Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease. Due to disruption of biochemical processes, excessive dryness, peeling, redness occurs, inflammatory processes develop, and itching is felt. It develops under the influence of allergens, and is often combined with bronchial asthma, food allergies, and allergic rhinitis. It appears in the first years of life, most often before 12 months or at the age of 2-3 years, when the children's diet expands and many allergenic foods enter it. With proper treatment and care, the disease enters the stage of stable, long-term remission, but can manifest itself in adolescents, young and elderly people during contact with allergens, a weakened immune system, and after stress.
Symptoms
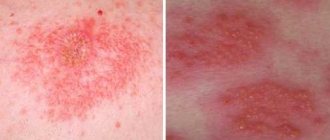
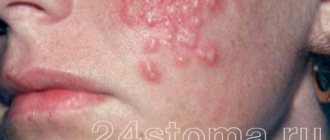
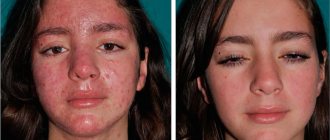
With atopic dermatitis in children, skin tightness, redness appears, the skin flakes, feels rougher to the touch, and thickening may appear. Microscopic bubbles form, around which moisture is released. The child is worried and scratches the affected areas. When an infection occurs, local inflammation develops and the wounds heal poorly. With significant spread in young children, general intoxication of the body manifests itself: the temperature rises, the peripheral lymph nodes enlarge. Due to severe itching, sleep and appetite are disrupted, and the child often cries. Dermatitis most often affects the face, neck, armpits, scalp, groin, areas under the earlobes, popliteal fossae, and elbows.
Diagnostics
Treatment of skin diseases always begins with differential diagnosis. There are basic criteria on the basis of which a diagnosis is made.
Diagnosis is carried out by an allergist or dermatologist. To suggest a diagnosis by visual examination, it is enough to observe three main and three additional criteria in the patient (these are symptoms that are divided into 2 such groups.).
Among the main criteria:
- itching;
- type of skin manifestations;
- the presence of any atopic or allergic disease in the family;
- wave-like course of the disease “exacerbation - relapse”.
There are much more additional or so-called minor criteria; we partially named them in the “Symptoms” section.
In addition to them, we can indicate:
- the appearance of the first symptoms before the age of 2 years;
- increased levels of total and specific IgE antibodies;
- white or mixed dermographism;
- the presence of a Denny-Morgan line (longitudinal fold under the eye);
- keratoconus.
In NEARMEDIC clinics you can undergo a full examination. It is not necessary to use all of the diagnostic techniques listed below; the doctor will prescribe the necessary ones individually, depending on the results of the examination and medical history.
- A blood test can also reveal eosinophilia as a nonspecific sign.
- Determination of allergen-specific IgE in the blood and skin tests allow one to assess the presence of food allergies (a negative result is useful for diagnosing atopic dermatitis; it allows one to exclude food allergies from the mechanism of the disease).
- A general analysis of the amount of IgE - a large amount in the blood may indicate dermatitis, but a low level cannot refute it with 100% probability.
Prevention
Atopy is translated from Latin as strangeness. The causes of the disease cannot always be determined. But long-term observation of patients and members of their families has revealed that it develops more often:
- with a genetic predisposition - if the parents are healthy, the probability of developing dermatitis in the child is 20%, if one of them is sick - 50%, if both are sick - 80%;
- in case of unfavorable pregnancy, active or passive smoking of the expectant mother, consumption of food that provokes allergy attacks, use of certain medications;
- when a newborn is in a dusty room, insufficient care for his personal hygiene;
- with prolonged exposure to allergens that enter the child’s body with food through the respiratory tract.
Breastfeeding for up to 6 months and avoiding allergy-provoking foods reduces the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
Causes of dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis has a hereditary predisposition and is associated with allergic diseases. The likelihood of illness increases. If the parents have bronchial asthma, blood pressure itself, allergies.
The following factors can provoke an exacerbation to one degree or another:
- the level of pollution in the city where the child lives and temperature conditions;
- gender – the disease occurs more often in boys;
- mother's age - the older she is, the higher the risk of having a child with atopic dermatitis.
There are also less global, but important factors, including:
- dry air - it makes sense to humidify dry air, especially in areas where children live and spend their leisure time;
- frequent use of simple soap, which washes away the lipid film, and the skin is left without protection;
- digestive problems;
- stress and nervous tension;
- household irritants - cosmetics, creams, cigarette smoke, wool;
- presence of food allergies.
Food products can provoke the onset of the acute stage, so food allergens should be promptly identified and eliminated from the diet of an adult or child. In addition to the most aggressive ones (cow's milk, chocolate, citrus fruits, fish, eggs), the problem can be provoked by more harmless food options - potatoes, cereals or apples.
Food allergens, as a rule, are relevant until the age of 3; at older ages, other causes of exacerbations - inhaled allergens - become more important. These include dust mites, mold spores, hair and feathers from pets and birds, and detergents. To eliminate this cause of exacerbations, it is important to carry out prevention - get rid of textiles and regularly clean.
What to feed a child with atopic dermatitis
In order not to provoke an exacerbation of dermatitis, to relieve itching and redness of the skin, you need to follow a diet. Foods that burden the immune system are excluded from the children's diet: citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, honey, seafood. Red (strawberries, cherries, currants, apples) and exotic (mangoes, coconuts, pineapples) fruits are dangerous.
Split meals are recommended: small portions every 3-4 hours. It is better to boil, stew, bake, but not fry. Do not use spices, black pepper. The diet should be balanced and contain enough protein, vitamins, and microelements.
Avoid giving your child sugary carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and other snacks for as long as possible. If the infant is receiving breast milk, introduce new foods carefully. Add the product once a week to make sure it doesn't cause breakouts. After meals and between meals, offer your baby clean boiled water.
What is atopy
The term “atopy” refers to an abnormal reaction of the body to an allergen, which generally explains the nature of the disease.
With the development of atopy, there is an overproduction of IgE antibodies, which are responsible for the appearance of an allergic reaction. AD belongs to the same group of diseases as urticaria, hay fever and bronchial asthma. The pathology is immune-dependent, since the main factor in its development is a mutation in genes. Specifically, we are talking about the genes encoding filaggrin. This structural protein is located in the skin and is involved in the formation of the skin barrier, preventing water loss and the entry of allergens and microorganisms. For this reason, the pathology is inherited from one of the parents, most often from the mother.
Interestingly, atopic dermatitis was essentially known back in ancient times. In those days, this disease was called “idiosyncrasy.” That is, the name reflected the mechanism of development of the pathology - as an increased reaction to an allergen - but did not explain its etiology.
The term “atopy” was first used in 1922 to define the body’s increased sensitivity to external factors.
Skin care
To relieve itching and prevent infection of the affected skin, you need to properly care for your skin:
- It’s better not to take a shower, but to take a cool bath for about 10 minutes; use medicated bathing products with a soft base that cleanse but do not dry the skin;
- moisturizing and softening – the skin should not be dry to prevent flaking and cracking; regularly apply a moisturizer recommended by a dermatologist;
- Do not let your child scratch the affected areas to avoid infection - apply anti-itching products to the atopic areas.
Cream or gel relieves discomfort during an exacerbation and allows you to sleep, eat, and play peacefully. Apply the drug to cleansed skin, treat atopic lesions and the areas around them. Do not exceed the recommended dosage and frequency of use.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
Rating of the best remedies for atopic dermatitis
To treat atopic dermatitis, use special children's products recommended by a dermatologist. During exacerbations, medications are prescribed for oral administration, application to atopic areas and general body care:
- preparations for removing allergens from the body - Enterosgel, Lactrofiltrum, Enterodes;
- skin softening products – Atopic cream for daily care;
- drugs that relieve itching - Panthenol spray;
- bathing products - soft shower gels for atopic dermatitis should be purchased at the pharmacy: dermatologists recommend using Atopic bathing gel from head to toe.
Diaper dermatitis - symptoms and treatment
The prognosis is favorable. In the vast majority of cases, the disease is not dangerous and, as a rule, does not require specific medications. It usually goes away on its own after stopping the use of diapers and performing proper skin care [18].
To prevent diaper dermatitis, a set of measures is used: ABCDE (abbreviation for English words):
- A - air (air);
- B—barrier;
- C - cleansing (cleansing);
- D - diapering (diaper changing)
- E - education (training).
Air - air . This means frequent air baths when the child is not wearing a diaper. It is recommended to carry out air baths for at least 5-10 minutes when changing a diaper [19].
Barrier - barrier . Use of protective creams. Their application is necessary every time you change diapers. Most often they contain zinc, dexpanthenol, petroleum jelly, and lanolin. These creams create a protective film that separates the skin from the irritating effects of urine and feces.
Cleansing - cleansing . If the skin in the diaper area is inflamed, a daily bath will help remove irritants and reduce the risk of fungal and bacterial infections. Cleaning is carried out with water, it should be gentle, you can use cotton balls or cotton cloth. Baby wipes should only be used on intact skin. They should not contain parabens, alcohol, fragrances, irritants or allergens, and the pH should be neutral. After bathing, you need to gently pat your skin with a towel, avoiding friction [20].
Diapering - changing diapers . Diapers should be changed every 2 hours (every hour for newborns) or after each bowel movement or urination. It is better to choose a diaper with high absorbency. The better the diaper absorbs, the better it keeps the skin dry. Although there is currently no data showing which type of diaper is best for preventing diaper rash, cloth diapers are generally less absorbent than most disposable diapers. If a child develops diaper dermatitis while using cloth diapers, then it is better to switch to disposable diapers during the illness. You need to make sure that the diaper is not too tight, especially when worn at night. A loose diaper will rub less against your skin. Let your baby's skin dry completely before putting on a new diaper. It is also important to prevent the sticky pads from sticking to your baby's skin. Hands should be washed before and after changing diapers to prevent the spread of germs that have caused infection on the baby's skin [21].
Education - training . Educating parents on proper child care is important. It is necessary to provide them with clear instructions regarding daily skin care and information about which skin care products are beneficial and which may be harmful [22].
Bathing
After a light shower to thoroughly cleanse your entire body, apply Atopic Bathing Gel to damp skin from head to toe, massage lightly and rinse thoroughly. Dry your baby with a soft towel using blotting, but not rubbing, movements. After water treatments, apply Atopic skin softening cream for daily care. Apply it several times throughout the day: after washing your hands and washing your face.
When taking a bath, the water temperature should not exceed 36 degrees. Place your child in the water and offer him toys or other entertainment. After 5-7 minutes, apply Atopic Bathing Gel from head to toe and rinse well. After bathing, use Atopic cream for daily care, and if itching bothers you, let the cream absorb, and then treat the affected skin with an anti-itching drug.
How to choose products that are right for your child
A dermatologist may recommend not one, but several drugs to choose from. They have a similar mechanism of action, but their prices may differ significantly. It depends on the active and auxiliary substances, manufacturer, and release form. When choosing a cream for a child’s atopic skin, you need to take into account possible individual intolerance to individual components.
You need to purchase drugs from well-known manufacturers with a good reputation: Russian, European, American. It is equally important to contact large pharmacy chains that work directly with manufacturers and control the quality of drugs on sale - this will protect you from purchasing counterfeit drugs. Consider the age of the child: choose creams and gels with a pleasant smell so that the child enjoys going to the shower.v
When choosing drugs for oral administration, it is preferable to buy syrups, powders, drops, rather than tablets and capsules that are difficult for a child to swallow.
Forecast
In approximately 70% of patients whose atopic dermatitis began at an early age, the symptoms completely disappear over time, while in the rest they recur under the influence of external circumstances. The prognosis of the disease is favorable, but its presence can lead to social maladjustment. With timely, high-quality treatment, to which the patient shows great responsibility, it leads to stable remission.
Since atopic dermatitis has a general allergic tendency, it is possible to develop other allergic diseases in the future, usually associated with the respiratory system (allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, etc.).