What are the common types of benign formations (tumors):
- lipomas;
- fibroids;
- angiolipomas;
- benign fibrous histiocytomas;
- neurofibromas;
- schwannomas;
- hemangiomas;
- tendon cell tumors;
- myxomas.
Benign soft tissue lesions rarely metastasize but are often large and deep. However, some formations behave very aggressively. Diagnosed invasion of nearby tissue increases the chance of incomplete removal and the possibility that the tumor will return. In adults, the most common benign soft tissue tumor is lipoma. In children - Baker's cyst. Most often, lipoma and hemangioma are observed in both adults and children.
What is basalioma
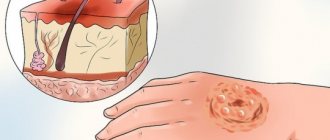
Basalioma (basal cell carcinoma) is most often a small formation on the skin in the form of a nodule or ulcer. It is usually mistaken for a simple sore that becomes covered with a serous crust. A depression with a crust may also appear in the form of a nodule. If the crust is removed, an ulcer will appear in this place, which will grow deeper and wider. The ulcer may disappear, but the tumor will continue to grow in the periphery.
Basal cell carcinoma can be confused with keratoacanthoma (sometimes only after a thorough history of the disease can a correct diagnosis be made). An incorrect diagnosis will lead to unjustified surgical treatment, which will result in a very bad cosmetic defect: it is difficult for a surgeon to work with this formation - it is no different from a tumor. In this case, keratoacanthoma will go away on its own in 2–3 months.
How dangerous is basal cell carcinoma?
Metastases rarely occur with basal cell carcinoma; some patients “grow” the tumor for years without any significant deterioration in their general health. That is, at first glance, this disease does not seem so dangerous. However, without proper treatment, basal cell carcinoma can lead to severe damage to the skin and soft tissues. If we omit the aesthetic aspect, then this is an open wound, due to which the risk of infection by various viruses and bacteria increases. In the worst case, if basalioma is not treated, cartilage and bone tissue will be destroyed.
How to treat basalioma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma should begin as early as possible: in advanced cases, the disease is more difficult to treat, which leads to at least a poorer cosmetic effect.
There are several methods for treating basal cell carcinoma. Which one to choose depends on the shape, size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s age and concomitant diseases. This can be radiation, laser or photodynamic therapy, surgical excision, chemical or cryotherapy, radio wave therapy. In all these cases, the main goal is to remove the tumor. The most radical methods are surgical excision and photodynamic therapy.
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy is a relatively new method of treating malignant tumors, which patients are practically unaware of. Its essence lies in the fact that the tissue is exposed to light with a certain wavelength. Tumor cells accumulate a substance (photosensitizer) and are destroyed when exposed to light. The cosmetic effect in this case is much better than when using other methods. In addition, photodynamic therapy can remove tumors that cannot be removed surgically. For example, if the corner of the eye, upper or lower eyelid is affected.
| Rice. Basalioma | Rice. 5 days after PDT |
| Rice. 3 weeks after PDT | Rice. 2 months after PDT |
More information on the topic of uterine fibroids:
Uterine fibroids, Submucosal uterine fibroids, Subserous uterine fibroids, Removal of uterine fibroids, Removal of the uterus for fibroids, Author's treatment methods, Laparoscopic myomectomy, Hysteroscopic myomectomy, Control hysteroscopy, Pregnancy after laparoscopic and open myomectomy, Uterine artery embolization (UAE), Uterine fibroids - sizes in weeks, Multiple fibroids, Large uterine fibroids, Uterine fibroids - hormones or surgery?, Uterine fibroids in combination with endometriosis, Uterine fibroids in combination with adenomyosis, Hysteroresectoscopy of uterine fibroids, Interstitial uterine fibroids
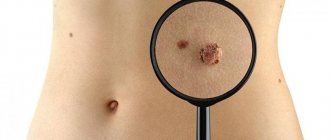
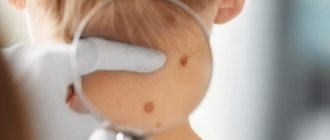
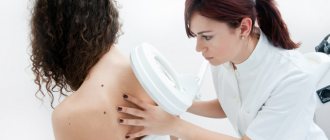
What is melanoma and how is it diagnosed?
Melanoma is the most dangerous cancer. However, it is not very well detected in the early stages in Russia. Such formations are usually flat, they may even be colorless. A competent doctor will always suggest that a person look at all formations on the body, even if the reason for the visit was a benign mole. In this way, serious problems are periodically identified. One of the important mistakes when diagnosing melanoma is biopsy. Such a procedure can provoke tumor dissemination, that is, its spread. Therefore, dermatoscopy plays a major role in the diagnosis of melanoma. To diagnose melanoma, you need to have certain knowledge when using a dermatoscope. Unfortunately, not every dermatologist or oncologist has the necessary skills.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is the most affordable method of treating skin cancer. Surgery is most effective in the early stages of cancer development due to the lack of tumor growth into nearby tissues. The surgeon removes the tumor and all affected areas. In the presence of metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes, their removal is indicated. If an aggressive form of the tumor develops, surgical intervention alone is not enough to completely get rid of the pathological focus.
A modern method of surgery to remove skin cancer is micrographic surgery using the MONS method. In this case, tumor cells are removed layer by layer under microscopic control. Each removed layer is sent for histological examination.
How to treat melanoma
The choice of treatment tactics for melanoma depends on its stage. In the initial stages, only removal of the formation may be necessary. In other cases, this cannot be limited - the patient will need to undergo systemic specific treatment.
The choice of method for removing the tumor depends on its condition and size. Only an oncologist can determine how best to remove the tumor. In addition to direct surgical removal, photodynamic therapy (PDT) can do this, but provided that the tumor cannot be removed with a scalpel.
You need to know that some skin manifestations (dermatoses) can be useful “signs” for the oncologist to identify internal malignant tumors.
In addition to melanoma and basal cell carcinoma, there is also squamous cell carcinoma. However, it is less common. In general, skin cancer is quite common, so if any suspicious formation appears on the skin, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will conduct an examination and find out whether there is cancer. And even if the answer is positive, the earlier the malignant tumor is “caught,” the greater the chance of success and a good cosmetic effect.
Malignant neoplasms of the skin - symptoms and treatment
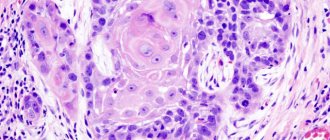
Malignant skin neoplasms (skin tumors, skin cancer) are one of the most common types of cancer, which in most cases appears on sun-exposed areas of the skin. Skin cancer develops from cells that, as a result of mutations, have acquired the ability to reproduce uncontrollably and have ceased to obey general regulatory mechanisms.
The key features of malignant neoplasms, in contrast to benign ones, are the ability to grow into surrounding tissues (invasive growth) and spread to various parts of the body with the formation of secondary foci - distant metastases. Malignant skin tumors can develop from different tissues:
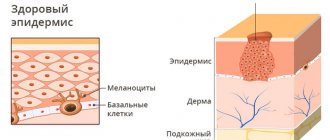
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type. It accounts for about 80% of all skin cancer cases. The tumor develops from the cells of the deepest—basal—layer of the epidermis. Normally, due to the division of basal cells, skin renewal occurs, but in this case this process is pathologized.
- Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 20% of all skin cancers. It develops from keratinocytes, the main cells of the epidermis.
- Melanoma is often mistakenly called skin cancer. Strictly speaking, in this case only malignant neoplasms from cells of the integumentary tissue (epithelium) are classified as skin cancer. Melanoma develops from melanocytes - cells that produce the pigment melanin, which can be found not only in the skin, but also in the mucous membranes, choroids of the eye, nail bed and meninges.
- Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, aggressive malignant tumor of neuroendocrine origin.
- Rare malignant skin tumors : various types of sarcomas (tumors of connective tissue), Kaposi's sarcoma, tumors of glandular tissue, lymphomas [1][2][3].
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are quite common in Russia. They make up 9.8% of all malignant tumors in men and 13.7% in women. Every year more and more cases are detected: from 2005 to 2015, the prevalence of the disease increased approximately 10 times [4].
Melanoma is a rarer malignant tumor. It accounts for only 1.4% of all cancers in men and 1.9% in women. However, unlike basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma, which usually grow very slowly, melanoma quickly spreads throughout the body, forming metastases, and much more often leads to the death of patients [5].
The prevalence of Merkel cell cancer among people of Caucasian descent is only 23 cases per 10 million population. Other skin tumors are also rare [3][6].
The most significant risk factor is skin exposure to ultraviolet radiation. By affecting skin cells, ultraviolet rays can cause changes in DNA that lead to malignant degeneration. The risks are increased for beach lovers and tanning salons. A person's chance of developing skin cancer in the future increases whenever they get sunburned. Sunburn is especially dangerous for children [2][4][5][9][11][12].
The lighter the skin, the more sensitive it is to ultraviolet rays. There are six skin phototypes. The first and second are the most vulnerable, the fifth and sixth are the most stable [2].
Other risk factors for skin cancer:
- Ionizing radiation . Until reliable methods of protection were developed, skin cancer was common among workers in radiography rooms.
- Chronic injuries, skin burns.
- Contact with carcinogenic substances : coal and briquette dust, arsenic, soot, etc.
- Infection caused by human papillomaviruses (HPV) types 16 and 18 , in some cases, is detected in squamous cell skin cancer in the area of the fingers and genitals.
- Red hair color is often associated with the first skin phototype and the risk of cancer.
- Age over 50 years for basal cell carcinoma. At the same time, melanoma is the most common type of malignant tumors at a young age.
- Disorders of the immune and endocrine systems . For example, the risks are increased in people who take drugs that suppress the immune system [4].
The risk of melanoma is also increased if a person has 10 or more dysplastic nevi - large moles (usually more than 5 mm) with uneven coloring and jagged edges, more than 100 moles in a lifetime, or a giant pigmented nevus that covers more than 5% of the body surface [5].
The likelihood of developing skin cancer increases with some hereditary diseases, such as Gorlin syndrome (a rare autoimmune disease, basal cell nevus syndrome).
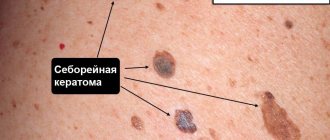
There is a fairly long list of precancerous skin conditions, such as scleroderma pigmentosum, actinic keratosis, senile keratoma, cutaneous horn, etc. Xeroderma pigmentosum can lead to melanoma.
Heredity also matters - the risk of getting sick increases if malignant skin tumors have already been diagnosed in close relatives [4][5].