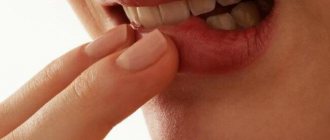
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. It is believed that children are most vulnerable to stomatitis. In adults, stomatitis does not occur as often. The instability of children to stomatitis is explained by the fact that they have a more delicate mucous membrane; children tend to constantly put something in their mouth and taste it, which contributes to the entry of microbes and accidental injuries. In addition, children's immunity is at the stage of formation, and therefore they are becoming acquainted with many bacteria and viruses for the first time. The first encounter with bacteria or, for example, with the herpes virus can be accompanied by a fairly violent reaction from the body.
Types of disease
According to ICD-10, aphthous stomatitis is assigned code K.12. Within the code there are three qualifying diagnoses, including K.12.0 - “recurrent aphthae of the oral cavity,” which also includes aphthous ulcers.
According to the form of occurrence, acute and chronic aphthous stomatitis are distinguished. The first is characterized by the appearance of ulcers and severe hyperemia - swelling, redness of the mucous membranes. Severe pain occurs, especially when eating or talking. Submandibular lymph nodes may enlarge and body temperature may rise.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis may be the result of improper or untimely treatment, as well as the inability of the immune system to cope with the disease. It is characterized by periodic exacerbations. Outside of exacerbation, symptoms may be erased or completely absent.
The disease is classified into three forms depending on the severity:
- light. From 1 to 2 afts up to 10 mm in size. Moderate pain during mechanical action, relapses occur no more than 2 times a year;
- average. Up to 5 aft, the course of treatment takes up to 3 weeks. The pain is quite pronounced, there is an enlargement of the lymph nodes, relapses up to 2 times a year;
- heavy. Multiple aphthae appear, severe pain. An increase in temperature occurs, and symptoms of general intoxication appear. Treatment takes up to a month, relapses occur up to 6 times a year.
Also, according to the form of occurrence, the following types of inflammatory diseases are distinguished:
- fibrous: blood microcirculation in the upper layer of the mucosa is disrupted, aphthae appear, covered with a fibrous film (plaque). Such ulcers heal completely within 14 days. The disease affects the mucous membrane of the lips, the lateral surfaces of the tongue, and transitional folds. This stomatitis recurs up to 3 times a year;
- necrotic. The epithelium is destroyed, the mucosal area dies. Replacement of tissues with normal epithelium takes from 14 to 30 days. This aphthous stomatitis is not accompanied by acute pain; it is usually observed in patients with severe diseases, including blood pathologies;
- grandular. Damage to the ducts of the minor salivary glands occurs. In this regard, aphthae form close to the glands, and drying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity occurs due to a decrease in saliva production. Ulcerations are painful and heal within 1–3 weeks;
- scarring. Damage to the cavity of the salivary glands leads to the involvement of connective tissue in inflammation. Aphthae are observed both at the location of the glands and on the mucous membranes of the pharynx and palate. The disease develops into large painful ulcers (up to 1.5 cm). Healing takes up to 12 weeks; after the acute process, pronounced scars remain;
- deforming. The most severe form of the disease, which provokes changes in connective tissue. Aphthae heal extremely slowly, which is accompanied by deformation of the palate, lips, and sometimes narrowing of the oral cavity occurs (if aphthae was observed in the corners of the mouth).
Ask a Question
Pain due to inflammation of the salivary glands
In cases where a person feels pain on both sides of the tongue, the cause may be inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland. It arises as a result of:
- Complications of another disease (inflammation of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, anemia, vitamin deficiency, dental diseases);
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of salivary flow caused by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms indicating inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Dry mouth – it always seems like there is not enough saliva;
- Pain that is observed not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- Redness of the mucous membrane, thickening or swelling under the tongue;
- Putrid taste.
If you observe such signs in yourself, you should immediately go to the dentist and undergo a course of therapy. Otherwise, an abscess may develop or the disease may become chronic.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
Not all causes of aphthous stomatitis are fully understood. The mechanism of aft formation is often associated with activation of the local immune system - immune cells begin to destroy the epithelium of the mucous membranes, which leads to ulcers.
Local reasons include the following:
- allergic reactions;
- pathogenic microorganisms;
- mechanical damage (biting mucous membranes, injury from sharp edges of fillings or orthopedic, orthodontic structures);
- temperature or chemical influences.
Systemic causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- menstruation, pregnancy in women;
- sudden cessation of smoking;
- enteropathy, celiac disease, malabsorption;
- blood diseases;
- diseases of the immune system;
- lack of vitamins;
- other systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus, Crohn's disease, HIV infection, etc.).
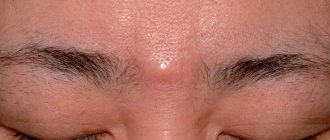
Why does a lump appear on the gum?
The accumulation of conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic microflora due to improper oral care leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane. Other reasons why a ball appears on the gum include:
- chemical, thermal or mechanical trauma to the periodontium;
- carious formations and their complications: periodontitis, pulpitis;
- inflammation of the wisdom tooth;
- eruption of molars;
- jawbone overgrowth;
- weak immune system;
- infectious pathologies of the oral cavity: herpes, candidiasis, stomatitis.
A lump in the mouth also occurs under other conditions: epulis, exostosis, fibroma, focal fibromatosis, malignancy, cyst and flux. The main thing is to promptly establish the causes of the pathology and begin treatment.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
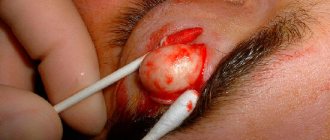
Usually, 1–2 days before the appearance of aphthae, areas of the mucous membrane with increased sensitivity are detected, and a burning sensation may occur. The aphthae themselves are round, have clear boundaries, and are covered with a gray or yellowish coating. Their size, as a rule, does not exceed 1 cm, and the mucous membranes around them turn red.
Such areas of erosion heal within up to 2 weeks without scarring. But in 1 case out of 10, the diameter of the ulcers is more than 1 cm, they affect deeper areas of tissue, and the borders of the pathological area may look raised. Healing in this case takes up to 6 weeks, after which a scar forms.
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by damage to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, the inside of the lips, the soft palate, tonsils, and the lateral surfaces of the tongue. This is due to the lack of keratinization of the epithelium in these areas. Much less often, aphthae appear on the hard palate, back of the tongue, and gums.
Diagnostic features
At the initial appointment, the dentist examines the oral cavity and analyzes complaints. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to distinguish this form of the disease from others, as well as differentiate it from other pathologies that have similar symptoms. For extensive lesions, different diagnostic methods may be used:
- clinical blood tests;
- microflora smear;
- blood for PCR to determine the causative agent of the disease;
- biopsy (if indicated).
They are also necessary for recurrent forms of the disease. In simple cases, laboratory diagnostics are not required; aphthae are determined visually by an experienced specialist.
With the help of a comprehensive examination, the doctor will determine which microorganism caused inflammation with subsequent ulceration of the mucous membrane. He also differentiates the disease from herpetic stomatitis and oncological pathology.
Most common reasons
Sometimes, the causes of glossitis are congenital, for example with a folded tongue. But most often the disease develops against the background of:
- Chemical and thermal burns.
Putting garlic paste on a sore tooth may not be such a good idea. And hot food is harmful to the mucous membrane of the tongue and stomach. - Infections.
Do you have a red spot on your tongue and it hurts? This may be a symptom of a fungal (candidiasis), viral (herpes), bacterial (Helicobacter, spirochete, staphylococcus, streptococcus) infection. - Mechanical damage.
Gnawing on nuts is dangerous not only for teeth, but also for the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue. Sometimes constant mechanical impact is caused by incorrect prosthetics. - Lack of vitamins
, especially group B. This affects tissue metabolism, resulting in inflammation of the mucous surface. - Psychoneurological factors.
With stress or neurological disorders, the tongue becomes inflamed quite often.
Features of treatment
The main goal of treating aphthous stomatitis is to completely get rid of the disease or at least reduce the frequency of relapses to a minimum. Therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation, relieving unpleasant symptoms, and accelerating the recovery processes of the mucous membrane.
For each specific case, the doctor will develop a set of measures. The main ones include local and systemic drug treatment.
Rinsing with antiseptics can be done using medications or mouth rinses that contain antibacterial components. An alternative to rinsing is to use a spray. Typically, the treatment regimen includes 2-3 sessions of 1-minute rinsing immediately after brushing your teeth.
Local treatment methods include the application of gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Occlusive agents can reduce pain and speed up the healing of mucous membranes. They form an insoluble film on the ulcer, protecting the affected area from exposure to adverse factors.
Local glucocorticoid therapy is used against the background of immune diseases, as well as when standard measures are ineffective. They eliminate pain and quickly relieve inflammation, shortening the healing period. Such products are used only according to indications and are available with a prescription. In some cases, it is advisable to inject the drug under the base of the ulcer; this is done by a doctor.
Epithelialization drugs are used after acute inflammation has resolved. The specialist will prescribe a gel with an analgesic and healing effect, usually this occurs 5–6 days after the start of complex therapy.
Local laser therapy can relieve pain, speed up the healing process, and minimize the risk of relapse.
Systemic treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults involves taking the following drugs:
- antihistamines (anti-allergic, anti-edematous effect);
- glucocorticoids (anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect);
- immunomodulators (to stimulate defenses and accelerate recovery).
And if antiallergic drugs can be recommended to any patient even in the absence of information about the exact causes of stomatitis, then other drugs are prescribed only according to indications: in case of acute severe course of the disease, frequent relapses, and the presence of severe systemic pathologies. An additional method of treatment is vitamin therapy - taking vitamins C, group B.
In addition to the main course of treatment, all patients without exception are recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, avoid taking too hot drinks and dishes, and spicy, irritating foods. It is better to give preference to toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate, this component can provoke the disease.
It is important to continue your oral hygiene, even if it is difficult. To make brushing your teeth easier, choose a soft toothbrush. If the disease recurs frequently, it is necessary to pay attention to the general state of health, promptly treat teeth and gums, replace fillings and dental structures.
If the ball in your mouth does not cause discomfort
The color of the bubble will help the doctor make a diagnosis. A white lump on the gum indicates the presence of exostosis or purulent exudate. A red or bloody ball indicates the development of inflammation. If the growth matches the shade of the tissue, it is the initial stage of epulis, flux, or a malignant tumor. When the tumor does not hurt, this indicates the presence of one of the pathologies:
A fistula is a white ball on soft tissues that appears under or on a tooth. There is a hole on the surface for the release of pus. If, when pressed, suppuration flows out of the bladder, the patient does not feel pain. If the hole is closed with pus or bloody clots, the patient will experience discomfort with any impact.
A fistula is often formed due to advanced periodontitis, accompanied by periodontal hyperplasia. Overgrown tissue is good soil for the proliferation of microorganisms. In this case, the patient urgently needs treatment for periodontitis.
In the absence of therapy, the fistula enters a chronic stage, which can only be eliminated through surgical treatment. The progression of the disease must not be allowed, otherwise you may lose healthy molars.
Hematoma is a round lump on the inner surface of the cheek. Sometimes it occurs in the form of a dark bluish swelling on top of the gums. Blood accumulates in or around the root of the molar. The mucous membrane grows, the patient experiences discomfort and cannot completely close the jaw. The main reasons: consequences of filling or tooth extraction, gum damage, poor blood clotting.
Hematomas are generally not dangerous. Processes take place in the body through which soft tissues are cleared of bloody clots. After some time, the bubble disappears, but if the seal remains, you need to visit a dental clinic.
Exostosis is a hard blister that is an abnormality in which the bones protrude and protrude from the jaw. Gradually, the lump increases in volume, which causes discomfort and pain. Exostosis can be provoked by various reasons:
- jaw damage;
- heredity;
- congenital disorders;
- tissue diseases after molar removal.
An examination by a dentist or an x-ray will help detect the disease. The formation will need to be removed if the development of a malignant tumor is suspected.
Epulis is a pedunculated bubble in the form of a mushroom-shaped growth on the periodontium. The tumor may be the same color as the gums or red. The reasons causing the development of pathology include:
- improper filling of the molar or too large a filling;
- dental plaque, stone;
- jaw damage;
- malocclusion;
- hormonal imbalance;
- poor prosthetic material or incorrect prosthetics.
The symptoms of epulis resemble gingivitis; for diagnosis, the dentist prescribes radiography and histology to the patient. With their help, the degree of destruction of bone tissue at the site of the epulis lesion is determined. Mostly, pathology occurs in children during the growth of primary molars and in women.
Papilloma or fibroma is a bubble on the gum, sometimes a benign formation that does not pose a threat to the health or life of the patient. They are formed in people of different genders and ages. Predisposing factors to the appearance of a lump can be: damage to the mucosa, stress, systemic pathologies, heredity.
Papilloma is an enlargement of the papillary layer of skin. The bubble grows gradually, but with reduced immunity, systemic pathology, or stress, growth accelerates, but without turning into a malignant tumor. A papilloma neoplasm looks like a smooth, soft lump on the mucous membrane of a white or pink shade on a thin stalk.
Papilloma often does not create any discomfort. But after some time it may increase in size. You should consult a dentist and get tested.
Features of treatment in children
The dentist will tell you how to treat aphthous stomatitis in a child. You can contact him at the direction of your pediatrician or on your own if you find characteristic ulcers in the oral cavity. The treatment regimen is the same as that used in the treatment of adult patients, but there are some differences: children under a certain age cannot rinse the mouth, so preference is given to drugs for application to mucosal ulcers. Otherwise, the treatment regimen is developed individually, taking into account the severity, symptoms of the disease, frequency of relapses, and the presence or absence of concomitant ailments in the child. Symptomatic therapy can be used to quickly alleviate the baby’s condition.
Specialists at STOMA clinics successfully treat aphthous stomatitis. By contacting us, you will receive qualified assistance, detailed recommendations on the treatment and prevention of relapse of the disease, and comprehensive assistance from dentists of all specializations, if necessary.