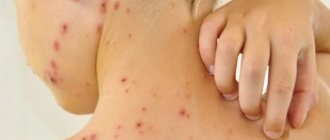
Pustular skin diseases
– a wide group of pathologies caused by streptococci and staphylococci as a result of weakening of the body’s protective functions, as well as adverse external influences – hypothermia, skin injuries, poor nutrition.
Symptoms of pustular diseases
can manifest themselves in the epidermis, hair follicles (folliculitis), sweat glands (hidradenitis, etc.) sebaceous glands (furunculosis). The rashes can be minor and not cause much discomfort, or they can occur in a severe form in the form of painful formations - boils, deep abscesses and other ailments.
Treatment in such cases can only be prescribed by a specialist!
The patient is recommended to observe the rules of personal hygiene, use antibiotic ointments and drugs and, if there are no contraindications, use physiotherapy methods, immunostimulating drugs, taking antibiotics orally, intravenously or intramuscularly, depending on the severity and extent of the disease, as well as antihistamines and desensitizing drugs.
Skin as an organ
Skin is the dense outer covering of a person.
It is an independent organ that performs specific functions. First of all, the skin is necessary to protect internal organs from physical, chemical and microbiological influences. In addition, the skin contains a large number of receptors that provide tactile, temperature and pain sensitivity. Damage to the integumentary tissue always increases the risk of developing an infection or inflammatory process. Diseases of internal organs can also cause skin lesions. Cover departments:
- The epidermis is the outermost part of the skin, formed by five layers of cells. The upper layer of the epidermis is represented by dead (keratinized) cells necessary for the formation of a biological barrier. The lower layers ensure the renewal of the cellular composition of the epidermis.
- The dermis is the middle layer of the skin. This is the area where smooth muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerves, glands, hair follicles and other structures are located.
- Adipose tissue is the deepest layer of the skin, mainly consisting of adipose tissue. This section of the organ provides protection to underlying tissues from temperature changes and external physical influences.
Scientists include external respiration, water-salt regulation, vitamin D formation and blood deposition as additional functions of the skin. The structure of the skin differs in different parts of the body. Thus, the thicker skin of the soles of the feet does not contain hair follicles. Nails, which are derivatives of the skin, form at the tips of the fingers. Also, different areas of the skin differ in the number of sweat and sebaceous glands.
Classification
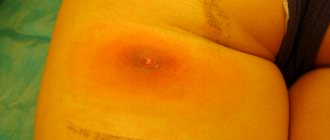
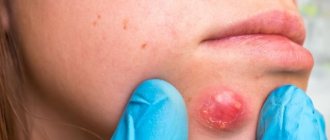
Pyoderma is not a separate disease. In medicine, this term is used to refer to any pathologies manifested by purulent skin lesions. Different types of pyoderma differ in the depth of damage to the skin and the causative agent of infection. The most common type of pyoderma is a boil, which is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle.
Other types of pathology:
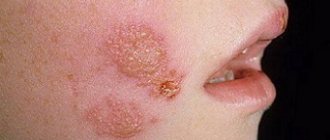
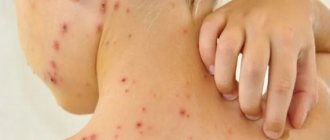
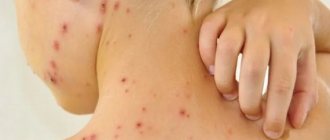
- Streptoderma is superficial pyoderma, in which multiple ulcers appear on the surface of the patient’s face, torso and limbs. A bullous rash occurs due to the invasion of streptococci into the skin.
- Ecthyma vulgaris is a streptococcal infection of the deep layers of the skin. Blisters with pus and deep ulcers form on the surface of the skin.
- Folliculitis is a pustular inflammation of the hair follicles caused by fungal or bacterial invasion. Whitish-yellow ulcers appear in the hair growth area. The release of exudate when the abscess membrane ruptures leads to the appearance of an ulcer.
- Intertrigo is a lesion of skin folds, characterized by swelling, redness and tissue deformation. Also, blisters filled with pus appear on the surface of the skin.
- Carbuncle is an infectious lesion of the skin. A carbuncle is a purulent-necrotic ulcer that quickly spreads in the peripheral direction. The inflammatory process reaches the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Furunculosis is a purulent lesion of several hair follicles at once. This form of pyoderma can occur against the background of chronic infection.
- Sycosis is a staphylococcal lesion of the scalp due to bacterial invasion of the hair follicles. Often, multiple ulcers appear in the area of beard growth in adult men.
- Gangrenous pyoderma is the appearance of a deep purulent-necrotic ulcer reaching the subcutaneous tissue. Large ulcers can reach 20 cm in diameter. Hemorrhages may form in the area of skin damage. This pathology is usually not associated with infection.
Only an experienced dermatologist can determine the type of disease by external signs. Some pathologies manifest themselves simultaneously in several forms of skin lesions.
Causes
Neutral, opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms are constantly present on human skin. These are fungi and bacteria that do not penetrate deep tissues and do not provoke the development of infection. The constancy of the microflora of the skin and the inhibition of the vital activity of microorganisms allows maintaining the integrity of tissues. Weakening of the body's defense systems can provoke the proliferation of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms with damage to various layers of the skin. In some cases, ulcers are not associated with infection.
The main mechanism of pyoderma formation is due to the infectious process. Pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply and produce toxins that damage the skin. The immune system immediately begins to fight the infection by activating inflammatory processes and protective cells. The release of inflammatory mediators leads to even greater damage to the skin. Destroyed cells and dead microorganisms form purulent exudate that accumulates in various cavities.
Possible causes of the disease:
- Damage to integumentary tissues due to cuts, combing, as well as chemical and thermal exposure. Violation of the integrity of the epidermis causes the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into less protected areas of the skin. In addition, cuts and burns themselves cause an inflammatory response.
- Disruption of the body's defense systems. In some cases, immune cells begin to attack healthy tissue. The most severe form of autoimmune damage to integumentary tissues is pyoderma gangrenosum. In addition, allergic and autoimmune processes increase the risk of tissue infection.
- Penetration of parasites into the skin. This is a rare variant of the etiology of the disease. Parasitic invasion can also lead to a purulent-inflammatory process.
Clarifying the cause of the disease is necessary to select a treatment method and prevent relapses.
Treatment of bacterial skin infections
It should start from the early stages and be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In some cases, local treatment with antibacterial ointments and wiping with antiseptics is sufficient. Widespread rashes, deep pyoderma, require the prescription of systemic antibiotics. In chronic cases, the doctor may recommend autohemotherapy and immune drugs.
Surgical treatment is carried out if the abscess does not open on its own or if a rough scar must be avoided. Laser coagulation and physiotherapy are used to restore tissue.
It is important to identify and treat concomitant diseases, eliminate adverse external effects on the skin, and select nutrition.
Risk factors
The etiology of pyoderma is not limited to the mechanisms of formation of the purulent-inflammatory process. Dermatologists know the forms of predisposition to this disease associated with lifestyle, heredity and the patient’s individual history.
Known risk factors:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Constant skin contamination increases the risk of infection.
- Overheating or hypothermia of integumentary tissues. Temperature changes disrupt the functions of local immunity. Often, after hypothermia, the skin becomes a gateway to infection.
- Age. In newborns and the elderly, pyoderma most often occurs due to insufficient effectiveness of local immunity.
- The presence of a large number of allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases (especially in children.)
- Pathologies of the endocrine system. The condition of the skin largely depends on hormonal influences.
- Metabolic diseases: diabetes and obesity.
- Congenital and acquired immunodeficiency conditions.
- Poor nutrition leading to a deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements in the body.
- Unfavorable family heredity. Skin diseases may be associated with the transmission of genetic mutations.
The causative agents of pyoderma dermatitis are found in the environment and on the surface of the integumentary tissue. These are staphylococci, streptococci and some pathogenic fungi. People often become infected with pyogenic bacteria in a hospital setting.
Symptoms
The external manifestations of pyoderma depend on the depth of damage to the skin, the causative agent of the infection and other factors. Many dermatitis manifests itself in several types of skin formations at once. Additional symptoms may be due to the underlying cause of the pathology and the effect of bacterial toxins on the body.
Symptoms of body intoxication:
- dizziness and weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sleep disturbance;
- increased body temperature;
- decreased appetite;
- headache;
- chills.
If the symptoms listed above appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. The infection that causes pyoderma can spread through the blood and damage internal organs. Self-removal of skin lesions increases the risk of sepsis.
Symptoms and causes, what to look for
Furunculosis and carbunculosis are serious pathological phenomena. Symptoms include general malaise and fever. Over time, the patient's general condition may worsen. Inflammation takes on a wide scale. The necrotic process can involve nearby tissues, penetrating deeper into the subcutaneous tissue and muscles, and pus can spread throughout the fascia. This is fraught with purulent meningitis, peritonitis and sepsis. When pustules with purulent contents appear, surgical intervention is necessary.
Hidradenitis, abscess and purulent wounds do not require delay, but immediate surgical treatment. These infectious diseases quickly cause complications, especially in patients with reduced immunity (patients with diabetes mellitus, lymogranulomatosis, tuberculosis, anemia, etc.).
Diagnostics
To undergo the examination, you must make an appointment with a dermatologist. The doctor will ask the patient about complaints and study medical history to identify risk factors for the disease. The next stage of diagnosis is an initial examination of damaged skin. The dermatologist evaluates the shape and size of the ulcers, and also determines the depth of tissue damage. To clarify the cause of pyoderma and the severity of the patient’s condition, instrumental and laboratory examinations are prescribed.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Dermatoscopy is a method of visual examination of areas of tissue damage. To determine the type of disease, the doctor uses an optical or digital device that allows you to repeatedly enlarge the image (photo). Dermatoscopy is used to search for specific signs of different types of pyoderma and differential diagnosis.
- Microbiological examination of the contents of blisters, boils and other pathological structures. The doctor carefully punctures the membrane of the bladder and collects the exudate in a sterile container. In the laboratory, specialists inoculate the material on various nutrient media to identify the causative agent of the disease. After specifying the type of causative agent of dermatitis, specialists conduct a test for the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. Bacterial culture is the most reliable way to diagnose the infectious form of the disease.
- Blood analysis. In the treatment room, a nurse collects venous blood and sends the material to the laboratory. First of all, specialists evaluate the ratio and quantity of blood cells. An immunological test can detect signs of an autoimmune disease. Also, if necessary, serological diagnostics are carried out: specialists look in the blood for specific antibodies produced by the body in response to infection. It is often necessary to exclude a sexually transmitted infection.
In case of nonspecific symptoms, the doctor must exclude the presence of other diseases with similar symptoms. For this purpose, differential diagnosis of toxicerma, epidermolysis bullosa, pemphigus vegetans and fungal skin lesions is carried out. The presence of HIV infection is excluded. If necessary, a consultation with an immunologist, allergist, rheumatologist and infectious disease specialist is scheduled.
Treatment
The method of treatment depends on the depth of damage to the integumentary tissue, the identified cause of pyoderma, the extent of the process and the complications that arise. Most often, local treatment is sufficient. The doctor opens the ulcers, removes the exudate and treats the affected skin with antiseptic solutions. If necessary, topical antibiotics are used. A serious condition, accompanied by intoxication of the body and damage to internal organs, requires hospitalization.
Additional treatments:
- Prescribing antibiotics in the form of tablets, intramuscular or intravenous injections. Typically, such treatment is necessary for systemic infection. Before receiving the results of a drug sensitivity test, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.
- Use of corticosteroids in the form of topicals or tablets. These medications are necessary to suppress the autoimmune process and relieve inflammation. If necessary, immunomodulators and cytostatic medications are prescribed.
- Physiotherapy. The effect of ultra-high frequency electric current on the skin improves the condition of the tissues.
- Prescribing additional medications, such as antihistamines and painkillers.
During treatment, your doctor may prescribe a special diet and vitamin supplements. When prescribing a course of antibiotics, the specialist constantly monitors the patient’s condition.
Cost of consultation with a doctor?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a dermatologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a dermatologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with the obstetrician-gynecologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 2100 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 1600 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Prevention
Preventing infectious and inflammatory skin diseases on your own is not a difficult task.
Basic methods of prevention:
- hygienic skin care;
- timely treatment of cuts and burns;
- treatment of chronic infections;
- regular examinations by a dermatologist for chronic skin diseases;
- control blood sugar levels in diabetes.
Consultation with a dermatologist and immunologist will help the patient learn more about methods of prevention and treatment of pyoderma.
Where to sign up for treatment for pustular diseases in Moscow?
At a multidisciplinary medical center you can always sign up for treatment for pustular diseases
. Our medical center is located between the Konkovo and Belyaevo metro stations (South-Western Administrative District of Moscow in the area of the Belyaevo, Konkovo, Teply Stan, Chertanovo, Yasenevo, Sevastopolskaya, New Cheryomushki metro stations " and "Trade Union"). Here you will find highly qualified personnel and the most modern diagnostic equipment. Our clients will be pleasantly surprised by our quite affordable prices.