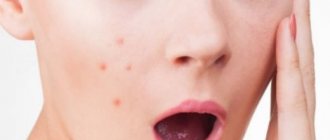
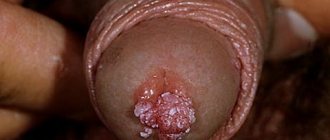
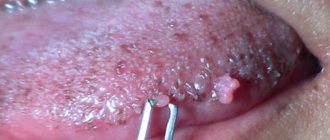
Papillomas are a widespread phenomenon in modern society. According to medical statistics, they are observed in one form or another in 80% of people and are benign small tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes of different parts of the body. They are only one of the manifestations of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), of which there are more than 190 types. Among them, viruses with high, medium and low oncogenic risk are distinguished. Therefore, in addition to an aesthetic drawback, papillomas can pose a serious danger to human life and health, since some of them can transform into malignant tumors.
What is HPV
The human papillomavirus affects only humans, and its main mode of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is most common among sexually active people. This explains the fact that most often infection occurs at a young age at the beginning of sexual activity and at its peak, i.e. 15-25 years. Moreover, several strains (types) of HPV can be present in the human body at the same time, provoking the appearance of different types of tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
Infection with the virus occurs when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes with particles of exfoliated skin or mucous membrane of an infected person. They attach to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cytoplasm of the cell, and subsequently into the nucleus. It is the cell nucleus that contains DNA, which is damaged by HPV. As a result, when the affected cell divides, the consequence will be the formation of not healthy new cells, but those that already have altered genetic information, which leads to failures in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This causes the appearance of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can also be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show external signs of human papillomavirus infection, but he will act as a carrier and can infect others through unprotected sexual intercourse or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to the formation of papillomas. This depends on the strength of the person’s immunity, but more often the first small papillomas appear 1-6 months after infection.
The human papillomavirus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not allow it to provoke cell proliferation. But when the immune system is weakened as a result of certain factors, the body’s defenses fall, the virus becomes more active, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- non-oncogenic – strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk – strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk – strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
HPV strains of high oncogenic risk have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is integrated into the DNA of a human cell, its anticancer protection decreases. Oncoproteins destabilize the genome of skin cells, provoke their active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with strains of the human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk.
The magnitude of the danger that papillomas pose directly depends on the type of HPV. Infection with strains with a high oncogenic risk is dangerous due to the development of:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal cancer, etc.
70% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV.
But even when infected with strains of low oncogenic risk and the formation of papillomas, they should be treated carefully. Convex neoplasms are often injured by items of clothing, bleed and tend to become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort is caused by formations on the genital organs, which cause severe discomfort and complicate the conduct of an intimate life. In such cases, a secondary infection may occur, which can cause the development of purulent-septic complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost any internal organ, which leads to disruption of their functioning. Thus, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract often occurs, which causes difficulty breathing.
How to remove age spots on the face
Seborrheic keratosis
Due to the existing likelihood of malignancy, consultation with an oncologist or dermatologist-oncologist is necessary about the possibility of removing the formations.
The method of correction is surgical removal.
Senile lentigo
Correction is possible by prescribing cosmetics - the treatment regimen corresponds to the classic treatment of pigmentation and includes 3 points:
- Exfoliants
- Lightening agents
- Antioxidants
Prevention of the recurrence of lentigo is the regular application of sunscreen with SPF and preparations with antioxidants to the skin, because there is a failure of the skin's own antioxidant defense system.
IMPORTANT! If, over the age of 55 years, there are pigment spots and formations on the skin, the clinical picture of which does not correspond to that described above, a face-to-face consultation with an oncologist is necessary. Prescribing lightening procedures and medications without consulting this specialist is undesirable!
After consulting a dermatologist, lightening drugs are prescribed and retinoids are preferred.
Causes of papillomas formation and risk factors
HPV can be transmitted sexually, as well as from an infected mother to a child during childbirth. The contact and household route of transmission of the virus cannot be ruled out, i.e. by sharing towels, clothes, etc. This explains the high prevalence of HPV in the world. Self-infection is also possible. In this case, if one papilloma is injured, the virus can be transferred to healthy areas of the skin and infect them.
The main causes of HPV infection are frequent changes of sexual partners and unprotected sexual contacts.
But infection with a virus does not always lead to the formation of papillomas, condylomas, etc. The likelihood of developing papillomatosis depends on various factors:
- immunodeficiency of any origin, including taking drugs that suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants, cytostatics, etc.), the presence of HIV infection, radiation injury;
- a decrease in the body’s defenses against the background of physiological changes during pregnancy;
- early onset of sexual activity, when the immune system is not yet fully formed and strengthened;
- microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes;
- infection with highly oncogenic strains of HPV;
- the presence of several types of HPV in the body at the same time;
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), in particular gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and C, etc.;
- hormonal imbalances;
- exhaustion of the body, hypovitaminosis, chronic fatigue and severe stress;
- multiple births and abortions;
- the presence of severe chronic diseases, in particular diabetes;
- maintaining an unhealthy lifestyle, having bad habits;
- poor living conditions.
Older and overweight people are more prone to the formation of papillomas. At the same time, their tumors often form in the folds of the skin, which contributes to their injury and inflammation.
Rules for using retinoids
IMPORTANT! It is a serious mistake for a cosmetologist if he avoids prescribing retinoids for fear of side effects: redness, erythema, dryness and flaking. These symptoms can be easily avoided if you follow the recommendations:
- Use cosmetics with retinol from professional brands
Are you tempted to buy an inexpensive retinoid product at the pharmacy? It is important to know the differences:
In pharmaceutical forms, synthetic analogues of retinol are used, which are more aggressive on the skin and are more likely to provoke retinoic dermatitis ;
Professional cosmetic preparations contain natural forms of retinol , which are gentle in operation, while providing all the necessary functions to the skin;
Professional cosmetics with retinol contain ingredients with a brightening effect to enhance effectiveness, as well as a calming and restorative effect - for ease of use.
- Follow the recommended application regimens
Each drug has its own scheme of use, which must be familiarized with before use. The difference in the frequency of application of the product is related to the percentage and form of retinol.
A number of serums and creams with retinol are used daily in the evening (up to 0.5%), and products with 1-2% retinol according to an increasing scheme, very often from the first week from 1 time per week, gradually increasing to a multiplicity - in the evening every other day, to 4-5 weeks of use.
- Apply locally to age spots
If there are no additional indications for the use of retinol, it is enough to apply the product only to the area of age spots.
- Use only at night
Retinoids are applied to the skin only in the evening - a single rule for all products with retinol! A single application is enough, it is important not to forget to apply sunscreen with SPF to the skin in the morning, as retinoids increase, thin the stratum corneum and increase the skin's vulnerability to ultraviolet and other rays.
However, regular use of mineral SPF reduces all threats from the sun to zero and makes the use of retinol completely safe!
- Patience!
The work of retinoids is physiological, so the result of use is not immediately visible. Expect a lasting visible effect in about the second month from the start of use. However, we hasten to please you - the result, thanks to the gradual physiological effects of retinol, is persistent and pronounced. It is possible to completely get rid of age spots within 6-8 months of use.
Brightening Serum DermaQuest
Designed specifically for the comprehensive fight against age spots - contains 2% retinol , enriched with snow-white lily stem cells and Bakuchiol.
Serum benefits:
- A high working concentration of 2% retinol effectively normalizes the functioning of melanocytes, while effectively repairing damage and rejuvenating the skin.
- Rich complex of whitening ingredients with multidirectional action :
- Stem cells of the white lily,
- Bakuchiol (Vitamin A simulator) further increases the effectiveness of the drug,
- Hexylresorcinol is a safe analogue of hydroquinone, its activity is 4 times higher
- Botanical extracts with brightening effects
BONUS when using!
The serum is designed for complete comprehensive care for skin with age spots - in addition to the brightening effect, it effectively moisturizes due to the content of hyaluronic acid, rejuvenates the skin thanks to Retinol and antioxidants, and also softens and restores barrier function - it contains Jojoba oil and Aloe extracts.
Safety – does not contain hydroquinone;
Brightening serum works against all types of pigmentation, including deep, stagnant and long-standing ones.
Application according to a special scheme:
In the 1st week, apply - 1 time, in the 2nd - 2 times, in the 3rd - 3 times a week, in the 4th and subsequent 4 times a week.
Types and symptoms
Neoplasms caused by HPV infection can form on the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body, including the face, neck and décolleté. They can also form on the arms, legs, back, genitals, including the perineum, labia minora and majora, vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, especially along the coronary sulcus and frenulum. Damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, esophagus, bladder, conjunctiva of the eye, trachea and other internal organs is possible.
The human papillomavirus can lead to the appearance of neoplasms of various types. In general, they can be divided into 3 groups, although in all cases the cause of their appearance is the same - infection with the human papillomavirus.
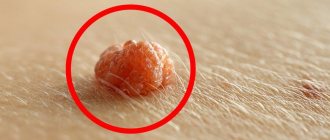
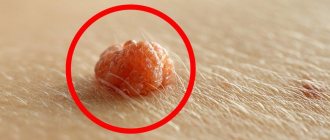
- Papillomas are benign neoplasms of pink, white, pearl or light brown color, most often forming on the eyelids, lips, chest, armpits, and neck. They are located singly and usually do not tend to merge even with multiple lesions. Papillomas are usually round or lumpy, resemble the head of a cauliflower, and often have a stalk.
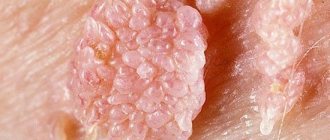
- Condylomas are benign formations of a dirty brown or paler color in the form of a cock's comb or many villi united by a common base. They are most often found in the genital area, anus and near the mouth. They tend to merge with each other and, as a result, cover large areas of the body. Their appearance is caused by infection with HPV types 6 and 11. There are pointed, flat and intraepithelial condylomas.
- Warts are uneven, light, benign tumor-like formations in the form of a plaque or small nodule on the surface of the skin of the hands, near the nails, feet, face, and front of the body. Warts can be similar to papillomas, but differ from them in that they have a wide base. They usually occur when infected with HPV types 1-5, 7-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19-24.
Such tumor-like formations can vary in size from a few millimeters to large growths covering large areas of the skin or mucous membranes.
Also, neoplasms may differ in appearance, which directly depends on the type of HPV that entered the body. The most common ones are:
- Vulgar or ordinary - protrusions of dense consistency with a diameter of more than 1 mm. They tend to merge and be located in groups.
- Plantar warts are protruding above the surface of the skin, often painful bumps with a shiny surface and rim. A characteristic feature is the absence of a skin pattern. They provoke the formation of HPV types 1, 2, 4.
- Flat papillomas are soft, smooth, flat, usually round growths that have a normal skin color or slightly yellowish, pinkish. They can provoke itching, so they are often injured, painful and inflamed. The reason for their formation is HPV strains 3 and 10.
- Filiform (acrochordas) are one of the most common papillomas, especially among elderly patients. Most often they are found on the face, around the eyes, in the groin, armpits, and neck. They are yellowish in color and tend to gradually enlarge, turning into bumps with a dense but elastic consistency.
- Genital warts in the perineal area, genitals.
Papillomas can be visible to the naked eye or located deep in the skin or mucous membranes. In the latter case, they are called endophytic and one of their manifestations is cervical dysplasia. Damage to the female internal genital organs by papillomatosis may be indicated by:
- itching, burning, weeping in the perineal area;
- profuse leucorrhoea;
- spotting, particularly after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort during intimacy.
Sometimes papillomatosis can provoke pain in the back and pelvis, weakness, swelling of the legs and causeless weight loss. Such signs are among the most alarming, as they may indicate the development of complications of HPV infection.
Age spots
After 55–60 years, unattractive spots often appear on the face, which cause grief and concern for many.
- Gives an unkempt look
- Emphasize age
- Causes cancer alertness or fear of cancer development
Pigment spots on the hands - about the reasons for their appearance and how to get rid of them - read here .
There are two types of age-related pigmentation: seborrheic keratosis and lentigo senile.
Senile lentigo
It occurs during the period of hormonal age-related changes, the reason is a decrease in sex hormones produced by the body.
Clinical picture: flat brown spots with blurred boundaries, which indicates a sufficient depth of their occurrence. The size of the spots can vary and reach up to 1 cm in diameter.
Seborrheic keratosis
Formed in areas with an increased number of sebaceous glands, i.e. on seborrheic areas.
Clinical picture: spots of brown and dark brown color, distinctive features - rise above the surface of the skin, the spots themselves have a greasy surface, covered with horny scales.
The rashes have a characteristic localization - these are seborrheic areas of the skin - the back, chest and face (mainly the T-zone).
The spots are benign, but it is necessary to exercise oncological vigilance, up to a 20% chance of their malignancy.
Diagnostics
If papillomas form on the body, face or genitals, you should consult a dermatologist. This will allow not only to diagnose human papillomavirus infection at an early stage, but also to take measures to prevent the formation of new elements, as well as monitor changes in existing ones.
It is especially important not to delay visiting a doctor if there are signs of growth, change in color of the papilloma, unpleasant odor or pain in the area where it is located.
First of all, the doctor will perform a dermatoscopy, i.e., an examination of the tumors using a special magnifying device. This will make it possible to determine their nature, as well as to notice dangerous signs indicating a high probability of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, not to mention the formation of a cancerous tumor. When detected at an early stage of development, they can be successfully treated and have a favorable prognosis in the future.
Patients are recommended to be tested for the presence of STDs, especially if condylomas are detected in the genital area. Also in such situations, women are advised to consult a gynecologist, and men - a urologist. This is important for diagnosing the presence of human papillomavirus infection of the cervix, urethra, etc. and, if necessary, prescribing appropriate treatment.
To confirm papillomatous infection, patients are usually prescribed a PCR test. With its help, it is possible not only to confirm or refute infection with the human papillomavirus, but also to accurately determine the strains.
Treatment and removal of papillomas
Treatment of human papillomavirus infection is always complex. Of course, you can simply remove the disturbing papilloma, but in this case there is a high risk that a new one or even several will soon form in its place. Since the main reason for the formation of papillomas is a decrease in the body’s own defenses, which allows HPV dormant in the body to become more active, patients with papillomatosis are first prescribed drug therapy. It includes taking immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. For extensive lesions of the skin and mucous membranes by papillomas, cytotoxic drugs can also be prescribed. But their use is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since they can provoke serious side effects.
If a patient is diagnosed with concomitant infections or diseases, he must be prescribed treatment appropriate to the situation, and sometimes it is additionally necessary to obtain advice from a specialized specialist and undergo therapy under his supervision.
Condylomas of all types are subject to mandatory removal, as well as papillomas, which are often injured and inflamed. In other cases, removal is carried out at the request of the patient. But it is possible to begin eliminating visible manifestations of HPV infection only after completing treatment for concomitant diseases, if any have been identified, and while antiviral therapy is continued.
In general, all modern methods of destruction or removal of papillomas can be divided into 2 large groups:
- chemical - involve the use of various chemical compounds to remove papillomas, including trichloroacetic acid, Solcoderm, Ferezol, Collomak, etc.;
- physical - involve the removal of papillomas surgically, using electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser, radio wave or plasma coagulation.
After removing the papilloma by one method or another, it is important to use topical products prescribed by your doctor to speed up healing and eliminate the risk of infection.
The success of treatment and especially the removal of papillomas depends on the strength of the immune system. In its normal state, in 90% of cases, within 2 years from the moment of infection, HPV is suppressed or even completely destroyed. But this does not guarantee that there is no risk of re-infection or the formation of new papillomas. If immunity is reduced due to certain factors, papillomatosis becomes chronic, periodically relapses and can lead to serious complications.
In order to prevent infection with dangerous strains of HPV and the development of severe complications, it is recommended, especially for girls, to be vaccinated with Gardasil or Cervarix vaccines between the ages of 9 and 25.
Surgical removal of papillomas
The essence of the method is to remove the tumor using a scalpel, which is associated with the formation of scars and an increase in healing time. Therefore, it is used only when it is necessary to remove a large papilloma or in cases where it is necessary to conduct a histological examination, since the formation of malignant cells is expected in it.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, which ensures its painlessness. The doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor itself, including surrounding healthy tissue. This is necessary to eliminate the risk of re-formation of papilloma in the same place. If it has a pedicle, it is cut with surgical scissors, and the blood vessel that fed the neoplasm is “sealed” using an electrocoagulator. The remaining wound is sutured, treated with an antiseptic and covered with a sterile bandage.
Today, surgical removal of papillomas is mainly carried out if there is suspicion of the formation of cancer cells.
Cryodestruction
The method involves the use of low temperatures to destroy papilloma cells. This is achieved through the use of liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is -196° C. The essence of the procedure is to use a special attachment or touch the papilloma with a cotton swab dipped in liquid nitrogen. Under its action, the water contained in the cells instantly turns into ice crystals, which destroy them from the inside. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia or without it, since the exposure time to liquid nitrogen does not exceed 5-20 seconds.
The complexity of the method lies in choosing the correct duration of exposure in order to remove the papilloma to its full depth and not harm healthy tissues, which will lead to scar formation.
Immediately after treatment with liquid nitrogen, a white spot forms at the site of the papilloma. Subsequently, a small blister with clear or pinkish liquid contents forms on it, and the surrounding skin turns red and may swell slightly. This may be accompanied by minor discomfort such as a burning or tingling sensation.
After 3-4 days, the blister bursts, and in its place a crust forms, which itself falls off after a few days, revealing healthy young skin. Under no circumstances should you pierce the bubble yourself or injure it or the crust in any other way.
Cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen is possible only in cases where the possibility of the formation of malignant cells in it is completely excluded. This method is most often used to remove papillomas and condylomas on:
- centuries;
- face;
- small joints;
- genitals.
Laser removal of papillomas
The use of a laser to remove papillomas is also possible only in cases where their malignancy is completely excluded. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and consists of evaporating moisture in papilloma cells using thermal laser energy. Thus, a focused laser beam is directed at the tumor. The duration of exposure does not exceed 1 minute.
As a result, a crust forms at the site of the papilloma, and the surrounding skin turns red and swells. The crust will come off on its own within a week. It should not be wetted and steamed for 3 days, nor should it be torn off or injured, as this can lead to the formation of scars. In addition, for 2 weeks after removal of the papilloma, you should protect the treatment area from sunlight. Otherwise, there is a high probability of hyperpigmentation of this area.
When removing papillomas on the face with a laser, decorative cosmetics should not be applied to the affected area until complete healing.
After the crust falls off, healthy pink skin is exposed, which gradually acquires a normal shade. This is the main advantage of laser removal of papillomas, since it is not associated with the formation of scars. They can only form when large tumors are removed and the rules of care in the postoperative period are violated. Also, laser removal completely eliminates the risk of wound infection and is an absolutely bloodless method, since under the influence of thermal energy, instant coagulation of small blood vessels occurs.
Using a laser, papillomas are mainly removed on:
- hands;
- legs and feet;
- face;
- centuries;
- neck;
- genitals.
Laser is the only reliable way to remove plantar warts, as their roots can go 1 cm or more deep into the tissue.
Electrocoagulation of papillomas
The essence of the method is to use electric current to remove papillomas. Using a special device called an electrocoagulator, the doctor captures the papilloma and cuts it off within healthy tissue. In this case, bleeding is completely absent, since the thermal energy of the current is enough to coagulate small blood vessels. But the procedure can be painful, especially if it is necessary to remove a tumor in areas of the body with delicate skin.
After electrocoagulation, a crust also forms. And the entire recovery period takes 7-10 days. After the crust falls off, the skin underneath should be protected from damage and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The method is used to remove papillomas in different parts of the body. Moreover, electrocoagulation can also be used in cases where it is necessary to conduct a histological examination of the neoplasm and accurately determine its nature. But the result of the procedure completely depends on the qualifications and experience of the doctor, however, as in other cases, since if the removal is not deep enough, the papilloma can form again in the same area.
Radio wave surgery
This method is one of the most advanced in removing papillomas of any kind. It involves the use of a special Surgitron device. But at the same time, it has much in common with laser removal of papillomas. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, and the actual removal occurs due to the effect of radio waves on the tumor. Thanks to them, it is possible to completely cut off papilloma of any size and location, and also avoid the formation of scars.
Chemical removal of papillomas
The method involves regularly applying special compounds to the papilloma that destroy their cells, which leads to the subsequent loss of the tumor. But when using such drugs, it is important to exercise maximum caution and not allow the substance to come into contact with healthy skin.
Most often, drugs such as:
- Condylim;
- Solcoderm;
- Solkovagin;
- Collomak;
- Feresol.
Thus, anyone can encounter the formation of papillomas. There is no effective prevention of HPV infection, and vaccines only protect against the most dangerous strains of the virus in terms of cancer risk. However, in most cases they do not cause significant inconvenience to a person, with the exception of condylomas in the genital area and anus, which must be removed. In any case, you can get rid of any papillomas quickly and effectively, but since it is impossible to completely destroy HPV in the body with medication, and there is always a risk of being infected again or with a different strain, there is a possibility that the problem will return again. The only reliable way to minimize the likelihood of papillomas formation is to strengthen the immune system. And if they do appear and represent a cosmetic defect or interfere with a person’s daily life, contact a dermatologist. The doctor will be able to accurately differentiate papillomas from other skin tumors and solve this problem in a matter of minutes.
Papillomas on the body
Papillomas on the body
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease that manifests itself externally in the formation of skin growths of various shapes, colors, sizes, and localizations on the body. The number of strains included in the group of HPV viruses includes about 100 units. The infection is highly contagious. Today, according to scientists, at least 70% of the planet’s population are carriers of one strain or another.
Causes of papillomas
Why do papillomas appear? The cause is the penetration of the virus into the body through damaged areas of the skin. However, in some infected people, HPV does not manifest itself in any way, remaining in a latent state for many years. In others, a strong immune system is capable of destroying pathological microorganisms within two years of infection.
However, spontaneous healing is the exception rather than the rule. A pathological formation on the skin is a sign of activation of the virus. This occurs when factors favorable to the active phase appear, many of which are practically inevitable in the life of a modern civilized person. This is why papillomas appear on the body:
- Decreased immunity.
- Chronic depression and stress.
- Alcoholism and smoking.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives.
- Frequent colds and flu.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Taking cytostatics or immunosuppressants.
Interestingly, overweight and obese people have an increased risk of developing papillomas on the body due to sweating of the skin folds. In women, growths form under the breasts, in the abdomen and back, in men - in the groin area. Age does not matter: papilloma on the body can appear in a young, elderly person and even a child.
Routes of entry of the virus
The cause of papillomas is always associated with damage to the epithelial layer of the skin through which the infectious agent penetrates. Close contact with an HPV carrier or a person who already has tumors on their body is the main route of infection. During sexual intercourse, the use of a condom does not provide any guarantee, since papilloma, as a source of infection, can be located on any part of the body and mucous membrane.
The virus in the external environment, especially warm and humid, remains viable for a long time outside the human body. That is why infection often occurs in public places: baths, saunas, swimming pools, health centers. Household infection can occur in a cosmetology office, a beauty salon, even a hairdresser, if the master uses unsterile tools and objects.
Cases of transmission of the virus from mother to newborn are also not uncommon. If the mother is a carrier, the baby becomes infected with HPV during birth or subsequently when skin-to-skin contact becomes constant.
Treatment methods
Most HPV strains are not dangerous to human life and health, and the papillomas they provoke extremely rarely degenerate into cancerous tumors. However, such a risk, albeit minimal, still exists, especially if the neoplasm is constantly exposed to mechanical stress. Inflammatory reactions, the rapid spread of growths, and injury can give impetus to the transformation of “wart” cells into atypical ones.
Whatever the reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the body, treatment of pathological growths is mandatory: you should not ignore them in the hope of self-cleansing the skin. There is no universal and 100% effective medicine to combat HPV. Complex therapy is required, which is prescribed by a dermatologist after verification of the strain.
Complex treatment methods include:
- destruction of neoplasm;
- drug treatment aimed at activating the immune system;
- external antiviral treatment to reduce the external activity of HPV.
Diagnostics, which determines the type of virus, helps the doctor adjust treatment and make it more effective. The reason for failures in trying to cope with the problem on your own is precisely because a non-specialist will not be able to select the optimal drug and adequate treatment regimen.
Medications to combat a viral attack are divided into three types according to their effects:
- antiviral (Panavir, Izorpinazine, Viferon, Inosiplex);
- immunostimulating (Likopid, Immunomax);
- growth-destroying destructor agents (Supercleaner, Verrukacid, Dermavid).
The viral infection that causes the skin lesions does not respond to any one treatment method. Only an integrated approach guarantees a positive result.
Do I need to remove growths?
Papillomas on the body are considered by many to be an aesthetic problem. But the danger is that the virus is able to influence the genome of cells and provoke their uncontrolled division. This means that the skin growth is potentially dangerous, since it can become a source of formation of atypical cells.
Removal of growths is mandatory in the following cases:
- The papilloma is constantly injured (located on the neck, face, axillary and intimate areas), and experiences mechanical friction.
- The growths are growing rapidly.
- Located on the genitals.
- Changed color, increased in size, became painful, bleeding, with separated contents.
An important nuance: removal of formations does not mean a complete cure for HPV. The virus can be in an inactive state in the body, which can be achieved with timely antiviral treatment and maintained throughout life due to strong immunity.
Methods for removing skin lesions
The destruction of papillomas is carried out in clinics using special instruments and devices. Excision performed by a specialist is effective and safe, but each method has its own characteristics.
Surgical method. Traditional removal of papillomas with a scalpel is gradually being replaced by modern, less traumatic methods. Surgical removal is accompanied by a long healing period, the risk of complications and scarring.
Chemical destruction. Possible in relation to a single growth and several small neoplasms. The destruction of papilloma is carried out with a chemical preparation based on organic and inorganic acids. The method has a high rate of relapse: in half of the cases, papilloma reappears.
Cryodestruction, or freezing with liquid nitrogen. The neoplasm is exposed to ultra-low temperatures, which destroy living cells. The effectiveness of the method is the same as with chemical destruction: 50%.
Electrocoagulation. The method is painful and traumatic. Papilloma is removed using electric current. After the procedure, there is a long recovery period, and the risk of post-coagulation syndrome is high.
Laser removal. A modern, highly effective and most preferred method used for pathological neoplasms of any location. It has many advantages, ensures complete removal of the growth without damaging adjacent healthy tissue.
Advantages of the laser method
The use of a laser beam is indeed preferable if it is possible to choose a method for removing papillomas. The method is 100% effective, completely safe and virtually painless. However, that's not all. Other advantages of the method are also undoubted.
- Bloodless and atraumatic. The laser beam acts only on the affected tissue, while simultaneously sealing small blood vessels. After removal of the growth, no scars remain and healthy tissue is not injured.
- Elimination of the risk of skin infection due to the non-contact method and high beam temperature. The laser has disinfecting properties.
- No pain. The patient will only feel a slight burning sensation that lasts less than a second.
- The ability to use a laser on any part of the body and mucous membranes.
- Complete removal of papilloma from the skin with guaranteed absence of relapse.
- Fast and comfortable recovery period.
Laser removal of tumors is carried out quickly, within a few minutes. The technique has practically no restrictions and is used at any age, including children.
How is the procedure performed?
Removal is carried out in a sterile cosmetology office and does not require preparation or hospitalization. All additional conditions that will have to be met relate to increasing the effectiveness of the procedure.
The growths are removed during one session, which takes from 5 to 15 minutes. In exceptional cases, when the affected area is large, the doctor will prescribe 2-3 procedures to reduce discomfort.
Anesthesia is not performed: it is not necessary. If the growth is large, local anesthesia may be used at the patient's request.
The doctor covers the treated skin with a sterile adhesive plaster and gives recommendations for further body care.
Rehabilitation period
Laser removal involves a violation of the skin, and therefore requires a certain amount of time for the area of the body cleared of papilloma to heal. As a rule, complete tissue restoration occurs within a week, in exceptional cases it lasts up to ten days.
During the entire rehabilitation period, you need to follow certain rules that will ensure rapid regeneration of the skin and prevent secondary infection. Recommendations for the entire recovery period are as follows.
- Do not take long water treatments (swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna) and do not swim in open water. Instead of a bath, for hygienic purposes, limit yourself to a shower.
- Make sure that the treatment area does not overheat or overcool.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight; in extreme cases, use sunscreen with a high UV filter (at least 35). Do not sunbathe in a solarium.
- Avoid mechanical impact on the skin, as well as contact with strong chemicals.
- Do not try to speed up the natural healing process by tearing off dense epithelial crusts. As a result, scars or long-lasting red spots may form.
A correctly performed procedure does not cause any complications and does not require a follow-up visit to the doctor. You should come for a consultation only if unfavorable signs appear: thickening of the tissue at the site of the papilloma, redness, swelling, pain.
Remember that only professional removal of papilloma in a specialized clinic guarantees complete cleansing of the skin and reduces the risk of complications to zero.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no reliable protection against HPV. The high viability of the virus during direct contact makes infection, if not inevitable, then very likely.
You can prevent the appearance of papillomas on the human body if you reduce the likelihood of infection to a minimum. You need to follow the simplest preventive rules:
- Avoid public places with a dubious reputation. Do not visit baths, swimming pools and saunas where sanitary standards are not observed.
- Do not use personal hygiene items of a stranger.
- Do not use reusable samples of cosmetic products from distributors and cosmetic stores.
- Use the services of a reliable cosmetologist, massage therapist, or hairdresser, paying attention to the reputation of the specialist and the level of sanitation in the room where the procedure is performed.
- Do not try on shoes and clothes if there is damage to the skin on your body.
- Enter into intimate relationships deliberately, have one sexual partner.
- Strengthen the immune system: eat right, get enough exercise, stop smoking, don’t abuse alcohol.
It is important to undergo regular preventive medical examinations to identify hidden diseases. Consultation with an andrologist-urologist for men and a gynecologist for women once a year is mandatory. If you notice a growth on your body, be sure to consult a dermatologist. The earlier treatment for papilloma is started, the higher the likelihood and the easier the path to a successful outcome.
You can undergo a full course of treatment for HPV infection with removal of papillomas using a laser at the Galaktika aesthetic medicine clinic (Moscow).