Infection with HPV (human papillomavirus), which usually provokes the appearance of condyloma, is lifelong and is found in the blood. Therefore, none of the methods for removing this growth provides a 100% guarantee of complete relief from the disease. Only its external manifestation is removed.
At the same time, it is worth noting that relapses of condylomas are not so frequent, so it is worth treatment. As practice shows, only in 30 percent is a recurrence of these growths likely. It all depends on the state of the immune system and the body’s individual ability to resist infection.
Choosing a technique for removing genital warts in men
The choice of technique for removing genital warts in men is determined by:
- their number,
- sizes,
- localization
- individual characteristics of the patient’s body,
- capabilities of the medical clinic.
Genital warts, laser removal
If a diagnosis of genital warts has been made, removal by laser or diathermocoagulation can lead to the formation of scars.
Therefore, such techniques are undesirable when localizing warts in the area of the external genitalia.
Removal of genital warts in a medical facility
In the case of treatment of human papillomavirus infection in a medical institution, regardless of the chosen technique, their removal is carried out by a dermatovenerologist.
This eliminates possible incomplete removal of warts with subsequent relapse of the pathological process.
In the clinic, measures are taken to prevent complications.
Such as bleeding, damage to healthy cells or infection of the area of manipulation.
After removal of a wart, a venereologist gives recommendations regarding the prevention of their reappearance.
Advantages of laser coagulation of condylomas
- efficiency is more than 95% with minimal risk of relapse;
- there is virtually no likelihood of complications such as infection, bleeding, scarring, skin hyperpigmentation;
- selectivity of exposure, the laser cauterizes only diseased tissue;
- no pain, since the procedure is carried out with mandatory anesthesia;
- rapid recovery and recovery (up to 3-4 weeks);
- the ability to evaluate the visual effect of treatment after just a few days;
- minimum contraindications.
Removing genital warts at home
It is impossible to carry out high-quality removal of genital warts at home.
This is due to the lack of necessary equipment to perform various therapy techniques.
The use of aggressive chemical compounds to cauterize warts can lead to serious complications such as burns of healthy areas of the skin, as well as incomplete removal of genital warts.
To remove genital warts, it is best to go to a medical facility and see a specialist.
This will allow for high-quality treatment, reduce the likelihood of relapse, and provide not only a therapeutic, but also a cosmetic effect.
Disadvantages of laser destruction
Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting the high cost of the procedure, as well as in some cases the occurrence of side effects, such as redness, burns, skin pigmentation, fever, allergic reaction, swelling. Keloid scars may appear in patients with hormonal imbalances. But all negative symptoms usually go away within the first day.
To successfully get rid of condylomas, three factors are important: an experienced doctor, the absence of contraindications and compliance with recovery recommendations. Be healthy!
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Removal of condylomas: tests
A study must be carried out before removing any growths.
Tests help not only to identify the virus, but also to identify malignant neoplasms.
The best method for detecting the virus is PCR diagnostics.
It is based on identifying the DNA of the causative agent of the disease.
Even in a small amount of material, the virus will be detected.
Tissue samples from growths are used as biomaterial.
If there are a large number of condylomas, it is important to take samples from different places.
As a result of the analysis, the doctor receives quantitative indicators on the basis of which a diagnosis is made.
Important! After treatment and removal of condylomas, it is necessary to take a second test.
It will show whether the therapy is chosen correctly.
Quantitative PCR can be used to monitor treatment.
When can you resume intimate life?
After removal of tumors, provided there are no complications, it is allowed to begin sexual relations no earlier than 3 weeks later. This period is necessary for complete healing of wounds in intimate places. People who had sex earlier complained of unpleasant pain and bleeding.
If treatment is conservative, you should complete a full course of therapy, taking into account sexual rest. After the complete disappearance of condylomas, you can begin sexual activity no earlier than a month later. At earlier stages, redness, burning and the formation of microcracks are possible. Therefore, during contact the person will be in pain.
In cases of elimination of tumors in the vulva, it is recommended to resume sexual life no earlier than 3 months from the date of surgery. In this case, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist who will tell you how long a woman is ready for a full life in a particular case.
Having sex with an unverified partner means increasing the likelihood of infection.
Of course, a person cannot know in advance whether his partner is sick. Therefore, if the relationship has reached the stage of sexual activity, talking about sexually transmitted diseases should not cause embarrassment. It is better to talk with your partner about a dangerous disease and undergo a diagnostic examination together. This will help avoid an unpleasant illness and keep both partners healthy. The article has been verified by the editors
Removal of anal warts
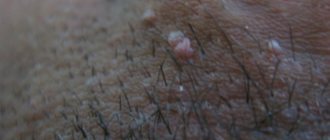
The localization of condylomas can be very different.
They are also found in the anus.
Growths can be single or group.
When condylomas grow, they become like cauliflower inflorescences.
In this case, the question of their radical removal is raised.
Among the methods used in medical practice to remove perianal condylomas, the most popular are:
- Removal using laser,
- Exposure to liquid nitrogen,
- Radio wave therapy,
- Use of an electric knife or scalpel.
In the latter case, the wound heals within a month.
With laser removal, regeneration is quite fast.
Self-regression of condylomas
The sexually active population can become infected with HPV during their lifetime; according to statistics, 80% of people are susceptible to this. The majority self-heal from HPV without clinical manifestations and without treatment. This occurs due to the activation of the local and general immunity of the infected person. In approximately 10% of patients, the virus has clinical manifestations, these include anogenital condylomas and patients with precancer and cervical cancer.
As practice shows, condylomas in pregnant women regress on their own after childbirth, especially in the vagina.
Removal of mucosal condylomas
The mucous membrane is a favorite place for the formation of condylomas.
Their localization can be varied: from the mucous membrane of the genital organs to the oral cavity.
The growths cause severe discomfort and interfere with the patient’s normal life.
Important! Condylomas can be removed only as prescribed by a doctor.
Making decisions on your own is not recommended.
If removal is unavoidable, the following methods are used:
- Laser removal. In this case, the risk of condylomas reoccurring is reduced.
- Liquid nitrogen can destroy the structural structure of the growth. After such exposure, condylomas die off.
- Electrocoagulation. Using electric current, the cells of the growth are destroyed.
- Radio wave method.
- Surgical intervention. This method is not used very often.
After removal of condylomas from the mucous membrane, the next stage begins - healing.
In the oral cavity the process occurs faster than in the genital area.
Removal of condylomas on the mucous membrane is possible with the Surgitron device.
This is a modern and safe technique.
How long does it take for wounds to heal after removal of condylomas with Surgitron?
Quite rapid healing is noted; the very next day, the wound heals.
Complete regeneration takes 2–4 weeks.
Much depends on the location of the growth.
Is it painful to remove condylomas in men,
What pain relief is used when removing condylomas for men?
Emla cream is often used as an anesthetic if the procedure is performed on the skin.
When removing in a sensitive area, a solution of 10% lidocaine is used.
Sometimes the doctor applies intradermal ultracaine and lidocaine to the surface of the skin.
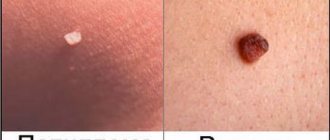
Why do condylomas need to be removed?
The aesthetic aspect is, of course, important, but the removal of condylomas must be taken seriously, since they can develop from benign to malignant. Condylomatosis of the anogenital area causes a number of uncomfortable sensations: severe itching; burning sensation; a high percentage of the likelihood of injury followed by severe bleeding, which may result in infection of the damaged area; large condylomas can ooze, smell unpleasant, cause inflammation and irritation; Condylomas can become malignant.
There are cases when formations disappear on their own, without outside surgical or medicinal intervention. But it is important to understand that only small formations that are visualized on the skin and mucous membranes for no more than 3 months are capable of self-removal.
Removal of condylomas in the urethra
The appearance of condylomas in the urethral canal causes patients a lot of inconvenience:
- Discomfort when urinating.
- Problems with ejaculation.
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
It is necessary to immediately consult a urologist.
Most often, laser destruction is used to remove condylomas in the urethra.
Other methods are used less frequently, as they severely damage the mucous membrane of the urethral canal.
Growths that are located inside the urethra are removed as carefully as possible.
Often limited by therapeutic methods.
Complications after removal of condylomas in the urethra in men:
- If the wound is poorly cared for, it can become infected.
- Inflammation of the walls of the urethral canal.
- Narrowing of the urethra.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to constantly monitor the attending physician and carefully care for the place where the growths were previously located.
Clinical observation
Visit 1.
Patient O., 22 years old, complained of discharge from the genital tract and discomfort when urinating. She was diagnosed with low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) based on cervical cytology at 8 months. ago, confirmed twice. The woman is heterosexual, has had two partners, and has been in a new relationship within the past 4 months. She used combined oral contraceptives for 8 months. as a method of birth control. At the time of consultation she was not taking any other medications. Was not vaccinated against HPV.
History of the disease.
Discharge from the genital tract first appeared at 9 months. back. On the recommendation of a friend, I used suppositories (according to her, a combined antimicrobial drug) with a temporary effect. A month after treatment, discharge appeared again. When visiting a doctor, genital condylomas in the vagina and vulva were diagnosed against the background of vaginitis; the results of the Pap test revealed LSIL. Dequalinium chloride was recommended, which gave a temporary effect, after which removal of condylomas of the vagina and vulva was performed using argon plasma ablation. Surveillance is recommended for LSIL.
From the anamnesis.
She denies surgical interventions and suffered from chicken pox among childhood infections. Sick with acute respiratory diseases 3-4 times a year. Denies smoking and other bad habits. Heredity: mother has uterine fibroids, obesity. The allergic history is unremarkable.
Accompanying illnesses
: chronic gastritis in remission, cystitis.
Gynecological history.
Menstruation from the age of 12, regular, moderate, 4–5 days every 27–30 days. Sexual life from 21 years of age. There were no pregnancies. Previously, I visited a gynecologist for 8 months. ago, when hormonal contraception was recommended and condylomas were removed using argon plasma ablation.
Inspection
. Height - 162 cm, weight - 57 kg. Skin of normal color, tendency to dry skin. Blood pressure - 110/70 mm Hg. Art. The mammary glands are developed correctly, symmetrical, round in shape, soft on palpation.
Status genitalis.
The external genitalia are developed correctly.
Female pattern hair growth. The mucous membranes of the vulva and in the urethral area are slightly hyperemic. On the inner surface of the labia minora, in the area of the vestibule and vaginal walls, there are multiple small condylomas. The discharge is flaky, in moderate quantities. The cervix is conical in shape and not visually changed. Per vaginal
: free vaults, uterine body in
anteflexio
, normal shape and size, dense, painless. The appendage area is painless.
Swabs taken
for oncocytology and HPV test, smear for flora and STI pathogens, after which
colposcopy
. The colposcopic picture is adequate, the cervix is covered with squamous epithelium. After a test with a solution of 3% acetic acid, a small ectopia with a type 1 transformation zone was revealed on the exocervix. There are whitish areas with delicate acetowhite epithelium and small papillary growths with a vascular loop inside. The junction of squamous and columnar epithelium is visualized. Conclusion: abnormal picture of the 1st degree, transformation zone of the 1st type, condylomas. LSIL?
Preliminary diagnosis.
Anogenital warts. LSIL? Vulvovaginitis. Hormonal contraception. Monitoring the use of contraceptive medications.
Recommended: 1) Pap test; 2) PCR diagnostics for STIs + HPV; 3) a smear to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness; 4) examination of the sexual partner; 5) barrier methods of contraception.
Visit 2.
The results of the survey have been received.
Smear to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness:
epithelium in moderate quantities, leukocytes - 30–40 in the field of view, in some places completely;
rod flora, abundant; diplococci were not found, Trichomonas vaginalis
were found, fungal spores and mycelium were found, “key cells” were not found.
PCR diagnostics for STIs:
negative.
HPV test with typing:
HPV types 31 and 11.
Pap test
: LSIL.
Diagnosis
. Mild cervical dysplasia. Recurrent anogenital condylomas. Trichomonas infection. Vulvovaginal candidiasis. Human papillomavirus infection. Monitoring the use of contraceptive medications.
Recommended:
1) metronidazole 500 mg orally 2 times a day for 7 days; 2) sertaconazole 1 suppository 1 time per day. intravaginally at night for 7 days; 3) planned cervical biopsy.
Visit 3.
Examination 5 days after completion of treatment.
No complaints. On examination:
there are multiple small condylomas on the inner surface of the labia minora, in the area of the vestibule and vaginal walls. There are no signs of inflammation. In the speculum: the vaginal mucosa is pink, the discharge is physiological. The condylomas have slightly decreased in size compared to the previous visit. A targeted biopsy of the cervix was performed.
Histological conclusion
: genital warts, LSIL.
Diagnosis.
Anogenital warts are multiple. LSIL. Monitoring the use of contraceptive medications.
Considering the young age, the absence of discrepancies in the examination results and persistent HPV infection with the presence of recurrent multiple genital warts against the background of chronic inflammation, the doctor recommended immunotherapy with Polyoxidonium® according to the regimen of 1 suppository (12 mg) daily intravaginally for 3 days, and then 1 suppository every other day with a total course of 10 injections.
Visit 4.
Check-up after 3 months. No complaints. On examination there are no condylomas. The Pap test showed: NILM (Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy - there are no intraepithelial changes or malignant processes). The next examination is recommended after 6 months.
Visit 5.
Check-up after 6 months. No complaints. On examination: there are no condylomas. Pap test was performed, result: NILM. Control is recommended once a year.
This clinical observation demonstrates the clinical effectiveness of prescribing anti-inflammatory etiotropic therapy in combination with immunotherapy with Polyoxidonium® for recurrent small multiple condylomas of the vulva and vagina and LSIL.
Wound after removal of condylomas: care
After the patient has had condylomas removed, the skin requires special care.
This is due to the fact that healthy skin cells that surround the place where condylomas have formed are affected.
After the papilloma is removed, a kind of sore forms in its place, which will soon fall off.
In its place will appear young skin, which must be protected from mechanical damage.
Care is necessary, so the inflammation will go away faster.
Antiviral agents are often prescribed - ointments, gels, sprays.
This helps avoid relapse.
Is it painful to remove condylomas?
In most cases, removing growths in intimate places or from mucous membranes is an unpleasant procedure, but painless.
The most gentle ways to remove condylomas are liquid nitrogen and laser.
These techniques usually do not require anesthesia.
When removed with nitrogen, the patient only feels cold.
Pain may appear after removal of the growths, it all depends on the location of the condylomas.
Removal using electric current is almost painless for the patient.
The doctor uses painkillers during this therapy.
Many people feel pain when anesthesia is administered; this is done using a syringe.
Patients often wonder whether it hurts to remove condylomas with a laser.
When using a high-quality painkiller, the procedure is painless.
You can remove condylomas with Surgitron quite quickly.
If their area is small, anesthesia is not required.
For large volumes or multiple formations, Emla cream or lidocaine is used.
When choosing a good anesthesia drug, removal occurs painlessly for the patient.
During the process of removing condylomas using the radio wave method, the doctor can always change the intensity of the radio wave.
Cervical condylomas
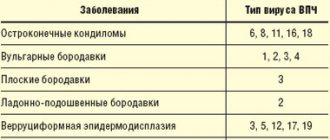
Cervical condyloma is one of the types of HPV manifestations. Infection with this disease also occurs during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. In the absence of exophytic (visible) condylomas on the penis, the sexual partner may not be aware of the carriage of this virus.
Cervical condyloma is not always a consequence of HPV types 6 or 11. The cervix is also affected by other types of viruses, which also have an oncogenic risk.
A special feature of condyloma on the neck is its shape. Condyloma can be flat and not visible when examined in a mirror, or it can be protruding (typical). Flat condyloma of the cervix is detected during colposcopy. This painless technique involves examining the vulva, vagina and cervix under a microscope, stained with special solutions. Areas affected by flat condyloma are highlighted after staining with solutions.
To finally confirm the diagnosis, in addition to a cytological examination (Pap test), a PCR test for HPV and a biopsy or removal of the altered area with histological confirmation are performed.
It should be noted that any formation on the cervix, even a typical genital wart, after removal must undergo histological examination. If the gynecologist has no doubts about the diagnosis of cervical condyloma, then when using treatment methods after which it is not possible to conduct histology, it is necessary to take a biopsy before treatment.
Sex after genital wart removal
Everyone knows that HPV cannot be completely cured.
The therapy is aimed at strengthening the human immune system and reducing viral activity.
After such procedures, HPV goes into a latent state, which does not exclude the reappearance of growths.
Important! Sexual contacts must be excluded for the entire period of treatment.
You can resume intimacy when the wounds have completely healed.
Sex after removal of condylomas is possible after 2 to 4 weeks.
It is important to use a condom.
Only then can infection of the sexual partner be excluded.
Relevance
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) and has ample evidence of its carcinogenic effects in various locations.
Adaptive mechanisms of evasion from various elements of the immune system allow the infection to remain in the body for quite a long time. Fortunately, most HPV infections are suppressed by the immune system, even if the process takes 1–3 years after infection, and only a small number of those infected develop cancer.
Natural immune control of HPV infection is achieved by innate and adaptive immunity, including specific antibodies and effector T cells. An important role in the recognition and elimination of cells affected by the virus is played by the cellular component of immunity: macrophages, natural killer cells (NK cells) and cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD4+ and CD8+) [1].
Compared to cellular immunity, humoral immunity occurs later and has less effect. One of the latest studies on the role of the antibody response showed a decrease in the concentration of sIgA, regardless of the degree of damage to the cervix. Subsequent immunotherapy had a positive response in the form of normalization of the level of these antibodies [2].
Recent studies have shown the role of cytokines, chemokines and antimicrobial proteins (defensins) in suppressing the expression of viral genes, as well as in creating conditions for the elimination of HPV [3].
The problem of persistence is associated with a decrease in local immunity, which is not capable of causing the elimination of HPV. Concomitant infectious and inflammatory diseases of the lower genital tract play an important role. An epidemiological study conducted in 2022 showed that high-risk HPV infection is comorbid with bacterial vaginosis in 20.5% of cases, with Chlamydia trachomatis in 15.7%,
and more than half (51.6%) - with
Ureaplasma urealyticum
[4]
.
Chronic inflammation not only reduces the chance of cure, but also tactically changes the approach to the management of such patients, often postponing planned surgical treatment until complete sanitation.
At the moment, there are no methods of etiotropic influence on the virus itself or its replication process. Virus persistence remains an unresolved problem in gynecology. Therefore, attempts are being made around the world to activate the immune component of the local defense of the mucous membrane, which will lead to curbing the proliferation of HPV and preventing the transition of neoplasia to precancerous conditions. The clinical observation below demonstrates an approach to the management of a patient with a long history of HPV infection and the development of diseases of the lower genitalia against this background.