Perianal condylomas are growths on the skin in the form of papillae, which are located in the anal folds and around the anus. They can be single or form large foci. Despite their apparent harmlessness, these tumors pose a danger to human health. Their appearance is caused by the activity of the human papillomavirus, and under certain conditions, condylomas can cause squamous cell carcinoma.
Of the 100,000 residents of St. Petersburg, 165 people are infected with HPV subtypes that provoke the formation of perianal condylomas.
Clinical picture of condyloma
Condyloma is a benign change caused by more than 30 low-risk HPV types (most commonly 6 and 11). In men, they are most often found in the external genitalia (penis, foreskin) or in the anal area.
There are several forms, the most common of which are:
- genital warts (condyloma accuminata);
- flat warts (condyloma plan);
- giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma;
- bowenoid papulosis;
- genital wart (Condyloma accuminata).
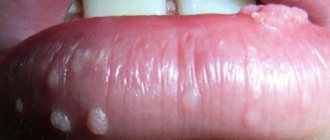
The neoplasm appears soft, pink, with a rough surface and outwardly similar in shape to cauliflower. Less commonly, they can fuse together and form clusters larger than 6 cm. They can appear at any age, but usually occur in young, sexually active people aged 20 to 40 years.
In men, they are mainly located at the tip of the penis or in the anal area, but they can also be found inside the urethra or in the groin area.
Particular attention should be paid to condylomas in children, as they can develop as a consequence of sexual abuse.
Prevention of perianal condylomas
The risk of infection with genital perianal condylomas can be minimized by streamlining sexual life and using barrier contraceptives. If the virus is already present in the body, you should not try to get rid of emerging growths on your own. This can lead to unpredictable consequences, including their malignancy (malignization).
Measures to strengthen the body will also help prevent the occurrence of perianal condylomas:
- proper nutrition;
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- taking vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants.
Regular examinations with a doctor and periodic self-examination of the perineum will help to avoid complications. You can identify condylomas from the photos that are at the beginning of this article. Even if the tumors are small, you should not put off visiting a proctologist.
Treatment of condyloma
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the cauterization of condyloma with high frequency current. Most often it is used if the area covered by condyloma is small. Blood loss is minimal, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is absolutely painless.
Surgical laser
Surgical removal of condyloma with a laser is one of the most effective treatment methods. The advantage of laser technology is high precision without blood loss, since only changed tissue is removed. At the same time, the laser beam destroys all viruses, bacteria and fungi. The surgical field remains completely sterilized, which accelerates wound healing without postoperative scars and deformities.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a method of freezing tissue for destruction. Liquid nitrogen is usually used, the temperature of which is -195.8 ° C.
The mechanism of action involves the formation of ice crystals in the treated tissue, which causes cell destruction. Capillary spasm after the procedure can last up to 48 hours. This tissue anoxia (lack of oxygen) causes further cellular damage, primarily in the marginal parts of the treated area.
Surgically and locally applied drugs
Removal of condyloma with a surgical knife (scalpel) is used for visible genital warts on the penis or around the anus.
Topically used drugs are podophyllin (herbal resin), podophyllotoxin (Condylox), imiquimod (Aldara).
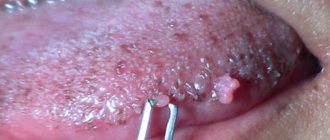
What do condylomas look like - photo
Externally, condylomas of the perianal region are no different from genital warts on other parts of the body. These are small flesh-colored papillae, but they can be pink, grayish or light brown.
At the initial stage of development, neoplasms look like small, single, smooth warts. Usually they do not cause discomfort, and therefore remain unnoticed by the patient.
As the disease progresses, the neoplasms increase in size and spread over a large area, forming conglomerates. At this stage, they may resemble cauliflower heads, as you can see if you look at the photo below.
Even when they spread over large areas, condylomas are always located in islands, between which there are areas of unchanged skin. Moreover, after growing “broadly”, genital perianal condylomas begin to grow in length. As a result, the growths become like grapes.
At this stage, condylomas located in the anal folds can interfere with normal bowel movements. This has become the most common reason for visiting a doctor.
Natural Treatment for Condyloma
- Apple Cider Vinegar – Soak a piece of cotton wool in apple cider vinegar and soak the affected area and leave it on for a while.
- Pineapple juice - apply fresh pineapple juice to cotton wool or, better yet, gauze, hold the preparation on the condyloma for about 10 minutes, then rinse. The procedure should be repeated twice a day.
- Aloe Vera – Apply a thick layer of Aloe Vera gel to the area affected by warts. Repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day for at least 2 weeks.
- Tea Tree Oil – Apply 3 drops of tea tree oil to gauze and apply to the infected area. Tea tree is known for its anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antifungal effects.
- Eat as healthy as possible.
- Wear clean underwear.
- Pay attention to the dryness of the genital area; sweating creates conditions for the proliferation of bacteria and fungi.
- Do not touch or scratch genital warts.
- Avoid intercourse because it not only causes pain and discomfort, but can also cause more problems for your sexual partner.
- Do not try to pick or squeeze genital warts, as this may lead to a more serious infection.
Symptoms and signs of perianal condylomas
The appearance of perianal condylomas is not always noticeable, since the formations can be located not only on the skin around the anus, but also inside it. If the external papillae can be felt with your hand during hygiene procedures, then the internal ones grow to a certain point without causing concern. However, this lasts until they reach a length of several millimeters.
Large condylomas of the perianal area cause constantly increasing discomfort:
- a foreign object is felt in the anus;
- after defecation, tingling or burning occurs in the anus;
- severe, prolonged itching occurs in or around the anus.
With further growth, external growths can also cause constant concern in the form of itching and burning, periodic bleeding due to injury to condylomas by hard sutures, for example. With strong growth in length, condylomas located in the anal folds and directly in the anus make defecation difficult.
Additionally, local inflammatory processes may be observed, since bacteria, fungi, and sweat secretions accumulate in large loose growths. The process is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling, discharge of blood or pus, pain that intensifies during bowel movements, while sitting or walking, as well as when wearing tight-fitting underwear.
Condylomas of this type often appear not only around the anus, but also on the genitals, as well as on the mucous membrane of the rectum.
What types of condylomas are there?
There are several types of condylomas based on their shape:
- Flat;
- Pointed;
- Wide.
Flat condylomas are flush with the skin and look like spots.
They are rare, but are considered the most dangerous.
Condylomas acuminata are growths.
They look like warts and rise above the surface of the skin.
Widespread condylomas are called condylomas, which are caused by the entry of treponema into the body.
Pointed formations are quite common.
What is the prevention of diseases caused by HPV?
Examination of sexual partners of patients with diseases caused by HPV has no proven value in terms of preventing their occurrence/recurrence. However, theoretically, timely and complete removal of OCs and intraepithelial lesions can reduce the risk of these diseases, including cervical cancer. It has not been proven that condoms can protect against HPV transmission, but their use reduces the risk of developing OCs and cervical cancer. The most promising method of preventing and treating the early stages of diseases caused by HPV are specific polyvalent (for HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18) vaccines, which are currently in clinical trials. In summarizing the known information about diseases caused by HPV, the US Center for Disease Control (CDC) draws attention to the public's knowledge of the following key points:
- HPV is an extremely common STD
- It is rarely possible to identify the source of infection due to the highly variable incubation period
- The natural progression of diseases caused by HPV is often benign, and treatment sometimes requires several months. Relapses often occur (up to 50% of cases).
- OCs are most often caused by HPV types that do not cause cervical cancer
- Infectiousness of sexual partners decreases over time
- The effectiveness of condoms in protecting against HPV has not been proven. However, the use of condoms by patients with HPV for new sexual contacts is considered mandatory.
- You should tell new sexual partners that you have previously been infected with HPV
Women, especially those of sexually active age, need to know that the basis for the prevention of cervical cancer is mandatory annual preventive examinations by a gynecologist with a cytological examination of the cervical epithelium according to Papanicolaou, as well as, if necessary, HPV typing, colposcopy and cervical biopsy.
Prevalence of HPV infection
- 1The peak incidence of HPV infection occurs between 20 and 24 years of age, during which period maximum sexual activity is observed.
- 2In women, condylomas are recorded somewhat more often. The incidence ratio of women to men is 1.4:1.
- HPV 3 is the most common sexually transmitted infection.
- 4The likelihood of infection increases with the number of sexual partners.
- 5The earlier the onset of sexual activity, the higher the likelihood of infection.
Risk factors:
- 1Smoking.
- 2Use of oral contraceptives and refusal of barrier contraception.
- 3Frequent change and a large number of sexual partners.
- 4Early onset of sexual activity.
Modern methods of treating genital warts
Genital warts (synonyms: condylomata acuminate, viral condylomas, genital warts, genital warts) are diseases caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Diseases caused by HPV are among the most common contagious viral infections in humans. HPV is a small, round, double-stranded DNA virus with a diameter of 50 to 55 nm. To date, more than 80 types of HPV have been described (Table 1). Infections caused by HPV are highly specific to the epidermis, since HPV has a tropism for epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes.
Genital warts are highly contagious. Infection occurs through contact, most often sexually. The virus can survive for a long time on infected objects. Small abrasions, cracks or abrasions serve as entry points for the virus. The virus can also spread by autoinoculation. Lack of personal hygiene, wearing tight underwear, maceration of folds in obese people, as well as immunodeficiency conditions contribute to the development of lesions over a large area of the skin.
Over the past 20 years, there has been an increase in the incidence of genital warts. In the United States, genital warts (or genital warts) are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The incidence of genital warts exceeds 106.5 cases per 100 thousand US population, which is about 0.1% of the entire population [1]. Close attention to this disease is explained by the fact that some of the types of HPV that cause genital warts can lead to malignancy of the process. The most potentially dangerous are types 16 and 18. It is no coincidence that it is important to promptly diagnose and treat genital warts. Recurrence of genital warts is not always associated with re-infection, but can be caused by reactivation of the virus.
Clinical picture. The incubation period lasts from 3 weeks to 6 months and averages about 2.8 months. Men and women are equally susceptible to this disease. The average age of patients ranges from 22 to 25 years.
Typically, genital warts are localized on the genitals and in the perianal area. In HIV-infected patients, genital warts may appear in unusual places, such as the face, eyelids, and ears. In men, the most common locations are the penis, urethra, scrotum, perianal, anal and rectal areas [2]. The elements of the rash are flesh-colored, can be represented by smooth papules the size of a pinhead, and in the initial stages of development are not always noticeable on the penis. To identify them, a test is carried out with 5% acetic acid. After treatment of the skin, the color of the papules becomes whitish. Subsequently, the papules grow and take on a warty or thread-like shape, resembling cauliflower or cockscomb. As a rule, genital warts are multiple and located in groups.
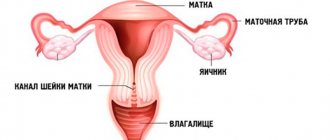
In women, the clinical picture of genital warts can be varied. Classic exophytic lesions on the external genitalia are common and easily detected during examination, but they can also be accidental findings during colposcopy or sigmoidoscopy. On the labia minora and on the vestibule of the vagina, condylomas are moist, velvety or multiple finger-like growths and occupy a significant area. Condylomas in the cervical canal are found in 20% of women infected with HPV and with genital warts localized on the external genitalia. Localization of genital warts on the cervix or in the cervical canal is considered an unfavorable factor, as it can contribute to the development of cervical cancer [3].
Even with timely and rational treatment, genital warts often recur. This is due to the fact that the virus can remain in an inactivated state for a long time in apparently healthy areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Differential diagnosis of genital warts is carried out with secondary syphilis (condylomas lata), molluscum contagiosum, bowenoid papulosis, lichen planus, lichen planus, angiokeratomas, angiofibromas on the coronal sulcus of the glans penis, folliculitis, soft fibroma, pilar cyst (Table 2).
Diagnosis of genital warts is usually not clinically difficult. Additionally, in some cases, a test is carried out with 5% acetic acid. To do this, a medical napkin moistened with a solution is placed in the area of the expected localization of genital warts for 5–10 minutes, after which the rash acquires a whitish tint [4].
When diagnosing genital warts, it is necessary to conduct testing for syphilis and HIV infection.
A biopsy is indicated for those patients who suspect precancerous lesions or squamous cell carcinoma. Removing genital warts does not reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer. Therefore, all women who have a history of genital warts should undergo an annual cytological examination of cervical smears in order to timely detect the oncological process.
Treatment and prevention
Using condoms reduces the risk of infecting sexual partners. It is impossible to completely remove HPV; you can only remove genital warts, easing the patient’s condition and reducing the risk of infecting a sexual partner. There are several treatment methods for genital warts. They all have certain disadvantages.
Cryodestruction is one of the most commonly used treatment methods. The affected surface is treated with liquid nitrogen using a cotton swab or spray. The treatment is repeated every 1–2 weeks until all condylomas are completely removed. The method rarely leads to scarring and is low cost. Cryodestruction can cause severe pain. It is not always possible to treat the entire affected surface at once. In some cases, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation may develop after cryodestruction.
Diathermocoagulation is a painful method of treatment and leaves behind permanent scars, therefore it is used only for the removal of single condylomas.
Laser removal is carried out using carbon dioxide and neodymium YAG lasers (yttrium aluminum garnet lasers). Scars may remain after removal.
Drug treatment methods. Condilin (podophyllotoxin) - 0.5% solution in 3.5 ml bottles with an applicator. The component of Condilin, podophyllotoxin, is the most active in the composition of the plant extract of podophyllin; when applied topically, it leads to necrosis and destruction of genital warts. The advantage of this treatment method is that the patient can independently treat the affected areas of the skin in accessible areas. Using a plastic applicator, the drug is applied to the condyloma; All condylomas are gradually wetted, but no more than 50 pieces at a time (in area no more than 10 cm2). The drug should be applied with caution, avoiding healthy areas of the skin. The first time the treatment is carried out by a doctor or nurse, teaching the patient how to apply the drug correctly. After treatment, the preparation must dry to avoid irritation of the surrounding skin or ulceration. Condilin is applied 2 times a day for 3 days, and then take a 4-day break. The duration of treatment should not exceed 5 weeks. Contraindications for the use of the drug are pregnancy, lactation, childhood, and the use of other drugs containing podophyllin.
Solcoderm is a mixture of acids: 65% nitric, 98% acetic, as well as lactic and oxalic acid and copper nitrate; Available in the form of a solution (ampoules of 0.2 ml). After it is applied to the surface of the skin, it turns yellow, after which mummification of the treated tissue occurs. Treatment must be carried out by medical personnel. The drug is applied to the surface using a glass capillary or applicator, after which the drug must dry. It is allowed to treat an area of no more than 4–5 cm2 at a time. If necessary, treatment can be repeated after 4 weeks. Application of the drug may be accompanied by severe burning and pain, in some cases hyperpigmentation and scarring may occur.
Interferon preparations are injected directly into genital warts. The procedure is painful and requires repeated treatment.
Trichloroacetic acid in a concentration of 80–90% is applied directly to the condylomas. Its remains are removed with talc or sodium bicarbonate. If necessary, treatment is repeated at intervals of 1 week. If after 6-fold treatment genital warts remain, then it is necessary to change the treatment method.
Literature
- KR Beutner, TM Becker, KM Stone. Epidemiology of HPV infections // J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1988; 18: 169–172.
- S. M. Syrjanen et al. Anal condylomas in men // Genitour. Med. 65: 1989; 216–224.
- MJ Campion. Clinical manifestations and natural history of genital human papillomavirus infection // Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. North. Am. 1987; 14: 363–388.
- D. E. Fitzpatrick, D. L. Eling. Secrets of dermatology // M.: ZAO Publishing House BINOM, 1999. 511 p.
L. P. Kotrekhova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor K. I. Raznatovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Moscow
Symptoms
The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 3-6 months, in some cases it can be reduced to several days or increased to several years, depending on the reactivity of the body.
At the site where genital warts appear, the patient may notice the following symptoms:
- itching and burning;
- secretion from formations;
- discomfort (during friction against underwear, the act of urination or defecation);
- swelling, change in color, bleeding due to trauma.
If genital warts are located in the anus, the patient may complain of distension in the rectum, pain during bowel movements, traces of blood or mucus.
Prevention
The main goal of prevention is to prevent relapses.
For this, the doctor prescribes the following drugs:
- Immunal;
- Cycloferon.
Cycloferon is also prescribed for molluscum contagiosum. In another article you can see a photo of molluscum contagiosum.
It is also recommended to give up bad habits:
- smoking;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Vitamin therapy is also prescribed . To prevent relapse, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and use barrier contraceptives (condoms).
Diagnostics
The problem of diagnosing and treating human papillomavirus is associated with the high growth and spread of incidence, significant contagiousness and oncogenic potential of human papillomavirus (according to WHO statistics, HPV was detected in more than 12% of cases in squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal).
Diagnosis of genital warts in men includes:
- collection of anamnesis of the disease and complaints made by the patient (duration, nature of formations, presence of accompanying symptoms);
- consultation and examination of a urologist, dermatovenerologist, proctologist;
- performing laboratory tests and PCR studies for DNA typing of the human papillomavirus and its quantity;
- PCR or ELISA diagnostics of concomitant sexually transmitted diseases;
- anoscopy, proctoscopy for localization of condylomas in the anus;
- cytological examination of genital warts.
Clinical manifestations
Patients with condylomatosis may experience discomfort in the lower abdomen.
They are short-term, mild in nature.
Men rarely attach importance to them, citing other possible problems.
There are burning and itching sensations in the places where condylomas form.
Pain during intercourse is often noted.
The general condition may be accompanied by discharge from the urethra.
Delaying going to the doctor can lead to the development of new symptoms.
Their appearance indicates the involvement of other organs in the process.
Patients begin to complain of weakness, apathy, and lack of physical strength.
Headaches develop, and body temperature may increase.
It is often accompanied by chills and lethargy.
Forecast
The recurrence rate of condylomas within 1 year from the end of treatment reaches 50% and is associated with the following reasons:
- 1Re-infection during sexual intercourse.
- 2Long incubation period of HPV.
- 3Preservation of the virus in the surrounding unchanged skin.
- 4General weakening of the immune system.
Video Photo Tables
Provocateurs of appearance
Certain conditions are required for formations to appear.
These include:
- Alcohol consumption;
- Smoking;
- Lack of proper nutrition;
- Little physical activity;
- Fatigue, psycho-emotional overload;
- Neglect of hygiene;
- Cracks in the skin of the genital organs;
- Weak immunity;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Lack of barrier contraception;
- UV irradiation.
If several factors are present at once, this can accelerate the development of the disease.
Why are condylomas dangerous?
Condylomatosis can be called a benign disease.
It is important to eliminate the growths in time, otherwise their area may increase.
Injury and complications may develop.
A bacterial infection can be associated with papillomavirus.
This will lead to the development of inflammation, which is called balanitis or balanoposthitis.
When the formations are localized in the lumen of the urethra, infection causes urethritis.
It manifests itself as pain when passing urine.
Damage to the mucous membrane by inflammation causes strictures to appear.
These are connective tissue cords that appear in the lumen of the canal and tighten it.
As a result, a person experiences difficulty in excreting urine and new infectious processes.
Condylomas of the anal area cause damage to the mucous membrane of the anus.
If a bacterium gets on an open wound surface, paraproctitis develops.
This is an inflammation of the anal area of a purulent nature.
Characteristic symptoms are bleeding during bowel movements and severe pain.
Condylomatosis has a rather unaesthetic appearance.
This provokes psychological discomfort in men and entails a decrease in libido.
Problems arise during sexual intercourse.
The most dangerous complication is the development of a malignant neoplasm at the site of the condyloma.
An oncological process, cancer of the glans penis, develops.
Causes of genital warts in men
The etiological factor in the occurrence of genital warts in men is infection with the human papillomavirus.
Other reasons are:
- decreased general and local immunity;
- the presence of chronic foci of infection;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- STDs (mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, etc.);
- chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- unprotected sexual intercourse, a large number of different sexual partners;
- anal sex;
- use of common personal and intimate hygiene items (washcloths, towels, underwear), etc.
Make an appointment