canal;
- Spend more time outdoors and try to follow the generally accepted daily routine (it is advisable to sleep at least 8 hours);
- Under no circumstances should you overcool your ears during the cold season, so buy a hat;
- protect your ears from water, especially chlorinated water, getting into them (you should get a special swimming cap);
- if a person wears a hearing aid, it is necessary to regularly clean the device and use special ear drops;
- do not start treatment for otitis media and boils, otherwise it will be difficult to get rid of the crust in the auricle;
- drink still mineral water as much as possible , because it will help improve your metabolism;
- try to avoid stressful situations (you can improve your perception of the world around you by doing yoga or reading books on self-development and psychology);
- start eating a balanced diet (fruits, vegetables, herbs, cereals, meat and dairy products).
Important point! If dandruff in the ears is left untreated, acute mycosis may develop. The fungus acts not only locally, but also begins to penetrate deep into the tissues of the body.
To treat dandruff in the ears, you need to use an integrated approach - at the same time eliminate the cosmetic problem with the help of ointments, lotions and tablets, and also begin to lead a healthy lifestyle, eating foods rich in fiber and vitamins. Remember to drink at least 2.5 liters of water per day.
You should not think that the white grains will immediately begin to disappear; at least 2 months must pass for the skin on your ears to regain its previous healthy appearance.