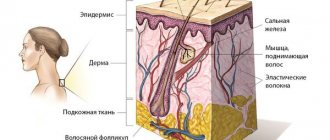
Why can a mole get bigger?
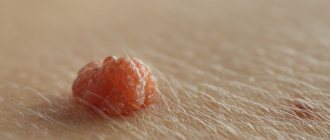
As I have written many times, a mole consists of nevus cells. They are a bit like melanocytes, which are what cause our skin to turn brown after tanning. They, like melanocytes, produce pigment and therefore most moles are brown. Pigment cells divide very rarely, if not almost never divide. However, this can occur under the influence of certain factors. The most studied of these causes are sunlight and pregnancy.
Intense sunlight
is a damaging factor for our skin.
The pigment melanin, which was mentioned above, protects our skin from its negative effects. Sometimes the intensity of production of this substance is not enough for protection and the body gives a signal to divide nevus cells and melanocytes. As a result of this, we may see an increase in our moles and the appearance of new ones.
Read more about sun protection in this article.
Pregnancy.
I will assume that many of the women reading this article have noted the growth of existing moles and the appearance of new ones in this difficult period of life.
The fact is that during pregnancy you can grow a whole new person in 9 months. For tissue growth, hormones are needed, which are secreted by the body in considerable quantities. The child grows, and along with him, the nevus cells of moles also come under the influence of the mother’s hormones. As a result, just like when exposed to sunlight, we can notice the growth of moles and the appearance of new ones
.
In addition to these two factors, there are probably others, however, they are still waiting for their researchers.
WAYS TO REMOVAL RED MOLES IN THE FACE CLINIC
At the FACE clinic, red moles are removed in several ways.
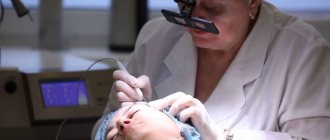
The surgical method involves removing small red moles on an outpatient basis. But this procedure is not suitable for excision of angiomas on the face.
The laser removal method is the most popular because it is applicable even for deep-lying angiomas.
Initially, the surface of the angiomas is treated with a special anesthetic gel, or an anesthetic drug is injected with a syringe, after which the mole is exposed to laser radiation. After 24 hours, a crust appears at the site of laser exposure, which disappears after 1-3 weeks without additional intervention.
Also, in clinics of PERSONS they practice cauterization of moles using coagulation or carbon dioxide and nitrogen, which does not pose a danger to human health and does not leave scars on the skin. Local anesthesia is first administered, so the patient feels pain during the procedure.
How to distinguish a large mole from melanoma?
Here it is important not to “rely on” only one sign. In the ABCD rule, which, of course, is very important in diagnosing melanoma, there are at least 3 other signs - A
(asymmetry) -
asymmetry
,
B
- (border) -
edge, border
and
C
- (color) -
color
.
All three of these characteristics are assessed only together, and not separately. This means that even if a mole is slightly asymmetrical, but has a smooth edge, is evenly colored and its size does not exceed 5 mm, most likely everything is fine with it. Moreover, there is such a type of moles - dysplastic nevi
, which most often have 2 signs at once - an uneven edge and an asymmetrical shape. However, in the vast majority of cases they are benign.
Allergic processes
Such skin reactions are increasingly common among modern people.
Allergic pimples usually do not hurt, they are numerous and itchy.
May be accompanied by a burning sensation.
Extensive rashes may affect pigmented areas of the skin.
As a result, everything looks as if a person suddenly developed a lot of pimples in the form of moles.
If the allergy is quite active, then after the process subsides and resolves, peeling and crusts remain.
You cannot rip it off, as it can easily cause infection.
Congenital nevi
Separately, it is worth dwelling on congenital large moles (nevi). Moles that appear during the first year of life are also called congenital. Studies have shown that the risk of developing into melanoma in such nevi is higher than in those that appeared during life. This is especially true for congenital moles whose size exceeds 20 cm. For them, the risk ranges, according to various sources, from 6 to 30%. Many dermato-oncologists recommend removing such nevi immediately
when the child reaches 10-12 years of age, when the risk of anesthesia is less than at an earlier age.
WHEN YOU NEED TO PAY ATTENTION TO THEM
Specialists from LIC clinics recommend investigating the nature of the origin of red moles, not the subject of oncology, and only after that getting rid of them. After studying the results of the study, the doctor will select the optimal method for removing angiomas.
After red moles have been removed, it is recommended to refrain from visiting saunas, solariums and sunbathing.
Despite the fact that angiomas are usually not dangerous and do not cause harm or discomfort, in most cases, exposure to external factors can cause them to degenerate into malignant formations. This occurs due to damage or exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, if you accidentally scratch or catch a mole, bleeding may begin.
You need to be more attentive to those skin areas where there is a possibility of rubbing them with clothing - this is the neck, shoulders, stomach, chest. Convex moles are the most vulnerable, so they should be removed if possible.
Red moles located on the lips, mouth, ears and eyes are also dangerous.
If the angioma begins to itch, this is a signal that you should immediately seek advice from a specialist or an oncology clinic. Itching may indicate the growth of the tumor and its degeneration into malignant.
When red moles start to itch, you need to figure out what exactly is the reason; without qualified specialists it won’t be possible, since these are the consequences of hormonal disorders or a malfunction of the body’s systems.
NOTE! After studying laboratory tests, specialists at LIC clinics will determine what causes the appearance of alarming signs and how to act to get rid of them. Just remember that you should never scratch angiomas.
How does an oncologist determine whether a mole is benign?
For an experienced specialist, in most cases, one look at a mole is enough to determine whether there is a suspicion of melanoma or not. The ABCD rule is only part of the mole assessment algorithm. In addition, the consistency of the mole, the form of its growth (“pedunculated” or not), the nature of the surface, the history of changes in the mole, etc. are important. A number of other signs can be identified by dermatoscopy. In doubtful cases, it may be necessary to evaluate additional human parameters. These include skin phototype, the presence of melanoma in relatives, taking certain hormonal drugs, etc. Only when more than one obvious
sign
will the oncologist recommend a biopsy (removal) with histology.
Of course, when assessing parameters such as asymmetry, border and color, there is some subjectivity in the assessment. The mole will seem quite asymmetrical to one doctor, but not to another. In doubtful situations, I try to adhere to the “better safe than sorry” tactic.
Dermatoscopy of a pimple on a mole
Dermatoscopy allows one to establish the nature of the process with sufficiently high accuracy.
This is a non-invasive technique.
Its essence is to study a suspicious area of skin at high magnification and under bright light.
This way you can look at the signs of inflammation in the area of the mole - an expanded capillary network, swelling of cells and intercellular space, accumulation of immune tissue macrophages.
The formation of new vessels, atypical cell shape, growth of melanocytes beyond the pigment layer, and infiltration of the basal epithelium speak in favor of the neoplasm.
Briefly about the main thing:
Large moles are neither friends nor enemies. In the vast majority of cases, these are just manifestations of nevus cell division under the influence of sunlight or hormonal changes in the body. Melanoma in general is a fairly rare disease. At the same time, I do not recommend relying on your own conclusions when assessing your moles, because in the absence of experience, they can be either false positive or false negative. Congenital nevi larger than 20 cm, in my opinion, are best removed as early as possible.
If you still have questions, the following will help you:
- In-person appointment with an oncologist
(St. Petersburg and Leningrad region) - Mole removal
with histology (St. Petersburg and Leningrad region) - My online consultation (from anywhere in the world)
TYPES OF RED MOLES
Angiomas can be star-shaped, dot-shaped, or cavernous.
Punctate angiomas are ordinary spots with clear boundaries. If small blood vessels (capillaries) extend from the contours of the mole, then it is a star-shaped variety. Many red spots accumulated in a small area represent a cavernous angioma.
As a rule, red moles appear after 30 years of age; they can rarely occur in children and adolescents. They do not pose a danger to human life.
If red moles form, you should undergo a preventive examination by a dermatologist. When it comes to health, make sure there is no cause for concern.
What complications may arise after mole removal?
If the scar hurts after removing a mole, a relapse is possible.
This happens in cases where, during surgery, not all melanocytes were eliminated; new birthmarks begin to form from the smallest particles remaining.
If moles grow again, they may need to be removed again.
If the wound becomes infected during the postoperative period, the following symptoms may occur:
- increased feeling of itching, weeping
- bleeding
- purulent contents are released from the wound
- the place of the mole is swollen and hurts
- swelling of surrounding tissues (lasts more than three days)
- increase in body temperature (over 38 degrees)
Healing after mole removal: can it hurt and for how long?
What to do if a mole hurts after removal, as well as the area around it?
Sometimes after surgery you may experience discomfort, pain and even a burning sensation.
More often this is observed after surgical removal of the nevus and adjacent tissues.
Minor soreness and discomfort may be present for up to one week, and an itchy sensation may also occur.
After removing the nevus, the wound and surrounding areas are treated with antibacterial ointments or a weakly concentrated solution of potassium permanganate twice a day for 5-7 days.
After surgery, a scab (crust) is formed at the site of mole removal, which protects the damaged area from infection.
In order not to injure the healing surface in the first 7-10 days, the use of a washcloth, taking a bath, sauna, or applying cosmetics is strictly prohibited.
After 8-9 days, the scab disappears, and healthy pink skin appears underneath.
Very often, patients are interested in whether it can hurt and how long it will take for the skin to heal after removal of a mole?
Pain may be present, but not always, and as a rule, if all medical recommendations are followed, it disappears within 2-3 days.
The main condition for rapid recovery is the complete exclusion of direct sunlight.
If the operation is planned to be performed in the summer, it is necessary to avoid going to the beach for 3-4 weeks.
Also reduce the frequency of being outside in the open sun.
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES
People with red moles should not have special restrictions. These formations do not require special care or specific treatment.
But some recommendations from experts should still be followed. As mentioned above, the only thing that can be dangerous is mechanical impact, hence the possibility of damage.
Specialists at LIC clinics recommend removing angiomas in places where there is a risk of injury. Also, avoid excessive sunbathing near water, as water increases exposure to ultraviolet rays. But if it so happens that you cannot avoid them at all, then you should use protective creams with a filter of at least SPF 30.
Diagnosis and treatment
Although the etiology of most birthmarks is still unknown, some have a family connection. Diagnosis is based on history and appearance.
Diagnosis of birthmarks
Most birthmarks are only cosmetic, but some types of nevi are associated with an increased risk of skin cancer. Therefore, for any nevus (pigmented birthmark) that changes color or size, itches or becomes inflamed, careful observation is required. A biopsy may be necessary to rule out malignant changes.
Treatment for birthmarks depends on their type, as well as the presence of other troubling conditions. This usually involves surgical or laser treatment.
Vascular birthmarks are also treated with laser photocoagulation, which targets the affected blood vessels with a laser.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can make an appointment by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Risks of the appearance and development of melanoma
One of the main factors in the development of melanoma is an increase in the duration of exposure to ultraviolet radiation in people whose skin is not genetically adapted to it. As a rule, this type includes people with white skin that is not prone to tanning. Representatives of dark and dark skin, on the contrary, suffer from melanoma much less frequently (10-20 times less often). In addition to genetic predisposition, there are other risk factors:
- Physical – ionizing radiation, trauma, excessive insolation, fluorescent lighting;
- chemical – contact with nitric acid, benzene, coal and pharmaceuticals;
- biological - with alcohol and certain medications (for example, estrogen-containing hormonal drugs).
External biological characteristics of the body that increase the risk of developing melanoma also include: the first two skin phototypes (in which the skin is light and prone to sunburn), the presence of freckles and lentigo, a family history, and immune disorders. Based on the above factors, 3 risk groups are distinguished, which are more likely to undergo screening examinations according to indications.
Which doctor should I contact about a mole?
There are several medical specialties that treat nevi: dermatologist, oncologist, surgeon. There is also a separate doctor for skin tumors - an oncodermatologist.
Visit to the dermatologist
A dermatologist is the first doctor you should contact about a mole. It is this specialist who, in most cases, is able to exclude a malignant process based on the results of examination and dermatoscopy.
Why go to a surgeon?
If the mole turns out to be benign, but is constantly subjected to friction or pressure, then it can be removed by a surgeon. You can contact a plastic surgeon if you have an aesthetic problem such as a mole on the face or other visible areas of the skin. For such nevi, if they do not raise questions regarding their benignity, laser removal is recommended.
When should you contact an oncologist?
If you have a mole with signs of malignant degeneration, you can immediately contact an oncologist. A doctor in this specialty has the necessary knowledge and skills for the surgical treatment of melanoma and other malignant skin tumors. The earlier cancer is detected, the more favorable the future prognosis will be.
Can the problem be solved by a cosmetologist?
Removal of moles in beauty salons and offices is possible only by a cosmetologist who has a higher medical education. There are several ways to remove a benign formation on the skin: laser method, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation. The patient needs to consult an oncologist before having the nevus removed by a cosmetologist, since, for example, after laser removal the possibility of histological examination of the tissue is lost.
Oncologist-mammologist
Women who have moles on the skin of the breast with signs of a possible malignant process should be examined by a breast oncologist. A doctor in this specialty selects a treatment plan taking into account the characteristics of the structure and functioning of the mammary glands.
What does a dermato-oncologist do?
The specialist studies nevi and prescribes tests to determine the nature of the neoplasm.
Conducts differential diagnostics, assesses the likelihood of transforming a benign process into a malignant one.
First, a visual inspection is carried out.
Then specialized equipment is used for a more detailed study - a dermatoscope.
If there are risks of malignancy or the process of malignancy has already started, surgical intervention is prescribed.
The operation is performed by a surgeon using general or local anesthesia.
Pigmented birthmarks
A pigmented birthmark gets its color from the presence of an abnormal group of pigment cells in the skin. The colors of pigmented birthmarks can vary from black to brown.
Pigmented birthmarks
Although most moles are small and round, there are large specimens that have different colors. Moles can be either smooth, so they are flush with the skin, or raised above the surface of the skin.
Birthmarks can have a smooth or rough texture. Some commonly encountered moles in everyday life are called by special names that characterize their color. For example, there are "cafe au lait" moles, which take their name from their typical light brown color. Some people develop dark brown "coffee" moles.
Mongolian spots are another common type of nevi that are bluish-gray in color and are most often found in dark-skinned children. They are usually present at birth and visible over the back and buttock area.