Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
Fibroids are a group of benign neoplasms that affect various tissues of the human body. Tumors are formed from collagen fibers with varying densities and elasticity. Foci of pathology can be located on the skin, bones and walls of internal organs of children and adults. Oncologists consider fibromatosis as a precancerous condition.
General information
Single or multiple fibromas can affect the lungs, mammary glands, liver, skin, oral mucosa, etc. The proliferation of connective tissue occurs under the influence of various factors: unfavorable environmental conditions, severe injuries, bacterial or viral infections. When making a diagnosis and developing a treatment strategy for a patient, dermatologists, oncologists and surgeons take into account laboratory data. Information about the morphology of the tumor allows doctors to assess the risk of its malignant degeneration.
Preparatory stage
Laser removal of skin tumors does not require special preparation. The only thing is that you cannot get into the procedure without a preliminary examination of the fibroid.
You need an in-person consultation, where a cosmetologist:
- conduct a visual examination and dermatoscopy;
- clarifies the contraindications;
- will prescribe tests to clarify the diagnosis.
The presence of any diseases or medications can seriously affect the quality of the procedure. Equally important is the identification of the fibroma itself, including testing the tumor for benignity. It is impossible to confirm this without biopsy results. The patient may also be asked to take a general blood test and go for an ultrasound.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The causes of fibroids are varied. Doctors identify several factors that contribute to the formation of connective tissue tumors in patients’ bodies:
- systematic use of alcohol and tobacco;
- repeated injuries to the skin, muscles, bones;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the region of residence;
- the predominance of fatty, spicy and sweet foods in the diet of children and adults;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- immunosuppression due to the use of immunosuppressants.
Doctors often diagnose fibromatosis in people working in chemical production. Benign skin tumors can develop under the influence of excessive sun exposure. Damage to internal organs is often a consequence of endocrine disorders.
Danger of the disease and complications
Fibroids are not dangerous to the body. Most are perceived as a defect in appearance. However, injuries caused by careless shaving, rubbing clothes or other methods are fraught with complications such as pain, bleeding, infection, necrosis (a disease in which skin cells die, and neglect of the disease is critically dangerous for the body).
Cutaneous fibroma rarely transforms into a malignant tumor; mucosal growths are more susceptible to this.
Normally developing fibroma grows slowly, but with hormonal imbalance, tumor growth accelerates and without proper treatment, the formation can reach the size of a chicken egg.
In this case, fibroma negatively affects neighboring tissues and organs, disrupting their functioning. The soft type of formations, in case of problems in the body, increases the total number, which is why a dozen growths may appear in a small location.
Kinds
Doctors use several typologies of fibroids. The most common classification takes into account the localization of the tumor focus: the pathological process can affect the skin (for example, desmoid fibromatosis), internal organs (fibrosis of the uterus, mammary gland, lungs), mucous membranes of body cavities (gingival fibroma), bone tissue (non-osteogenic fibromatosis).
Desmoid tumors form on the skin of the back, limbs and chest. Externally, the tumor looks like a growth with a bumpy surface up to 50 millimeters in diameter. About 5% of patients experience malignant transformation of tumors - a small fibroma on the skin of the shoulder or thigh can lead to the development of skin cancer.
Fibrous lesions of the uterus and other internal organs of the human body can affect various tissues: muscle, epithelial, glandular. Often the diseases are asymptomatic; the focus of the pathology is discovered by chance - during ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or radiography.
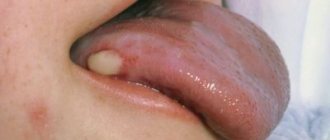
Odontogenic neoplasms form in the oral cavity. The pathological process develops slowly, the patient does not experience pain. If left untreated, the tumor can reach significant sizes and lead to jaw deformation.
Non-osteogenic tumors form in the femur and provoke the destruction of the tubular bones of the skeleton. In an advanced stage, the disease causes a pathological bone fracture. Rarely (3–5% of clinically diagnosed cases) the tumor decreases in size without surgical intervention. Other types of bone tumors grow aggressively. Thus, desmoplastic fibroma can double in volume in 2–3 weeks.
Features of laser removal
Initially, the main method was traditional surgery, which was accompanied by pain and long recovery. The transition to laser removal of skin tumors has reduced these shortcomings to a minimum.
The beam of the device works pointwise, burning only “excess” tissue. And damaged capillaries are sealed at high temperatures. In addition, ultraviolet radiation only affects the surface of the skin, without affecting the body itself. All this minimizes trauma from the procedure.
Laser equipment is optimal for eliminating skin defects in hard-to-reach and delicate areas:
- earlobe;
- areas around the eyes;
- areas with mucous membranes, including the tongue.
Problems can only arise when treating the feet. Tumors in this area often grow not only in breadth, but also in depth: the laser power may not be enough. Another point is that the device literally evaporates pathogenic cells. If the fibroma requires additional examination, it is removed using Surgitron or a scalpel.
Symptoms
The development of the tumor process is accompanied by moderate pain and a feeling of fullness. In 55–60% of cases, the pathology is asymptomatic. The likelihood of developing specific signs of fibromatosis depends on the type and location of the tumor. Fibromatosis of cartilaginous tissue is characterized by increasing symptoms - from mild pain when performing movements to complete loss of mobility of the upper or lower limb.
Specific symptoms develop when fibroma affects the patient’s internal organs. Thus, fibrosis of the uterus can cause bleeding that is not related to a girl’s menstrual cycle. Fibrous lesions of the lungs provoke difficulty breathing and shortness of breath in a child or adult after short physical activity.
Photo of a tumor under the skin on the leg
A hard fibroma is located in a hard capsule, there is no pain when pressed, the capsule practically does not move to the sides, and is most often located on a wide base. A hard fibroma rises above the surface of the skin; when squeezed between the fingers, indentations remain on the fibroma. Two types of fibromas develop in the lower extremity region: dermatofibromas and plantar fibrous formations.
Plantar fibromas affect the soles of the feet, while dermatofibromas affect the entire surface of the lower extremities. The greatest discomfort is caused by hard fibroids that develop on the foot - they interfere with wearing shoes and cause pain when walking. Constant traumatic impact on the plantar fibroma can cause malignancy of the tumor. Doctors recommend removing fibroids on the foot to avoid the development of a malignant disease.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of fibroids is performed by doctors of various specializations - dermatologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists, etc. Methods for confirming the primary diagnosis are determined by the location of the benign neoplasm. At the first stage of the examination, patients receive a referral for radiography. Computed tomography allows you to determine the exact size of the tumor and identify signs of its invasion into adjacent organs.
Fibrous formations in bone and cartilage tissue are detected during scintigraphy. If necessary, the doctor can take a biopsy sample for laboratory tests. Microscopy of the obtained biomaterials will allow doctors to assess the morphological structure of tumor cells and the likelihood of their malignant degeneration.
Benign neoplasms of the female reproductive system are often detected during ultrasound examinations. The focus of the pathological process has less echogenicity compared to adjacent tissues.
Indications for laser removal
Regardless of the type and location, the dermatological defect must be benign.
Using a laser, tumors of various types are eliminated:
- moles;
- lipomas;
- warts;
- papillomas;
- condylomas;
- adenomas of the sebaceous glands;
- angiomas;
- keratomas, etc.
Indications for laser fibroid removal:
- uncontrolled growth;
- persistent swelling of nearby skin areas;
- soreness;
- severe peeling;
- itching;
- the formation is located in a place where it creates inconvenience and/or is often injured.
The reason for removal may be purely cosmetic when the formation:
- spoils appearance;
- just do not like.
Fibroma is strongly recommended to be eliminated if there are suspicious changes in its shape or color. Just before this you need to consult a doctor and undergo at least a minimal examination.
Treatment
The treatment strategy for fibroids is determined by the doctor after the patient undergoes diagnostic procedures. For small tumor sizes and localization of the pathological focus on the skin, a conservative approach is used. Dermatofibromas can dissolve with steroid injections. Surgery is performed in cases of high risk of tumor malignancy.
Fibroids are removed in several ways. Small tumors on the skin are excised using a laser. The advantages of this method are minimal rehabilitation time and high efficiency.
Removing fibrous formations using an electric knife minimizes the risk of bleeding (small vessels are sealed under the influence of current). As an alternative method for removing overgrown collagen fibers, the surgeon may choose a radio wave knife. The use of this equipment reduces trauma to the patient’s healthy tissue.
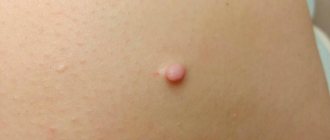
Soft skin fibroma
Soft fibroma is similar in appearance to papilloma and grows to a large size. Soft fibroma is most often located on a stalk and can be easily removed with a laser. Unlike hard fibroids, soft fibroids contain fatty tissue. It is less dense, has brown hyperpigmentation, or its color does not differ from the color of the skin.
Prognosis and prevention
When patients seek medical help in a timely manner, doctors can formulate a favorable prognosis in 75–80% of cases. The likelihood of a complete recovery of a child or adult is reduced when fibromatosis is advanced or secondary pathologies are attached to the disease.
Preventive measures are simple - patients are advised to avoid repetitive trauma to the skin, soft tissue and bones. Persons working in hazardous industries must undergo regular preventive examinations. Children and adults should eat a healthy diet and include adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
How does the procedure work?
The doctor works in a treatment room. All manipulations are carried out using disposable gloves. Disinfection of a wound with an ultraviolet ray does not eliminate the requirements for sterile conditions.
The cost of removing fibroids on the face with a laser is around 1000 rubles. In other areas of the body, you will have to pay for the size and number of tumors. Most clinics indicate an area of 1 cm2 in the price list. The average price depends on the area:
- Intimate - 1000 rub.
- Heads - 1000 rub.
- Eye - 2000 rub.
- Mouth and mucous membranes - 2500 rub.
- Bodies - 700 rub.
Anesthesia and doctor's consultation are not included in the cost of the procedure.
Features of the rehabilitation period
The healing process takes a matter of days - about 3-5 days. A specific crust forms at the site of the intervention, which peels off after a few days and falls off on its own. It should not be forcibly removed, as there is a risk of infection. To ensure healing goes as quickly and smoothly as possible, follow these recommendations:
- do not wet the intervention area;
- for 2 weeks, refuse to visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, ponds;
- Do not sunbathe until the wound is completely healed.
Immediately after the manipulation, you can return to your usual activities; no special regime is required. If you want to quickly, painlessly and safely get rid of an unwanted tumor, sign up for a consultation with a GMS Hospital surgeon!
Removal of breast fibroadenoma
Preparation for removal of breast fibroadenoma includes a consultation with a mammologist and undergoing diagnostic tests. Methods for diagnosing breast fibroadenoma include:
- breast biopsy;
- ECG of the heart and consultation with a therapist;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood test for pathogens of hepatitis B and C, HIV and syphilis;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
After diagnosing fibroadenoma, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment. At the initial stage of fibroadenoma, sectoral resection (partial removal) is performed. Removal of breast fibroids is performed under local anesthesia. After removing the formation, the surgeon applies a cosmetic suture using self-absorbing threads.
For large breast fibroadenoma, total resection of the tumor and the affected gland is performed. Typically, the operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts from one to two hours.
Removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids
Removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids is carried out after their diagnosis. A gynecologist or surgeon conducts an examination, studies the medical history and, if necessary, prescribes additional tests (ultrasound of the pelvic organs, laboratory tests).
After diagnosis, the gynecologist prescribes an individual treatment regimen for fibroids of the uterus and ovary, which includes drug therapy (anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs) and surgical removal of fibroids. Methods for surgical removal of uterine and ovarian fibroids include:
- hysteroscopic surgery for fibroids of the uterus and ovary - performed through the vagina using a long thin probe with a built-in backlit video camera, the image from which is transmitted to the monitor;
- laparoscopy of fibroids of the uterus and ovary - a minimally invasive intervention during which the fibroid is removed through several small punctures in the lower abdomen;
- open surgery - access to the uterus is provided through an incision in the lower abdomen along a natural fold of skin; it is performed in the presence of large fibroids.
The duration of the operation to remove fibroids of the uterus and ovary is 1-2 hours. The evening before the operation and on the day of the intervention, you should not eat, and two hours before the start of the operation you should not drink.
Benign bone formations
Bone tumors
- a relatively rare pathology. Benign formations are more common in young people; as a rule, they are localized in the tubular bones, while lesions in the lower extremities are found twice as often as in the upper extremities.
Modern classification of benign bone tumors:
1) Bone-forming tumors: osteoma, osteoid-osteoma, osteoblastoma
2) Cartilaginous tumors: chondroma, chondroblastoma, osteochondroma
3) Giant cell tumor
4) Vascular tumors: hemangioma, lymphangioma
5) Other connective tissue tumors: lipoma, fibroma
6) Other tumors and tumor-like lesions: neurofibroma, odontoma, solitary bone cyst, aneurysmal bone cyst, non-ossifying fibroma, eosinophilic granuloma, fibrous dysplasia.
Diagnosis of tumor formations of bones is difficult due to the lack of obvious early symptoms - pain is not expressed or absent; tumor growth is absent or very slow, bone deformation without changes in the surrounding soft tissue.
The capabilities of various radiation methods for diagnosing skeletal diseases have now expanded significantly. However, at the first stage, all patients need to undergo classical radiography in standard projections, depending on the area of interest, since this method is basic and most accessible, and allows in almost all cases to obtain the necessary information and make the correct diagnosis without using expensive and inaccessible imaging techniques such as CT and MRI.
Benign bone tumors are characterized by the following general radiological signs: clear contours, a rim of sclerosis, often swelling of the bone, absence of periosteal reaction, slow growth, solitary nature of the lesion.
Osteoma
There are spongy osteoma, osteoma consisting of cortical and spongy substance, and osteoma from a solid compact substance. The first two types are observed on long tubular bones; compact osteomas affect the flat bones of the skull.
- spherical, spiky shape, - the tumor sits on the bone on a wide, regular stalk, — the cortical layer in osteoma is not damaged. - contours are smooth, even, - the spongy network of bone and tumor continuously passes into each other. | |
- round, spherical or ovoid shape, - the tumor gives a homogeneous structureless shadow. |
|
- males are affected 4 times more often, - observed mainly at the age of 10-20 years, - localization: cortical layer of the diaphysis of long tubular bones (tibia and fibula), in the spine - in the area of the arches or spinous processes, - morphologically - a delimited formation, a “nest” located in compact or spongy bone tissue and surrounded by a wide zone of sclerotically compacted bone, - calcification of osteoid tissue is more pronounced in the center of the lesion - the picture is “eggs in a nest”: the focus of destruction is a “nest” - round, oval in shape, small in size (diameter 0.5-1 cm); zone of sclerotic compaction of bone tissue - clearly delimits the “nest” of the tumor, along the periphery it passes into the unchanged bone structure. |
|
- in addition to bone tissue, it also contains cartilage, covering the surface of the tumor in the form of a cap, - comes from the humerus, from the meta-epiphyses in the area of the knee joint, in the head of the fibula, thoracic spine (comes from the arches or processes), - the tumor sits on a wide stalk and rises on the bone in the form of a cauliflower. - its surface is lumpy, its contours are sharply defined, - the cortical substance of the bone passes to the surface of the tumor or protrudes into the middle of the growth, crumbling into separate layers of bone, running in the form of rays to the surface of the tumor, - its pattern is not homogeneous, consists of bone islands, fan-shaped bundles and septa lying among the light background of cartilage, — osteochondromas have a high potential for malignancy. |
Chondroma - phalanges, metacarpals, metatarsals, less commonly carpal bones, vertebral processes, anterior ends of the upper ribs, pelvic skeleton, sternum and very rarely long tubular peripheral bones are affected, - in small cylindrical bones, chondromas nest in the diaphysis and epiphyses, in large tubular bones - only in the metaphyseal bones, - as a rule, cartilaginous tumors are multiple and are most often observed in one or more on the phalanges of the hands and metacarpal bones, - most often the process is bilateral, but not symmetrical. | |
- tumors are spherical or oval, sometimes located centrally and swell the bone from the inside, sometimes eccentrically and more superficially and are associated only with the cortex of the bone, - the tumor consists of a transparent, cartilaginous background on which islands, dots of lime or bone substance are visible, - the outer contours are smooth and, with a benign course, are not interrupted, - at the site of fusion of tumor balls, the bone septum is sometimes thick, in other cases it is thinned or absent, - with damage to the epiphyseal cartilages, one can see inhibition of bone growth in length or its curvature, - often centrally located chondroma is complicated by a pathological fracture, - the cortical layer is uneven and thickened in places, - with chondroma, the surface of the bone is rough. |
|
- affects people aged 20 to 40 years, - localization femur - distal end, proximal end of the tibia, distal end of the radius. From flat bones - pelvic bones and scapula, very rare localization in the vertebrae, - loneliness and isolation of the lesion, - the location of the tumor is characteristic in the epimetaphyseal region, which is significantly swollen and deformed, has the appearance of a coarsely tuberous hemisphere, a club, - the tumor reaches the articular cartilage and breaks off, - grows in all directions, but the main growth occurs along the long axis of the bone towards the c/3 diaphysis of the bone, - the diameter of the tumor can increase the normal diameter of the tumor by 3-5 times. | |
- with large tumors, the cortex dissolves and the tumor is surrounded on all sides by a thin shell consisting of the walls of superficially located cells. | |
- marginal saucer-shaped defect, — the cortical layer at the affected area is absorbed, and at the border with the defect the crust is sharpened, not undermined and does not have any periosteal layers, - the contours of the defect are sharp, - pathological fractures in 12% of cases. |
Hemangioma
This is a vascular tumor, comes from the bone marrow of those bones that contain red bone marrow, can be observed at any age and does not depend on gender, the favorite localization is the vertebral body and flat bones of the skull, and is asymptomatic.
When a hemangioma is localized in the flat bones of the cranial vault, the following occurs: - swelling of the bone and destruction of the cortical layer, the periosteum is raised by the tumor, - a structural pattern is characteristic - thin and coarser bone beams scatter from the center of the tumor to its surface in a radial or fan-shaped manner. | |
X-ray picture of hemangiomas in the vertebrae: - instead of the normal structure of the vertebra, vertical, and sometimes single, horizontal, transverse, coarse columns and trabeculae appear, - individual oval or round enlightenments are visible, bordered by a dense bone border, - the vertebral body has the appearance of a swollen barrel, the arches are often involved in the process. |
|
- initially, the central focus of bone destruction is round in shape, has a structureless hemogenic appearance, is bordered by a shell-like thinned bone crust, without periosteal reaction, - then a focus of calcification appears in the center of the tumor, connected to the periphery by sometimes radially located linear bone bridges, - pathological fractures are possible. |
- odontogenic (dental) ectodermal origin, i.e. develops from the enamel organ and has a typical histological structure, - occurs in the lower jaw, upper jaw, also in the tibia and ulna, - occurs at any age, but more often in young people (from 15 to 35 years), - a focus of bone resorption growing from the depths of the central areas of the lower jaw, the cortical layer swells from the inside out and often becomes thinner, — at first the defect is homogeneous, then large or small cellularity appears (due to cyst-like degeneration of the tumor tissue). |
Benign bone tumors are a pathology that can affect both infants and the elderly. Most of these formations have a favorable prognosis in terms of quality of life and malignancy. The exception here is cases of giant cell tumor, which is capable of degeneration. Timely detection and adequate treatment help avoid serious deterioration in the patient’s health.
Recovery after fibroid removal
The recovery period after fibroid removal is usually up to seven to ten days. After removal of breast fibroids, you must visit a doctor or nurse every day or every other day to apply dressings. In addition, you should minimize physical activity, wear bandages, and eat a healthy and balanced diet. After removal of fibroids of the uterus and ovaries, it is also necessary to wear a postoperative bandage and lead a healthy lifestyle (eat properly, avoid overwork, stress, and maintain a sleep schedule).