The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
List of herpes remedies:
- Herpes during pregnancy
- Is herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
- Herpes during pregnancy on the lips
- Genital herpes during pregnancy
- Herpes type 1 during pregnancy
- Herpes type 2 during pregnancy
- Treatment of herpes during pregnancy
Description of herpes during pregnancy
Herpes during pregnancy is the appearance of specific rashes on the skin of the face, lips and other parts of the body, as well as mucous membranes that are in direct contact with the environment, due to the multiplication of the herpes virus in the body of a pregnant woman. The importance of this topic will never lose its relevance, since herpes infection has accompanied humanity since its inception and will exist as long as it is possible to penetrate into a susceptible organism.
In this regard, pregnant women are in a special position. Indeed, in this case, the herpes virus has not one victim, but two. The female body is initially more susceptible to this infection than the male body. And pregnancy further reduces immune defense mechanisms, especially during certain periods of the gestational period, which are called critical for both mother and fetus.
The possibility of infection of pregnant women with the herpes virus depends on many factors. One of them is the body’s initial immune abilities and infection that precedes pregnancy. When a woman becomes pregnant, all metabolic processes in it are directed towards preserving the fetus and ensuring its vital functions. If the resources of the pregnant woman’s body are very limited, then there is a high risk of infection with any type of herpetic infection.
Types of herpes
There are several of them. It makes sense to dwell on each of them briefly to fully understand how each of them can end for a pregnant woman and her baby.
Herpes simplex virus
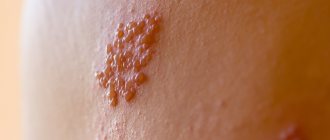
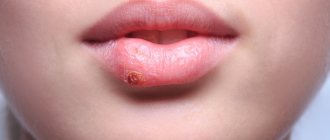
Belongs to the first type of varieties of this pathogen. It is characterized by the fact that it parasitizes and multiplies on the skin of the face and lips, as well as in the mucous membranes. Clinically it manifests itself as painful itchy blisters, which burst, leaving behind small eroded surfaces covered with thin crusts. Rarely causes more widespread lesions in pregnant women.
2nd view
Herpetic infection of the second type affects the genitals. In this case, the rashes are localized on the skin or mucous membranes of the labia and vagina. The clinical features of the morphological elements of the rash are similar to those described in the section on herpes simplex. Only the localization differs.
3rd view
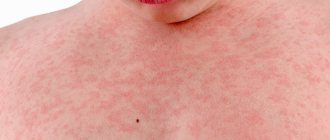
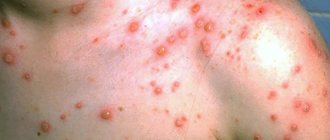
Chicken pox, and as its consequence, shingles, are manifestations of the third type of infection with the herpes virus. The first disease is characterized by the prevalence of the lesion and the brightness of the rashes throughout the body. Shingles is a local rash along large nerves, accompanied by severe pain in the affected area. Fortunately, it is rare in pregnant women.
4 and 5 views
The fourth and fifth types of herpes are the two insidious viruses that both doctors and expectant mothers are afraid of. The first of them, the Epstein-Barr virus, if it penetrates the body, it lives in it almost as long as its owner will live. At the same time, it affects a lot of tissues: lymphatic, nervous, internal organs, causing low-grade inflammation in them. Cytomegalovirus, which is a representative of the fifth class of herpes, has a high affinity for the liver, spleen and nervous tissue.
A woman can become infected with any of these viruses both during pregnancy and after it. The main routes of transmission are the contact of viral agents on the skin or mucous membranes through direct contact with them (infected objects, kissing, sexual intercourse) or through the air, when they enter the body through the respiratory tract and nasal cavity.
Is herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
This question is probably the most important for all pregnant women who, before pregnancy, were in one way or another associated with a herpetic infection. It is not for nothing that all pregnant women, when registering at any antenatal clinic, are examined in detail, including tests for TORCH infection. This abbreviation denotes the most common infections dangerous to mother and fetus, two of which belong to the herpes family. These are cytomegalovirus and genital herpes.
What exactly is the danger of these two pathogens in relation to pregnant women is worth considering in more detail to highlight the importance of this issue. For the body of pregnant women, both of these representatives of the herpes family do not pose a great threat. After all, the genital type does not manifest itself in anything other than local changes, and cytomegalovirus is not dangerous for adults, even in a state of pregnancy. Moreover, it can be present on the skin or mucous membranes without causing any disorders.
It turns out that the main target of these pathogens, which are relatively harmless to women, is the body of the fetus and newborn baby. Even all the most powerful maternal defense mechanisms, such as the placenta, immunoglobulins and other factors of the immune system, are not capable of 100% protecting the baby. These features can cause serious consequences, since the herpes virus, especially cytomegalovirus, can easily cross the placenta. Moreover, if this happens in the early stages of gestation, when the placenta has not yet formed.
The consequences of intrauterine infection with herpes viruses depend on the stage of pregnancy and the gestational age of the baby. The sooner this happens, the worse the problems will be. Such negative effects are associated with the ability of herpes viruses to have a teratogenic effect and provoke the development in the fetus of a wide variety of malformations of almost all organ systems.
Most often, the nervous system, liver and heart are affected, especially in the early stages of intrauterine development, when their formation and initial differentiation occur. At this time, there is no placenta yet and viruses can easily reach the fetus. Extrauterine contact of a baby with herpes less often results in malformations, but damage to the brain (meningoencephalitis, hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure), heart (myocarditis, non-closure of some orifices, heart failure), and liver (severe hepatitis and underdevelopment of the bile ducts) occurs.
As for the danger of genital herpes for the fetus, there is an immediate threat in the prenatal period, but it is not great. All the danger lies with childbirth during the passage of the child through the birth canal, which is infected with herpes. In this case, there is very close contact between the child’s skin and the mucous membranes on which the viruses are located, with their penetration into the child. Already in the neonatal period, this can cause generalization of herpetic infection and the development of severe pneumonia in the baby, damage to the mucous membranes and brain.
An important aspect of the body's defense system against viruses and microbes
In the process of evolution, humans have developed various defense mechanisms that allow them to resist various infections. Thus, the interferon system IFN is one of the most important factors of the body’s resistance, participating in various immunological reactions. Interferons are a group of biologically active proteins or glycoproteins synthesized by the cell in the process of a protective reaction to foreign agents, which include viral infection. Currently, the concept of “interferon system” (SI) has emerged. It does not belong to any specific organ, but exists in every cell, so all of them can be infected with a virus and must have a system for recognizing and eliminating foreign genetic information. SI is configured to recognize “self and foe” and is “built-in” into almost all cells of the body, which allows it to actively influence the entire cascade of the body’s defense reactions from phagocytosis to inflammation, which makes it an important factor in nonspecific resistance. As a result of the study of interferons, their role was determined: control and self-regulation of processes in the body. The main effects of interferon protection: antiviral, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, preventing excessive cell proliferation, protection against radiation and others. Herpesvirus infections cause an imbalance in the interferon system, inhibit the cellular and phagocytic reactions of the body (prevent the detection, absorption and removal of viral particles). Restoration and normalization of the body’s defense mechanisms is the preventive task of antiviral therapy.
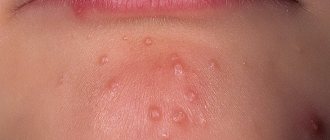
Herpes during pregnancy on the lips
Pregnancy is often accompanied by the formation of painful and itchy rashes on the skin or mucous membrane of the lips. This is nothing more than herpes. The second half of pregnancy is much less likely to be complicated by its appearance, which cannot be said about the first half. This is due to the fact that the appearance of a partially foreign fertilized egg in the uterus is a kind of stress for the woman’s body. Against this background, a certain intoxication occurs with the development of toxicosis and a decrease in immune status. Naturally, in this case the body is completely defenseless. The result is herpes on the lips. If the general condition of pregnant women is disturbed, this may cause the process to spread to the mucous membranes and face. Generalization of the process is an indication for immediate seeking medical help at an antenatal clinic. After all, when the infection enters the bloodstream, it can penetrate to the fetus, causing disruption of its development or even miscarriage.
All detailed information about herpes on the lips
There is no need to worry too much about isolated herpetic rashes on the lips, since there is no danger to the developing baby. Over time, everything will get better, the female body will adapt to new conditions, herpes will be defeated by immune cells and natural defense mechanisms.
Genital herpes during pregnancy
One of the really pressing problems during pregnancy is herpetic lesions of the genital organs in pregnant women. Infection can occur both before pregnancy and at any time during pregnancy. You can only become infected with this virus through sexual contact if your sexual partner is infected or carries the genital herpes virus. Most often, such situations arise either from casual sexual intercourse before pregnancy, or from a regular sexual partner who himself accidentally became infected with this virus.
Infection during pregnancy, fortunately, rarely occurs, but if it does occur, it occurs exclusively in the first half.
In typical cases, the genital herpes virus does not cause complications in the fetus, as it is retained by the placenta. But, if a pregnant woman has a history of immunodeficiency and a decrease in protective resources, in such cases generalization of the infection with its spread to the fetus is possible. Such a turn of events can cause intrauterine death of the child or the development of severe malformations and deformities. The risk of infection of the baby is extremely high during childbirth.
Read more information here about genital herpes
For pregnant women themselves, genital herpes is no more dangerous than for women who are not pregnant. Manifestations and symptoms are identical and are limited to painful blistering rashes on the genitals and perineal skin. They are accompanied by itching and severe discomfort. Long-term carriage of genital herpes can cause the growth of cancerous tumors and chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
Effects of therapy with VIFERON
“The use of the drug VIFERON® from the 14th week of pregnancy contributed to:
– exclusion of signs of hematogenous infection;
– reducing the frequency of ascending infection by 4.5 times;
– reducing the incidence of pathology in newborns (infectious and non-infectious);
– exclusion of structural changes in the central nervous system in newborns;
– increasing the frequency of births of healthy children by 2 times [1];
According to available data: “The inclusion of the drug VIFERON® in complex therapy helps reduce:
– threats of termination of pregnancy 2 times;
– polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios by 3 times;
– gestosis by 2.5 times;
– the frequency of replicative forms of the virus is 2 times (HSV from 79.3% to 45%, CMV – from 62.2% to 33.3%);
– the frequency of relapses of concomitant bacterial vaginosis is more than 1.5 times (mycoplasma and ureaplasma);
– the total number of non-infectious complications of the perinatal period by 2.5 times (from 28.6% to 12%)
– the total number of cases of IUI in newborns increased 5 times (from 26.7% to 5.2%);
– the incidence of severe forms of IUI doubled (from 25% to 11.3%) [2].
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Sources:
- Bocharova I.I., Novikova S.V., Malinovskaya V.V., Vyzhlova E.N., Parfenov V.V. Perinatal aspects of herpesvirus infections // Medical Advisor. Gynecology. 2022.1/(41).
- IN AND. Krasnopolsky, T.G. Tareeva, V.V. Malinovskaya. Monitoring of pregnant women with viral infections of the herpes family // Medical technology. – M. 2016. – 40 p.
i https://www.lvrach.ru/
ii https://medi.ru/
Loading...
Take other surveys
Herpes type 1 during pregnancy
The herpes virus of the first type is characterized by the fact that it has tropism (attraction) to epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. It also has the ability to penetrate the lymphatic system (lymph nodes and ducts), settling in them for life. No less often, these viruses penetrate the nerve trunks and ganglia. All this suggests that this type of herpes infection can constantly recur, which depends on the ability of the immune system to keep viruses under control.
More about herpes type 1
When applied to pregnancy, these data suggest the following. Usually, in pregnant women, herpes may appear for the first time, or it may worsen in the case of an existing infection before pregnancy. Clinically, this is manifested by a rash on the lips and face in the form of small blisters filled with clear liquid and located against the background of reddened skin. The rash is painful and accompanied by itching. With this typical course, there is no threat to the fetus. But no one can guarantee that the virus will not begin to progress and spread into the systemic bloodstream. If this happens in the second half of pregnancy, the placenta can protect the baby from the virus. But when the placenta is not yet formed, and the virus enters the blood, the fetus is completely unprotected, which can cause severe malformations and even fetal death.
How to behave if the disease manifests itself
Speaking about household habits, it is worth noting that hand hygiene during a relapse of herpes is very important. Do not touch the affected area with your hands, because the infection can be transferred from the face to the genital area. Infection of the birth canal before childbirth may lead to a caesarean section. Herpetic infection in pregnant women requires mandatory treatment under the supervision of a specialist. If a pregnant woman is surrounded by someone with signs of infection, close contacts should be avoided: kissing, sex, and you should not share dishes, linen, or towels with the patient.
Herpes type 2 during pregnancy
Herpes viruses of the second type parasitize and multiply in the genital area. This affects the mucous membranes and surrounding perianal skin. Infection with this pathogen can be primary or secondary to pregnancy. If a woman was a carrier of genital herpes before pregnancy, this type of infection is called secondary. Primary is the type of herpetic lesion that first appears after pregnancy. This type of infection is much less common, but is always more severe compared to an exacerbation of an existing process.
Dangers to both the pregnant woman and the child may arise under the following circumstances:
- The occurrence of herpes manifestations for the first time during pregnancy. Such women do not have the appropriate antibodies that would neutralize the pathogen. It takes a long time to form an adequate immune response, during which the virus can penetrate to the fetus and cause severe developmental disorders;
- A severe decrease in the immunity of pregnant women infected with the herpes virus type 2 before pregnancy. Moreover, even without clinical manifestations, it is able to penetrate the placenta, affecting the child’s body in utero;
- During childbirth, when the baby passes through an infected birth canal. This will inevitably end in infection with the development of herpetic meningitis, pneumonia and other diseases in the newborn.
More about herpes type 2
The presence of clinical or laboratory signs of type 2 herpetic infection is a contraindication for natural childbirth. Delivery by cesarean section is indicated.
Treatment regimen:
Pregnant women from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation) are recommended to use the drug VIFERON® 500000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours for 10 days, then for 9 days 3 times with an interval of 3 days (on the fourth day) 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours. Then every 4 weeks until delivery VIFERON® 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation), the use of the drug VIFERON® 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 10 days. Ointment for local and external use (interferon content 40,000 IU) is applied in a thin layer to the lesions 3-4 times a day and rubbed in gently. Duration of therapy – 5 – 7 days. You can also use Gel (interferon content 36,000 IU). A 0.5 cm strip is applied using a spatula or a cotton swab/cotton swab to a previously dried affected surface 3–5 times a day for 5–6 days; if necessary, the duration of the course is increased until the clinical manifestations disappear. It is advisable to start therapy at the first signs of relapse: tingling, redness, itching.