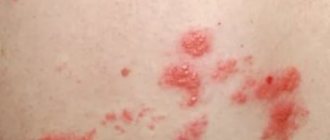
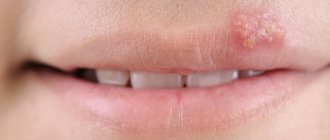
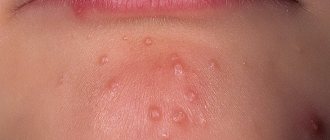
Herpes rashes on the buttocks have their own characteristics.
Primarily due to the fact that such localization of the rash is not typical for labial or genital forms of infection.
Nevertheless, the number of people with herpetic lesions of the buttocks does not decrease from year to year, but increases.
Therefore, the attention of doctors to this form of infection does not weaken.
At the beginning of the 21st century, doctors already know quite a lot about the causes of herpes rash on the buttocks.
Prevention and treatment measures have been well studied.
And although no one has yet been able to completely cure herpes, it is quite possible to minimize the negative impact of the disease on a person’s life.
Below we will tell you what you need to do for this.
Herpes: general description of pathology
Actually, the Herpesviridae family includes several types of herpes viruses.
The most common types are type 1 and type 2, which cause the rashes known to many.
The varicella zoster virus (VZV type 3 or Varicella Zoster Virus) also belongs to this family.
Skin manifestations in humans are usually caused by herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 (HSV 1 and HSV 2).
Very rarely, the rash occurs due to reactivation of VZV type 3.
Rash on the buttocks is possible in two cases:
- HSV 1 or HSV 2 entered the human body through the genitals, that is, through sexual transmission. Then the pathogens remain forever in the neurons of the lumbar spinal cord, from where they periodically exit back to the skin.
- Herpes viruses type 1, 2 or 3 are completely out of control of the immune system, in such cases the rashes are massive, numerous and protracted.
Usually, herpes on the buttocks occurs in parallel with damage to the genital organs.
For most people, the first active episode develops 2-14 days after infection.
The more massive the infection, the shorter the incubation period.
Causes of herpes
All variants of herpes infection occur against the background of the activity of the virus of the same name of different types. Since upon initial penetration into the human body the pathogen no longer leaves it, it is important to know the factors that can provoke the activation of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- seasonal colds;
- any conditions that provoke a decrease in immune defense (poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis and others);
- exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases;
- contact with an infected patient.
The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, so it is extremely difficult to completely prevent a child from encountering pathogenic particles.
Spread of herpes
Routes of infection depend on age.
Thus, children usually become infected from contact with sick adults or when using a sick towel.
In adults, herpes appears after unprotected sex or kissing.
The mechanism of autoinoculation has also been proven.
This is when herpes viruses in one person move from the face to the genital area and vice versa.
So a cold on the lips may well be combined with herpes of the buttocks.
Types of disease in children
There are 80 types of herpes virus, of which 8 are dangerous to humans. The nature of the disease and the type of herpetic rash depend on the type of herpes simplex virus (HSV):
- Type 1 HSV - looks like cold-like rashes in the form of blisters on the lips, causes herpetic stomatitis and herpetic encephalitis.
- Type 2 HSV – manifests itself as a rash on the genitals (genital herpes).
- Type 3 HSV – causes chickenpox and recurrent herpes zoster.
- The 4th type of HSV - Epshane-Barr virus, causes malignant lymphoma and infectious mononucleosis - an acute viral disease with fever, damage to the respiratory tract, lymph nodes, liver, spleen and blood.
- Type 5 HSV – cytomegalovirus; affects the respiratory system, internal organs, intestines, eyes, brain, nervous and urinary systems.
- Type 6 HSV - causes viral eczema - exanthema - pseudorubella-type rash;
- The 7th and 8th types of HSV have not been sufficiently studied. Source: A.G. Lateral Herpesvirus infections in children - an urgent problem of modern clinical practice // Children's infections, 2010, No. 2, pp. 3-7
Herpes: provoking factors
Despite the huge number of people infected, not everyone gets a rash.
The main reason for recurrence of herpes infection is weakening of the immune system, temporary or permanent.
The following factors can cause a subsidence of the body’s defenses:
- poor nutrition with vitamin deficiencies
- Unhealthy Lifestyle
- hypothermia or overheating
- severe chronic diseases - diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction
- serious bacterial infections, such as lobar pneumonia
- chronic stress
- acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV infection/AIDS)
All of the above conditions can cause another exacerbation of the infection.
Symptoms of herpes on the buttocks
Rashes on the buttocks almost always indicate a fairly severe course of herpes.
Therefore, along with local symptoms, general symptoms are often noted.
Local symptoms:
- discomfort, burning and pain limited to a specific area of the buttock, while the skin is calm
- after 12-24 hours, blisters appear at the site of pain
- blisters are small, grouped in several pieces
- filled with a clear liquid that quickly becomes cloudy
- within a day or two, the blisters burst, leaving behind small erosions or ulcers
- in 2-3 days they become covered with crusts and dry out
The crusts fall off within 5-7 days, revealing pale, clean skin underneath.
Throughout the attack, the rash is disturbing - the person experiences a burning sensation and pain.
Given the location, it becomes painful to sit.
In addition, due to the movements of the buttocks when walking or when a person sits down, the crusts crack and peel off early.
This causes even more pain and delays recovery.
General symptoms are characteristic of the primary process, which develops at the end of the incubation period:
- weakness, dizziness
- increase in body temperature to 39-40˚C
- headache
- poor appetite
- aches minor body aches
With repeated attacks, general symptoms are usually absent.
The localization of the rash is of particular importance.
If they are concentrated in a cluster, closer to the perineum, then this indicates a fairly typical version of the infection caused by HSV type 1 or 2.
But when the rash looks like a stripe, a broken line, is localized on the lower back, in the upper or middle part of the buttocks, and is terribly painful, then these are signs of a type 3 herpes attack.
The same herpes zoster, zoster.
Virus activity
Most often, children are faced with the herpes simplex virus, which manifests itself in the form of that same cold on the lips.
Herpes on the lips or chickenpox are not as dangerous for a child as herpetic lesions of the eyes, genitals, and internal organs.
Externally, herpes appears as a rash on the skin or mucous membranes. It usually looks like small blisters that eventually burst and become sores. In addition to the rash, there is burning and itching.
How often the herpes virus is activated is influenced by hereditary predisposition and the state of the immune system. The weaker the child’s immunity, the more susceptible he is to virus attacks.
Newborns up to 1 year of age are protected by maternal antibodies. The peak incidence is observed at the age of 2-3 years. By the age of 15, up to 90% of adolescents are infected with HSV. The pathogen is in an inactive state in the body and does not cause discomfort. Under unfavorable conditions, HSV is activated. Source: A. Taieb, N. Diris, F. Boralevu, C. Labreze Herpes simplex in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnostic value of clinical signs, clinical course // Ann Dermatol Venerol, 2002, v.129, No. 4, p.603—608
Causes of exacerbations and relapses of herpes in children:
- decreased immunity due to severe and prolonged illnesses;
- severe shocks and chronic stress;
- systematic fatigue;
- hypothermia;
- taking hormonal medications;
- endocrine pathologies;
- hormonal changes in adolescence;
- systematic unbalanced diet;
- complicated seasonal colds;
- chemical and radiation anticancer therapy;
- excessive physical activity. Source: M.N. Kankasova, O.G. Mokhova, O.S. Pozdeeva Frequently ill children: the view of an infectious disease specialist // Practical Medicine, 2014, No. 9(85), pp. 67-71
Special and atypical variants of herpes on the buttocks
The typical clinical course may vary depending on a number of conditions.
Let's consider the features of HIV, pregnant women and pediatric patients.
All patients from these categories have a high risk of developing atypical forms.
Then the rash on the buttocks acquires features that are not characteristic of herpes:
- erythematous (hyperemia)
- bullous with blisters
- edematous without vesicles
- ulcerative-necrotic
In total, more than 10 atypical forms are known; it is very difficult for an inexperienced eye to recognize herpes in them visually.
Due to the loose fatty tissue, which is quite developed on the buttocks, especially in children and older women, the edematous form is more common in this area of the body.
Causes of eczema on the buttocks
The prevalence and appearance of the rash on the butt, like other symptoms, largely depends on the causes of the disease.
The main reasons include:
| Contact with an irritating substance |
|
| Allergic reaction |
|
| Infection |
|
In children, the most common cause is diaper dermatitis, which is contact dermatitis by nature, but several other factors play a role in its development. These are the moist warm environment under the diaper, mechanical irritation, exposure to urine, fungal infection.
Herpes with HIV
With HIV infection, the immune system suffers greatly, which is why herpes zoster-type rashes often occur.
Therefore, all such patients must be examined for HIV infection.
In addition, attacks are becoming more frequent; the buttocks are almost constantly covered with herpes blisters and crusts.
This option, along with a weakened immune system, creates favorable conditions for the addition of secondary pyogenic flora.
Redness, swelling, pain and purulent discharge appear.
Partly because of this, with a combination of HIV and buttock manifestations of herpes, the inguinal lymph nodes are often enlarged and the lymphatic vessels become inflamed.
Lymphostasis develops, the leg swells on one or both sides.
Types of herpes in infants
For babies in the first year of life, herpes comes in different types. The forms in which the herpes virus manifests itself are as follows:
- generalized;
- neurological herpes in newborns;
- localized.
In the first case, the generalized form of herpes in infants has the following clinical picture. The virus affected the internal organs and led to intoxication. The baby has difficulty breathing, he may vomit and belch, and the fever can sometimes be very strong.
With the neurological form of herpes, the virus spreads its influence to the nervous system and brain. If the infection occurred in utero, the child may have the following deviations from normal development: microcephaly, hydrocephalus, and the formation of calcifications. Symptoms here vary and are not always typical. The newborn baby appears lethargic or cries incessantly. In addition, the baby may experience a swollen fontanelle and convulsions. Localized herpes in infants. The virus appears in limited places on the child's body. These are the eyes, nasolabial area, etc.
In addition, herpes can be primary or secondary. Primary herpes in newborns can be a consequence of infection of the baby's mother during pregnancy. In addition to transmission of the virus through the placenta, the infection can be transmitted to the fetus during childbirth, when the baby passes through the birth canal. The method of entry of the herpes virus can also be domestic. A baby can become infected with the disease through the belongings of other children or through airborne droplets, as well as from parents.
How does secondary herpes develop? When an infection has entered the body of a newborn, it may not immediately manifest itself. The virus is suppressed by antibodies that the baby's mother transmits to him along with milk during breastfeeding. If the baby’s immune defense decreases, the herpes virus will be activated. In this case, the infection will spread throughout the body, approaching the skin and mucous membranes; visual manifestations of herpes will be visible as a specific rash.
The worst thing is if herpes in infants occurs on the genitals. In this case, the virus can infect the bladder and ureter. Also, such herpes, and it is called genital, can affect important internal organs, including the heart.
Pregnancy and herpes
Pregnancy is a condition in which the immune system also weakens slightly.
Therefore, approximately 15-20% of women experience an exacerbation of herpes, possibly localized on the buttocks.
Active viremia during an attack causes problems with the placenta and has a toxic effect on the fetus.
Therefore, a painful rash on the buttocks of a pregnant woman is a reason to consult a doctor and check the condition of the fetus.
Possible complications
Without timely and adequate treatment, herpes infection can cause severe complications:
- disruption of internal organs;
- eye diseases;
- deafness;
- sore throat;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- infertility.
Sources:
- A.G. Side. Herpesvirus infections in children - an urgent problem of modern clinical practice // Children's infections, 2010, No. 2, pp. 3-7.
- Taieb, N. Diris, F. Boralevu, C. Labreze. Herpes simplex in children. Clinical manifestations, diagnostic value of clinical signs, clinical course // Ann Dermatol Venerol, 2002, v.129, No. 4, p.603-608.
- M.N. Kankasova, O.G. Mokhova, O.S. Pozdeeva. Frequently ill children: the view of an infectious disease specialist // Practical Medicine, 2014, No. 9(85), pp. 67-71.
- I.F. Barinsky, L.M. Alimbarova, A.A. Lazarenko, F.R. Makhmudov, O.V. Sergeev. Vaccines as a means of specific immunocorrection for herpes infections // Questions of Virology, 2014, pp. 5-11.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Children's age and herpes
Children can become infected with herpes in utero.
The second most important way is to visit children's groups; in kindergarten, a child can dry himself with someone else's towel.
And they also have several important points:
- lack of own immunity - everyone who is bottle-fed is at risk for the disease
- the age of crossover of the leukocyte formula is approximately 5 days and at 5 years the activity of cellular immunity in children greatly sags, and this is a significant danger of the appearance of herpes on the buttocks
- more pronounced general symptoms - fever, weakness, nausea and vomiting, loose stools
In a state of suppressed immunity, a child's buttocks can sometimes be attacked by a virus like zoster.
But only if he had previously had chickenpox or suffered from it in an erased form.
Sometimes parents confuse herpes on the child’s buttocks with prickly heat or diathesis.
Little children cry and cannot say that the pimples on their butts are itchy or painful.
Therefore, it is better to show all children with a rash on the bottom to a doctor.
About the disease
Herpetic infection is a collective concept that is used to refer to diseases that are provoked by different types of the virus of the same name.
Traditionally, in pediatric practice, pathology caused by type 1 is encountered. This is the so-called labial herpes (rash on the lips). Its peculiarity is its chronic course. It is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. With adequate treatment of a child with symptoms of labial herpes, stable remission can be achieved. However, at this time the virus “hides” in the nerve ganglia (ganglia), where it can remain inactive for as long as desired. When favorable conditions arise (primarily decreased appetite), it is activated again. Another common form of herpes infection that can occur in children is varicella (chickenpox). The disease is provoked by the herpes virus type 3. It is important to remember that after successful recovery, the pathogen also goes into a latent form and persists in the nerve ganglia. The risk for the patient may be a reoccurrence of the infection. The type 3 virus, when reactivated, can cause herpes zoster, which is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture with a deterioration in the child’s well-being and the appearance of rashes along the intercostal nerves.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have extensive experience in early diagnosis and treatment of all pathologies caused by herpes viruses. Doctors provide the necessary monitoring and quality treatment for children with any form of herpetic infection.
Complications of herpes on the buttocks
Ignoring herpes on the buttocks almost always leads to the development of serious complications:
- development of scarring in areas of repeated rashes
- weakened immune system
- chronic lymphadenitis and lymphangitis - a feature of the process in the groin is the risk of developing lymphostasis and elephantiasis on one or both legs
- diseases of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis) - active replication of the herpes virus can provoke the synthesis of antibodies to thyroid cells with the development of severe hypothyroidism
La-Cri products against dermatitis on the buttocks
La-Cri pharmacy cosmetics were developed specifically to combat irritation on delicate children's skin. The action of the hypoallergenic composition is based on the natural strength of natural ingredients: extracts of avocado, walnut, olive, string, violet, licorice, bisabolol and panthenol.
- Cleansing gel gently removes impurities, soothing damaged skin.
- The cream actively acts on irritation, relieving itching and redness, and also promotes rapid skin restoration.
- The light emulsion is ideal for caring for the most delicate skin, even as sensitive as the skin of the armpits, for every day.
Diagnosis of herpes
Fortunately, most cases of herpes progress favorably, with relapses occurring no more than once or twice a year.
If the rash occurs more often, it makes sense to consult a dermatologist to clarify the diagnosis, further examination and prescribe treatment.
An experienced doctor can visually determine the fact of herpes.
Also for this purpose it is enough to mention that the rash on the buttocks occurs periodically and hurts.
Clinical protocols require the following studies:
- general blood and urine tests - general condition of the body
- determination by ELISA of antibodies to HSV types 1 and 2 or VZV type 3 in the blood - identification of the pathogen
- establishing the antibody avidity index - duration of infection
- scrapings and prints from rashes on the buttocks are used to perform a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) - accurate identification of the pathogen
- determination of antibodies to HIV
In addition to establishing the fact of infection, it is necessary to understand the causes of relapses.
The first step in this direction is screening for HIV infection, in which herpes breaks out very often.
How to avoid rashes?
If pimples appear in the buttocks area, you need to reconsider your diet. Toxins that enter the body through harmful foods may well cause rashes. Spicy and fatty foods are the most dangerous in this regard.
You'll also have to pay attention to your wardrobe. Tight clothing makes it difficult for air to reach the skin of the thighs, and synthetics often cause the development of allergic reactions, including acne. If these measures do not give the desired result, you need to consult a dermatologist.
Immunity indicators for herpes on the buttocks
An immunogram helps to get a complete picture of the characteristics of immunity.
To conduct such a study, the dermatologist engages an immunologist, who is responsible for deciphering the analysis.
An immunogram allows you to evaluate the most important indicators of cellular and humoral immunity:
- number of active lymphocytes and their ratio (CD3+ CD4+, CD3+ CD8+, CD3- CD16/56+, CD19+ cells)
- concentration of the main classes of antibodies in the blood (IgG, IgA, IgM)
- functional activity of macrophages
Clinical observations show that exacerbation of herpes infection is accompanied by a decrease in the number of CD4 cells.
At the same time, the functional activity of neutrophils decreases.
For a sick person, an immunogram study helps to more accurately determine the severity of the process.
Gives the most accurate forecast regarding the further course of the process.
Periodic conduct of such analysis during the remission stage allows timely identification of the threat of exacerbation and a course of preventive therapy.
Treatment of herpes on the buttocks
No one has yet been able to completely cleanse the body of the herpes virus.
And it is unlikely that this will be done in the next few decades.
The main goal of herpes treatment is to prolong remission as much as possible and reduce the duration of exacerbation.
For people with buttock rashes, this means maintaining quality of life.
Most cases can be managed on an outpatient basis.
But you need to keep in mind that the buttocks are not the most typical surface for herpes.
Therefore, if a generalized form of infection or its atypical course is detected, hospital treatment may be required.
Medications play a key role.
Based on their mechanism of action, they are divided into three groups:
- Agents with direct antiviral activity. All such drugs have a similar mechanism of action - they disrupt the functioning of enzymes, due to which herpes viruses synthesize new copies of themselves.
- Interferons and immunoglobulins. They have a stimulating effect on the immune system (interferons) or saturate human tissues with ready-made antibodies to herpes, and through this mechanism they help cope with the infection.
- Vaccines. They help activate the immune system and correct its tension in the direction of herpes viruses.
The first ones are used during the period of rashes.
The latter help the former and reduce the activity of viruses.
And vaccination increases the body’s resistance to the corresponding type of herpes to the maximum.
Causes of pimples
The buttock area has a thick layer of fat, the skin here is quite strong, it can withstand significant loads. But here rashes of a purulent-necrotic or infectious nature may appear. The main causes of acne on the buttocks are:
- Sedentary lifestyle. When sitting for a long time, circulation in the lower extremities is disrupted, tissue ischemia develops. Due to constant pressure, they are injured, resulting in purulent rashes;
- Dry skin. A decrease in the protective function leads to inflammation, and due to stagnation of blood in this area, toxins are localized;
- Disturbances in the function of self-cleansing of the skin. If dead particles of epithelium are not removed for a long time, they clog the pores and ducts of the glands;
- Endocrine disruptions, changes in the level of estrogen in women and androgens in men;
- Increased sweating, especially in hot weather. Excessive sweat production causes clogged pores and creates a barrier to oxygen.
Often, acne on the buttocks is a manifestation of an allergic reaction to cosmetics or a consequence of hypothermia. To avoid this situation, you should use proven cosmetics and avoid sitting on cold surfaces.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist from our consultants by calling +7 (495) 125-49-50
Prices for services Addresses of clinics Rash on the body Sexually transmitted diseases Tests at home Calling a dermatologist to your home
Treatment of exacerbation of herpes
The most critical period.
Since herpes hurts in the acute phase, it is painful for the patient (if the rash is localized on the buttocks) to sit and walk.
Family members and loved ones are at risk of becoming infected if this has not happened before.
An attack can be quickly stopped only by a combination of two methods - local and general.
It is imperative to take into account immunodeficiency as a cause of exacerbation, since this has its own characteristics in terms of treatment (connection of immune drugs).
Local therapy for herpes on the buttocks
Prescribed for all forms of herpes.
It consists of applying special ointments to the affected areas of the buttocks, which include antiviral drugs.
Local anesthetic, softening and stimulating additives are used as auxiliary components.
In principle, the same ointments that are used to localize the rash on the lips and other parts of the body are suitable for local treatment of herpes on the buttocks:
- Acyclovir ointment 5% on the affected area of the buttock from the appearance of the first symptoms (even with still healthy skin) 4-6 times a day until the crusts completely fall off
- gel with recombinant interferon alpha-2b 3-5 times a day until pain and erosion disappear
- Allomedin gel up to three times a day for 5-7 days
- zinc-based ointments - drying effect is important for extensive lesions, herpes rashes between the buttocks
- any ointments and creams with local anesthetics (anesthesin, lidocaine)
- antiseptics – brilliant green, fukortsin
- pain-relieving ointments and gels – kamistad, lidochlor, fastin-1
It is allowed to use alternative drugs to acyclovir - penciclovir (Fenistil-Pentsivir).
Iodine cannot be used.
Through the use of balanced and adequate local therapy, the duration of the acute phase of infection can be significantly reduced.
This means that a person is more likely to be able to sit down, walk and ride a bike calmly.
It also serves as an excellent prevention of infection to others.
Unfortunately, many patients prefer to limit themselves to local treatment.
And this is a big mistake, since no ointment or cream helps prevent the next attack.
Genital herpes in women symptoms
Genital herpes in women is clinically manifested by signs typical of GI in another location. Symptoms of genital herpes include painful blisters (rarely sores) in the infected area. After the initial infection, the blisters may recur periodically. The frequency of their occurrence varies among different people, but the place of occurrence is the same each time and is called “Locus minoris.” This sign of genital herpes in women is a characteristic feature not only of this form, but also of herpes virus infection in general.
The most characteristic symptoms of genital herpes in women:
- Rashes on the mucous membranes and skin of the genital organs,
- Painful sensations
- Itching, burning,
- Difficulty urinating
- Mucopurulent discharge from the genitals,
- Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
Buy Vaccine Vitagerpavac - apteka.ru
How does genital herpes manifest in women?
Genital herpes on the labia is the most common place where rash elements appear. In addition to the external genitalia, damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, urethra and bladder is possible. In some cases, in addition to herpes on the labia, women have lesions of the urethra, cervical canal (cervical canal), uterine body, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and rectal ampulla. The weaker the immune system, the higher their likelihood.
The fastest way to detect the manifestations of herpes of the labia.
Why does herpes appear on the labia, vaginal walls, and cervix in women?
Women are infected with HH 4-6 times more often than men with the same number of sexual partners. This is due to the presence of larger areas of the mucous membranes of the external genital organs.
What does genital herpes look like in women?
Genital herpes in women photo
Symptoms of genital herpes in women photo
Systemic therapy for herpes
It is recommended to start with injectable forms of drugs based on acyclovir or drugs of the next generations.
For example, penciclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir and others.
The specifics of prescriptions depend on the form and severity of the infection.
Primary attack or mild form with exacerbations no more than 2 times a year.
One of the options is used:
- Acyclovir tablets 250 mg 2 times a day for up to 5 days
- Valacyclovir in the same regimen, but 0.5 g
- Famciclovir 250 mg twice daily
Any regimen should be supported by the use of rectal suppositories based on IFN alpha-2b, 0.5-1.0 million IU twice a day for the entire period of taking antiviral drugs.
Recurrent herpes, when a rash appears on the buttocks every 3 months, needs to be treated in two stages.
The first is as indicated above, plus additionally immune drugs.
For example, inosine pranobex (groprinosine) 500 mg 4 times a day for 10 days.
Then, to consolidate the effect, you need to take maintenance therapy for at least 9 months:
- acyclovir 250 mg twice a day
- valacyclovir 250 mg once a day
- famciclovir 125 mg once a day
The most severe cases, when the rash on the buttocks persists almost constantly, and herpes spreads to other parts of the body, require hospital treatment.
Parenteral forms of drugs are prescribed here.
Since the injections are more effective and have a slightly lower risk of side effects, the course is extended to 21 days.
Added to the main scheme:
- anti-inflammatory (relieve pain and swelling)
- antibiotics (prevention of secondary infections of the skin of the buttocks)
- probiotics (prevent complications of antibiotic therapy, increase the overall level of immunity)
- multivitamin preparations
During the maintenance phase, tablets can be used again.
For HIV, HAART is prescribed.
For people without such an infection, after cleansing the skin of the buttocks and other areas of the body, a polyvalent herpetic vaccine is recommended.
According to the scheme, necessarily with revaccination after 6 months.
How to treat genital herpes in women?
It must be emphasized that it is necessary to treat genital herpes in women only after consultation with a doctor.
It should also be noted that currently there are no drugs for herpes that can remove the virus from the human body and lead to a complete cure. Therefore, treatment is aimed at suppressing the virus in the body and, most importantly, restoring immunity.
Genital herpes in women is treated to:
- prevent complications
- prevent relapse of the disease,
- to prevent transmission of the virus and infection of children, loved ones, sexual partners, work colleagues, etc.,
- prevent a decrease in quality of life,
- prevent further weakening of immunity.
Drug treatment comes down to 3 stages:
- suppressing an outbreak or relapse of the disease with the help of antiviral (chemo) drugs, interferons;
- restoration of the body's defenses - immunity with the help of general strengthening agents, probiotics, vitamins, interferons;
- vaccination with the antiherpetic vaccine "Vitagerpavak".
How to treat genital herpes?
Effective antiviral chemotherapy drugs for herpes are drugs such as acyclovir, as well as its more effective second-generation derivatives: valacyclovir, Valtrex, famciclovir, penciclovir. These drugs have a comparable mechanism of action and clinical effectiveness, they help to quickly and effectively reduce the severity of symptoms, subjective sensations, and the duration of relapse, but they cannot cure the infection (completely remove the virus from the body).
Acyclovir and its analogues act only on the active herpes virus, but do not affect viruses that are in a latent state. A common disadvantage of acyclovir-containing drugs is the inability to prevent relapses of the disease and infection with a related type of virus and a negative effect on the immune system. Further suppression of the immune system leads to the emergence of resistant strains of the virus. Antiviral chemotherapy drugs are used occasionally in a short course (5-10 days) for primary herpes or for relapses of herpes.
For herpes, it is possible to use antiviral agents topically. This helps lead to a significant reduction in the time of appearance and regression of rashes due to the high bioavailability of active substances at the site of the lesion. Acyclovir (ointment, cream) and the new drug Penciclovir (1% cream Fenistil® Pencivir) have proven themselves well. The effectiveness of Fenistil® Pentsivir is 20–30% higher than acyclovir-based cream. Fenistil® Pencivir cream can be used in patients over 12 years of age. If there is resistance to acyclovir-containing drugs, antiviral drugs with a different mechanism of action (foscarnet, isoprinosine, panavir, aloferon, etc.) are used.
During pregnancy, for the purpose of treatment and prevention of recurrence of genital herpes and infection of the fetus, herpes medications in tablets (Acyclovir, tablets) are prescribed starting from the second trimester of pregnancy in consultation with a doctor.
The presence of side effects from the use of chemotherapy drugs contributed to the introduction of modern, effective and harmless drugs - interferon drugs - into the treatment of herpes. The ability of interferons to suppress the multiplication of a virus in the human body explains the need for their use (giaferon, viferon, genferon, etc.). The effectiveness of Giaferon is 30% higher than the effectiveness of other drugs in this group, because also contains hyaluronic acid, an independent immunomodulator. Their use as antiviral agents and immunomodulators, stopping relapses of the disease and correcting immunity, allows them to be effectively used in the treatment of pregnant women and nursing mothers, and to prevent intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Is it necessary to talk about the importance of treatment aimed at strengthening defenses and preventing relapse of genital herpes? In cases of moderate and severe forms of the disease (relapse once every 3 months or more often), to increase the effectiveness of treatment, treatment regimens, along with antiviral drugs, include immunocorrective drugs: immunomodulators, interferons, vitamins, restoratives, immunoglobulins and probiotics. It should be noted that immunotherapy leads to deep remission, i.e. to restore immunity, allows you to shorten the duration of treatment, reduce the toxic effect of chemotherapy drugs on the body, prevent the formation of resistance to them and lead to deep remission, i.e. to restore immunity.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment of herpes virus infection, a group of virologists and infectious disease specialists led by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. V.A. Isakov* developed a step-by-step, comprehensive method for treating and preventing recurrence of the disease using the drugs described above:
- Stage 1 of treatment – relief of the acute period of the disease (chemotherapy, interferons),
- Stage 2 – restorative therapy, immunocorrection,
- Stage 3 – specific immunoprophylaxis – vaccination with the antiherpetic vaccine Vitagerpavak,
- Stage 4 – clinical observation.
Chemotherapy drugs and interferons only suppress the virus in its active stage, but the vaccine treats, normalizing immune defense, and therefore belongs to the group of therapeutic vaccines.
It should be noted that special attention is paid to restoring the body’s immunological reactivity with the help of medication and anti-relapse treatment using general tonic agents, vitamins, interferons, probiotics, and immunoglabulins. Immunoprophylaxis at the final stage of treatment with the antiherpetic vaccine Vitagerpavak allows you to restore specific antiviral immunity, i.e. achieve suppression of the virus and normalization of immunity, leading to long-term (many years) remissions. This technique was called the “Russian method of treatment” in the West.
It is important to remember and consider that:
- Herpetic infections are a consequence of impaired immunity.
- In mild forms of the disease (exacerbation no more than once every 3 months), there is slight immunosuppression. Therefore, vaccination can be carried out immediately, without restorative treatment (7-10 days after healing of herpetic eruptions with an interval of 7-10 days, in the amount of 5 injections).
- In moderate and severe forms of the disease (recurrence once every 3 months or more often), it is necessary to eliminate severe immunosuppression by prescribing general tonic drugs, vitamins, immunomodulators, probiotics, and only then begin vaccination (10 days after healing of the rash with an interval of 10 days in the amount of 5 injections). It is necessary to carry out 4 courses of vaccination with an interval of 3 months under the cover of Giaferon (1 suppository 2 times a day rectally - 5 days).
The effectiveness of treatment is more than 86%, which is confirmed by the results of its use for 12 years and numerous studies of effectiveness conducted by leading scientists and clinicians of the Russian Federation in various fields.
The Vitagerpavak vaccine is used during the period of remission of the disease. The purpose of vaccination is to activate cellular immunity, i.e. its immunocorrection.
The use of the Vitagerpavac vaccine has a number of advantages over antiherpetic drugs, as evidenced by studies conducted in leading medical institutions in Russia.
Prof. N.S. Potekaev** and Associate Professor M.A. Samgin (Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases of the I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University) studied the effectiveness of the Vitagerpavak vaccine in 233 patients with recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips . The treatment was the Vitagerpavac vaccine. It was shown that regular vaccination led to an increase in the period of remission to 1-3 years. Over time, 5 years after regular 4-year vaccination, 88 patients were examined: a positive effect was noted in 72% of patients with a recurrent form of herpes; complete cure - in 42 patients, significant improvement - in 24 patients.
In another study, the vaccine was studied in 3,000 patients with frequently recurrent forms of herpesvirus. Dynamic observation of patients over a period of 3 to 5 years showed that vaccine therapy led to a complete cessation of disease relapses in 1890 patients (63%), to a decrease in the frequency of relapses in 810 people. (27%). The lack of effect was detected in 240 (8%) patients (MD, professor, head of the department of skin and venereal diseases of the RUDN University, A.L. Tishchenko).
In a study conducted by Prof. Barinsky I.F. et al., **** at the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Research Institute of Virology named after. DI. Ivanovsky" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Moscow, it was shown that in patients with frequently recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips, 6 months after vaccine therapy (Vitagerpavak) a significant improvement (increase in the inter-relapse period by 3 times) was noted in 19 (31.1%) patients, improvement (increase in remission by 1.5–2 times) - in 35 patients (57.3%) and only in 7 (11.6%) patients the therapeutic effect was weak or absent. As a result of vaccination, the majority of patients (38 people) stopped treatment due to improvement. In 52% (20 patients) of them, clinical symptoms of recurrent herpes were completely absent.
Prof. Barinsky I.F. et al.,*** also conducted a comparative study of the effectiveness of the vaccine alone and in combination with the immunostimulant Giaferon in patients with frequently recurrent herpes, including herpes on the lips. The means of treating herpes were: the polyvaccine Vitagerpavak and the immunostimulant Giaferon. Patients of group 1 (28 people) were prescribed the Vitagerpavac polyvaccine in combination with an immunostimulant. Patients of group 2 (25 people) received only the vaccine. Efficacy was assessed by reducing the duration and intensity of clinical manifestations of genital herpes during relapse and increasing the duration of the interval between relapses. When using the vaccine in combination with Giaferon, a positive result was noted in more than 96% of cases, when using one vaccine - in 84% of cases. The conducted studies demonstrated the advantage of the combined method of vaccine therapy and the immunostimulant “Giaferon”. The proposed combined treatment regimen made it possible to prevent relapses of herpes, including herpes on the lips.
Dynamics of clinical parameters in patients with recurrent HH during vaccine therapy
| Clinical indicators | Before vaccine therapy | After vaccine therapy |
| Duration of remission | 2 months | 6 months in 36 (59.0%) patients |
| Relapse rate | 5–10 times a year | 2–3 times a year |
| Duration of relapse | 3–8 days | 2–3 days |
Of interest are the results of a study using the Vitagerpavac vaccine conducted by Prof. A.A. Kasparova et al. (Research Institute of Eye Diseases of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences), with the participation of patients with ophthalmoherpes caused by the herpes simplex virus. Of 114 patients with ophthalmoherpes with frequently recurrent forms, relapses of the disease completely stopped in 71 patients (63%), their frequency became significantly less frequent in 32 (27%) and did not change in only 11 people. (10 %). Analysis of the results revealed a 5-fold reduction in the frequency of relapses and a 3.2-fold reduction in the duration of relapses per 1 patient suffering from herpetic keratitis, keratoiridocyclitis and iridocyclitis. When studying the blood of patients with herpes using PCR and MFA methods, it was revealed that the use of an inactivated vaccine was accompanied by the elimination of viremia.
In the above-mentioned studies, it was also shown that vaccination was accompanied by a 3-4 times increase in specific reactions of T-cell immunity, against the background of a constant level of B-cell immunity reactions. The study of T-cell immunity reactions showed an increase in the specific T-killer activity of lymphocytes and the activity of NK cells. Vaccination contributed to the cessation of viremia both after the end of vaccination and in long-term follow-up (after 6 months). Vaccination using Vitagerpavak led to a pronounced immunocorrective effect, reducing immune disorders from degrees 3 and 2 to 1. After 6 months after vaccination, immune disorders corresponded to the 1st degree.
The above results of long-term studies of the Vitagerpavak vaccine indicate the reliable effectiveness of the vaccine in preventing relapses of herpes infections against the background of activation of cellular immunity reactions and specific desensitization.
If you are faced with the question “how to get rid of genital herpes”, and other methods have proven to be ineffective, then you should definitely pay attention to this method of preventing relapses of the disease.
How to treat genital herpes using the Vitagerpavac vaccine?
The basic vaccination regimen using the Vitagerpavac vaccine: 0.2 ml of the vaccine is injected intradermally into the flexor surface of the forearm. The vaccination cycle consists of 5 injections, which are carried out at intervals of 7-10 days. For a lasting preventive effect, repeated courses of vaccination are necessary. In case of herpetic rashes, the intervals between injections should be increased to 14 days. After 6 months, revaccination is carried out (5 injections). In severe forms of the disease, revaccination is carried out after three months, 4 courses over 1.5 - 2 years.
Where can I get vaccinated?
Vaccine for the prevention of chronic herpes virus infection.
1 package – full course of treatment.
Vaccination course: 5 injections, given at intervals of 7-10 days. Store at a temperature of 2-8 ºС. The drug can be transported at a temperature of 9-18 ºС, but not more than 3 days.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment and prevent relapses of genital herpes in people with weakened immune systems, along with drug treatment, it is necessary to pay attention to strengthening the body's defenses. Particular attention should also be paid to the prevention of factors that contribute to decreased immunity and exacerbation of herpes infection.
Briefly about the Vitagerpavac vaccine:
Compound:
— The drug is a lyophilisate for preparing a solution for intradermal administration — Contains specific inactivated antigens of herpes simplex virus types I and II grown on a continuous cell line VERO, acceptable by WHO as a substrate for the production of vaccines
Indications:
- Patients with CGI are subject to vaccination.
- Preparing women with a history of recurrent chronic herpetic infection for pregnancy.
- HIV-infected patients in stages 1-2 of the disease.
Contraindications to the use of the vaccine:
- Active stage of herpes
- Acute infectious and non-infectious diseases
- Chronic diseases in the stage of exacerbation or decompensation
- Malignant neoplasms
- Pregnancy
- Presence of active AIDS symptoms
Herpes on the buttocks: traditional and alternative medicine
Now there are quite a lot of effective medications that have a direct effect on herpes.
Therefore, the use of folk remedies for this infection with localization of the rash on the buttocks cannot be considered justified.
As an option, you can apply lotions to sore spots with chamomile infusion and sea buckthorn oil.
But you shouldn’t count on traditional medicine to get rid of relapses.
Treatment
If herpes is detected in a child, the following treatment is prescribed. These are antiviral drugs (tablets and ointments), immunostimulants, and interferons are also prescribed. The method of use - tablets, ointments or even injections - is determined exclusively by the attending physician. The dosage is prescribed individually for each little patient. Self-medication in this case is extremely dangerous and can lead to tragic consequences. You must strictly follow all doctor's instructions to avoid further complications.
Let's talk in detail about medications that can be prescribed to infants:
- drugs to suppress infection;
- immunomodulators and immunostimulants;
- antipyretics and pain relievers (suppositories, suspensions);
- antihistamines;
- antiseptics;
- antibacterial agents if microbial infections have joined the virus;
- To heal and dry wounds and ulcers on the body, brilliant green and sulfur-based ointments are prescribed.
Also, if a child has symptoms such as convulsions due to herpes, then anticonvulsant medications are prescribed. To relieve itching on a child's skin, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used. This is chamomile, calendula. You can also use rosehip oil, etc. Such products will not only remove discomfort on the skin where there is a rash, but will also help the wounds heal faster and relieve inflammation.
The baby needs to drink plenty of fluids. If a mother feeds her baby with breast milk, then she needs a balanced and proper diet. You should consume foods rich in vitamins and microelements. As auxiliary measures, isolation of the newborn from contact with strangers and maintaining the personal hygiene of mother and baby at a high level are used. Care must also be taken to ensure that the baby does not scratch the affected areas. To do this, use clothes that cover the baby's fingers. It is sold in special stores for newborns. They also use so-called scratch pads, hand pads, etc.