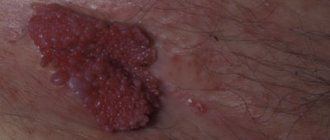
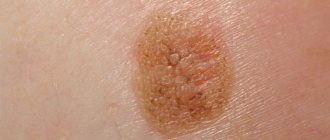
Skin formations in the intimate area, similar to warts, appear for various reasons and occur in people of both sexes. They can be a consequence of human papillomavirus infection, syphilis, benign in nature, or be a cancerous tumor. Therefore, any warts in the groin in men first need to be diagnosed and then removed. Warts that appear in the perineal area are nothing more than genital warts. They are somewhat more common in men, especially in the groin.
Rice. 1. Genital wart in the groin
What it is?
Anogenital warts are growths protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes that appear on the genitals or in the anus.
They are formed after infection with the human papillomavirus. In total, more than a hundred types of the virus are known, and it can also cause ordinary warts. They differ from anogenital ones in location and form on the skin of the palms, knees, fingers, protrude above it, feel compacted to the touch, and can grow together. The types of virus that cause anogenital warts are not associated with cervical cancer. In 70% of cases it is caused by a number of other types of pathogens. However, such neoplasms require monitoring and treatment by a dermatologist or venereologist. Read more about it in our article “Human papillomavirus”.
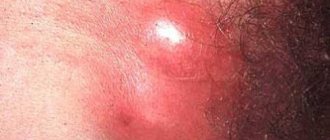
Atheroma
The origin of atheroma is fundamentally different from lipomas. Atheroma develops from the sebaceous glands of the skin. For various reasons, the gland duct becomes clogged, secretion accumulates in the gland, which gradually begins to increase in size. Atheroma is defined as a small (from 0.5 to 2 - 3 cm) formation, which always rises somewhat above the skin and is always fused to it (i.e. the skin above the atheroma does not move), and can grow slowly. Atheroma always has a capsule and contains atheromatous masses resembling crushed lard.
Because The atheroma is connected to the external environment by a duct; there is always a threat that it will become infected through the duct and suppuration will occur. In this situation, moderate pain appears in the area of the previously “quiet” atheroma, the formation quickly (over several days) increases in size, redness appears around it, and body temperature may rise. Suppuration of atheroma requires urgent surgery.
Reasons for development
The appearance of anogenital warts in 90% of cases occurs after infection with HPV types 6 or 11. From the moment of infection to the growth of neoplasms on the skin, an average of 11-12 months passes in men, and 5-6 months in women. The rapid growth of genital warts is associated with immunity deficiency and pregnancy. Frequent maceration of the skin (its swelling, wrinkling due to prolonged contact with water) can accelerate the spread of neoplasms.
Figure 1. Human papillomaviruses. Photo: iLexx/Depositphotos
Urologists
Erkov Igor Viktorovich Urologist andrologist
Cost of admission 2500
₽
Make an appointment
Fomenko Alexander Pavlovich Urologist andrologist
Cost of admission 2500
₽
Make an appointment
Transmission routes
Both adults and children can become infected with the human papillomavirus. In adults, the most common route of transmission is through sexual intercourse. Infection can occur through contact with an affected area of skin. The types of HPV that cause anogenital warts can also be transmitted through anal sex. Using condoms reduces the risk of infection, but does not completely eliminate it. People who frequently change sexual partners are at risk.
Important! Infection with the human papillomavirus is possible even from a person with an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Children become infected with HPV in several ways. If a pregnant woman is infected, the virus can be transmitted to the baby during childbirth. Prenatal transmission (before birth) is rare. Infection is also possible through contact with affected areas of the skin.
Outpatient treatment of warts on the genitals
The only effective way to combat genital warts, recognized throughout the world, is to remove them.
There are several methods that can help you get rid of unpleasant tumors in a matter of minutes:
- Laser therapy procedure. It is performed under local anesthesia using a colposcope, which makes it easier to view the intervention area. Laser therapy is very effective and leaves no possibility of relapse. For numerous condylomas, the procedure is repeated every other week.
- Cryotherapy is the freezing of lesions with liquid nitrogen. Used at weekly intervals. Hyperpigmentation or scarring develops after cryotherapy. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the experience of the doctor.
- Trichloroacetic acid. This is a strong caustic substance that causes tissue necrosis as soon as the composition is applied to the affected areas. This method of combating condylomas is effective with small changes, and its effectiveness is estimated at 51-81%. Relapses occur in 36% of patients. Side effects: Excessive use of the drug leaves deep wounds and scars.
- Surgical methods. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. The highest level of cure is provided by curettage and electrosurgery methods. Condylomas after such treatment recur in less than 19% of cases.
- Photodynamic therapy - 5-aminolevulinic acid. The method can be used alone or in combination with laser therapy, cryotherapy or curettage. The advantage is a low percentage of side effects and a high percentage of successful procedures.
Cryotherapy
Laser therapy
Photodynamic therapy
Types of warts
HPV can cause several types of skin lesions.
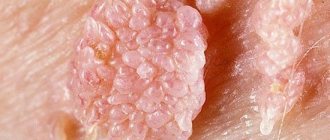
Condylomas acuminata
Neoplasms protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. They may consist of nodules with a loop-like structure, the surface may be variegated. Their appearance may be accompanied by discomfort and itching (not in all cases). Condylomas are localized in the groin, perineum, anus, and genitals;
Papular rash
They look like a rash, are flat, almost do not protrude above the surface of the skin, and are localized in the same way as genital warts;
Stains
Areas of discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals (grayish-white or red spots appear);
Bowenoid papulosis
A sexually transmitted disease, which is accompanied by the formation of many nodules of discolored color (brown, gray, red) on the mucous membrane and skin of the genital organs. Later, such nodules merge into large papules;
Giant condyloma
Papillomas merging with each other (look like small warts), forming a large lesion.
Figure 2. Condylomas and warts. Source: CC0 Public Domain
The appearance of warts and other growths due to HPV may be accompanied by discomfort and itching. In rare cases, the affected areas of the skin may crack, bleed, and become painful.
Lipoma
This is a benign formation consisting of adipose tissue. In essence, it is a local accumulation of adipose tissue under the skin. Lipoma is a benign tumor, although in rare cases, liposarcoma, a malignant formation, can develop under its mask.
Lipomas manifest themselves in the form of soft-elastic subcutaneous formations, mobile, painless, and can slowly increase in size. The skin over lipomas is not changed and easily moves over them. Small lipomas are not visible at all; they can only be detected by palpation. Larger lipomas stand out as “bumps” of round or oval shape. The size of lipomas is very variable - from 1-2 cm to 20 cm or more. Lipomas never become inflamed or suppurate.
Risks during pregnancy
In women infected with the human papillomavirus, pregnancy can provoke the appearance of anogenital warts and their growth. The virus can cause abortion. The mother can transmit the virus to the child during pregnancy (rarely), during childbirth (more often), and during subsequent contacts. For a newborn, HPV is dangerous due to damage to the respiratory tract (development of respiratory papillomatosis, breathing problems, voice formation).
To reduce the risks associated with HPV when planning pregnancy, it is advisable to undergo preventive examination and treatment when the virus is detected. If pregnancy has already occurred, treatment is performed before 36 weeks, using laser or cryodestruction, electrocoagulation to remove tumors. If there are extensive lesions, operative delivery is recommended to reduce the risk of infection to the baby.
In what cases is tumor removal prescribed?
Experts recommend seeking help if there are indications:
- pain when wearing tight shoes or walking for a long time;
- bleeding in the affected area;
- uneven coloring of the neoplasm;
- rapid growth, association of individual lesions into masses.
If you still have doubts about whether it is worth removing the tumors, seek the advice of a specialist.
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor if neoplasms, nodules, compactions, or areas of discoloration appear on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs or anus.
During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the clinical manifestations and examine the affected areas.
To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests may be performed:
- PCR diagnostics with determination of the genotype of the virus; it is additionally possible to determine the degree of viral load. Biomaterial – vaginal smear, scraping from the urethra, cervical canal.
- Morphological, cytological examination to assess the risk of oncological pathology.
Photo: freepik.com
The severity of the condition is assessed by the number of tumors, the volume of affected tissue during examination and laboratory testing (the number of copies of HPV DNA in the test samples is determined).
Important ! Anogenital warts are treated using destructive methods (cryodestruction, laser destruction, electrocoagulation). In this regard, before treatment, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis are required.
Diagnosis is carried out by specialists from dermatovenerology departments. Additionally, consultations with specialized doctors may be required:
- a urologist if the tumors are localized inside the urethra;
- a proctologist if warts grow extensively in the anal area;
- obstetrician-gynecologist when planning and managing pregnancy;
- immunologist (for relapses of the disease or immunodeficiency states).
Treatment of papilloma virus in men
If a man has condylomas on the head of the penis, treatment is carried out in two directions:
- Remove growths.
- Conduct shock antiviral therapy.
None of them have any advantages, since the doctor prescribes treatment based on their examination data and the tests obtained. Often these treatments are complementary to each other.
Drug therapy complements the process of removing papillomas in men. With its help, the immune system is strengthened to avoid relapse, since removal of papillomas again brings the patient to the doctor with the same symptoms of the disease in 30% of cases.
The patient is prescribed immunostimulants: polyoxidonium, immunal, cycloferon, etc. These drugs are prescribed only by a therapist or urologist.
Treatment
The main direction of treatment is the destruction of anogenital warts. In 70-80% of cases, after removal of tumors they do not reappear. Several methods are used for destruction.
Photo: zhykova / Depositphotos
Electrocoagulation
Destruction of neoplasm tissue under the influence of high frequency current. Around the area of the neoplasm, extensive thermal damage to tissue occurs (formation of a dry crust). After it heals, there are no traces of exposure left on the skin.
Laser destruction
Laser exposure at a controlled depth to remove tumors within clear boundaries. Once the wart tissue is destroyed, there is no bleeding and there is no need to close the wound.
Cryodestruction
Destruction and removal of tumors using liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of ultra-low temperature, instant tissue necrosis occurs, followed by rejection and wound healing.
Radiosurgery
It involves the generation of a high-power radio wave that passes through the tumor tissue, destroying it.
If the area of damage to the mucous membranes or skin is extensive, it is possible to remove the tumors surgically. With any method of destruction, the affected area is disinfected and anesthetized before the procedure.
It is also possible to use chemical and cytotoxic methods for the destruction of anogenital warts. For this purpose, local drugs are used that gradually destroy the tumor tissue. Such treatment requires caution and can only be carried out as prescribed by the attending physician.
Important! Attempts to remove anogenital warts on your own can be dangerous: you can injure healthy tissue, cause infection, and provoke the growth of tumors. If the wart was torn off by accident, you need to treat the affected area with an antiseptic, stop the bleeding, and consult a doctor.
Figure 3. Structure of a wart. Source: CC0 Public Domain
In addition to methods of destruction of anogenital warts, local immunomodulators and nonspecific antiviral drugs can be used.
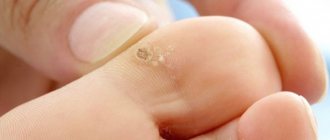
Where do plantar warts come from?
HPV enters the body from the outside. Pathogens love moist environments. You can become infected by wearing someone else's shoes, neglecting the rules of hygiene in pedicure salons, baths, saunas or swimming pools. A virus suppressed by the immune system may not manifest itself for years. But in a weakened body, viral particles begin to divide very quickly. The propagation of plantar strains is facilitated by:
- increased sweating of the feet;
- uncomfortable tight shoes;
- microcracks in the skin;
- fungal infections of the feet;
- circulatory disorders due to joint deformation: arthritis, arthrosis, flat feet.
Within the epidermis, the virus first infects the basal layer. Then it provokes the proliferation of keratinized particles, forming characteristic hard plaques on the skin.
The main symptom of this form of HPV is severe pain while walking. The roots reaching the lower layer of the dermis constantly injure the nerve endings. Many patients have to give up their usual shoes and use thick, soft insoles to alleviate the pain.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of anogenital warts, you need to reduce the risk of HPV infection. To do this, they exclude casual sexual intercourse and use barrier methods of protection.
An obligatory part of prevention is vaccination:
- for women, a two-, four- or nine-valent vaccine is used with a single or double revaccination;
- For men, a quadrivalent or ninevalent vaccine is used.
Vaccination to protect against HPV infection is recommended to begin in childhood. Immunization for girls can be performed from 7 years of age, for boys - from 9 years of age. For girls, HPV vaccinations are especially important because of the risk of cervical cancer associated with the virus.
Papillomas in the groin: why are they dangerous?
The localization of neoplasms in open areas of the body makes them vulnerable.
After all, here they are exposed to frequent trauma with the risk of bleeding and infection.
However, being in closed areas of the body, for example in the groin, papillomas cause no less trouble.
Here they are also often damaged and, as a result, are at risk of malignant degeneration.
Papillomas in the groin occur with equal frequency in both women and men .
An increase in their number occurs due to the activation of papillomavirus against the background of weakening immune resistance.
With hypothermia, alcohol abuse, prolonged stress.
As well as immunosuppressive conditions and diseases accompanied by immunosuppression.
Papillomas in the groin area occur as a manifestation of human papillomavirus infection and are called condylomas.
They are flesh-colored or pinkish in color, resemble cauliflower in appearance, and are on a thin stalk.
Located in the anogenital area, they cause a lot of suffering to patients.
Because they are painful and can bleed if damaged.
If papillomas appear in the groin , you should consult a dermatovenerologist.
The doctor will conduct an examination, determine the nature of the tumors and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Diagnosis is carried out by visual examination and, if necessary, dermatoscopy.
As well as laboratory tests (PCR), during which DNA of the papillomavirus is detected in the body.